Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Zener Diode Characteristics
Caricato da
PercivalEgau0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
270 visualizzazioni1 paginaLab, electronics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoLab, electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
270 visualizzazioni1 paginaZener Diode Characteristics
Caricato da
PercivalEgauLab, electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
1
EE221 BASIC ELECTRONICS
LAB 3 : ZENER DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
1. OBJECTIVE: To plot forward and reverse characteristics of a Zener Diode.
2. EQUIPMENT: DATS 7000 Breadboard, 6.8-V zener diode, 1-k resistor, 470- resistor.
3. INTRODUCTION
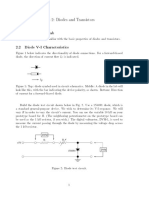
A zener diode (symbol shown above) is a heavily doped diode. In forward bias it operates
normally like the ordinary diode. In reverse bias it conducts only leakage current until the reverse
voltage is large enough to break down the junction. This reverse breakdown occurs at low
voltages is reversible and not destructive to the diode. The breakdown occurs in either of two
ways. The first, called Field-Effect Breakdown, is for the applied reverse voltage may pull the
electrons across the reverse biased pn-junction causing the diode to conduct in reverse bias. The
second way, called Avalanche Breakdown, is for the applied voltage to accelerate electrons
which in turn knock other electrons out of their normal orbits causing rapid conduction of current.
Both these effects occur at relatively low voltages which can be controlled during manufacture.
Zener diodes are available with fixed breakdown voltages of 2.7, 3.3, 3.9, 4.7, 5.1, 5.6, 6.8 V up to
75 V or more breakdown voltages. This series of voltages has values which almost follow
standard E12 values of resistors.
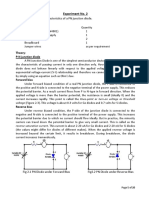
4. PROCEDURE
4.1 Zener Diode in Forward Bias
a) Draw a circuit with the zener diode in forward bias in series with a 1 k resistor across a
15 V variable dc supply. The resistor will be used for measuring current as well as for
limiting the current through the diode.
b) Measure the actual value of your 1 k resistor and build the circuit. Include two voltmeters
for measuring V
D
and V
R
.
c) Starting from supply voltage of 0 V, slowly increase the supply voltage taking V
D
and V
R
readings up to but not exceeding 15 V supply. CalculateI
D
and plot the Forward-Bias
I-V characteristic (V
D
and I
D
) of the diode. Do not exceed 15 V supply.
4.2 Zener Diode in Reverse Bias
a) Draw a circuit with the zener diode in reverse bias in series with a 470 resistor across a
15 V variable dc supply.
b) Measure the actual value of your 470 resistor and build the circuit. Include two
voltmeters for measuring V
D
and V
R
.
c) Starting from supply voltage of 0 V, slowly increase the supply voltage taking V
D
and V
R
readings up to but not exceeding 15 V supply. CalculateI
D
and plot the Reverse-Bias I-V
characteristic (-V
D
and I
D
) of the diode.
d) Plot also the V
D
vs V
S
graph.
5. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
Explain the graph in 4(d). Examine your results and draw any comparisons or differences in
behaviour between the zener diode and the ordinary rectifier signal diodes and LED used in Lab 2.
LAB REPORT: Your lab report should be written in full so that it is understandable to
anyone who reads it without having seen this Lab sheet.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Study of Diode CharacteristicsDocumento6 pagineStudy of Diode CharacteristicsBhavyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex 305Documento51 pagineEx 305DineshKumarCholkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesDa EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- 1-Diode Characteristics and Rectifier CircuitsDocumento17 pagine1-Diode Characteristics and Rectifier CircuitsAnjan SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Da EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- BECE LabManualDocumento15 pagineBECE LabManualDrakie SumanilNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualDocumento61 pagineElectronic Devices & Circuits: Laboratory ManualFadila IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 19EEE181 ReportDocumento14 pagine19EEE181 ReportabcdNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocumento9 pagineElectronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsVy NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp111 ManualDocumento58 pagineExp111 ManualTapan JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab reportTTDocumento13 pagineLab reportTTPaa Kwesi ArhinfulNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeDocumento5 pagineExperimentally Study The IV Curves of DiodeMuhammad Tehreem100% (1)
- Experiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyDocumento15 pagineExperiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyJessica Laine TumbagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec8261 CD Lab ManualDocumento92 pagineEc8261 CD Lab ManualthasleemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 2Documento10 pagineExp 2Enas QtaifanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics LabDocumento60 pagineBasic Electronics Labrahulsingle67% (3)
- Purpose: Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocumento7 paginePurpose: Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsshahidNessuna valutazione finora
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocumento4 pagineEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode Characteristicsdonatello84100% (3)
- 3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.Documento4 pagine3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.BBA UniversityNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationDocumento3 paginePHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationNurul Naafizah SulaimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Physics Lab ManualDocumento6 pagineApplied Physics Lab ManualAbdul MunimNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Documento32 pagineEee 111 Lab Manual 2-8 (Latest)Ismot Jahan MoniNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI Laboratory 2Documento2 pagineEMI Laboratory 2DEO SALVACIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Theejaswini PhyDocumento22 pagineTheejaswini Phyindianaashika72Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2Documento41 pagineCH 2avishek aviNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 45Documento11 pagineExp 45tanmay sonawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab1 Diode Characteristics1588856822Documento2 pagineLab1 Diode Characteristics1588856822badalabhinav10Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lab Manual EeeDocumento106 pagineEDC Lab Manual EeeVishnu Kumar NadarNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lab ManualDocumento68 pagineEDC Lab ManualRocky AdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDocumento27 pagineElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diode, BJT, Zener, MosfetDocumento10 pagineDiode, BJT, Zener, MosfetSundar Krishna MoorthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 Eng NaderDocumento8 pagineExperiment 1 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp-A2 230224 110136 PDFDocumento5 pagineExp-A2 230224 110136 PDFKashish GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientech Manual - 1Documento19 pagineScientech Manual - 1Piyush Patel0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Diode Circuit Ee b2 76 PDFDocumento50 pagineChapter 1 Diode Circuit Ee b2 76 PDFajay RCBNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lab ManualDocumento63 pagineEDC Lab Manualranjitha gavniNessuna valutazione finora
- I-V Characteristics of Diode-Final-RUBEL MIA-5096190105Documento12 pagineI-V Characteristics of Diode-Final-RUBEL MIA-5096190105Md Rubel hosainNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)Documento12 pagineLaboratory Report Cover Sheet: 21Ecc211L - Devices and Digital Ic Lab Third Semester, 2023-24 (Odd Semester)nikunj sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diodes and Their ApplicationsDocumento6 pagineDiodes and Their ApplicationsKarla Alberto TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 01 P-N DiodeDocumento5 pagineLab 01 P-N DiodeyayayehNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lab ManualDocumento45 pagineEDC Lab ManualChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- Experiment - 15: AIM: To Study Zener Diode Characteristic. ApparatusDocumento2 pagineExperiment - 15: AIM: To Study Zener Diode Characteristic. ApparatusChirag PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Goals of This Lab 2.2 Diode V-I Characteristics: DVM 1k R +5VDocumento4 pagine2.1 Goals of This Lab 2.2 Diode V-I Characteristics: DVM 1k R +5VRMK BrothersNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual ECE 1Documento15 pagineLab Manual ECE 1Macky Malupangue100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Diode Circuit Final 24 PDFDocumento45 pagineChapter 1 Diode Circuit Final 24 PDFMahankali SwathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering-B.tech-Eee-2ndDocumento31 pagineLab Manual Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering-B.tech-Eee-2ndDeepanshu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics 1Documento42 pagineElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron DeviceDocumento112 pagineElectron DevicekrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec0221 Ed Lab ManualDocumento68 pagineEc0221 Ed Lab ManualGoutham ShanNessuna valutazione finora
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocumento34 pagineKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 5 Diodes 05Documento5 pagineExp 5 Diodes 05api-3717843Nessuna valutazione finora
- EC6361 Electronics LaboratoryDocumento97 pagineEC6361 Electronics LaboratoryBaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 02Documento7 pagineExp 02M. Ahmad RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor of Engineering Honours Degree in Telecommunications EngineeringDocumento9 pagineBachelor of Engineering Honours Degree in Telecommunications EngineeringBRIGHT TZZZY CHINGWENANessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 01Documento6 pagineAssignment 01Z S PlaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2Documento2 pagineLab 2Daniel MakahlehNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IDocumento20 pagineDC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IMohannad S. AlghamdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics I: DiodesDocumento31 pagineAnalog Electronics I: DiodesRachul heenimNessuna valutazione finora
- Final PPT of Carbon NanotubesDocumento29 pagineFinal PPT of Carbon Nanotubesmkumar_5481450% (2)
- Site Preparation, Layout, Installation, and Hydration of Geosynthetic Cementitious Composite MatsDocumento8 pagineSite Preparation, Layout, Installation, and Hydration of Geosynthetic Cementitious Composite Matsomar TahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 - WEEK 2 - MEASURES OF POSITION For GROUPED DATADocumento16 pagineQ4 - WEEK 2 - MEASURES OF POSITION For GROUPED DATAEllaineeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Click125 82K60H30Y 0Documento169 pagineClick125 82K60H30Y 0yeoj manaNessuna valutazione finora
- Qap For Steam TurbineDocumento3 pagineQap For Steam TurbinedgmprabhakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Time ResponseDocumento105 pagineTime ResponseFrogie HuniebieNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 DZM 24Documento1 pagina6 DZM 24Wai Phyoe AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report Welding (SMAW) - FizaDocumento13 pagineLab Report Welding (SMAW) - FizaCheng Yee71% (7)
- Chapter 9 EnglishDocumento53 pagineChapter 9 Englishhoda melhemNessuna valutazione finora
- ADAT Optical Audio Data Generator and Encoder V1401Documento8 pagineADAT Optical Audio Data Generator and Encoder V1401mylitalindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Textile AssignmentDocumento8 pagineTextile AssignmentMahmudul Hasan Khan40% (5)
- C05 - Stationary Potential EnergyDocumento73 pagineC05 - Stationary Potential Energyyttan1116Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpDocumento37 pagineA Compendium of Blog Posts On Op Amp Design Topics: by Bruce TrumpJustine ManningNessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessors and Digital ICs For Control of Power Electronics and DrivesDocumento79 pagineMicroprocessors and Digital ICs For Control of Power Electronics and DrivesTianmingyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Center of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Documento6 pagineCenter of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Sador YonasNessuna valutazione finora
- AC 23-8B Flight Test Guide App 1Documento22 pagineAC 23-8B Flight Test Guide App 1Ladislao PazmanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrosyl Complexes of RutheniumDocumento26 pagineNitrosyl Complexes of RutheniumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNessuna valutazione finora
- GOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDDocumento14 pagineGOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDVansh sareenNessuna valutazione finora
- KinematicsDocumento5 pagineKinematicsUnicornpop PopNessuna valutazione finora
- Serto Up To Date 33Documento7 pagineSerto Up To Date 33Teesing BVNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 2 Main Control Valve: 1. StructureDocumento23 pagineGroup 2 Main Control Valve: 1. StructureАлексейNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of 8086Documento38 pagineApplications of 8086Ajay PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ - Difference Between A Virtual Function and A Pure Virtual Function - Stack OverflowDocumento2 pagineC++ - Difference Between A Virtual Function and A Pure Virtual Function - Stack OverflowNeli MkhatshwaNessuna valutazione finora
- 88543-Activity Week 3 (Language of Mathematics)Documento2 pagine88543-Activity Week 3 (Language of Mathematics)Mylene L RimandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kindergarten-DLL Week 1 (June 3-7, 2019)Documento7 pagineKindergarten-DLL Week 1 (June 3-7, 2019)Ma. Cristina DumallagNessuna valutazione finora
- Logika Gerbang Nand DatasheetDocumento4 pagineLogika Gerbang Nand DatasheetNur Indah ArifaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Audi A6 2.7t Component LocationDocumento3 pagineAudi A6 2.7t Component LocationLucian MicurescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Boakye Danquah Mphil Analytical Chemistry PG 1: THE 'Heart'' of Electronic Noses ' Chemosensors''Documento21 pagineBoakye Danquah Mphil Analytical Chemistry PG 1: THE 'Heart'' of Electronic Noses ' Chemosensors''Alexander Appiah-KubiNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 MathDocumento3 pagineGrade 7 MathMarie Antonette SandiegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsDocumento12 pagineTesting & Maintenance of Rotating Machines Type Tests, Routine Tests & Special Tests of 1 & 3 Phase Induction MotorsPKNessuna valutazione finora