Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Hokie Stone PDF
Caricato da
JohnBird00000 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
41 visualizzazioni4 pagineVarious images
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoVarious images
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
41 visualizzazioni4 pagineHokie Stone PDF
Caricato da
JohnBird0000Various images
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
While Virginia Tech invents the future, it does not forget its
past. Nowhere is this reverence for tradition more evident
than in the vista of the campus. Surrounding the Drilleld
at the center, numerous towering structures stand stately and
strong, clad in the signature limestone that denes campus
buildings.
Virginia Tech was born as a land-grant college, and appropri-
ately, its distinctive buildings have been constructed from the
product of Southwest Virginia geology. Te university mines
the distinguishing limestone at its own quarry on the fringes
of Blacksburg. Originally called our native stone, the rock
has become known more familiarly and more aection-
ately as Hokie Stone.
Prevailing through the ages
More than a century and the beginning of a new millen-
nium have passed since Virginia Agricultural and Mechani-
cal College rst appeared on the Blacksburg horizon. Over
the years, the schools name has changed, wars have started
and ended, prosperity has risen and fallen, celebration and
tragedy have left their marks. Trough it all, Virginia Techs
heart and soul have prevailed; so, too, has its Hokie Stone.
Virginia Tech does not discriminate against employees, students, or applicants
on the basis of age, color, disability, gender, national origin, political afliation,
race, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, veteran status, or any
other basis protected by law. Anyone having questions concerning discrimina-
tion or accessibility should contact the Ofce of Equity and Access.
Produced by University Relations 2014 VT/0614/2K/146400/RD/UR2014-0237
Dan Pezzoni 84, architectural historian
Virginia Tech is a product of Virginia soils
and ingenuity from beginning to end.
Virginia Techs Stone of Tradition
HokieStone
Bur russ Hall around 1940
Projecting a venerable image
Strong-armed stonemasons lay the nished limestone
blocks to form buildings designed in neo-Gothic architec-
ture, specically and more descriptively called Collegiate
Gothic. Harkening back to such venerable British universi-
ties as Oxford and Cambridge, this building style was stra-
tegically selected for the image it projects.
Te earliest campus buildings were made of brick and
were detailed with Victorian characteristics. Tis look met
with considerable and ocial disfavor. Techs leaders in
the late 19th and early 20th centuries were in consensus
Eggleston Hall (above) with closeup of one of its gargoyles (right)
that the campus buildings bore an unsettling resemblance
to the cotton mills and shoe factories of the time. Te
universitys fth president, Joseph D. Eggleston (1913-
1919), described his displeasure succinctly, referring to the
original buildings as resembling poverty-stricken mills.
In an eort to combat the stereotype of Virginia Tech as a
low-brow vocational school, Eggleston ensured that when
it came to campus construction, bricks were out and lime-
stone blocks were in.
President Joseph D.
Eggleston
The marriage of neo-Gothic
and Hokie Stone
Te changeover to Hokie Stone came during the administra-
tion of President John M. McBryde (1891-1907). Te rst
building using the native limestone was the campus YMCA,
constructed in 1899. Richmond architect W.F. West de-
signed this modest structure, known today as the Liberal Arts
Building, in the Romanesque style.
Neo-Gothic architecture, however, did not make its debut
until 1905 with the construction of the Chapel, which had
been planned as a brick building. Faced with an unavailabil-
ity of bricks, the builders turned to native limestone for the
structure that served in its later days as the campus library.
But the rst building designed in neo-Gothic architecture
and native limestone was the rst McBryde Hall, constructed
in 1914 and razed in 1966. Today, the sculptures from its
faade can be seen along the walkway on the west end of the
second McBryde Hall.
College campuses across the nation were adopting the neo-
Gothic (or Gothic Revival) style of architecture in the early
20th century. Presidents McBryde and Eggleston approved
this motif in order to visually underscore their desire for the
still-young college in Blacksburg to be accepted as a full-
edged institution of higher learning.
The original McBryde Building of Mechanical Arts (top) combined Hokie
Stone with the neo-Gothic architectural style. The newer McBryde
(above) was completed in 1971.
President John M. McBryde
One mason, one ton, one day
Virginia Techs quarry operations produce some 50 tons
of Hokie Stone per week, or about 2,500 tons
per year. A single ton of the stone will cover about 35
square feet on a building.
So what does this amount of stone look like? Torgersen
Hall, which includes a stone bridge that spans Alumni
Mall and connects the building with Newman Library,
is composed of about 2,700 tons of stone.
To envision this mass of rock in human terms, each
mason can shape about a ton of stone a day.
Te process used to arrive at that point includes cutting,
dressing, and packing the stone.
Quarry workers use black powder, a somewhat quieter
excavation explosive, to blast Hokie Stone from its mother
formation. Te properties of this powder produce large,
clean cuts of stone, thereby minimizing pulverization into
wasted dust. Containing dust and noise is essential since
the quarry is virtually surrounded by residential areas.
Te 40-acre quarry, which employs about 15
people, provides 80 percent of the stone used in
campus construction. To ensure variations in color, the
university purchases the remaining 20 percent from a
farm in Montgomery County, but Virginia Tech quarry
employees process it.
Large chunks of stone are moved to an area for drilling,
splitting, and sawing.
First, big, irregular pieces are drilled along their natural
seams.
Ten a cylindrical hydraulic splitting mechanism, which
is inserted into the drilled holes, applies 300 tons of
force to break the stones along the seams.
Once split, the stone is placed in a bridge saw and con-
verted into consistently sized building stone.
Tese stones are then fed into a hydraulic breaker that
fractures the rock with 300 tons of force.
Finally, the Hokie Stone is placed on pallets and shrink-
wrapped for delivery to the job site.
Torgersen Hall, which includes a stone
bridge that spans Alumni Mall and connects
the building with Newman Library, is
composed of about 2,700 tons of stone.
Many sizes, many purposes
Te use of Hokie Stone ranges from the towering to the
tiny. Te Smart Road Bridge over Wilson Creek, for exam-
ple, soars as the states highest bridge. Its supporting pillars
contain Hokie Stone, adding a scenic quality to the bridges
engineering. In Northern Virginia, a Hokie Stone bench
sits beside a Japanese maple tree as a symbol of hope in the
wake of the April, 16, 2007, tragedy. On the main campus
in Blacksburg, 32 blocks of Hokie Stone memorialize each
victim of the tragedy. As for tiny uses of the dolomite,
Hokie Stone is the focal point in various items of jewelry.
Smart Road Bridge
Eggleston ocially ignited this dramatic change in the
campus architecture, and his set-in-stone vision endured,
except for a brief departure from the style in the late 1960s
and early 1970s. Te change followed a national trend,
which had turned to modernism in architecture. Cassell
Coliseum and Cowgill, Whittemore, and Derring halls are
prominent examples of campus buildings of that time.
But in the 1990s a Board of Visitors committee expressed
an intent that henceforth Hokie Stone should be used in all
buildings constructed on the central campus, and in 2010
the entire board passed a resolution making that sentiment
ocial policy.
Hokie Stone also features prominently in Te Inn at Vir-
ginia Tech and Skelton Conference Center, an architectural
showpiece built with 2,741 tons of stone. If youre count-
ing, thats 82,236 individual blocks. A typical campus
building uses about 1,500 tons of stone.
An earth-shaking event
Hokie Stone is dolomite, a mineral found in the Appa-
lachian Mountains and most prevalent in Virginia, Ten-
nessee, and Alabama. A sedimentary rock, it formed from
calcium and magnesium carbonate and occurs in muted
shades of pink, red, gray, brown, and black.
In the timeline of geology, dolomite formed at the same
time as sh, insects, and reptiles, making it somewhat of
a geological newcomer. Te formation of this limestone
(technically known as Chepultepec and Kingsport dolo-
mite) was an earth-shaking event. Continental drift forced
the coastal planes of Africa and North America to collide,
creating wrinkled layers of faults and folds. As these layers
were pushed near the Earths surface, they formed the stone
that distinguishes Virginia Tech today.
Environmental changes caused the color variations of Hok-
ie Stone. Te older pinkish dolomites resulted from their
formation during an era when the region faced an arid,
desert-like climate that had a bleaching eect on the rocks.
Te darker gray and black colors come from a time of
swampy and wetter conditions.
Virginia Tech quarry
The Inn at Virginia Tech and Skelton Conference Center (above) and
the Holtzman Alumni Center (right)
McComas Hall
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Papaya Growing in The Florida Home Landscape: DescriptionDocumento7 paginePapaya Growing in The Florida Home Landscape: DescriptionJohnBird0000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Papaya: Organic Farming in The Tropics and SubtropicsDocumento35 paginePapaya: Organic Farming in The Tropics and SubtropicsspectabearNessuna valutazione finora
- Fe-C Phase DiagramDocumento34 pagineFe-C Phase DiagramYoung-long Choi100% (1)
- Market Organic FT CoffeeDocumento19 pagineMarket Organic FT CoffeeJose MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Iron PDFDocumento122 pagineIron PDFMadan YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Small-Scale Coffee Processing MethodsDocumento8 pagineSmall-Scale Coffee Processing MethodsMcAriek Julu NahashonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Life of Birds GuideDocumento25 pagineThe Life of Birds GuideJohnBird0000Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Edward Resume 102908Documento2 pagineEdward Resume 102908edwardblanco03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Door Reinforcement DesignDocumento1 paginaDoor Reinforcement DesignP.MannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Design Validation Guide 2023 Volume IIIDocumento176 pagineAdvance Design Validation Guide 2023 Volume IIIkeffy_bfkNessuna valutazione finora
- Diked & Spill Protection: Dike Protection Fixed Mount Low Level Foam MakersDocumento4 pagineDiked & Spill Protection: Dike Protection Fixed Mount Low Level Foam MakersAamerMAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- BS StandardsDocumento13 pagineBS StandardsShyam Prasad K S100% (3)
- Ensayo ASTM E84 Panel RocaDocumento5 pagineEnsayo ASTM E84 Panel RocaToniHospitalerNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Summary in ContractDocumento3 pagineProject Summary in ContractJeboy ChackoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling of Bridges For Inelastic Analysis: Saiidi@unr - EduDocumento80 pagineModelling of Bridges For Inelastic Analysis: Saiidi@unr - Eduhasan aziziNessuna valutazione finora
- Pearl Academy Jaipur Adapts Traditional ArchitectureDocumento4 paginePearl Academy Jaipur Adapts Traditional ArchitectureDivakar AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Alberta Building Code Guide to Energy Efficient Home ConstructionDocumento45 pagineAlberta Building Code Guide to Energy Efficient Home ConstructionAl7amdlellah100% (2)
- Boiler Structure Erection MethodDocumento76 pagineBoiler Structure Erection MethodSuman GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical NotesDocumento1 paginaElectrical NotesKenneth MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- City Walk ReportDocumento21 pagineCity Walk ReportSekh SamimNessuna valutazione finora
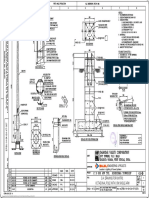
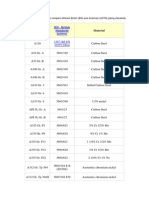
- Study Material ON: S.M. No. Rev. No. Effective DateDocumento15 pagineStudy Material ON: S.M. No. Rev. No. Effective DateAbhishek AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Pavement DesignDocumento15 pagineFlexible Pavement Designপ্রিয়দীপ প্রিয়ম100% (1)
- My Dream House ProjectDocumento12 pagineMy Dream House ProjectRobyn TinneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems of Wiring - A Guide to Cleat, Casing, CTS, Lead Sheathed, Conduit and Their ApplicationsDocumento57 pagineSystems of Wiring - A Guide to Cleat, Casing, CTS, Lead Sheathed, Conduit and Their ApplicationsShantanu ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Pile Foundation EstimateDocumento2 paginePile Foundation EstimateBinod RaazNessuna valutazione finora
- North American Specification For The Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members, 2001 EditionDocumento103 pagineNorth American Specification For The Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members, 2001 EditionClaudio IanneceNessuna valutazione finora
- Max-3 Plus (420-2700) Technical Information & Assembly Instructions Manual PDFDocumento60 pagineMax-3 Plus (420-2700) Technical Information & Assembly Instructions Manual PDFFlorentina SanduNessuna valutazione finora
- Csyc12mkf Service ManualDocumento71 pagineCsyc12mkf Service ManualcoronaqcNessuna valutazione finora
- WRAP-A120 Stansted To Braintree Bypass Case HistoryDocumento7 pagineWRAP-A120 Stansted To Braintree Bypass Case HistorysandycastleNessuna valutazione finora
- Froling P1 Pellet Installation Operating InstructionsDocumento74 pagineFroling P1 Pellet Installation Operating InstructionsAlastair MortonNessuna valutazione finora
- Misk - Method Statement Tracker (Till 21-June-21)Documento13 pagineMisk - Method Statement Tracker (Till 21-June-21)ehteshamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pour CardDocumento2 paginePour Cardsuchendra singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Turner's IOR Key to Risk ManagementDocumento9 pagineTurner's IOR Key to Risk Managementremya_392830015Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Way Ball ValvesDocumento17 pagine3 Way Ball ValvesSagar Bhosale100% (1)
- Sika PDS E SikaPumpDocumento2 pagineSika PDS E SikaPumplwin_oo2435Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Study of Seismic Performance of Multistorey Diagrid Structures With Conventional StructuresDocumento5 pagineComparative Study of Seismic Performance of Multistorey Diagrid Structures With Conventional StructuresInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Design Review Checklist PDFDocumento2 pagineStructural Design Review Checklist PDFyosiboyNessuna valutazione finora