Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Coordination MCQ
Caricato da
Subhasish SauDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Coordination MCQ
Caricato da
Subhasish SauCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CO-ORDINATION CHEMISTRY set 1
1
The ______ sphere is enclosed in brackets in formulas for complex species, and it
includes the central metal ion plus the coordinated groups.
(a) ligand (b) donor (c) oxidation (d) coordination (e) chelating
2.
In coordination chemistry, the donor atom of a ligand is
(a) a Lewis acid. (b) the counter ion (c) the central metal atom.
(d) the atom in the ligand that shares an electron pair with the metal.
(e) the atom in the ligand that accepts a share in an electron pair from the metal.
3.
onsider the coordination compound, !a
"
#$t(!)
%
&. The Lewis acid is
(a) #$t(!)
%
&
"-
(b) !a
'
(c) $t (d) $t
"'
(e) !
-
4.
onsider the coordination compound, (
"
#u(!)
%
&. ) coordinate co*alent bond
exists between
(a) (
'
and !
-
(b) u
"'
and !
-
(c) (
'
and #u(!)
%
&
"-
(d) and ! in !
-
(e) (
'
and u
"'
5.
+i*en the list of ligands and their corresponding names, choose the pair that
disagree.
LI+)!, !)-.
(a) /0
-
hydroxo
(b) !
-
cyanide
(c) l
-
chloro
(d) 0
"
/ )1ua
(e) !0
2
ammine
.
3elect the !orre!t I4$) name for5 #6e6
%
(/0
"
)
"
&
-
(a) dia1uatetrafluoroiron(III) ion (b) dia1uatetrafluoroferrate(III) ion
(c) dia1uatetrafluoroiron(I) ion (d) dia1uatetrafluoroferrate(I) ion
(e) none of these
".
3elect the !orre!t I4$) name for5 #o(!0
2
)
7
&
"'
(a) hexammoniacobaltate(II) ion (b) hexaamminecobaltate(II) ion
(c) hexammoniacobalt(II) ion (d) hexaamminecobalt(II) ion
(e) hexammoniacobalt ion
#.
8hich name9formula combination is !/T correct:
6/;-4L) !)-.
(a) #o(!0
2
)
%
(/0
"
)I&3/
%
tetraamminea1uaiodocobalt(III) sulfate
(b) (#r(!0
2
)
"
l
%
& potassium diamminetetrachlorochromate(III)
(c) #-n(!)
<
&
"-
pentacyanomanganate(II) ion
(d) #!i(/)
%
& tetracarbonylnickel(=)
(e) a#$tl
%
& calcium tetrachloroplatinate(II)
$.
8hat is the oxidation number of the central metal atom in the coordination
compound
#$t(!0
2
)
2
l&l:
(a) 9> (b) = (c) '> (d) '" (e) '2
1%.
(?alance @ond Theory) -agnetic measurements indicate that #o(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
has 2
unpaired electrons. Therefore, the hybridiAation of the metalBs orbitals in
#o(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
is5
(a) sp
2
(b) sp
"
d (c) dsp
"
(d) sp
2
d
"
(e) d
"
sp
2
11.
8hich one of the following complexes can exhibit geometrical isomerism:
(a) #$t(!0
2
)
"
l
"
& (s1uare planar)
(b) #Cn(!0
2
)
"
l
"
& (tetrahedral)
(c) #u(!0
2
)
%
&
"'
(s1uare planar)
(d) #o(!0
2
)
<
l&
"'
(octahedral)
(e) #u(!)
"
&
-
(linear)
12.
) molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image is said to exhibit
which of the following:
(a) geometrical isomerism (b) optical isomerism (c) linkage isomerism
(d) reacti*e isomerism (e) coordination isomerism
13.
In which one of the following species does the transition metal ion ha*e
d
2
electronic configuration:
(a) #r(!0
2
)
7
&
2'
(b) #o(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
(c) #o6
7
&
2-
(d) #6e(!)
7
&
2-
(e) #!i(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
14.
(?alence @ond Theory) The coordination complex, #u(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
has one unpaired
electron. 8hich of the following statements are tr&e:
(>) The complex is octahedral. (") The complex is an outer orbital complex.
(2) The complex is d
"
sp
2
hybridiAed. (%) The complex is diamagnetic.
(<) The coordination number is 7.
(a) >, % (b) >, ", < (c) ", 2, < (d) ", 2 (e) %, <
15.
(rystal 6ield Theory) 8hich one of the following statements is 'A(SE:
(a) In an octahedral crystal field, the d electrons on a metal ion occupy the e
g
set of
orbitals before they occupy the t
"g
set of orbitals.
(b) ,iamagnetic metal ions cannot ha*e an odd number of electrons.
(c) Low spin complexes can be paramagnetic.
(d) In high spin octahedral complexes,
oct
is less than the electron pairing energy,
and is relati*ely *ery small.
(e) Low spin complexes contain strong field ligands.
1.
(rystal 6ield Theory) 8hen the *alence d orbitals of the central metal ion are split
in energy in an octahedral ligand field, which orbitals are raised )east in energy:
(a) d
xy
and d
x
"
-y
" (b) d
xy
, d
xA
and d
yA
(c) d
xA
and d
yA
(d) d
xA
, d
yA
and d
A
"
(e) d
x
"
-y
" and d
A
"
1".
(rystal 6ield Theory) 0ow many unpaired electrons are there in a strong field
iron(II) octahedral complex: (a) = (b) > (c) " (d) % (e) 7
1#.
(rystal 6ield Theory) onsider the complex ion #-n(/0
"
)
7
&
"'
with < unpaired
electrons. 8hich response includes all the following statements that are tr&e, and
no false statements:
I. It is diamagnetic. II. It is a low spin complex. III. The metal ion is a d
<
ion.
I?. The ligands are weak field ligands. ?. It is octahedral.
(a) I, II (b) III, I?, ? (c) I, I? (d) II, ? (e) III, I?
1$.
(rystal 6ield Theory) onsider the *iolet9colored compound, #r(/0
"
)
7
&l
2
and
the yellow compound, #r(!0
2
)
7
&l
2
. 8hich of the following statements is false:
(a) @oth chromium metal ions are paramagnetic with 2 unpaired electrons.
(b)
oct
for #r(!0
2
)
7
&
2'
is calculated directly from the energy of yellow light.
(c)
oct
for #r(/0
"
)
7
&
2'
is less than
oct
for #r(!0
2
)
7
&
2'
.
(d) ) solution of #r(/0
"
)
7
&l
2
transmits light with an approximate wa*elength
range of %=== 9 %"== angstroms.
(e) The two complexes absorb their complementary colors.
2%.
(rystal 6ield Theory) 3trong field ligands such as !
-
5
(a) usually produce high spin complexes and small crystal field splittings.
(b) usually produce low spin complexes and small crystal field splittings.
(c) usually produce low spin complexes and high crystal field splittings.
(d) usually produce high spin complexes and high crystal field splittings.
(e) cannot form low spin complexes.
.COORDINATION CHEMISTRY- set-2
1. Mohrs salt is a
(a) Single salt (b) Double salt (c) Complex salt (d) Chelate
2. Potassium ferrocyanide is
(a) Sigma compound(b) Pi compound (c) Double salt(d) Complex salt
3. Ethylene diamine is
(a) Unidentate ligand (b) Bidentate ligand (c) Polydentate ligand(d) Chelating ligand
4. Copper complex of elthylene
(a) Unidentate ligand (b) Tridentate ligand (c) Polydentate ligand (d) Chelate
5. In potassium ferroayanide, the coordination number of iron is
(a) Two (b) Four (c) Six (d) Eight
6. The coordination number of Ag in potassium argentocyanide is
(a) One (b) Two (c) Three(d) Four
7. The oxication number of Cu in [Cu[NH
3
]
4
]SO
4
is
(a) One (b) Two (c) Three(d) Four
8. Potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) is
(a) Anionic complex (b) Caironic complex (c) Neutral complex(d) None of these
9. Diammine silver (I) chloride is
(a) Anionic complex (b) Cationic complex (c) Neutral complex(d) Chelating complex
10. The neutral complex is .
(a) K[Ag (CN)2] (b) [Ag (NH3)2] Cl (c) Ni (CO)4 (d) [CO (Cl6)]
3
COORDINATION CHEMISTRY- set-3
1. Which one of the following compounds will exhibit linkage isomerism
(a) [Pt (NH3)2 Cl2] (b) [Co (NH3)5 NO2] Cl2 (c) [Co (NH3)4 Cl2] NO2 (d) [Ag (NH3)2] NO2
2. Which one of the following complexes will show ionization isomerism
(a) [Co (NH3)4 Cl2] NO2 (b) [Cr (H2 O]6 Cl3 (c) [Co (NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6] (d) K (Ag (CN)2]
3. Diaminopropane exhibit
(a) Coordinate isomerism (b) Lignad isomerism (c) Linkage isomerism (d) Optical isomerism
4. Dichloro diammine platinum exhibit
(a) Optical isomerism (b) Geometrical isomerism (c) Linkage isomerism (d) Coordination
isomerism
5. Out of the following which complex will exhibit optical isomenism
(a) Ni (CO)4 (b) Na2 [Ni (CN)4] (c) Co (H2 N. CH2. CH2 NH2) Cl2 (d) [Ni (H2 O)6]
2+
6. Which of the complexes has bonds only
(a) Ni (CO)4 (b) Pb (C2 H5)4 (c) Fe (C5 H5)2 (d) Fe (CO)5
7. Ferrocene complex is
(a) Sigma bonded (b) bonded (c) Both of there(d) None of these
8. Which one of them is not a bonded complex
(a) Dibenzene Chromium (b) CH3 Mg Br (c) (C2 H5)2 Zn (d) Al2 (CH3)6
9. Which one of the complex is not bonded
(a) Ferrocene (b) Dibenzene Chromium (c) Ni (CO)4 (d) (CH3)2 Cd
10. Among the following ions which one has the highest paramagnetism
(a) [Cr (H2 O)6 ]
3+
(b) [Fe (H2 O)6 ]
2+
(c) [Cu (H2 O)6 ]
2+
(d) [Zn (H2 O)6 ]
2+
COORDINATION CHEMISTRY set-4
>.The coordination number and oxidation state of
Cr
in
( ) [ ]
3 4 2 3
O C Cr K
are, respecti*ely
(a) % and '" (b)7 and '2 (c)2 and '2 (d) 2 and =
".The complex compounds which result from the coordination of carbon monoxide are
known as
(a) .lectronic (b)arbonyls (c)arbonates (d) arbon permono
2.-ixture
mol X 02 . 0
of
Br SO NH Co ] ) ( [
4 5 3 and =.=" mol of 4 5 3
] ) ( [ SO Br NH Co
was prepared in "
litre of solution
> litre of mixture X ' excess
Y AgNO
3 .
> litre of mixture X ' excess
Z BaCl
2
!umber of moles of Y and Z are
(a) =.=>, =.=> (b)=.=", =.=> (c)=.=>, =.=" (d) =.=", =.="
%.8hich of the following organometallic compound is
and
bonded
(a) 3 3
) (CH Fe
(b)
] ) ( [
2 5 5
5
H C Fe
(c)
+ 2
3 5
] ) ( [ NH CO Co
(d)
)] ( [
4 2
2
3
H C n PtCl K
<.In
( ) [ ] ,
4 4 3
SO NH Ni
the *alency and coordination number of
Ni
will be respecti*ely
(a) 2 and 7 (b)" and % (c)% and " (d) % and %
7.o9ordination number of
Fe
in the complexes
( ) [ ] ,
4
6
CN Fe
( ) [ ]
3
6
CN Fe
and
[ ]
4
FeCl
would
be respecti*ely
(a) ", 2, 2 (b)7, 7, % (c) 7, 2,2 (d) 7, %, 7
D./n hydrolysis 2 2
) ( SiCl Me
will produce
(a) 2 2
) ( ) ( OH Si Me
(b)
O Si Me
2
) (
(c)
n
O Si Me O ] ) ( [
2 (d)
) (
2
OH SiCl Me
E.8hich of the following represents a chelating ligand
(a)
O H
2 (b)
OH (c)
DMG
(d)
Cl
9. 4
CuSO
reacts with
KCN
solution and forms
(a) 2
) (CN Cu
(b)
) (CN Cu
(c)
[ ]
4 2
) (CN Cu K
(d)
( ) [ ]
4 3
CN Cu K
>=.In the process of extraction of gold,
;oasted gold ore
+ + + OH X O H CN
O
] [
2
2
Identify the complexes #X& and #Y&
(a)
2
4 2
] ) ( [ , ] ) ( [ CN Zn Y CN Au X
(b)
2
4
3
4
] ) ( [ , ] ) ( [ CN Zn Y CN Au X
(c)
4
6 2
] ) ( , ] ) ( [ CN Zn Y CN Au X
(d)
2
4 4
] ) ( [ , ] ) ( [ CN Zn Y CN Au X
>>.) solution of potassium ferrocyanide would contains ...... ions
(a) " (b)2 (c) % (d) <
>".8hich one of the following complexes is an outer orbital complex
(a)
+ 3
6 3
] ) ( [ NH Co
(b)
4
6
] ) ( [ CN Mn
(c)
4
6
] ) ( [ CN Fe
(d)
+ 2
6 3
] ) ( [ NH Ni
)tomic nos 5
28 , 27 , 26 , 25 Ni Co Fe Mn
>2.8hich one of the following has largest number of isomers :
(a)
+ 2
2 3
)] ( ) ( [ CO H PP Ir
(b)
+ 2
5 3
] ) ( [ Cl NH Co
(c)
+
] ) ( [
2 4 3
Cl NH Ru
(d)
+
] ) ( [
2 2
Cl en Co
(R F alkyl groupG en F ethylenediamine)
>%.8hich kind of isomerism is exhibited by octahedral
Cl Br NH Co
2 4 3
) (
:
(a) +eometrical and IoniAation (b)+eometrical and /ptical
(c) /ptical and IoniAation (d)+eometrical only
><.8hich one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism (en F
ethylenediamine)
(a) cis H
] ) ( [
2 2 3
Cl NH Pt
(b)trans H
] ) ( [
2 2
Cl en Co
(c) trans H
] ) ( [
2 2 3
Cl NH Pt
(d)cis H
] ) ( [
2 2
Cl en Co
>7.
4
] EDTA [
is a5
(a) -onodentate ligand (b)@identate ligand (c) Iuadridentate ligand (d)
0exadentate ligand
>D.8hich of the following statements is incorrect :
(a) In
], ) ( [
6 3
CN Fe K
the ligand has satisfied only the secondary *alency of ferric
ion.
(b)In
], ) ( [
6 3
CN Fe K
the ligand has satisfied both primary and secondary *alencies
of ferric ion.
(c) In
], ) ( [
6 4
CN Fe K
the ligand has satisfied both primary and secondary *alencies
of ferrous ion.
(d)In
, ] ) ( [
4 4 3
SO NH Cu
the ligand has satisfied only the secondary *alency of
copper.
>E.8hich of the following is considered as an anticancer species.
(a)
1
1
1
]
1
Cl N H
Pt
Cl N H
3
3
(b)
1
1
1
]
1
3
3
NH Cl
Pt
Cl N H
(c)
1
1
1
1
1
]
1
Cl Cl
CH Pt
CH Cl
2
2
||
(d)
1
1
1
]
1
Cl Cl
Pt
Cl Cl
>J.)n a1ueous solution of 2
CoCl
on addition of excess of concentrated HCl turns
blue due to formation of
(a)
] ) ( [
2 4 2
Cl O H Co
(b)
2
4 2
] 2 ) ( [ Cl O H Co
(c)
2
4
] [CoCl
(d)
] 2 ) ( [
2 2
Cl O H Co
"=.The correct order for the wa*elength of absorption in the *isible region is
(a)
+ +
< <
2
6 2
2
6 3
4
6 2
] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ O H Ni NH Ni NO Ni
(b)
+ +
< <
2
6 3
2
6 2
4
6 2
] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ NH Ni O H Ni NO Ni
(c)
+ +
< <
4
6 2
2
6 3
2
6 2
] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ NO Ni NH Ni O H Ni
(d)
+ +
< <
4
6 2
2
6 2
2
6 3
] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ ] ) ( [ NO Ni O H Ni NH Ni
">.In which of the following pairs both the complexes show optical isomerism
(a) cis-
3
2 2 4 2
] ) ( [ Cl O C Cr
, cis-
] ) ( [
2 4 3
Cl NH Co
n(b) 3 3
] ) ( [ Cl en Co
, cis9
Cl Cl en Co ] ) ( [
2 2
(c)
Cl dien PtCl )] ( [
,
2
2 2
] [ Br NiCl
(d)
] ) ( ) ( [
3 3 3 3
NH NO Co
, cis9
] ) ( [
2 2
Cl en Pt
"".8hich of the following compounds shows optical isomerism
(a)
+ 2
4 3
] ) ( [ NH Cu
(b)
2
4
] [ZnCl
(c)
3
3 4 2
] ) ( [ O C Cr
(d)
3
6
] ) ( [ CN Co
Ans*ers to Coord+nat+on-1
1. (d) 2. (d) 3. (d) 4. (b) 5. (b) . (b) ". (d) #. (c) $. (d) 1%. (d) 11. (a) 12. (b) 13. (a) 14. (b)
15. (a) 1. (b) 1". (a) 1#. (b) 1$. (b) 2%. (c)
Answer : COORDINATION CHEMISTRY-2
1. (b) 2. (d) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (c) 6. (a) 7. (b) 8. (a) 9. (b) 10. (c)
Answer COORDINATION CHEMISTRY : -3
>.(b) ". (a) 2. (b) %. (c) <. (c) 7. ( ) D. (b) E. (a) J. (d) >=. (b)
)nswer 5 oordination hemistry 5 %
1. (b) Its coordination number will be 7 because it is bonded with three bidentale ligands.
/xi. !o. of Cr in
] ) ( [
2
3 4 2
1
3
O C Cr K
is
0 ) 1 ( 3 ) 2 ( 3 + + + x
3 + x
2. (b) e.g. 4 5
) ( , ) ( CO Ni CO Fe
etc.
3. (a)
+
3
mole 02 . 0
4 5 3
] ) ( [ AgNO Br SO NH Co
AgBr NO SO NH Co
+
) ( mole 02 . 0
3 4 5 3
] . ) ( [
+
2
mole 02 . 0
4 2 5 3
] ) ( [ BaCl SO Br NH Co
4
) ( mole 02 . 0
2 5 3
] ) ( [ BaSO Cl Br NH Co
!
+
/n using one lit. solution, we will get =.=> mole y and =.=> mole z.
4. (b)
] ) ( [
2 5 5
5
H C Fe
is the organometallic compound which has and bonds present.
5. (b)
2
4 4
0
3
] ) ( [
SO NH Ni
x
2 0 ) 2 ( 0 + + + x x
is *alency and % is C.N. of Ni.
. (b) o9ordination number is e1ual to total number of ligands in a complex.
". (c)
n
O
CH
CH
Si O O nH
CH CH
Si
Cl Cl
n
,
_
+
1
1
1
]
1
3
3
|
|
2
3 3
2
#. (c) @ecause it is a polydentate ligand which binds the central atom nickel forming a ring like
structure.
$. (d)
cuprate tetrac!o "ota##$um
4 3 4
] ) ( [ 4 CN Cu K CuSO KCN +
1%. (a)
+ + + OH CN Au
O
O H CN ] ) ( [
ore %ol&
'oa#te&
2
2
2
[ ] [ ]
+
2
4 2
) ( ) ( CN Zn Zn CN Au .
11. (d) $otassium ferrocynide
] ) ( [
6 4
CN Fe K
will ioniAe as
] ) ( [
6 4
CN Fe K
(
+
+
4
6
] ) ( [ 4 CN Fe K
3o, it will gi*e fi*e ions in solution.
12. (d) omplex ion 0ybridiAation of central atom
4
6
] ) ( [ CN Fe
3 2
"# d (inner)
4
6
] ) ( [ CN Mn
3 2
"# d (inner)
+ 3
6 3
] ) ( [ NH Co
3 2
"# d (inner)
+ 2
6 3
] ) ( [ NH Ni
2 3
d "# (outer)
13. (d)
+
] ) ( [
2 2
Cl en Co
shows geomerical as well as optical isomerism.
14. (a)
15. (d)
1. (d)
.thylenediamine tetraacetate ion (.,T))
CO
NH
2
cis
NH
2
H
2
N
H
2
N
Br
Br
CO
NH
2
Trans
NH
2
H
2
N
H
2
N
Br
Br
CO
cis
NH
2
H
2
N
H
2
N
Cl
Br
NH
2
CO
NH
2
Trans
NH
2
H
2
N
Br
Cl
NH
2
CO
en
en
Cl
Cl
CO
en
en
Cl
Cl
-irror
N
CH
2
O = C O
C O
O
=
H
2
C
! CH
2
! CH
2
! N
CH
2
O
C = O
CH
2
O
C
O
=
"
They ha*e six donor atoms. poly dentate ligands ha*e flexidentate character. It is not
necessary that all the donor atoms present in the polydentate ligands should form co9
ordinate bonds with central metal atom or ion.
1". (a,d) In
] ) ( [
6 3
CN Fe K
the ligand are negati*e which is present in coordination spheres shows
a dual beha*iour. It may satisfied both primary K secondary *alencies while neutral ligand
satisfied only secondary *alencies.
1#. (a) is Isomer of
] ) ( [
2 2 3
Cl NH Pt
is used as an anticancer drugs for treating se*eral type of
malignant tumours. 8hen it is inLected into the blood stream the more reacti*e Cl groups
are lost so the Pt atom bonds to a N atom in guanosine (a part of ,!)) This molecule
can bond to two different guanosine units K by bridging between them it upsets the normal
reproduction of ,!).
1$. (c) CoCl
"
is a weak Lewis acid, reacting with chloride ion to produce salt containing the
tetrahedral #CoCl
%
&
"H
ion. CoCl
"
is blue when anhydrous, and a deep magneta colour when
hydrated, for this reason it is widely used as an indicator for water.
2%. (a) The absorption of energy or the obser*ation of colour in a complex transition compound
depends on the charge of the metal ion and the nature of the ligands attached. The same
metal ion with different ligands shows different absorption depending upon the type of
ligand. The presence of weak field ligands make the central metal ion to absorb low energies
i.e.# of higher wa*elength. The field strength of ligands can be obtained from
spectrochemical series. i.e.
(weak field) $
H
M Br
H
% &
"H
M Cl
H
M NO
2
H
M '
H
M OH
H
M H
"
O M NH
2
M NO
"
H
M CN
H
M CO
(strong field)
21. (b) #Co(en)
2
&Cl
2
cis9#Co(en)
"
Cl
"
&Cl
22. (c)
2
'
en
en
en
C
o
(9form
C
o
mirror
2
'
l9form
en
en
en Co
mirror
'
C
l
en
en
C
o C
l
C
l
C
l
'
en
en
C
o
Cr
OX
OX
OX
H2
OX
OX
OX
Cr
H2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento29 pagineAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Seal Face MaterialsDocumento19 pagineMechanical Seal Face MaterialsKamlesh Kamlesh Etwaro100% (1)
- Welding Distortion and Its ControlDocumento53 pagineWelding Distortion and Its ControlAnnamalai Ram JGC100% (1)
- Chapter 7Documento56 pagineChapter 7itsjc0% (1)
- Some Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocumento2 pagineSome Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry83% (6)
- Chemistry Practical MCQsDocumento16 pagineChemistry Practical MCQsamrita kumari0% (1)
- All MCQS First YearDocumento85 pagineAll MCQS First YearNazimEhsanMalik25% (4)
- Chemistry McqsDocumento51 pagineChemistry McqsEngr Muhammad MubeenNessuna valutazione finora
- ch13 ProblemsDocumento84 paginech13 Problemsbrownhazel67% (6)
- ASTM A600-92a High Speed SteelDocumento14 pagineASTM A600-92a High Speed Steelkarob87100% (1)
- ch09 TestbankDocumento84 paginech09 TestbankPatrick Malcolm Santos80% (5)
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsDocumento13 pagineChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Gate Papers PDFDocumento326 pagineSolved Gate Papers PDFPreeti Singh100% (3)
- CH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersDocumento10 pagineCH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersBUCH203Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohol, Ether & Phenol - QuestionDocumento3 pagineAlcohol, Ether & Phenol - Questionbest badmintonNessuna valutazione finora
- Qoii0708 CO 17 TIFDocumento34 pagineQoii0708 CO 17 TIFLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- Mcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanDocumento29 pagineMcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanMalikXufyanNessuna valutazione finora
- NMR 1Documento3 pagineNMR 1amitNessuna valutazione finora
- NMR HandoutDocumento23 pagineNMR HandoutVirendra Singh RajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Org Part 1 With AnsDocumento7 pagineOrg Part 1 With AnsDeepak PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Colligative PropertiesDocumento61 pagineColligative PropertiesSubhasish Sau100% (1)
- ACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SDocumento12 pagineACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SMohamad HabbabaNessuna valutazione finora
- LS 0 2 2d3125 024a74a09e7e0-OrganometallicsDocumento15 pagineLS 0 2 2d3125 024a74a09e7e0-OrganometallicsHamit Rana100% (1)
- NMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocumento71 pagineNMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDeepak SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem MCQ FinalDocumento258 pagineChem MCQ FinalDare DevilNessuna valutazione finora
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIDa EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- MCQ Chapter 8 Coordination CompoundDocumento7 pagineMCQ Chapter 8 Coordination CompoundSavien Brandan100% (3)
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsDocumento9 pagineAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsGyanendra Vikram Maurya100% (1)
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocumento9 pagineAlcohols and Phenolsdivya divyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Documento14 pagineAromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Raj ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Organometallic Compounds Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocumento8 pagineOrganometallic Compounds Questions and Answers - Sanfoundryمحمد احمد مجیبNessuna valutazione finora
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocumento6 pagineSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- Model Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Documento4 pagineModel Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Khalid AbeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz No. 5 HeterocyclesDocumento3 pagineQuiz No. 5 HeterocyclesGezem GigantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1Documento195 pagineOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1aditya kumar Agarwal100% (1)
- All MCQs in OneDocumento22 pagineAll MCQs in OneNo NameNessuna valutazione finora
- IsomerismDocumento16 pagineIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- CSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesDocumento32 pagineCSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesShiksha PortalNessuna valutazione finora
- NMR SpectrosDocumento29 pagineNMR Spectroshareesh13h100% (1)
- Redox MCQsDocumento7 pagineRedox MCQsHarsh Walavalkar100% (1)
- MCQ On Mass Spectroscopy: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 Msc-I Organic ChemistryDocumento3 pagineMCQ On Mass Spectroscopy: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 Msc-I Organic ChemistrySarita YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Photochemistry of Carbonil Compound1Documento16 paginePhotochemistry of Carbonil Compound1Naveen Agarwal100% (1)
- IIT JAM Chemistry Test PaperDocumento15 pagineIIT JAM Chemistry Test PaperAnil Kumar100% (1)
- LS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsDocumento8 pagineLS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsHamit RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeyDocumento3 pagineAlkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeySameer HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice SheetDocumento4 pagineAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice Sheetsameeryad72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocumento6 pagineAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- A - 2 (Isomerism, Reaction Mechantism) - Question PaperDocumento14 pagineA - 2 (Isomerism, Reaction Mechantism) - Question PaperSachin DedhiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocumento29 pagineChapter 12: Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionAnonymous Ngsu7C4aNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Unit# 2Documento8 pagine02 Unit# 2Muhammad Bilal ChemIstNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarDocumento5 pagineMcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarPhoton Online Science Academy0% (1)
- Surface Chemistry MCQs - Questions - Paper 1Documento7 pagineSurface Chemistry MCQs - Questions - Paper 1krishna prasad ghantaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ For Question PaperDocumento11 pagineMCQ For Question PaperAjay Sharma Shankyan100% (2)
- Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonDocumento6 pagineChapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonSukhi Sohal0% (1)
- 12 Chemistry MCQ CH 5Documento95 pagine12 Chemistry MCQ CH 5Anshika Tripathi100% (1)
- ConformationsDocumento8 pagineConformationsrameshiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Name Reaction Reagent Assignment PDFDocumento21 pagineName Reaction Reagent Assignment PDFSandipan SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento38 pagineChapter 4Rebecca Campbell100% (1)
- The Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocumento19 pagineThe Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersRohit Chavariya100% (1)
- MCQ Steroids and HormonesDocumento10 pagineMCQ Steroids and Hormonessara khaledNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperDocumento3 pagineNEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperGanga DharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Solution Csir Net Dec 2015 FinalDocumento26 pagineDetailed Solution Csir Net Dec 2015 FinalAamer100% (9)
- Chapter 21 II PDFDocumento23 pagineChapter 21 II PDFadelNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ ElectrochemistryDocumento28 pagineMCQ ElectrochemistrySubhasish Sau100% (1)
- Jee 2018-4Documento8 pagineJee 2018-4Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemestry English Part-1 NewDocumento322 pagineChemestry English Part-1 Newaml11052Nessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Assesment For JeeDocumento13 paginePeriodic Assesment For JeeSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio MoleculesDocumento17 pagineBio MoleculesSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Xii 1,2,3 SolutionDocumento50 pagineClass Xii 1,2,3 SolutionSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Detail Practice and Concept Buildingfor Jee2018-1: Chemical Bond-1Documento11 pagineDetail Practice and Concept Buildingfor Jee2018-1: Chemical Bond-1Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee On OrganicDocumento5 pagineJee On OrganicSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Class X CBSE Chapter-1Documento14 pagineClass X CBSE Chapter-1Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Xii Solution 3Documento22 pagineClass Xii Solution 3Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaseous StateDocumento2 pagineGaseous Statealeena'Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept Foe Icse-XDocumento11 pagineMole Concept Foe Icse-XSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Equilibrium PartDocumento17 pagineChemical Equilibrium PartSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- CLASS XII Halo Alkane - HaloareneDocumento35 pagineCLASS XII Halo Alkane - HaloareneSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolute Configuration RSDocumento13 pagineAbsolute Configuration RSSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Class - XI - 5Documento44 pagineClass - XI - 5Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Claass 27Documento88 pagineClaass 27Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee Exam On Alcohol-JeeDocumento15 pagineJee Exam On Alcohol-JeeSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
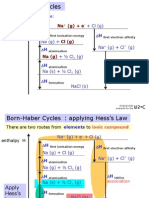
- Na (G) + E: Eg For Sodium Chloride: + CL (G)Documento4 pagineNa (G) + E: Eg For Sodium Chloride: + CL (G)Subhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Transition Elements - Model Questions PDFDocumento6 pagineTransition Elements - Model Questions PDFSubhasish Sau100% (1)
- Board ExamDocumento20 pagineBoard ExamSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Iupac: Important Points To Remember-1 For Jee-Aipmt: 1) Root WordDocumento29 pagineIupac: Important Points To Remember-1 For Jee-Aipmt: 1) Root WordSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 35 Bohr Theory of HydrogenDocumento14 pagineCH 35 Bohr Theory of HydrogenSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry: Richard F. Daley and Sally J. DaleyDocumento47 pagineOrganic Chemistry: Richard F. Daley and Sally J. DaleySai Swaroop MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Science Unit 9 The Coordination CompoundDocumento22 pagineClass 12 Science Unit 9 The Coordination CompoundjimcarryfromindiaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 35 Bohr Theory of HydrogenDocumento14 pagineCH 35 Bohr Theory of HydrogenSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Radius PresentationDocumento11 pagineAtomic Radius PresentationSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- The Coordination Number and Oxidation State ofDocumento24 pagineThe Coordination Number and Oxidation State ofSubhasish SauNessuna valutazione finora
- Asid Dan Bes Kimia Ting 4Documento74 pagineAsid Dan Bes Kimia Ting 4Wan Azzura Wan Ismail100% (1)
- All India Aakash Test Series For NEET-2020 TEST - 2 - Code-ADocumento18 pagineAll India Aakash Test Series For NEET-2020 TEST - 2 - Code-AShaestah FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Is - 412Documento12 pagineIs - 412raje_58Nessuna valutazione finora
- Processed Ekspor Mineral 2000 2010Documento11 pagineProcessed Ekspor Mineral 2000 2010Khalis Mahmudah100% (1)
- Investigating The Effect of The Deep Cryogenic Heat Treatment On The Corrosion Behavior of The 1.2080 Tool SteelDocumento8 pagineInvestigating The Effect of The Deep Cryogenic Heat Treatment On The Corrosion Behavior of The 1.2080 Tool SteelGwee YongkuanNessuna valutazione finora
- William Corbett, SSPC PCS KTA-Tator, IncDocumento23 pagineWilliam Corbett, SSPC PCS KTA-Tator, InccocorruoNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw LewisDocumento3 pagineDraw LewisclrgeekNessuna valutazione finora
- The Most Expensive Materials in The World PDFDocumento10 pagineThe Most Expensive Materials in The World PDFAnonymous gL38AGom29100% (2)
- Zinc Oxide 40%Documento2 pagineZinc Oxide 40%iloveit52252Nessuna valutazione finora
- (Chemical Laws) Yr 10intl Wk1Documento23 pagine(Chemical Laws) Yr 10intl Wk1Victor OkosunNessuna valutazione finora
- Fake Ash Laura's Turquoise Based TestsDocumento8 pagineFake Ash Laura's Turquoise Based TestsTim CarlsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - P Block ElementsDocumento2 pagineAssignment - P Block ElementsYash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MCP22% G CoaDocumento1 paginaMCP22% G CoaJosue UriñaNessuna valutazione finora
- 330 17CV551 APC Module 1 NotesDocumento17 pagine330 17CV551 APC Module 1 NotesPRAVEENA KUMARA VNessuna valutazione finora
- Salt Analysis ProcedureDocumento7 pagineSalt Analysis ProcedureNivetha Shree ANessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content by Winkler Redox TitrationDocumento5 pagineQuantitative Determination of Dissolved Oxygen Content by Winkler Redox Titrationneesan222Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biofuel Sector in Sri Lanka: Assignment 01Documento4 pagineBiofuel Sector in Sri Lanka: Assignment 01BiNtH AbDeeNNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding HandbookDocumento37 pagineWelding HandbookVijo JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Solutions WorksheetDocumento2 pagineClass 12 Solutions WorksheettyrtybtNessuna valutazione finora
- Msds Pfad - Berkah-1Documento4 pagineMsds Pfad - Berkah-1Afif AncikNessuna valutazione finora
- 9701 w13 QP 35 2 PDFDocumento12 pagine9701 w13 QP 35 2 PDFNeural Spark Physics CieNessuna valutazione finora
- MSM Unit 4Documento10 pagineMSM Unit 4YAZI 77Nessuna valutazione finora
- S1112PS IIIc 15Documento6 pagineS1112PS IIIc 15Dexter JaducanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Demonstrating Job's Method With Colorimeter or SpectrophotometerDocumento2 pagineDemonstrating Job's Method With Colorimeter or Spectrophotometeriabureid7460Nessuna valutazione finora
- LME Special Contract Rules For Copper GRADE ADocumento4 pagineLME Special Contract Rules For Copper GRADE Aadelafuente2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Casein PDFDocumento3 pagineCasein PDFEasy ways2017Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stella-Aerosol - WD Spray - MSDSDocumento4 pagineStella-Aerosol - WD Spray - MSDSseitoikeshi9Nessuna valutazione finora