Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Verification Clering
Caricato da
Raj Murthy0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
163 visualizzazioni121 pagineThe management of working capital in today's context is a challenging task. A firm's profitability is determined mainly the way in which the working capital is managed. Working capital management provides summarized view of the financial position and operation of the company.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe management of working capital in today's context is a challenging task. A firm's profitability is determined mainly the way in which the working capital is managed. Working capital management provides summarized view of the financial position and operation of the company.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
163 visualizzazioni121 pagineVerification Clering
Caricato da
Raj MurthyThe management of working capital in today's context is a challenging task. A firm's profitability is determined mainly the way in which the working capital is managed. Working capital management provides summarized view of the financial position and operation of the company.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 121
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 1
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The management of working capital in today's context is a challenging
task. The rising trend of price is the order of the day. Most of the business
concerns are forced to work under the constraints of shortage of funds, more
effective and efficient management of working capital only can ensure
survival of a business enterprise. Thus, working capital management is a
integral part of overall corporate management. A firm's profitability is
determined mainly the way in which the working capital is managed. This
requires greatest attention and efforts of the finance manager
The study of working capital management of KARNATAKA SOAPS AND
DETERGENTS LIMITED tries to find out and understand the functioning
of working capital management of the company. The company carries out its
business through its well-organized and maintained departments. The report
mainly covers on the accounts department, the importance of working capital
management, function of cash management, their way of working capital
maintaining the day-to-day cash management and their method of managing
the important books, statement and manuals.
The study of Stores Department covers the management of stores, important
inventory control technique exercised by the company, material classification,
codification of materials and determination of cost of materials. The company
maintains quality standards to meet the requirements of its customers.
Working capital management provides summarized view of the financial
position and operation of the company. Therefore, now a day it is necessary to
all companies to know as well as to show the financial soundness i.e. day to
day activities, position and operation of the company to their stake holders. It
is also necessary to company to know their financial position and operation of
the company.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 2
Thus, we can say that, working capital is a starting point for making plans
before using any sophisticated forecasting and planning.
The working capital management has shown a drastic improvement in the
period of the study. It is learnt that by the various corrective actions initiated
by the company, the performance of the company from the past few years is
moving on the track of profit. During the period of the study the company has
had a change in management, which has seen drastic changes in the handling
of the working capital and the overall outlook of the company. The study
shows that the company is gradually moving towards an conclude, a healthy
working capital management is utmost necessary for improving company
financial position and outlook of the industry.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 3
CHAPTER-1
INTRODUCTION
1.1INTRODUTION TO FINANACE
Finance is one of the major elements, which activates the overall growth of
the economy. Finance is the life blood of economic activity. A well-knit financial
system directly contributes to the growth of the economy. An efficient financial
system calls for the effective performance of financial institutions, financial
instruments and financial markets.
1.2 MANAGEMENT
In the present day industrial word, management has become universal. The
principals of management are being applied not only for managing business
concerns, but also to manage various other service sector institutions like
hospitals, educational institutions etc. Hence, management occupies such an
important in the modern place in the modern world that the welfare of the people
and the destiny of the country are very much influenced by it. With the increase in
the complexities of management of business concerns, the importance of
management has increased enormously.
1.3 WORKING CAPITAL
The management of working capital is an integral part of overall
corporate management .A business firm must maintain an adequate level of
working capital in order to run its business smoothly. It is worthy to note that
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 4
both excessive and inadequate working capital positions are harmful. Working
capital is just like the heart of the business. If it becomes weak, the business
can hardly prosper and survive. No business can run successfully without an
adequate amount of working capital. Thus working capital is the amount of
funds which is employed in short term operation, included in these operations
are such items as stock of raw materials and supplies needed for manufacture
stock of finished goods waiting for sale, semi processed items and components
that will soon emerge as final product, sundry debtors representing pending
collection against credit sales and short term investment.
1.4MEANING OF WORKING CAPITAL
Working capital is the difference between inflows and outflow of funds
.In other words, it is the net cash inflow .It is defined as the excess of current
assets over current liabilities and provisions Working capital. As an accountant
defines it, is the difference between current assets and current liabilities. This
over-simplified definition simply tells us hoe working capital is calculated.
1.5 DEFINITION OF WORKING CAPITAL
Working capital is commonly defined in accounting and financial analysis
as net current assets consisting of inventories, including goods, net receivables,
marketable securities, Bank balances and cash in hand.
According to SHOBIN Working capital is the amount of funds necessary to
cover to cost to cost of operating the enterprise.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 5
1.6 Objectives of working capital
Explain how the definition of working capital differences between
financial analysts and accountants.
o Understand the two fundamental decision issues in working capital
management-and the trade-offs involved in making these decisions.
Discuss the how to determine the optimal level of current assets.
Describe the relationship between profitability, liquidity, and risk in the
management of working capital.
Explain how to classify working capital according it itscomponents and
according to time (i.e., either permanent or temporary).
Describe the hedging (maturity matching) approach to financing and the
advantages/disadvantages of short -term versus long-term financing.
Explain how the financial manager combines the current asset decision with the
liability structure decision.
Maintenance of working capital at appropriate level, and Availability of ample
funds as and when they are needed.
1.7 IMPORTANCE OF WORKING CAPITAL
Adequate working capital creates certainty, security and confidence in the minds
of the persons in the management as well as in the minds of creditors and workers.
It creates a good credit standing for the firm because credit standing depends upon
the ability to pay promptly. A company with adequate working capital is always
able to meet current abilities.
It ensures solvency and stability of the enterprises it also ensures continuity in
production and sales.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 6
It enables the company to take advantage of cash discount offered by the suppliers
of raw materials or merchandise.
It enhances the prestige of the company and moral of its workers because a
company with adequate working capital is always able to pay wages and salaries
promptly and regularly.
It enables the company to procure loans from banks on easy and competitive
terms.
In times of boom, it enables the company to meet increasing demands for its
products.
In times of depression the company to overcome the crisis successfully.
It enables the company to hold carry on its business successfully and continued
progress and prospective.
It enables the company to carry on its business successfully and active continued progress
and prosperity.
1.8 PRINCIPLES OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
1. PRINCIPLE OF RISK VARIATION
PRINCIPLES OF
WORKING
CAPITAL
MANAGEMENT
PRINCIPLE OF RISK VARIATION
PRINCIPLE OF COST OF CAPITAL
PRINCIPLE OF EQUITY POSITION
PRINCIPLE OF MATURITY OF PAYMENT
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 7
Risk here refers to the inability of the firm to meet its obligation as
and when they become due for payment . Larger investments in current
assets with less dependence on short term borrowings increase liquidity ,
reduce risk and thereby decrease the opportunity for gain on the other hand
, less investment in current with great dependence on short term borrowings
increase risk reduces liquidity and increases profitability . However the goal
of the management should be to establish a suitable trade of between
profitability and risk .
2. PRINCIPLE OF COST OF CAPITAL
The various sources raising working capital finance has different
source of capital and the degree of risk involved . Generally , higher the risk
lower is the cost , and lower the risk higher is the cost . A sound working
capital management should always be maintained to achieve a proper
balance between these two current assets and current liabilities.
3. PRINCIPLE OF EQUITY POSITION
This principle is concerned with planning the total investment is
current assets . According to this principle , the amount of working capital
invested in each component should be adequately justified by firms equity
position . Every rupee invested should contribute to the net worth of the
firm .
4. PRINCIPLE OF MATURITY OF PAYMENT
This principle is concerned with planning the sources of finance for
working capital . According to this principle , a firm should make every
effect to relate maturities of payment to its flow of internally generated
funds .
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 8
1.9 CLASSIFICATION OF WORKING CAPITAL
CONCEPTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
1. From the point of view of concept
a.) Net working capital
b.) Gross working capital
KINDS OF WORKING CAPITAL
On the Basis of
Concepts
On the Basis of
Time
Gross
Working
Capital
Net Working
Capital
Fixed
Working
Capital
Variable
Working
Capital
Regular
Working
Capital
Initial
Working
Capital
Seasonal
Working
Capital
Special
Working
Capital
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 9
2. From the point of view of time
a.) Permanent working capital /Fixed working capital
b.) Temporary working capital/Variable Woking capital
1. ON THE BASIS CONCEPT
a.) NET WORKING CAPITAL
This is the difference between current assets and current liabilities .
Current liabilities are those that are expected to mature within on
accounting year and include creditors , bills payable and outstanding
expenses.
Investments in current assets represents a very significant portion
of the total investment in assets .
The working capital needs increase as the firms grows as sales
grow , the firm needs to invest more in debtors and inventories .
b.)GROSS WORKING CAPITAL
Gross working capital refers to the firms investment in current assets .
Current assets are the assets which can be converted into cash within a
short period say , an accounting year . Current assets include cash , debtors ,
bills receivables , short term securities etc .
It is equal to the total sum of the current assets and may
represent both owned capital and loan capital .
2. ON THE BASIS OF TIME
a.) PERMANENT WORKING CAPITAL
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 10
Permanent working capital is permanently locked up in the
circulations of current assets . It covers the minimum amount requested for
maintaining the circulation of current assets .
1. INITIAL WORKING CAPITAL
At its inception and during the formative period of funds to meet its
obligations . The need for initial working capital is for every company to
consolidate its position .
2. REGULAR WORKING CAPITAL
It refers to the medium amount of liquid capital required to keep up the
circulation of the capital from the cash inventories to accounts receivable
and from accounts receivables to back again cash .
b.)VARIABLE WORKING CAPITAL
It refers to the past of the working capital which changes with the
volume of business , it may be divided into two classes.
1. SEASONAL WORKING CAPITAL
There are many lines of business where the volume of operations
is different and hence the amount of working capital varies with the
seasons . The capital required to meet the seasonal working capital .
2. SPECIAL WORKING CAPITAL
The capital required to meet any special operations such as
experiments with new products or new technique of production and
making interior advertising campaign etc are also known as special
working capital .
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 11
1.10 Operating cycle or Working capital cycle:
In modern business, the concept of working capital has changed a
lot. In the present time a new concept know as operating cycle has emerged
and is gaining popularity. There is much difference between current and
fixed assets, as far as recovery of Investment is concerned.
Every business required many years to recover the investment in
fixed assets like plant and machinery, buildings etc. But investment in
current assets is recovered through a firms operating cycle. When stocks of
finished goods are sold and debtors are collected. usually firms operating
cycle is less than a year.
The term operating cycle implies the period of the required to convert
sales into cash. As per operating cycle concept working capital is that part
of capital which circulates in different firms such as cash. As per operating
INVESTMENTS
CASH FUND
RECEVIVABLES OPERATIONS
Service & production
Operating Expense
Credt sales
production
Cash collections
production
CASH
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 12
cycle concept working capital is that part of capital which circulates in
different firms such as cash to raw materials, to work-in-progress, to
finished good, to sales, to debtors, to cash. It is also called circulating
capital. The working capital rotates in such a way that money will be
blocked at different forms till recovery in form of cash. The can called cash
conversion cycle.
The operating cycle of any manufacturing firm has through three
stages.
Assembling of resource like raw materials, labour power and fuel etc.
Manufacturing the goods i.e. conversion of raw materials into work in
progress into finished goods.
Selling the goods i.e. cash sale/ credit sale. Credit sale creates book debts
or bills receivables.
The operating cycle of the manufacturing concern starts with the purchase
of raw materials and services and ends with the realisation of the cash. The
following steps are followed in between these:
Purchase of raw materials and services.
Conversion of raw materials into finished goods inventory.
Conversion of finished goods stocks into sales debtors and receivables.
Realisation of cash.
This cycle continues again from cash to purchase of raw materials and so
on. The length of a manufacturing firm is the total of inventory conversion
period and receivables conversion period. We can estimate the inventory
period the accounts receivables period and accounts payable period from the
financial statements of the firms.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 13
1.11 DETERMINANTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
NATURE OF BUISINESS
PRODUCTION POLICIES
CREDIT POLICY
INVENTORY POLICY
DETERMINANTS OF WORKING CAPITAL MARKET CONDITIONS
CONDITIONS OF SUPPLY
BUSINESS CYCLE
GROUTH AND EXPANSION
DIVIDEND POLICY
PROFIT LEVEL
1. NATURE OF BUSINESS
The nature of the business effects the working capital requirements to a great
extent. For instance public utilities like railways, electric companies ,etc need
very little working capital because they need not hold large inventories and their
operations are mostly on cash basis, but in case of manufacturing firms and
trading firms, the requirements of working capital is sufficiently large as they
have to invest substantially in inventories and accounts receivables.
2. PRODUCTION POLICIES
The production policies also determine the working capital requirement. Through
the production schedule i.e the plan for production, production process etc. The
KS & DL has big production process.
3. CREDIT POLICY
The credit policy to sales and purchase also affects the working capital. The
credit policy influences the requirements of working capital in two ways. The
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 14
credit terms granted to customers have a bearing on the magnitude of working
capital determining the level of book debt. The credit sales results is higher book
debt (re available) Higher book debt means more working capital.
On the other hand, if liberal credit terms are available from the suppliers of
goods [trade or], the need for working capital is less. The working capital
requirement of business is thus affected by the terms of purchase and sales and
role given to credit by a company by in its dealing with Cr and Dr .
4. INVENTORY POLICY
The inventory policy of a ks&dl also has impact on the working capital
requirements. Since a large amount of funds is normally locked up in inventories.
An efficient firm may stock raw material for a smaller period and may, therefore,
require lesser amount of working capital.
5. MARKET CONDITIONS
Working capital requirements are also affected by market conditions like
degree of competition. Large inventory is essential as delivery has to be off the
shells of credit has to be extended on liberal terry when market competition is
fierce or market is not very strong or is a buyers market.
6. CONDITION OF SUPPLY
If prompt and adequate supply of raw materials. Spares, stores, etc. is
available it is possible to manage with small investment in inventory or work on
Just in Time inventories principles. However if supply is erratic, scant, seasonal,
canalized through Govt. agencies etc. it is essential to keep larger stocks
increasing working capital requirements.
7. BUSINESS CYCLE
Business fluctuation leads to cyclical and seasonal changes in production
and affect the working capital requirements.
8. GROWTH AND EXPANSION
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 15
The growth in volume and growth in working capital go hand in hand,
however, the change may not be proportionate and the increased need for working
capital is felt right from the initial stages of growth.
9. DIVIDEND POLICY
Payment of dividend utilizes cash while retaining profits acts as a source as
W.C. Thus working capital gets affected by dividend policies. The Bemul follows
a liberal dividend policy will require more W.C than Co. that follows s strict
dividend policy.
10. PROFIT LEVEL
Profit level also affects the working capital requirements as a concern higher
profit margin results in higher generation of internal sands and more contributing
to working capital.
1.12ESTIMATING OF WORKING CAPITAL NEEDS
For the estimation of working capital the following methods are followed.
Current Asset holding period.
The two components as W.C. are current assets and current liabilities they have a
bearing on the cash operating cycle in order to calculate the working needs what is the
holding period of various types or inventories the credit collection period and the
credit payment period.
Ratio of sales.
To estimate working capital requirement as a ratio of sales on the assumption that
current asset change with sales.
Ratio of fixed investments.
To estimate W.C requirement as percentage of fixed investments.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 16
1.13 Management of working capital
Guided by the above criteria, management will use a combination of policies
and techniques for the management of working capital. These policies aim at
managing the current assets (generally cash and cash equivalents, inventories and
debtors) and the short term financing, such that cash flows and returns are acceptable.
Cash management.
WHAT IS CASH?
The term cash with reference to cash management is used in two sense .in a
narrow sense it include ,coins, currency notes, cheque, bank draft held by a firm
with it and the demand deposit held by it in bank . in broader sense it also include
near cash assts such as marketable securities and time deposit with banks .such
deposit can immediately be sold or converted into cash if the circumstances so
require .the term cash management is generally used for management of both cash
and near current assts.
FACTS OF CASH MANAGEMENT
Management of cash is concerned with the managing of
a. cash inflow and outflow of firm
b. cash flows within the firms and
Cash balances needed by the firm at a point of time by the financing of
deficit or of investing surplus cash. but it is difficult to predict cash flows
accurately .hence ,in order to resolve the uncertainty about cash flow
prediction and lack of synchronization between cash receipts and payments
,the firm should develop some strategies regarding the following four factor
of cash management.
1. CASH PLANNING
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 17
It is a technique to plan and control the use of cash it protects the
financial condition of the firm by developing projected cash statement from
forecasting of expected cash in flows and out flows for a given period the
forecasts may be used on the present operation or the anticipated future
operations .cash planning is very crucial in developing the overall operating
plans of the firm.
2. CONTROLLING THE LEVEL OF CASH BALANCES
As one of the basic objectives of cash management is to minimize the
level of cash balance, controlling the level of cash balance does not mean just
minimizing the level of cash balance within the firm .it means neither
ensuring that the level of cash balance is neither excessive nor inadequate
.(i.e. .optimum).
3. OPTIMUM CASH LEVEL
Company must decide about the appropriation level of cash balances to
be maintained. Both the cost of excess cash and danger of cash deficiency have
to be matched to arrive at optimum level of cash balance.
4. INVESTMENT SURPLUS CASH
All surplus cash has been properly invested so as to earn profit .the
company has to decide about the division of such cash balance borrowed from
bank deposit ,marketable securities on inter corporate loan.
An idea cash management system depends on the companys product,
organization structure, culture and option available.
Inventory management.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 18
Identify the level of inventory which allows for uninterrupted production but
reduces the investment in raw material and minimizes recording costs - and hence
increases cash flow. Besides this, the lead times in production should be lowered to
reduce work in progress (WIP) and similarly, the Finished Goods should be kept on as
low level as possible to avoid over production see supply chain management ;Just in
Time (JIT); Economic order quantity (EOQ); Economic quantity.
Debtors management.
Identify the appropriate credit policy, i.e. credit terms which will attract
customers, such that any impact on cash flows and conversion cycle will be offset
by increased revenue and hence return on capital (or vice versa); see Discounts
and allowances.
Short term financing.
Identify the appropriate source of financing, given the cash conversion
cycle : the inventory is ideally financed by the supplier; however, it may be
necessary to utilize a bank loan(or overdraft), or to convert debtors to cash
through factoring .
1.14 TECHNIQUES OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
Working capital management involves deciding upon the amount and
compositions of current assets and how to finance the assets. These decisions
involve tradeoff between risk and profitability.
Working capital balances are measured from the financial data of the
companys balance sheet. A study of the causes of changes of working capital that
take place in the balance from time to time is necessary. These changes can be
measured in rupee amounts and also in percentage by comparing current assets,
current liabilities and working capital over the given period.
The important tools of working capital are;
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 19
1. Ratio analysis of working capital
2. Funds flow analysis of working capital
3. Working capital budget
4. Trend analysis.
1. RATIO ANALYSIS OF WORKING CAPITAL
The ratio of working capital can be used by management as a means checking
upon the efficiency with which working capital is being used in the enterprise. The
important ratios of working capital management are.
a. TURNOVER OF WORKING CAPITAL RATIO
It can be calculated as net sales divided by average net working capital.
The turnover of net working capital ratio measures the rate of working capital
utilization. The ratio shows how many times working capital turns over in
trading transactions.
Formula: Net sales
Turnover working capital =
Net working capital
b. CURRENT RATIO
It can be calculated as current assets divided by current liabilities. The
current ratio measures the relative ability of a company to pay its short terms
debts. The ratio is used to reveal how well a company could meet a sudden
demand to pay off its short term creditors.
Formula: Current ratio = Current assets
Current liabilities
c. CURRENT DEBT TO TANGIBLE NET WORTH
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 20
It can be calculated as current liabilities divided by tangible net
worth. The ratio of current liabilities to tangible net worth shows how much
capital used in the enterprises has been provided by the short creditors and how
much by the owners.
Formula: Current liabilities
Current debt to tangible network=
Total net worth
d. QUICK RATIO ( ACID TEST RATIO)
Quick ratio can be calculated as quick assets divided by current liabilities. Quick
ratio establishes relationship between quick or liquid assets and current liabilities and
asset is liquid or quick if it can be converted in to cash immediately or reasonably soon
without a loss of value.
Formula: Quick assets
Quick ratio =
Current liabilities
e. INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO
Turnover ratio can be calculated at cost of goods sold by average
inventory. It shows the number of times the stock in trade is turned over in
business during a period. This ratio may be used to arise stock utilization and
efficiency of the firm in selling its products.
Formula: Cost of goods sold
Inventory turnover ratio=
Average inventory
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 21
f. DEBTOR TURNOVER RATIO
It can be calculated as sales divided by debtors. Debtors turnover indicates the
number of times the debtors are turnover during a year.
Formula: Sales
Debtors turnover =
Debtors
2. FUNDFLOW ANALYSIS OF WORKING CAPITAL
How it was possible to distribute divided in excess of current earning and in the
present of a net loss for the period.
How was the expansion in equipment, plant and machinery financed?
What happened to the proceeds of sales and plant equipment?
How was the retirement of department accomplished?
What becomes to the process of share issue or. It is an effective management tool to
study how funds have been procured for a business and how they have been employed.
This technique helps to analyze changes in working capital components between two
data. The comparison of current assets and current liabilities, at the beginning and at the
end of specific period shows changes in such type of current assets and resources from
which working capital has been obtained. Funds flow statement contributes materially to
the financial aspects of the answers to such questions.
Why the net current were down through the net income was upon vice versa.
Debenture issue.
How was the increase in working capital financed?
3. WORKING CAPITAL BUDGET
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 22
The working capital budget is an important phase of overall financing budgeting.
This budget should be distinguished from a cash budget. That is designed to measure all
the financial requirements of a business including funds for fixed assets, repayments of a
business including funds for fixed assets, repayment of loans, and similar items on the
other hand working capital assures that they are duly provided for. The objective is to
secure an effective utilization of investment.
4. TREND ANALYSIS
A trend analysis includes the changes which have been taking place from time to
time an individual item of current assets. Current liabilities and net working capital on the
basis of some standard year and its effect on working capital portion. It enables to
evaluate the upward and downward trend of current assets and current liabilities. These
are usually measured from review of the comparative balance sheets of a concern at the
end of the accounting years and results are drawn on the basis of trend shown by time.
1.15 SOURCES OF WORKING CAPITAL
Among the various available for financing working capital needs, a finance manager has
to select the best suitable source depending on the working capital needs of the
company.
Long term sources are;
1. Issue of shares
2. Issue of debenture
3. Pouching back of profit
4. Sale of fixed assets
5. Long term loans
The short term sources for financing working capital requirement can be classified into
Internal and external sources.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 23
INTERNAL SOURCES
1. Withdrawing the deprecation funds
2. Using the resources meant for taxation
3. Postponement of payment of accrued expenses
EXTERNAL SOURCES
1. Bank credit
2. Trade credit
3. Bills of exchange and other promissory notes
4. Public deposit (short term)
5. Customer deposit
6. Government assistance
7. Loans from directors
Security deposit from employees
1.16 ADVANTAGES OF WORKING CAPITAL
1. Solvency of the business
Solvency of the business
Goodwill
Easy loans
Cash Discounts
Regular supply of raw materials
Ability to face crisis
High morale
A
A
D
D
V
V
A
A
N
N
T
T
A
A
G
G
E
E
S
S
O
O
F
F
W
W
O
O
R
R
K
K
I
I
N
N
G
G
C
C
A
A
P
P
I
I
T
T
A
A
L
L
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 24
Adequate working capital helps in maintaining solvency of the business by
providing uninterrupted flow of production.
2. Goodwill
Sufficient working capital enables a business concern to make prompt payments
and helps in creating and maintaining
goodwill.
3. Easy loans
Concern having adequate working capitals, high solvency and good credit
standing can arrange from loans from bank and others easy and favorable terms.
4. Cash Discounts
a. Adequate working capital also enables a concern to avail cash discounts on
the purchase and hence it reduces cost.
5. Regular supply of raw materials
Sufficient working capital ensures regular supply of raw materials and continuous
Production.
6. Ability to face crisis
Adequate working capital enables a concern to face business crisis in emergency
such as depression because during such periods, generally, there is much pressure on
working capitals.
7. High morale
Adequacy of working capitals creates an environment of security, confidence, high
morale and creates overall efficiency in a business.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 25
1.17 DISADVANTAGES OF REDUNDANT OR EXCESSIVE
WORKING CAPITAL
1. Excessive working capital means ideal funds which earn no profit for the
firm and business cannot earn the required rate of return on its investments.
2. Redundant working capital leads to unnecessary purchasing and
accumulation of inventories.
3. Excessive working capital implies excessive debtors and defective credit
policy which causes higher incidence of bad debts.
4. It may reduce the overall efficiency of the business.
5. If a firm is having excessive working capital then the relations with banks
and other financial institution may not be maintained.
6. Due to lower rate of return investments, the values of shares may also fall.
The redundant working capital gives rise to speculative transactions
1.18 COMPONENTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
The composition of working capital varies from one business to another.
The composition of working capital of trading concern is quite different from
that of manufacturing. The term composition implies the various components
of working capital or constituent parts that are included in the working capital
are current assets and current liabilities.
Current asset
These are the assets which can be converted into cash within an
accounting year or within the operating cycle whichever is longer. Some of
these assets like stock of finished goods debtors and bills receivables may not
be converted into cash within the required period. Even then these assets are
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 26
still included in the list of current assets. Basically, the current asset include
inventories trade debtors, advances, investments, prepaid expenses and cash in
hand and cash at bank.
The components of current assets are shown in the following manner-
Inventories raw materials, stores and spares, work-in-progress, finished goods
etc.
Loans and advances- trade debtors, bills receivables, prepayments like prepaid
expenses- advance payment of taxes.
Investment-government securities, semi government securities, industrial
securities, private deposits.
Cash and bank balances- fixed deposits with banks, cash at bank- cash in hand
Current liabilities
These are the liabilities which are payable within an accounting year.
Usually, all those liabilities which are required to be paid within a year are
regarded as current liabilities. These liabilities include trade creditors, bank
overdraft, provisions for taxes, dividends and bonus, outstanding expenses etc.
Some of these liabilities may not strictly be described as current liabilities but
nevertheless these liabilities are included in the category of current liabilities.
The components of the current liabilities are in the following
manner-
Trade dues- Trade creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses.
Borrowing-loans from banks, public deposits, bank overdraft, cash credit.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 27
Advances received
Provisions-provision for taxation proposed dividend.
The three important methods of maintaining current assets at
optimum levels are:
Current assets and fixed assets ratio
Liquidity Vs Profitability
Cost benefit trade off
Current assets to fixed assets
Optimum level of current assets is required to maximise the share holder's
wealth and firm needs fixed and current assets to support particular level of
current assets by relating it to fixed assets.
Therefore, level of current assets = current assets/ fixed assets
Current Asset Policies:
Mainly there are three policies.
Conservative Policy:
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 28
Assuming fixed assets as constant and higher current assets or fixed
assets ratio indicates conservative policy. It implies that if liquidity is greater,
the risk is lower.
Aggressive Policy:
Lower current assets or fixed assets ratio indicates aggressive policy. It
implies that if liquidity is lower, the risk is higher.
Average Policy:
It is also called as moderate policy. It lies between conservative and
aggressive policy.
1.19 Liquidity Vs Profitability: Risky-Return off
The current assets holdings will depend upon its working capital policy
that it may follow conservative or aggressive policy. These policies involve
risk return tradeoffs. Under certainty condition larger investments in current
assets yield lower rate of return and smaller investment yield higher rate of
return. The working capital management policies f a firm largely affect its
profitability, liquidity, and structural health of organization. The most
important aim of working capital is profitability and solvency.
Solvency refers to ability to maturing obligations. For ensuring solvency
the firm should be very liquid which means it holds large amount of current
assets. Thus liquid firm has less risk of insolvency. Therefore the aim of
working capital policy is to provide enough liquidity to the firm.
To earn higher amount of profitability, the firm has to sacrifice solvency.
Because to maintain liquidity, firm has to in certain cost that, cost tied up in
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 29
current assets and that extent investment will idle and it affect the profitability
position. When firm wants to earn higher profitability it has to sacrifice
solvency and this pose firm the greater risk of cash shortage and stocks outs.
So the goal of working capital management is to maintain a trade off between
profitability and risk.
Cost benefits trade off:
The cost benefit trade off is different way of looking in risk- return off in
terms of cost of maintaining a particular level of current assets. These are two
types of costs involved in the current assets. These are two types of costs
involved in the current assets.
Cost of liquidity
Cost of illiquidity
Cost of liquidity
If the firms level of current assets is very high, it has excessive liquidity.
Its return on assets will be low as funds tied up in idle cash and stocks earn
nothing and high levels of debtors (through low rates of rates) increase with
level of current assets.
Cost of illiquidity
It is the cost of holding insufficient current assets. The firm will not be
in a position to honour its obligations if it carries too little cash. This may
force the firm to borrow funds at high rates of interest and adversely affect
credit worthiness of the firm and also it pose difficulties in obtaining funds in
future. So in determining the optimum level of current assets the firm should
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 30
balance the profitability solvency tangibles by minimizing total costs-costs
of liquidity and costs of illiquidity.
The cost of liquidity increases while the cost of illiquidity decreases and
vice versa. The minimum cost point indicates the optimum level of current
assets. Some of the approaches to study of working capital analysis or analysis
of working capital can be conducted through a number of devices, such as:
1.20 FORMAT FOR DETERMINATION OF WORKING CAPITAL
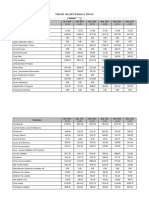
Particulars Amount Amount
Estimation of Current Assets
Minimum desired cash and bank balance Xxx
Inventories
R/M Xxx
WIP Xxx
Finished goods Xxx
Debtors
Total Current Assets
XXX
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 31
Estimation of Current Liabilities.
Creditors Xxx
Wages Xxx
Overheads Xxx
Total Current Liabilities
XXX
Net working capital
( current assets current liabilities)
Add: margin for contingency
XXX
Net working capital requirement. XXX
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 32
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 33
CHAPTE-2
RESEARCH DESIGN
2.1 INTRODUCTION
Every business needs adequate liquid resources in order to maintain day-to-day
cash flow. It needs enough cash to pay wages and salaries as they fall due and to pay
creditors if it is to keep its workforce and ensure its supplies.
Maintaining adequate working capital is not just important in the short-term.
Sufficient liquidity must be maintained in order to ensure the survival of the business in
the long-term as well.
Even a profitable business may fail if it does not have adequate cash flow to meet its
liabilities as they fall due. Therefore, when businesses make investment decisions they
must not only consider the financial outlay involved with acquiring the new machine or
the new building, etc, but must also take account of the additional current assets that are
usually involved with any expansion of activity.
2.2 TITLE OF THE STUDY
A STUDY OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KARNATAKA
SOAPS AND DETERGENTS LIMITED.
2.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The objectives of the project is to study
To have a brief account of operation and position of KS&DL.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 34
To get an idea of the practical application of the term working capital,
whose theoretical aspects was known to us in the past.
To know the business policies, systems and procedures followed to manage
working capital at KS&DL.
To know what role of working capital is managed at KS&DL and to know
working capital has contributed to the profit & loss of the company.
To prepare and analyze sources and application of funds and statement of changes
in working capital.
To study the management of inventories, account receivables and cash in KS&DL.
To suggest some work instructions regarding the defect in the working found if
any.
To study the ratio analysis of KS&DL.
2.4 SCOPE OF THE STUDY:
The developing economies are generally faced with the problem of
inefficient utilisation of the resources available to them. Capital is the scarcest
productive resource in such economies and proper utilisation of these
resources promotes the rate of growth, cuts down the cost of production and
above all improves the efficiency of the productive system .Fixed capital and
working capital are the dominant contributors to the total capital of the
developing country. Fixed capital investment generates production capacity
where as working capital makes the utilisation of that capacity possible. Thus
the study of working capital behaviour occupies an important place in
financial management. Working capital has occupies an important place in
financial management. Working capital has acquired a great significance and
sound position for objects of ''Profitability and liquidity''.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 35
2.5 STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM:
KS&DL is engaged in manufacturing of wide range of cosmetics and
toilet soaps which is even exported to the various countries around the world.
Since the industry scenario is such that it has a long selling cycle. Hence it has
a continuously increasing turnover. Belongs the operating cycle is long and the
working capital requirements are high. In such scenario it dwells upon the
management of the company to play according to the dynamics of the industry
in such a way that it leads to an advantage to the company. The management
should workout the optimal level of the working capital, which gives an ideal
trade-off between risk, return and profitability. The short-term solvency of the
firm depends upon proper management of working capital. This study is
conducted to analyses the efficiency of working capital management and its
impact profitability at KS&DL.
2.6 METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY:
Methodology is defined as a particular or a set of procedures, the
analysis of these principles or procedures of enquiry in a particular field. This
chapter gives a clear picture of how the study has been carried on. It
summaries the procedures followed by the company, other manuals, internet
and received journals.
The data extracted from the annual to annual reports of the company was
analyzes and further reduced to tables. To make it pictorial and easier to grasp
and understand the data was represented in graphical forms.
This is the study entirely based on;
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 36
Personal discussion.
Annual reports of KS&DL.
Published sources.
Simple statistical analysis.
Group discussion.
Under guidance.
Survey of internet.
2.7 PRIMARY DATA
The tolls used for primary data collection are purely based on
personal enquiry with the executives and staff of the entire department including
finance dept for collecting data about the company. This enquiry was done in order to
achieve and collect much information to make the project more effective.
2.8 SECONDARY DATA
The secondary data has been collected from various published
sources like journals, magazines etc. It is also obtained from published sources like
annual reports, company profile, books of accounts, other relevant text book etc.
2.9 TOOLS OF THE ANALYSIS
Tables, graphs, ratio analysis, inventory management, cash
management and receivables management, are to used to analyze the working capital
performance of KS&DL.
2.10 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
The analysis is limited to just five years of data for financial analysis.
The study conducted deals only impact of the working capital on profitability
without taking into consideration the risk involved.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 37
The study conducted throws light only on the impact of working capital on a
part of strategic management.
The figures and facts claimed in the annual reports and in other forms are
taken at face value.
Based on the available information, certain inference have been drawn.
A matter of policy, certain documents were confidential hence were not
accessible.
2.11 RESEARCH INSTRUMENT:
The technique used for the collection of the financial of the financial
statements data and other information as follows. The primary data were
collected by interaction and observation. The secondary data were collected
from the published annual reports, budgets manuals and the audited balance
sheet and profit and loss account, data base of the company.
2.12 OPERATIONAL DEFFENATIONS
Working capital management
Circulating capital means current assets of a company that are
changed in the ordinary course of business from to another, as for example,
from cash inventories, inventories to receivables, receivables into cash.
-Genestengerg
Cash management
Cash management has assumed importance because it is the most
significant of all the current assets, it is required to meet business obligations and it is un
productive when not used.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 38
Receivables management
Receivables management is the process of making decisions relating to
investment in trade debtors. Stated that certain investments in receivables are necessary to
increase the sales and the profits of a firm.
Inventory management
it is necessary for ever management to give proper attention inventory
management . a proper planning of purchasing , hand ling, storing, and accounting should
form a port of inventory management.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1INTRODUTION TO FINANACE
1.2 MANAGEMENT
1.3 WORKING CAPITAL
1.4MEANING OF WORKING capital
1.5 DEFINITION OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.6 Objectives of working capital
1.7 IMPORTANCE OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.8 PRINCIPLES OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
1.9 CLASSIFICATION OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.10 Operating cycle or Working capital cycle:
1.11 DETERMINANTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.12ESTIMATING OF WORKING CAPITAL NEEDS
1.13 Management of working capital
1.14 TECHNIQUES OF WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
1.15 SOURCES OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.16 ADVANTAGES OF WORKING CAPITAL
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 39
1.17 DISADVANTAGES OF REDUNDANT OR EXCESSIVE WORKING CAPITAL
1.18 COMPONENTS OF WORKING CAPITAL
1.19 Liquidity Vs Profitability: Risky-Return off
1.20 FORMAT FOR DETERMINATION OF WORKING CAPITAL
CHAPTER 2: RESEARCH DESIGN
2.1 INTRODUCTION
2.2 TITLE OF THE STUDY
2.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
2.4 SCOPE OF THE STUDY:
2.5 STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM:
2.6 METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY:
2.7 PRIMARY DATA
2.8 SECONDARY DATA
2.9 TOOLS OF THE ANALYSIS
2.10 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
2.11 RESEARCH INSTRUMENT:
2.12 OPERATIONAL DEFFENATIONS
CHAPTER 3:PROFILE OF THE INDUSTRY /COMPANY
3.1 Profile of the Dairy industry
3.2 Profile of the Karnataka soaps and Detergent Limited
CHAPTER 4: ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
CHAPTER 5: SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSIONS & SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Findings
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 40
5.2 Conclusions
5.3 Suggestions
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 41
Chapter - 3
PROFILEOF THE INDUSTRY
PROFILE OF THE COMPANY
INTRODUCTION TO SOAP INDUSTRY:-
Soap is one of the commodities, which has become has indispensable part of life
of the modern fantasy world. Since it is non-durable consumer goods, there is a
large. Market for it. The reasons such as government relations, environment,
toxicological allergy problems, increase in cost of raw material etc.
Following swadeshi movement in1905, few factories were set up and they were
1. Mysore Government Soap factory at Bangalore.
2. Godrej Soaps at Bombay.
The changing technology and even existing desire by the individuals and the
organization to produce a better product at a mere economical rate has also acted
as catalyst for the dynamic process of change. More soap manufactures are trying
to capture a commanding market share by in traducing and maintaining acceptable
products. The soap industry in industry in India faces a cutthroat competition,
while multinational companies dominate the market.
THE INDIAN SOAP INDUSTRY SCENARIO:-
The Indian soap industry has been dominated by handful of companies such as
1. Hindustan Levers limited.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 42
2. Tata oil Mills(Taken over by HLL)
3. Godrej Soaps Private limited
4. Recent entrants include-Colgate Palmolive Ltd.
-proctor & Gamble Ltd.
-Nirma Soap works.
-Wipro Ltd
The Indian Soaps industry continued to flourish very well until 1967-68, But
began to stagnate. Soon it started to recover and experienced a short upswing in
1974. This increase in demand can be attributed to:-
1. Growth of population.
2. Income and consumption increase.
3. Increase in urbanization.
4. Growth in degree of personal hygiene.
Soap manufactures are classified as, Organized and unrecognized sector.
KSDL is under sector.
PRESENT STATUS:-
MARKET SCENARIO
Indian is the market for cleansing products. The countrys per capita
consumption of detergent powers and bars stands at 1.6kg and soap at 543gms.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 43
Hindustan lever, which heralds over the cleaning business, sells in all over the
clearing business.
PROBLEMS OF SOAPS AND DETERGENT INDUSTEY
Industry faces some problems due to increase in the cost of raw materials.
The major ingredients like soda ash, linear alkyl benzene and sodium triply
phosphate poses number of serious problems in terms of availability. The demand
and supply gap of vegetables oil is 1.5 to 2lakhs tons and is met through imports.
HISTORY
India is a rich land of forest; ivory, silk, sandal; precious gems are magical charms
of centuries. The most enchanting perfumes of the world got their exotic spell with
a twist of sandal. The worlds richest sandalwood resources are from one isolated
stretch of forests Land in south India that is Karnataka.
The origin of sandalwood and its oil in Karnataka, which is used in making of
Mysore sandal soaps is well known as fragrant Ambassador of India &
sandalwood oil is infact known as Liquid Gold.
By the Inspection of His Highness Maharaja of Mysore late
Jayachamarajendra Wodeyrae, the trading of sandalwood logs started which was
exported to Europe and new destinations, but with commencement of First world
War India faced Severe Crisis on the business sandalwood.
This situation gave rise to start of an industry, which procedures value added
products I.e., of sandalwood oil. His Highness Maharaja of Mysore created this
situation as an opportunity by sowing the present of the Government sandalwood
oil factory, which is the present KS&DL. The project was shaped with the
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 44
engineering skills and expertise of the top level Late Sir M.Visvesvaraya, the great
Engineer who was the man behind the project.
Todays famous sandal soaps credit goes to the Sir Sosale Garalapuri Shastri who
incorporated the process of soap making using Sandalwood oil. He was an
eminent scientist in the field working at the Tata institute, Bangalore. He was sent
to England to master the fine aspects of soap manufacturing.
The maharaja of Mysore & Diwan Sir, M. Visvesvaraya established the
Government Soap factory during the year 1918. The factory was situated as a very
small unit near K.R circle, Bangalore with the capacity of 100 tons P.A. In
November 1918 the Mysore sandal soap was put into the market after sincere
effort and experiments were undertaken to evolve a soap perfume blend using
sandalwood oil as the main base to manufacture toilet soap. The factory shifted its
operation to Rajajjnagar industrial area, Bangalore in July 1957, where the present
plant is located. The plant occupies an area of 39 acres (covering soaps, Detergent
and Fatty and Acid divisions), on the Banglore-pune Highway, easily accessible
by transport services and communication. Another sandal wood oil division was
established during the year 1944 at shivmoga, which stopped its operations in the
year 2000 for want of natural sandalwood.
This factory started at a moderate scale in year 1916. The first product was
washing soap in addition ti the toilet in the year 1918. The toilet soap of the
company was made up of sandalwood oil.
In 1950 Government decided to expand the factory in two stages. The first stage of
expansion was done to increase the output to 700 tons per year and was completed
in the year 1952 in the old premises.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 45
The next stage of expansion was implemented in 1954 to meet growing demand
for Mysore sandal and for this purpose government India sanctioned license to
manufacture 1500 tons of soaps and 75 tons of glycerin per year. The expansion
project wroth of Rs.21lakhs includes the shifting of the factory to a newly laid
industrial suburban of Bangalore.
The factory started functioning in this new premise (i.e,. present one)from 1
st
July
1957. From this year onwards till date the factory had never looked back, it has
achieved growth and development in production scales and profits.
The industry has 2 more divisions one at shimoga and another at Mysore where
sandalwood oil is extracted. The Mysore division started functioning from 1917
and only during 1984 manufacturing of perfumed and premiere quality
Agarbathies was started. Right from the first log of sandalwood that rolled into the
boiler room in 1916, the company has been single-minded pursuit of excellence.
The project took shape with the engineering skills and expertise of
Top-level team under the leadership of Sir. M.Visvescaraya, Prof.watson and
Dr.Sudbrough. like this soap factory was started small unit and now it has grown
up to a giant size .
RENAMING
On 1
st
October 1980, the Government Soap Factory was renamed as
Karnataka soaps and Detergent Limited The company was registered as a public
limited Company. Today company produces varieties of products in the toilet
soaps, detergent, Agarbathies and Cosmetics.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 46
OBJECTIVIES OF KS&DL
To serve the national economy.
To attatin self-reliance
To promote and uphold its images as symbol of traditional products
To promote purity and quality products and thus enhance age old-charm of
Sandalwood oil.
To build upon the reputation of Mysore Sandal Soap based on pure sandal
oil.
To maintain the brand loyalty of its customer.
To supply the products mentioned above at most reasonable and
competitive rate.
VISION STATEMENT;-
Keeping pace with globalization, global trends and the stats policy for using
technology in every aspect of governance.
Ensuring global presence of Mysore Sandal product while leveraging its
unique strengths to take advantages the selective current technology,
scenario by intelligent and selective diversification.
Secure all assistance and prime status from Government of India, all
technology alliances.
Further, ensure Karnatakas pre-eminent as a proponent and provider of
technology services to the world status , nation, other states public and
private sectors
Making available technology product and services at the most affordable
price to the people at large, in keeping with the policy of a welfare state.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 47
Making all out of efforts to achieve reasonable profits .
Most importantly to earn the invaluable foreign exchange, both to the state
and to the country.
MISSION
To served the National Economy.
To attain self-reliance.
To promote purity and quality products.
To maintain the brand loyalty of its customers.
To build upon the reputation of Mysore Sandal Soap based on pure
sandal oil.
COMPETITTORS OF KS&DL PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
KS&DL is facing cut throat competition in national and international
market. Some of its main competitors are;-
M/S. Hindustan Uni Lever Ltd,
M/S. Godrej Soaps private Ltd.
M/S. Proctor & Gamble.
M/S. Wipro.
M/S. Nirms Soaps Private Ltd
M/S. jyothi laboratories.
KS&DL has the fowlling department;-
1) Finance and accounts.
2) Human Resources Development & Administration
3) Research and Development
4) Quality Assurance.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 48
5) Materials & Stores.
6) Marketing and Business Group
7) Production & maintenance.
8) Projects & Management information services
TRADEMARK OF KS&DL;-
The : SHARABHA
The carving on the cover is the sharabha, the trademark of KS&DL.
TRADE MARK
The sharabha is a mythological creation from the puranas which has a
body of a lion head and elephant, which embodies the combined virtues of wisdom
and strength. It is adopted as an official Emblem of KS&DL to symbolize the
philosophy of the company.
The sharabha thus symbolized a power that removes imperfections and
impurities, the maharaja of Mysore as his official emblem adopted it. And soon
took its pride of place as the symbol of the Government Soap factory of quality
that reflects a standard of excellence of Karnataka Sops and Detergent Limited.
SLOGAN;-
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 49
NATURAL PRODUCTS WITH EXOTIC FRAGRANCES
KS&DL has a long tradition of maintaining the highest quality standard,
right from the selection of raw materials to processing and packing of the end
product. The reasons why its products are much in demand Saudi-Arabia, Kuwait,
Qatar, South America, the entire toilet Soaps of KS&DL are made from raw
materials of vegetables origin and are totally free form animal fats.
POLICY OF KS&DL:-
Seek purchase of goods and services from environment responsible suppliers.
Communicate its environment policy and best practices to all its employees
implications.
Set targets and monitor progress through internal and external environment
impact during manufacturing.
Reuse and recycle materials wherever possible and minimize energy
consumption and waste.
MILE STONES OF THE COMPANY:
1918 - Government Soap Factory was started by Maharaja of Mysore with the
capacity of 112MTs/Annum near Cubbon park, Bangalore and the
MYSORE SANDAL SOAP was introduced into the market for the first
time.
1932 - Toilet soap production capacity was enhanced to 750MTs/Annum.
1944 - The second Sandalwood Oil extraction plant was started in Shimoga.
1954 - Foundation stone was laid by Sir M. Visvesvaraya for establishment of
new manufacturing facilities at Rajajinagar, Industrial Suburb, and
Bangalore.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 50
1957 - Factory was shifted from Cubbon Park to the new premises.
1965 - Started exporting its products to various Countries.
1967 - Celebrated its Golden Jubilee.
1970 - Production capacity was increased to 6000MTs/Annum, in a phase
wise with parallel modernization of various manufacturing equipments.
1974 - Mysore Sales International Limited was appointed as the sole selling
agent for marketing its products.
1975 - Synthetic Detergent plant for manufacture of Detergent cake and
Detergent powder was installed with Italian technology.
1980 - Government Soap Factory was converted into a Public Sector
Enterprise and the Company incorporated on 9th July 1980 and re-
named as KARNATAKA SOAPS & DETERGENTS LIMITED.
1981 - Fatty Acid unit was established to utilize Indigenously available minor
seed oils as the raw material for Soap manufacturing and to produce
Glycerine and Stearic acid.
1984 - Expanded the production capacity with modern manufacturing
facilities, which was available at that time to produce
26000MTs/Annum of Toilet soaps with different variants.
1987 - Company has taken over the marketing activities from M/s. MSIL and
established its own marketing network by opening seven Branches all
over India.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 51
1992 - Company has faced very stiff competition after liberalization in the
Country from different multi National Companies. Company was
registered with the Board for Industries and financial reconstruction
(BFR) New Delhi, as the Company suffered heavy losses.
1996 - The BIFR approved the rehabilitation package in September and
Company has taken stringent measures for the Cost control and
improving the productivity and sales. Company started making profits.
1999 - Company was certified with ISO 9001:1994 Certification by BSI for its
effective implementation of Quality Management Systems.
Company has launched MYSORE SANDAL GOLD- 125gms and
MYSORE SANDAL BABY-75gms in the premium segment.
2000 - Company was certified with ISO 14001 Certification by BSI for its
effective implementation Environmental Management System.
2003 - Company has wiped out entire carry forward losses of `.98.00 crores
and come out from BIFR.
Company has made profits continuously every year and it is the only
State Public Sector unit, which has come out of BIFR and making
continuous profits in the State.
2004 - The ISO certification was upgraded to ISO 9001:2000.
2008 - Company has introduced Hand wash liquids under the trade name of
Herbal Hand wash and Rose Hand wash liquids. Company has also
introduced liquid Detergent under the trade name of KLEENOL liquid
with different variants for Floor wash, Dish wash and Automobile
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 52
wash.
2009 - Company has established In-House state of the Art manufacturing
facilities for manufacture and filling of Mysore Sandal Talcum powder
and Mysore Sandal Baby powder. Company has reintroduced the
Talcum powder variants new outlook of containers.
2010 - The ISO certification was upgraded to ISO 9001:2008.
KS&DL AT GLANCE:-
Incorporated Name - Karnataka Soaps and Detergent Limited.
Address - Karnataka Soaps and Detergent Limited.
Bangalore pune high way
Post Box No.5531,Rajajinar.
Ph:080-3377691/3370469/23371108 to06
Email-Mysorsandal@vsnl.com
Website: WWW.mysorsanal.com
Year of Establishment- 1918
Constitution - wholly owned by Govt. of Karnataka
Undertaking3
Management - Govt. of Karnataka nominates/appoints Board
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 53
-Directors, Chairman & MD
Trade Mark - The trademark is SHARABHAH. It is the body \
of lion with the head of an elephant means blend
-ing the intelligence of lion with strength of an
-elephant.
Production range - toilet soaps, bar soaps, Detergent cakes,
Powders, Agarbathies, Cosmetics, baby products,
sandalwood oil.
Process know how - The facility is a pioneer in the manufacturer of
Various soaps and technology imported from
Italy.
Capacity of the unit - Licensed capacity is 26000 metric tons of Soaps
& 10000 M.Tons of Detergents & Per annum
Plants - At Bangalore
Soap plant
Detergent plant
Fatty Acid Plant
At Mysore
Sandal wood oil
Agarbathies
At shimoga
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 54
AN ISO-9001-2004
KS&DL with a tradition of excellence of over eight decades is committed
to customer delight, through total quality management and continuous
improvement through the involvement of all employees. KS&DL has got ISO
9002 certificate.
To improve the quality management system and to facilitate TQM in the
process of soap and detergent, the management took decision to obtain ISO 9002
by end of March 1999. According action plan was drawn and committee was set
up for the purpose during October 1998 with a mission statement.
The company gives initial training including conducting employees
awareness program me, document quality manual and quality system procurement.
In this direction company obtained the guidance from Consultancies,
Bangalore and Bureau of Indian Standards, Bangalore. Accordingly, company
standards registered for ISO 9002 by the end of March to the Bureau of Indian
Standards. Obtained the certificate by the end of March 1999 itself.
This is to project in the national and international market and also to
improve quality of products offered to the consumers with the assurance of quality
in the message.
The company got itself upgraded to ISO 9001-2004, Quality Systems in the
year 2004-05.
ISO 14001
The company is located in the heart of the Bangalore city. The management
of the company took a decision to get the ISO-14001 and become model to other
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 55
public sector for the techniques used and also to other Government units to spread
the message of maintenance of environment.
ISO-14001 and ISO-9001 will facilitate to improve the corporate brands in
the global market and it will help the company to improve the profits, year to year
on long term basis. The environment management system in the company through
this motive as follows:
Conservation of energy
Conservation of Surrounding
Conservation of resources
Equipped with latest technology and backed by full-fledged quality control and
R&D support, KS&DL is marching confidentially ahead in the new millennium. The
company is developing new products to meet the changing preferences of its
customers.
Is committed to preserve the natural environment in the production of its quality
products to the satisfaction of its customer.
Will comply with all statutory & regulatory requirements pertaining to
environment stipulated both state & central authorities.
Would invite & implement action to reduce all impacts that are likely to be a
source of concern to the environment
Would strive & set an example in protection & promotion of an eco-friendly
environment.
Is committed to prevent & minimize risks to the environment & conserve natural
resources by waging a war against wastes.
Will motivate every employee of the company in preserving the environment by
providing appropriate training.
Will make available a copy of environment policy, under environment
Management system on a written request to its manager (Environment & Policy)
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 56
PRODUCTS AT KS&DL WITH IMAGES
TOILET SOAPS
INCENSE STICKS TALCUM POWDER DETERGENTS
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 57
SANDALWOOD OIL LIQUID SOAP
THE BIRTH OF A LEGEND
The early yar of the 20
th
century witnessed the birth of a magical formula,
created from the finest and purest sandalwood oil, better known as liquid gold,
distilled exclusively at our divisions in Karnataka-Mysore. A Fragrant gift to the
world from the first Government soap Factory in India. Natured by the Maharaja
of Mysore, enriched with all the goodness of natural sandal wood oil, this unique
soap captured hearts and markets at home , as well as right across the globe
creating a fragrant legacy for the state of Karnataka. Karnataka soaps and
Detergents limited (KS&DL)is the ture of excellence for over eight golden legacy
of India. Continuing the tradition of excellence fot over eight decades, using only
the best grade sandal wood oil in its product range, KS&DL today in one of the
largest procedures of sandal wood oil and sandalwood soaps in the world.
SWOT ANALYSIS OF KS&DL
STRENGTHS:-
only soap in India that contains pure sandal and almond oil
Certified by ISO
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 58
Worlds largest production of sandal wood oil
4.Brand name form decades in soap market
4.Brand name form decades in soap market
Brand name form decades in soap market 6.Diversified product range help
the company to maintain stability.
WEAKNESSES
Distribution network weak in north and east
Absence of television advertisement
Neglecting freshness aspect
High oriented cost due to excessive labour force
Low turnover resulting in low profit.
OPPORTUNITIES
Traditional benefits that sandal is good for skin
Skin care is just gaining importance among consumers
Government support and large production capacity.
Advantages of being in the industry for a long time
Existence of vase market and huge demand.
THREATS
Other competitors products such as Rexona, Moti, Santoor etc.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 59
There is a need for renovation of plant and machinery
Government policy may reduce growth potential.
Other sandal soaps in the market.
MAN POWER DETAILS:
GROUP
BANGLOR
E
Mysore
Marketin
g
Branches
shivamoga Total
Executives 112 13 63 1 189
Non-
Executives 479 23 36 13 551
Total 591 36 99 14 740
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 60
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
Chairman
Managing Director
G.M
Finance
G.M
P&M
G.M
HRD
D.G.M
(Finance
)
D.G.M
(M I D)
D.G.M
(P&M)
D.G.M
(Materials
)
D.G.M
(QAD)
D.G.M
(R & D)
D.G.M (Mktng
& Export)
A.G.M
P & M
A.G.M
safety &
stores
A.G.M
Electrical
A.G.M
R & D
A.G.M
Mktg
A.G.M
D P
A.G.M
A/c &
Finance
D.G.M
(HRD)
A.G.M S O
D Mysore
Manager
H.R.D
Manager
Civil
Manager
P&M
Manager
Utility
Manager
Materials
Assistant
Manager
welfare
Assistant
Manager
CFGS
Manager
Electrica
l
Assistant
Manager
Accounts
Assistant
Manager
H.R.D
Assistant Manager
(M Ds Secretary
)
Assistant
Manager
P.R
Department
Material
Officer
Stores
Office
r
Junior
Assistant
Senior
Assistant
Junior
Office
r
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 61
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGAEMENT IN KARNATAKA SOAPS AND
DETERGENTS LTD.
The working capital in Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Ltd. is efficiently operated by
the Finance Department. The finance Department headed by Assistant General Manager
is actively involved in preparing, monitoring and reviewing the requirements of working
capital. It prepares cash flow statement and cash budgets monthly; prepares sales budget;
production budget; manpower material budget and other financial statements to estimate
the working capital need and compares the actual with the forecast. It also takes effective
steps to correct variations if any arises. The normal and peak periods of collection and
payments are analyzed and cash requirement is planned accordingly. It works out
important financial ratios regularly to make sure that the financial position of the industry
is sound.
Quarterly cash flow statement and budget are reviewed and are put up to the board
of directors .the finance department has been successful in adhering to the needs and
recommendations the Tandon/Chore committee. They are therefore, able to obtain
additional amount of borrowing from banks for working capital requirements if so
needed.
INTRODUCTION;
Working capital indicates circular flow of cash i.e., a sort of revolving fund starting
with cash used to pay raw material, labor and operating expenses and when finished
goods are ready for sale, the cash is recovered through sales of the finished goods/semi-
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 62
finished goods, either on cash or on credit. Thus we have a circular cash flow from cash
to inventories to receivable and back to cash.
Working capital refers to the flow of ready funds necessary to work.
Ordinarily speaking working capital is understood to imply the liquid funds representing
the excess of current assets over current liabilities or the difference between current
assets and current liabilities.
WORKING CAPITAL CYCLE;
In case of working capital there are cyclical changes.. The company purchases
the raw material which means the cash is converted into raw material. When finished
goods are produced raw materials are converted into finished stock. Then finished goods
are sold on credit to t5he customer4s when stock is cycle begins with cash and ends with
cash. So it is called as working capital cycle.
INVENTORIES
All raw materials except preference material will be at 2 months stock level. The
purchases are done in bulk depending on the availability and demand for finished goods.
The company normally kept 3 months stock of uninterrupted production.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 63
STOCK
Refers to the stock of chemicals. Perfumery material and packing material.
WORK-IN-PROGRESS
The period allowed as per the norms in 2 weeks.
FINISHED GOODS
Finished goods are kept in stock for one month generally by the company.
DEBTORS
The time period allowed by the company for debtors is 1.5 months.
CASH-IN-HAND
The company generally maintains liquid cash of Rs. 1-2 lakhs at any point of
time.
SUNDRY CREDITORS
The creditors for the company are the suppliers of raw materials, stores, materials, etc,
for which the company is generally allowed a credit of one month.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 64
MANAGING CASH FLOW
Since KS&DL is dealing with very few customers and that to with the government
entities, it does not adopt any techniques for accelerating cash collections and controlling
cash disbursements
INTRODUCTION;
ACCOUNT RECEIVABLES
Account receivables or trade credit is the most prominent force of the modern
business. Sit is considered as an essential marketing tool, acting as abridge for the
movement of goods through production and distribution stages to customers finally. AS
firm grants credit to protect its sales from the competitor and to attract potential customer
trade credit thus creates receivable or book debts, which the firm is expected to collect in
future. It also involves an element of risk as the cash payment has to be received; hence
they have to be carefully analyzed.
Receivable constitute a substantial portion of current assets of several firms.
They form about 1/3 part of current assets in India As substantial amount are tied up in
trade debtors, it needs careful analysis and proper management, for proper management
of receivable a concern must adopt an optimum credit policy.
OPTIMUM CREADIT POLICY
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 65
The optimum investment in receivables will be at a level where there is tradeoff
between costs and pr4ofitability. When the firm resorts to a liberal credit policy the
profitability of firm increase in account of higher sales. However, such a policy
collection cost. The total investment in receivable increase and thus the problem of
liquidity is created. On the other hand a stringent credit policy reduces profitability off
between the profit and sales that bring in receivables.
VARIABLES OF CREDIT POLICY:
A firm should establish receivable policies after carefully considering both benefit
and cost of different policies. These policies relate to:
1. Credit standards
2. Credit terms and
3. Collection procedures.
ACCOUNT RECEIVABLES MANAGEMENT IN KS&DL
The accounts receivables of Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Limited., is an
important component of working capital, if constitutes around 40% of the total amount.
CREDIT ANALYSIS;
The company does not call for any credit analysis as it is dealing with public
sector undertaking and Govt. Department etc. However a few private customers are
provided with credit after scrutinizing there past performance.
CREDIT TERMS;
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 66
Karnataka soaps and detergents limited. Provides credit to customers. The period
of which range from 30 to 45 days. In current assets of private customers. The sales and
services are rendered against an advance of full amount or 90% of the amount along with
the order.
CASH DISCOUNT;
The KS&DL does not provide any cash discount to the customers.
COLLECTION POLICY;
Monthly customers wise schedules/reporters are prepared by all the units the
KS&DL to know the age of receivable accounts, amount due etc. And necessary follow-
up actions are taken by the representative unit of KS&DL.
Maintain the creditors report in weekly & monthly.
CONTROL OF ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLES IN KARNATAKA
SOAPS AND DETERGENTS LIMITED;
Various reports which serve as a control device for accounts receivable are
prepared by all the units of Karnataka Soaps and Detergents Limited., and are submitted
to control office they include.
Monthly sundry debtors report.
Report on age of accounts and.
Weekly debtors report.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 67
Different units KS&DL prepares monthly reports indicating the credit sales to
customers and provide the opening balance at the beginning of the year, total dispatches
done during the month, realization figures and balance of bills not submitted and
outstanding.
One-month report is also prepared to analyze the age of each h account receivable.
The accounts due for more than one year and less than one year are analyzed. Customer
wise, to know why the amounts are outstanding. There is one more weekly debtors
report, which is prepared by finance department of each unit for the purpose of internal
control.
All these reports mentioned above, prepared by KS&DL units and are sent to the
companys corporate office at Bangalore on the basis of their reports. The finance
department in corporate office advises the different units in taking actions to reduce
investments in receivable. If any problems arise, the corporate office solves it. The
KS&DL also makes provisions for bad and doubtful debts on the basis of the period for
which debts have been outstanding.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 68
DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
Introduction:
The term Financial Analysis and Interpretation refers to the process of
determining financial strengths and weakness of the firm by establishing a strategic
relationship between the components of financial statements and other operating
data.
The purpose of financial analysis is to diagnose the information contained in
financial statements so as to judge the profitability and soundness of a firm. Financial
analysis means simplifications of financial data by methodical classification of data
given in the financial statements. Interpretation means explaining the meaning of
significance of data so simplified. The analysis and interpretation of financial
statements is used to determine the financial position and results of operations as
well.
Following are the common devices used to analyze the data. They are Ratio
analysis and trend analysis.
Ratio Analysis:
The ratio analysis is one of the most powerful tools of financial analysis. It is
the process of establishing and interpreting various ratios (quantitative relationship
between figures and groups of figures). It is with the help of ratios that the financial
statements can be analysed more clearly and decisions made from such analysis.
Significance or Importance of ratio analysis:
It helps in evaluating the firms performance: With the help of ratio analysis
conclusion can be drawn regarding several aspects such as financial health,
profitability and operating efficiency of the undertaking. Ratio points out the
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 69
efficiency of the firm i.e. whether the management has utilized the firms assets
correctly, to increase the investors wealth. It ensures a fair return to its owners and
secures optimum utilization of firms assets.
It helps in inter-firm comparison: Ratio analysis helps in inter-firm comparison by
providing necessary data. An inter- firm comparison indicates relative position. It
provides the relevant data for the performance of different departments. If
comparison shows a variance, the possible reasons of variations may be identified
and if results are negative, the action may be initiated immediately to bring them in
line.
It simplifies financial statement: The information given in the basic financial
statements serves no useful purpose unless it is interrupted and analyzed in some
comparable terms.
The ratio analysis is one of the tools in the hands of those who want to know
something more from the financial statements in the simplified manner.
It helps in determining the financial position of the concern: Ratio analysis
facilitates the management to know whether the firms financial position is
improving or deteriorating or it constant over the years by setting a trend with the
help of ratio analysis can know the direction of the trend of strategic ratio may help
the management in the task of planning, forecasting and controlling.
It helps in budgeting and forecasting: Accounting ratios provide a reliable data,
which can be compared, studied and analyzed. These ratios provide sound footing for
future prospectus. The ratios can also serve as a basis for preparing budgeting future
line of action.
Liquidity position: With help of ratio analysis conclusions can be drawn regarding
the liquidity position of a firm. The liquidity position of a firm would be satisfactory
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 70
if it is able to meet its current obligation when they become due. The ability to met
short term liabilities is reflected in the liquidity ratio of a firm.
Limitations of ratio analysis
The ratio analysis is one of the most powerful tools of financial management.
Through ratios are simplest calculate and easy to understand they suffer from some
serious limitations:
1. Limited use of a single ratio: A single ratio usually does not convey much of a
sense, to make a better interpretation a number of ratios have to be calculated which
is likely to confuse the analyst than help him in making any meaningful conclusion.
2. Lack of adequate standards: There are no well accepted standards or rules of
thumb for all ratios which can be accepted as norms. It renders interpretation of the
ratios difficult.
3. Change in price levels makes ratio analysis ineffective: Changes in price level
often make comparison of figures for a number of difficult.
4. Inherent limitations of accounting: Like financial statements, ratios also suffer
from the inherent weakness of accounting records such as their historical nature
ratios of the past are not necessary true indicators of the firms.
5. Changes accounting procedure: Changes in accounting procedure by a firm often
makes ratio analysis misleading.
6. Window dressing: Financial statements can easily be window dressed to present a
better picture of its financial and profitability position to outsiders. Hence one has to
be very careful in making a decision from ratios calculated from such financial
statements.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 71
7. Ratios are not always comparable: When the ratio of two firms are being
compared, it us should be remembered that different firms may follow different
accounting practices.
8. Incomparable: Not only industries differ in their nature but also the firms of similar
business widely differ in their size and accounting procedures etc. It makes
comparisons of ratios difficult and misleading. Moreover, comparisons are made
difficult due to differences in definitions of various financial terms used in the ratio
analysis.
9. Ratios no substitutes: Ratio analysis is merely a tool of financial statements. Hence
ratios become useless if separated from the statements. Hence ratios become useless
if separated from the statements from which they are compared.
Classification of ratios:
The use of ratio analysis is not confined to financial manager only. There are
different parties interested in the ratios analysis for knowing the financial position of
a firm for different purpose. In view of various users of ratios, there are many types
of ratios which can be calculated from the information given in the financial
statements. The three types of ratios are:
LIQUIDITY RATIO
Liquidity refers to the ability of a concern to meet its current obligations as
and when these become due. The short term obligations are met by realizing amounts
from current, floating or circulating assets should either be liquid or near liquidity.
These should be convertible into cash for paying obligations of short term nature. To
measure the liquidity of a firm, the following ratios can be calculate
i. Current Ratio
ii. Quick or Acid Test or Liquid Ratio
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 72
iii. Absolute Liquid Ratio or Cash Position Ratio
Current Ratio:
It can be defined as the relationship between current assets and current liabilities.
This ratio is a measure of general liquidity and is most widely used to make the
analysis of a short term financial position or liquidity of a firm. It is calculated by
dividing the total of current assets by total of the current liabilities
Current Ratio= Current Assets/ Current Liabilities
(1)Table showing current ratio of ks&dl
Years Current assets Current liabilities Current Ratio
2007-2008 88168955 475523005 1.85
2008-2009 1091372587 451607354 2.42
2009-2010 1239560593 561527841 2.21
2010-2011 1201140120 563447217 2.13
2011-2012 1120640446 373557127 2.99
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 73
Interpretation
From the above table, we can observe that the liquidity position of the company
during the year 2011-12 was high, which indicates that the firm was in a good position to
pay its current obligations. On the other hand, the funds are not utilized to its full
capacity. During the previous years, the current ratio has decreased, which shows the
improvement in the efficiency of current assets managements, which has achieved the
ideal current ratio. Thus the firm is efficiently utilizing its current assets.
1.85
2.42
2.21
2.13
2.99
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012
Current Ratio
Current Ratio
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 74
2) Quick or Acid Test or Liquid Ratio:
It may be defined as the relationship between quick assets and current or
liquid liabilities. An asset is said to be liquid if it can be converted into cash within a
short period without loss of value. In that sense, cash in hand and cash at bank are the
most liquid assets. The other assets which can be included in the liquid assets are
bills receivable, sundry debtors, marketable securities and short term or temporary
investments. Inventories cannot be termed to be liquid assets because they cannot be
converted into cash immediately without a sufficient loss of value, and even prepaid
expenses are also excluded from the list of quick assets because they are not expected
to be converted into cash. The quick ratio can be calculated by dividing the total of
the quick assets by current liabilities.
Quick Ratio = Quick or Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities
Quick assets= Current assets Inventories
Table showing the Quick ratio of KS & DL
Table 2:
Years Liquid assets Current liabilities Quick Ratio
2007-2008 585767733 475523005 1.68
2008-2009 683920100 451607354 1.2
2009-2010 721954754 561527841 1.29
2010-2011 675905562 563447217 1.51
2011-2012 631126126 373557127 1.23
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 75
Inference: It is inferred that the company has ability to meet its current liquid
liabilities. Hence, a firm having a high quick ratio may not have a satisfactory
liquidity position if it has slow paying debtors. On the hand, a firm having a low
quick ratio may have a good liquidity position if has fast moving inventories.
From the above table we can observe that during the previous years the liquid ratio
has been high compared to year 2007-08. 2008-09, 2009-10, 2010-11and 2011-12
the Quick ratio has increase during year to year which indicates the good
improvement of Management of Assets.
1.23
1.51
1.29
1.2
1.68
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012
Quick Ratio
Quick Ratio
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 76
3. Absolute Quick ratio
Although receivables, debtors and bills receivable are generally more
liquid than inventories, yet there may be doubts regarding their realisation into
cash immediately or in time. Hence some authorities are of the opinion that the
absolute liquid ratio should also be calculated together with current ratio and
acid test ratio so as to exclude even receivables from the current assets and find
out the absolute liquid assets. Absolute liquid assets include cash in hand and at
bank and marketable securities or temporary investments.
Cash Ratio =Cash and Bank +Short Term Securities /Current Liabilities
Table 3:
Table showing the Absolute Liquid ratio of KS & DL
Table 3:
Years Super Quick assets
Current
liabilities
Super Quick
ratio
2007-2008 334385423 308752365 1.083
2008-2009 255132910 246650794 1.03
2009-2010 285359727 292361773 0.97
2010-2011 24314138 273532955 0.87
2011-2012 377803712 373557127 1.01
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 77
Graph No 3
INTERPRETATION:
From The above Table, it is evident that the absolute liquid ratio is favorable on the part
of the company during the years 2007-08 on words years the absolute liquid assets
decreasing in year to year and 2010-11 the ratio rates is 0.87 and the 2011-12 the ratio
increased and developed their liquid assets ratio is 1.01 has good.
4. DEBTORS TURNOVER RATIO:
1.083
1.03
0.97
0.87
1.01
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
2007-2008 2008-2009 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012
Super Qucik ratio
Super Qucik ratio
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 78
Debtors or receivables turnover a ratio indicates the velocity of debt
collection of the concern. In simple words, it indicates the number of times the
average debtors are collected during a year.
Debtors Turnover Ratio= Total sales
Sundry Debtors
Table showing Debtors turnover ratio of KS & DL
Table 4:
years Total Sales Sundry Debtors
Debtors
turn
Ratio
2007-08
1286462008 113610156 11.32
2008-09 1533703531 154938144 10.93
2009-10 1647774737 168085689 9.8
2010-11 1649723232 153688661 10.73
2011-12 2118438529 141902642 14.92
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 79
Graph No 4
INTERPRETATION:-
Debtors turnover ratio indicates how promptly the company is collecting debtors.
There is no thumb of rule, which may be used as norm to interpret the Debtors turnover
ratio as it may differ from one concern to another depending upon the nature of
business. From the above table it is evident that the Debtors turnover ratio of KS & DL
has been 2007-08, 2008-09 and 2009-10 the decreasing and the 2010-11 and 2011-12
the debtors ratio will be rapidly increased in 14.92 has good.
11.32
10.93
9.8
10.73
14.92
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Debtors Turn over Ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 80
5. Creditors turnover ratio
Creditors turnover ratio is calculated on the same method as receivable
ratio is calculated. This shows the velocity of debt payment by the concern. This
ratio is calculated by dividing the annual credit purchase by the average creditors
or sundry creditors.
Creditors turnover ratio= Annual Credit purchases
Sundry Creditors
Table showing the Creditors turnover Ratio of KS & DL
years Annual credit purchases Sundry creditors
Ratio
2007-08 518909473 70184312 7.39
2008-09 847238335 69771274 12.14
2009-10 958986877 128921998 7.43
2010-11 969031446 90811161 10.67
2011-12 1226935401 39175572 31.31
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 81
Graph No.5
INTERPRETATION:-
A low creditors turnover ratio reflects liberal credit terms granted by suppliers.
While a high creditors turnover ratio show that accounts have been settled rapidly.
From the above table is clear that, the creditors turnover ratio of KS & DL 2007-08 the
ratio is showing 7.39, 2008-09 the showing 12.14, 2009-10 is showing 7.43 and rapidly
the ratio increased 2010-11 and 2011-12 the ratio showing is 10.67 and 31.31 is
creditors is good.
7.39
12.14
7.43
10.67
31.31
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Creditors turnover ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 82
6. WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
Working capital of a firm is directly related to sales. The current assets like
debtors, bills receivable, cash stock etc., and changes with the increase or
decrease in sales. Working capital turnover ratio indicates the velocity of the
utilization of net working capital. This ratio indicates the number of times the
working capital is turned over in a year.
Working capital turnover ratio= Net sales
Net working capital
Table showing the Working capital turnover Ratio of KS & DL
years Net sales Working capital
Ratio
2007-08 1286462008 406166550 3.17
2008-09 1533703531 639765233 2.41
2009-10 164774737 678032752 2.43
2010-11 1649723232 637692903 2.58
2011-12 2118438529 747083319 2.83
Graph No.6
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 83
INTERPREATION
Working Capital Turnover Ratio measures the efficiency with which the
working capital is being utilized by the firm. Low working capital ratio is advisable
for any firm, and maintaining a high working capital turnover ratio is not good for
any firm as it reduces the profitability of the concern. From the above table we
can infer that the working capital turnover ratio of KS& DL is increasing over the
year, which is not a healthy trend.
3.17
2.41
2.43
2.58
2.83
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Working capital turnover ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 84
7. DEBT-EQUITY RATIO
Debt Equity Ratio is also known as External-Internal Equity ratio. It is calculated
to measure the relative claims of outsiders and owners (i.e. Shareholders) against
the firm assets. This ratio indicates the relationship between the eternal equities
or outsiders funds and internal equities or shareholders fund. Dividing the
external equity by the total internal equity can derive it.
Debt equity ratio=Debt or External Equity
Equity Internal Equity
Table showing the Debt equity ratio of KS & DL
years Debt equity
Ratio
2007-08 100360972 455047041 0.22
2008-09 190711112 585940129 0.33
2009-10 163598904 661700146 0.25
2010-11 83506504 709741693 0.12
2011-12 83506504 812822955 0.10
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 85
Graph No.7
INTERPRETATION: -
Debt- Equity ratio is calculated to measure the extent to which Debt financing has
been used in a business. The ratio indicates the proportionate claims of the
owners and the outsiders against the firms assets. The purpose is to get the idea
of the cushion available to the outsiders on the liquidity of the firm. A low ratio is
generally viewed as favorable from the long-term creditors point of view,
because a large margin of protection provides safety for the creditors. The same
low ratio may be taken as unsatisfactory by the shareholders because they find
neglected opportunities for using low cost outsiders funds to acquire fixed assets.
Keeping in view the interest of shareholders and long-term creditors, debt equity
ratio of 1:1 is advisable. From the above table we can infer that the KS & DL has
maintained satisfactory ratio during the year 2008-09 increased & it has been
decreasing during the year 2009-10 onwards.
0.22
0.33
0.25
0.12
0.10
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Debt equity ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 86
8. FIXED ASSETS TO NETWORTH RATIO
The fixed assets to Network ratio establish the relationship between fixed assets
and shareholders funds. This ratio can be calculated by dividing the Net Fixed
Assets by shareholders funds.
Fixed Assets to Net worth Ratio=Net Fixed Assets
Shareholders funds
Table showing fixed Assets to net worth ratio of KS & DL
years Fixed asset Net worth
Ratio
2007-08 59055325 455047041 0.12
2008-09 69775758 585940129 0.11
2009-10 85830957 661700146 0.12
2010-11 92983953 709741693 0.13
2011-12 96957604 812822955 0.11
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 87
Graph No.8
INTERPRETATION:
Generally the purchase of FAs should be financed by Shareholders equity
including reserves, surplus and retained earnings. If the ratios are less than 100%,
it implies that owners funds are more than the fixed assets and the shareholders
provide a part of the working capital. The ratio is satisfactory when it is between
60% to 65%. From the above table, it is evident that KS & DL has not achieved
this ideal ratio. The firm has maintained very low ratio ranging below 20%.
Hence KS & DL has to achieve the ideal ratio in the coming years for better
utilization of the proprietors funds.
9. FIXED ASSETS TO LONG-TERM FUNDS RATIO
0.12
0.11
0.12
0.13
0.11
0.1
0.105
0.11
0.115
0.12
0.125
0.13
0.135
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Fixed Assets to Networth Ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 88
This ratio is also called fixed assets ratio. A variant to the fixed Assets to Net
worth is fixed Assets to Long-term funds. The long-term funds consist of
shareholders funds plus long-term debts. This is calculated as follows.
Fixed Assets Ratio=Net Fixed Assets
Total long-term funds
Table showing fixed Assets to Long-term funds of KS & DL
Table 9:
years Fixed asset equity
Ratio
2007-08 59055325 555408013 0.1
2008-09 69775758 778420599 0.08
2009-10 85830957 825299050 0.1
2010-11 92983953 1129345059 0.08
2011-12 96957604 1114480121 0.08
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 89
Graph No.9
INTERPRETATION:
This ratio indicates the extent to which the total fixed assets are financed by long
term funds of the firm. In other words this ratio indicates the mode of financing
the fixed assets.
Generally, the total of the fixed assets should be equal to the total of long-term
funds or say the ratio should be 100%. But in case the fixed assets exceeds the
total of long term funds it implies that the firm has financed a part of fixed assets
out of current funds or working capital which is not the good financial policy. And
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
0.09
0.1
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
0.1
0.08
0.1
0.08 0.08
Fixed Assets Ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 90
if the total long term funds are more than total fixed assets, it means that a part
of the working capital is financed but of long term funds of the firm. In case of KS
& DL the Fixed Assets to long-term funds is very low (i.e. below 15%) in all the
years, which shows the inefficiency of the company in proper utilization of long-
term funds.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 91
10. PROPRIETORY RATIO
Proprietary Ratio is a variant of Debt Equity ratio. It establishes relationship
between shareholders fund and total assets of the firm. The ratio of proprietors
funds to total funds is an important ratio for determining long-term solvency of
the firm. The components of this ratio are shareholders funds and total assets.
The total assets denote the total resources of the firm. This ratio can be
calculated by dividing the shareholders funds by total assets.
Proprietors Ratio=Share holders Funds
Total Assets
Table showing Proprietary ratio of KS & DL
Table 10:
years Shareholders funds Total assets Ratio
2007-08 455047041 100,28,91,528 0.45
2008-09 585940129 1213653313 0.48
2009-10 661700146 1386826891 0.47
2010-11 709741693 1356695414 0.52
2011-12 812822955 1488037248 0.54
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 92
Graph No.10
INTERPRETATION:-
Proprietary ratio represents the relationship of owners funds to total
assets. When the ratio is high the risk is low. The ratio below 50% may be
alarming for the creditors since they may have to lose heavily in the event of
companys liquidation on account of heavy losses. From the above table, we can
observe that the proprietary ratio has been maintained below 50%. Hence KS &
DL company has low of 2009-10 previous years and 2010-11years on words
increased the proprietor fund .
Series1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10
2010-11
2011-12
0.45
0.48
0.47
0.52 0.54
Proprietors Ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 93
11. OPERATING PROFIT RATIO:
This ratio establishes the relationship between the operating profit and net sales.
It is expressed in Percentage. This ratio is calculated by dividing the operating
profit by net sales.
Operating profit ratio= Operating ProfitX100
Sales
Operating profit = sales cost of good sold
Table showing Operating Profit Ratio:
Table 11;
years Operating Profit Net Sales Ratio
2007-08 122444174 1280980587
9.56
2008-09 124361250 1664701541
7.47
2009-10 143183402 1723349221
8.31
2010-11 97985018 1649398091
5.94
2011-12 201747457 2118438529
9.52
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 94
Graph No.11
INTERPRETATION
There is no ideal ratio for operating profit ratio. If the ratio is higher than it will
be better. Sales registered a steady increase throughout the years and operating
profit also increased, which results in increased of operating profit ratio, this is
mainly because of increase of sales and decrease in operating expenses.
0.00
1.00
2.00
3.00
4.00
5.00
6.00
7.00
8.00
9.00
10.00
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
9.56
7.47
8.31
5.94
9.52
Operating Profit
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 95
12. NET PROFIT RATIO
This ratio establishes the relationship between the net profit (after tax) and
sales. It indicates the efficiency of the Management in manufacturing,
administrative, selling and other activities of the business. This ratio is the over all
measure of the profitability of the business. Net profit ratio is calculated by
dividing the net profit after tax by sales.
Net profit ratio= Net Profit (after tax) X100
Net Sales
Operating Profit = Gross profit -- operating expenses
Table showing Net Profit Ratio:
TABLE 12:
years NET PROFIT Net Sales Ratio
2007-08 136826041 1286462008 1.06
2008-09 267719129 1664701541 0.16
2009-10 343479146 1723349221 0.19
2010-11 48041547 1649723232 0.02
2011-12 134518037 2118438529 0.06
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 96
Graph No.12
INTERPRETATION:
This ratio indicates the percentage of net profit earned by the enterprises on the
sales. This ratio indicates the firms capacity to face the adverse economic
conditions. From the above table, it is obvious that the Net profit ratio of KS & DL
is 2007-08 year the ratio shows 1.06 and it decreased 2008-09 0.16, 2009-10 is
increased 0.19 like 2010-11 the show 0.02 and increased the ratio 2011-12 is 0.06.
Series1
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
2007-08
2008-09
2009-10
2010-11
2011-12
1.06
0.16
0.19
0.02
0.06
Net profit ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 97
13 RETURNS ON SHAREHOLDERS INVESTMENT (ROI):
Return on shareholders investment popularly known as ROI or return on
shareholders fund is the relationship between the net profit (after tax and
Interest) and the shareholders funds. This ratio is calculated by dividing the net
profit after tax and Interest by shareholders investments.
ROI = Net Profit_______ X100
Shareholders funds
Table showing Return on share holders equity Ratio:
Table 13:
years Net Profit
Share Holders
Fund
Ratio
2007-08 120386357 318221 378.31
2008-09 116814479 318221 367.09
2009-10 93112149 318221 292.60
2010-11 63952597 318221 200.97
2011-12 134518037 318221 422.72
Graph No.13
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 98
INTERPRETATION
This is one of the important ratios used for measuring the overall efficiency of the
business enterprise. As the primary objective of every business concern is to
maximize its earnings, this ratio indicates the extent to which this primary
objective is being achieved. These ratios reveals how are the resources of the
business enterprise are being used. The ROI of KS & DL during the year 2007-08 is
has decreased on words the 2009-10 the ROI is 292.60 like2010-11 the decrease
the ROI is 200.97 and increased 2011-12is 422.72 the company earning of ROI is
40%-50% is average.
378.31
367.09
292.60
200.97
422.72
0.00
50.00
100.00
150.00
200.00
250.00
300.00
350.00
400.00
450.00
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
ROI
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 99
14. INVENTORY TURN OVER RATIO
Every firm has to maintain a certain level of inventory of finished goods so as
to meet the requirements of the business. But the level of inventory should neither be
too high nor too low. Thus, it is very essential to keep sufficient stocks in business.
Inventory turnover ratio is also known as stock velocity is normally calculated as
sales/ Average inventory. It indicates that the number of items the stock has been
turned over during the period and evaluates the efficiency with which firm is able to
manage its inventory. It is calculated as:
Inventory turnover ratio=Cost of goods sold
Average stock
Table showing Inventory turnover ratio:
Table 14:
years Net Sales Average Stock Ratio
2007-08 1286462008 69104139 18.62
2008-09 1533703531 69840087 21.96
2009-10 164774737 11806403 13.96
2010-11 1649723232 169014641 9.76
2011-12 2118438529 214016643 9.90
Graph No.14
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 100
INTERPRETATION
Stock is all the companies using turnover of short term liquidity of assets the companies
purchasing and manufacturing to finished goods thorough on selling goods is average that
company is the stock turnover is very good.
The KS&DL company the above table is stock turnover 2007-08 is 18.62 and increased
2008-09 is 21.96 after years the stock turnover is decreased in 2009-10, 2010-11 and
2011-12 is respectively 13.96, 9.76 and 9.90 is satisfying.
18.62
21.96
13.96
9.76
9.90
0.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Inventory turn over ratio
Series1
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 101
CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL
2011 2012 Increase Decrease
Current Assets
Inventories 525234558 489514320 35720238
trade receivables 134735562 149062722 14327160
Cash 240314138 377803712 137489574
Short term assets 77847473 104259692 26412219
Total(A) 978131731 1120640446
Current Liabilities
Trade payables 18521787 59829357 41307570
Other Current
Liabilities 128835682 167055833 38220151
Provisions 79992885 146671937 66679052
Total(B) 227350354 373557127
A-B 750781377 747083319 178228953
Increase/Decrease
Working capital 3698058 3698058
750781377 750781377 181927011 181927011
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 102
CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL
2010 2011 Increase Decrease
Current Assets
Inventories 517605839 525234558 7628719
trade receivables 172641760 165859182 6782578
Cash 285359727 240314138 45045589
Short term assets 213953267 189732241 24221026
Total(A) 1189560593 1121140119
Current Liabilities
Liabilities 292361773 273532954 18828819
provisions 269166068 289914262 20748194
Total(B) 561527841 563447216
A-B 628032752 557692903
Increase/Decrease
Working capital 70339849 70339849
628032752 628032752 96797387 96797387
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 103
CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL
2009 2010 Increase Decrease
Current Assets
Inventories 407452487 517605839 110153352
trade
receivables/Debtors 163529618 172641760 9112142
Cash 255132910 285359727 30226817
loans and advances 215257572 213953267 1304305
Total(A) 1041372587 1189560593
Current Liabilities
Liabilities 24665079 29236177 4571098
Provisions 204956560 269166068 64209508
Total(B) 229621639 298402245
A-B 811750948 891158348 70084911
Increase/Decrease
Working capital 79407400 79407400
891158348 891158348 149492311 149492311
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 104
CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL
2008 2009 Increase Decrease
Current Assets
Inventories 296012822 407452487 111439665
trade
receivables/Debtors 131596659 143615451 12018792
Cash 334385423 255132910 79252513
loans and advances 104944640 215257572 110312932
Total(A) 866939544 1021458420
Current Liabilities
Liabilities 308752356 24665079 284087277
Provisions 166770640 204956560 517858666 38185920
Total(B) 475522996 229621639 117438433
A-B 391416548 791836781
Increae/Decrease
Working capital 400420233 400420233
791836781 791836781 517858666 517858666
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 105
Changes in working capital in ks&DL
Years Increase/Decrease Working capital
2008-2009 400420233
2009-2010 79407400
2010-2011 -70339849
2011-2012 -3698058
Graph no
-100%
-50%
0%
50%
100%
2008-2009
2009-2010
2010-2011
2011-2012
400420233
79407400
-70339849
-3698058
Increae/Decrease Working capital
Increae/Decrease Working
capital
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 106
Chapter5
Findings and suggestions
Company has obtained loan from banks and various financial institutions.
The company essential utilizing the working capital . The funds collected from
various sources are utilized for current assets and fixed assets.
The inventory turnover ratio of the company, which was decreasing because
of the finished goods inventories in sales were poor, which has increased in
the year 2008-09.
Turnover of each asset of the company is variations because of the in
effluent in the cash management.
The company has improved and is making profits.
The working capital financing of Karnataka Soaps and Detergents limited
has been favorable. the total working capital and profit of the company
during the year has been increased. The return on investment will increasing
in 2011-2012 is 422.72
The cash and bank balance of KSDL has been increasing considerably.
The debtors turnover ratio of KSDL shows efficient management of
receivables.
The current ratio of KSDL has able to meet the standard norm of ratio of
2:1, which is often referred to, as banker is rule of thumb.
The company has been able to maintain its quick ratio above the standard
ratio i.e. 1:1.
Working capital is decreasing in 2010-2011 and 2011-2012.
Proprietary ratio is 50% is more getting.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 107
Operating profit is increased in 2007-2008and 2011-2012 is 9.56&9.52and
other years is less then that years.
The net sales of Karnataka soaps and detergents limited have been increased
considerably in the year 2011-2012
Even though small problems were found in the management of working capital, it
is observed that there is efficient working capital management in Karnataka soaps
detergents limited.
SUGGESTIONS
Commencement of effective forecasting of the working capital.
It will be better if KS&DL diverts a little portion of its funds to find assets,
which will provide the enterprise in undertaking expansion activities and
ultimately enhancing its sales and profitability.
Considering various aspects such as production schedule, labor cost, and net
sales should properly assess the requirement of working capital.
The company can make an attempt to increase the sales by increasing
advertisement and adding more distribution network.
The company should decrease the idle capacity in order to increase the
efficiency in the operation.
The company should make proper financial planning so that the available
funds are utilized in more efficient and effective manner.
Inventory should maintain same level.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 108
The company can contribute towards better turnover figures of its and
distribution network is strengthened.
The company should take immediate measures to reduce the length of
operating cycle, so that the cash flow is accelerated.
The company introduces many verities of products to increases the sales to
diversification of funds to other relevant business to earn more profit.
Increases the debtors, stock, bank balance and decrease the liabilities to use
positive working capital.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 109
CONCLUSION
From the study of the companys performance for the past five years and the
overall analysis of the organization, it can be concluded that Karnataka Soaps And
Detergents Limited has sufficient working capital to meet its current obligations
and day-to-day operations. The company is doing its best with their innovative
ideas by introducing new products with high quality and by adopting good
channels of distribution.
Working capital has emerged as a major factor in the profitability of the
business. The goal of working capital is to minimize the cost of working capital
while maximizing the firms profit. Thus, in a country like India, manner of
administration of working capital will determine to a very large extent the success
or failure of overall operations of a firm.
The production value has increased during the years and the sales and the
sales volume is retrieving to increase. But at the same time inventory turnover is
decreasing. The company should contribute towards inventory. It may fetch to
increase in production and also helps in increasing profit to the company.
It is worth noticing that its overall performance is favorable. But a little more
attention may be taken in managing the various aspects of working capital
management.
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 110
The company should continuously monitor the movement of its brands and
analyze fast moving regular and slow moving brands and adopt new marketing
strategy. Market opportunities have immense significance in the field of marketing.
In tomorrows economy the world will belong to those who will cultivate
imagination, creativity, flexibility, open mindedness, a taste for risk taking and an
innovative spirits. All these characteristics can lead the company on a successful
path.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Management accounting M.N.Arora
Reddy appannaya
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PRASSANA CHANDRA
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 111
sProfit & Loss Account for the year ended 31
st
March 2012
Particulars Mar-12 Mar-11 Mar-10 Mar-09 Mar-08
INCOME :
Sales 231.12 181.06 178.90 169.39 145.52
Less: Excise Duty 19.27 16.09 14.12 16.02 16.88
Net Sales 211.4 164.97 164.77 153.37 128.64
Other Income 3.80 3.43 2.22 6.06 2.09
Stock Adjustments (9.33) (2.47) 5.32 7.03 (2.64)
Total Income 206.31 165.93 172.31 166.46 128.09
EXPENDITURE :
Raw Materials 107.11 81.8 77.53 8o.19 54.14
Other Expenditure 77.69 72.74 79.97 73.44 61.35
Depreciation 0.64 o.57 0.49 0.39 0.35
Total 185.44 155.11 157.99 154.02 115.84
Operating Profit Or Loss 20.87 10.82 14.32 12.44 12.25
Less: Interest & finance
charges
0.67
0.52 0.82 0.72 0.45
Profit Or Loss Before Tax 20.20 10.3o 13.50 11.72 11.80
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 112
Less: Provision for
Taxation:
Current Tax 5.87 3.40 4.80 1.85 1.80
Fringe Benefit Tax - - - 0.21 0.70
Deferred Tax Asset 0.85 0.11 0.89 2.03 3.21
Dividend Tax - 0.26 0.27 - 0.45
Profit or Loss After Tax 13.48 6.53 7.54 7.63 5.64
Prior Period Expenditure - 0.33 0.14 1.40 1.46
Proposed Dividend - 1.59 1.59 - (2.7)
Tax - - - - 1.37
Profit OR Loss Brought
forward
13.48
4.61 5.81 6.23 0.11
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 113
Balance Sheet as at 31
st
March 2012
Amount As At
31-12-2009
Amount As At
31-08-2008
SOURCES OF
FUNDS :
Share Capital 31.82.21.000 31.82.21.000
Reserves Total 26.77.19.129 13.68.26.041
Exchange
Fluctuation
Reserve
17.69.358
Secured Loans 10.72.04.608 1.03.65.536
Unsecured
Loans
8.35.06.504
19.07.11.112 8.99.95.436 10.03.60.972
Total 77.84.20.599 2,480.15 55.54.08.013
APPLICATION
OF FUNDS :
Gross Block 30.96.23.620 29.61.06.154
Less :
Depreciation
23.98.47.860
23.70.50.829
Net Block 6.97.75.760 5.90.55.325
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 114
Investment 100 100
Deferred Tax
Asset
5.25.04.866 3.21.46.548
Current Asset
Loan &
Advance
Inventories 40.74.52.487 29.60.12.822
Sundry Debtors 16.35.29.618 14.63.46.670
Cash & Bank
Balance
25.51.32.910
33.43.85.423
Loan &
Advance
21.52.57.572
10.49.44.640
Investment In
gratuity trust
5.00.00.000
1.09.13.72 3.00.00.000 91.16.89.555
Less:Current
Liabilities
provision
Liabilities 24.66.50.794 30.87.52.356
Provision 20.49.56.560 16.67.70.640
Net Current
Assets
45.16.07.354 47.55.23.005
63.97.65.233 43.61.66.550
Miscellaneous
Expenditure
1.63.74.640 2.80.39.490
Profit and Loss
77.84.20.599 55.54.08.013
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 115
Account
Balance Sheet As At 31-march 2009-2010
Amount As At
31-3-2010
Amount As At
31-3-2009
Sources of funds
Shareholders
funds
a) share capital
31,82,21,0
00
31,82,21,000
b) reserves and
surplus
34,34,79,146 26,77,19,129
c) exchange
fluctuation reserve
17,69,358
2. Loan Funds:
a) secured loans 8,00,92,400 10,72,04,608
b) Unsecured loans 8,35,06,5048
,35,06,504
16,35,98,904 8,35,06,504 19,07,11,112
TOTAL 82,52,99,505 77,84,20,599
APPLICATION OF
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 116
FUNDS:
1.Fixed Assets
(a)Gross Block 32,72,62,896 30,96,23,620
Less Depreciation 24,14,31,939 23,98,23,620
(a)Net Block 8,58,30,957 6,97,75,760
2.Investments 100 100
3.Deffrred Tax
Assets
6,14,35,
241
5,25,04,866
4.Current
Assets,Loans&Advances
(a)Inventories 51,76,05,839 40,74,52,487
(b)Sundry Debtors 17,26,41,760 16,35,29,618
(c)Cash & Bank
Balance
28,53,41,76
0
25,51,32,91
8
(d)Loans &
Advances
21,39,53,26
7
21,52,57,57
2
(e)Investment in
gratuity trust
5,00,00,000 1,23,95
,60,593
5,00,00,000 1,09,13,72,58
7
Less:Current
Liabilities&provisio
ns
(i)Liabilities 29,23,61,77
3
24,66,50,79
4
(ii)Provisions 26,91,66,06
8
56,15,2
7,841
20,49,56,56
0
45,16,07,354
Net Current Assets 67,80,3
2,752
63,97,65,233
5.(a)Miscellaneous
Expenditure
1,63,74,640
Profit & Loss 82,52,9 77,84,20,599
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 117
Account 9,050
Balance Sheet As At 31-march 2010-2011
Amount As At 31-03-2011 31-03-2010
Sources of funds
Shareholders funds
a) share capital 31,82,21,0
00
31,82,21,00
0
b) reserves and surplus 39,15,20,69
3
34,34,79,146
c) exchange fluctuation
reserve
_ _
2. Loan Funds
a) secured loans 8,00,92,400
b) Unsecured loans 8,35,06,504 8,35,06,504 8,35,06,504 16,35,98,904
TOTAL 79,32,48,19
7
82,62,99,050
APPLICATION Of
FUNDS:
1.Fixed Assets
(a)Gross Block 33,64,88,84
3
32,72,62,89
6
Less Depreciation 24,35,o4,89
0
24,14,31,93
9
(a)Net Block 9,29,83,953 8,58,30,957
2.Investments 100 100
3.Deffrred Tax
Assets
6.25,71,241 6,14,35,241
4.Current
Assets,Loans&Advances
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 118
(a)Inventories 52,52,34,55
8
51,76,05,83
9
(b)Sundry Debtors 16,58,59,18
3
17,26,05,83
9
(c)Cash & Bank
Balance
24,o3,14,1
38
28,53,59,
727
(d)Loans &
Advances
18,97,32,3
41
21,39,53,
267
(e)Investment in
gratuity trust
8,oo,oo,oo
o
1,20,11,40,
120
5,oo,oo,o
oo
123,95,60,5
93
Less:Current
Liabilities&provisio
ns
(i)Liabilities 27,35,32,9
55
29,23,61,
773
(ii)Provisions 28,99,14,2
67
56,34,47,2
17
26,91,66,
o66
56,15,27,84
1
Net Current Assets 63,76,92,9
03
67,80,32,75
2
5.(a)Miscellaneous
Expenditure
- -
Profit & Loss
Account
79,32,48,1
97
825299,050
,
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 119
Balance Sheet As At 31
St
March 2012
Equity And
Liabilities
Amount As At
31-3-2012
Amount As At
31-3-2011
Sources of funds
Shareholders funds
a) share capital 31,82,21,000 31,82,21,00
0
b) reserves and surplus 49,46,955 81,28,22,955 39,15,20,693 70,97,41,693
2.Non Current
Liabilities
(a)Long Term
Borrwing
8,35,06,504 8,35,06,504
(b)Other Non Current
Liabilities
4,27,45,429 12,61,75,485
(c)long term Provisions 9888888888 30,16,57,166 20,99,21,377 41,96,03,366
3.Current Liabilities
(a)Short Term
Borrowing
(b)Trade Payables 5,98,29,357 1,85,21,787
(c )Other Current
Liabilities
16,70,55,833 12,88,35,682
d)Short Term
Provisions
14,66,71,937 37,35,57,127 7,99,92,885 22,73,50,353
Total 1,48,80,37,248 1,35,66,95,412
Assets
1.Non Current
Assets
a)Fixed Assets
(i)Tangible Assets 9,69,57,604 9,29,83,953
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 120
Total 9,69,57,604 9,29,83,953
b)non Current
Investments
100 100
c)Deffered Tax
Assets
5,40,41,821 6,25,71,241
d)Long Term Loans
And Advances
10,63,97,277 14,30,08,388
e)Currently
Investment(Gratuti
ty Funds)
11,00,00,000 36,73,96,802 8,00,00,000 37,85,63,681
2.Current Assets
a)Inventories 48,95,14,320 52,52,34,55
8
b)Trade Receivable 14,90,62,722 13,47,35,56
2
c)Cash &Cash
Equivalents
37,78,03,712 24,03,14,13
8
d)Short Term
Loans &Advances
10,42,59,692 7,78,47,473
e)Other Current
Assets
1,12,06,40,4
46
9781,31,731
Total 1,48,80,37,2
48
1,35,66,95,41
2
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT KS&DL
Govt First Grade for boys college Chintamani Page 121
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Working Capital Management Through Ratio AnalysisDocumento87 pagineWorking Capital Management Through Ratio AnalysisDasari AnilkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fci Project SreeDocumento94 pagineFci Project SreeLiju LawrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Marcoz 1 CompleteDocumento64 pagineMarcoz 1 Completemaaz bangiNessuna valutazione finora
- PCA & RD Bank PDFDocumento86 paginePCA & RD Bank PDFmohan ks100% (2)
- Final Project1Documento107 pagineFinal Project1Arun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 200 Final ProjectDocumento85 pagine200 Final ProjectmujeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Working Capital ManagementDocumento73 pagineProject On Working Capital ManagementAnjuElsa100% (2)
- DCCB ProjectDocumento14 pagineDCCB ProjectTUNGANA MANEESHANessuna valutazione finora
- Efficient Working Capital Management Key for Business SuccessDocumento82 pagineEfficient Working Capital Management Key for Business Successarunravi24120% (1)
- Project KavithaDocumento78 pagineProject KavithaMichael WellsNessuna valutazione finora
- FinanceDocumento67 pagineFinancericha panwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One: 1.1 Background of The StudyDocumento73 pagineChapter One: 1.1 Background of The StudyMusa TabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital at HeritageDocumento54 pagineWorking Capital at HeritageRajesh BathulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1: 1.1 Cash ManagementDocumento9 pagineChapter - 1: 1.1 Cash Managementgagana sNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Final Chapss PRNTDocumento78 pagineProject Final Chapss PRNTVignesh RvNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Study On Working Capital Management. at Bhilai Steel by Anil SinghDocumento86 pagineComparative Study On Working Capital Management. at Bhilai Steel by Anil Singhsattu_luvNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKING CAPITAL PRO SimlexDocumento78 pagineWORKING CAPITAL PRO Simlexboidapu kanakarajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 1: 1.1 Cash ManagementDocumento66 pagineChapter - 1: 1.1 Cash Managementgagana sNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital ManagementDocumento92 pagineWorking Capital ManagementHarish ChintuNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital Management at Mahindra MahindraDocumento61 pagineWorking Capital Management at Mahindra MahindraRatikant ParidaNessuna valutazione finora
- DattaDocumento66 pagineDattaJayasri MuraliNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento90 pagineUntitledsam coolNessuna valutazione finora
- "Working Capital and Funds Efficiency": BBM" by Chandan. T.LDocumento36 pagine"Working Capital and Funds Efficiency": BBM" by Chandan. T.LmechanicalmadhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Working CapitalDocumento125 pagineWorking CapitalNeeraj Singh RainaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Working CapitalDocumento97 pagineCH 7 Working CapitalAnkur AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 05Documento98 pagineUnit 05Shah Maqsumul Masrur TanviNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance ProjectDocumento66 pagineFinance Projectrajendra1pansare100% (1)
- Working Capital ManagementDocumento44 pagineWorking Capital ManagementAnjaliMoreNessuna valutazione finora
- WCM in Jocil - Siva Teja BonalDocumento113 pagineWCM in Jocil - Siva Teja Bonaltilak kumar vadapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- ForwardDocumento6 pagineForwardAbhijit RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project On Parag Dairy IndustryDocumento68 pagineFinal Project On Parag Dairy IndustrySNEHAM29100% (2)
- Accounts FinalDocumento41 pagineAccounts FinalmaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounts FinalDocumento41 pagineAccounts FinalmaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Working CapitalDocumento41 pagineWorking CapitalmaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounts Final Copy1Documento41 pagineAccounts Final Copy1maheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Receivables Management - Mba Project ReportDocumento76 pagineReceivables Management - Mba Project ReportRoja N57% (7)
- Chapter-I: 1.1. BackgroundDocumento82 pagineChapter-I: 1.1. BackgroundRakesh LamgadeNessuna valutazione finora
- WCM Toyota STDocumento18 pagineWCM Toyota STferoz khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro Review - Study On Working CapitalDocumento10 pagineIntro Review - Study On Working CapitalMathan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital Sagar CementDocumento98 pagineWorking Capital Sagar CementVamsi SakhamuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital Management Maruti SuzukiDocumento76 pagineWorking Capital Management Maruti SuzukiAbhay Gupta81% (32)
- Project Report On Working Capital ManageDocumento26 pagineProject Report On Working Capital ManageAahana BatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital Imp3Documento100 pagineWorking Capital Imp3SamNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Management Assignment - 1 Study On The Working Capital Practices of Reliance CompanyDocumento7 pagineFinancial Management Assignment - 1 Study On The Working Capital Practices of Reliance CompanyAlen AugustineNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Study On Working Capital With Reference To: Mr. Syed Mohammed ShahnawazDocumento77 pagineA Project Study On Working Capital With Reference To: Mr. Syed Mohammed ShahnawazRiyaz AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Working CapitalDocumento44 pagineWorking CapitalBharath GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 05 PDFDocumento98 pagineUnit 05 PDFRizki ResaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jim Financial ManagementDocumento37 pagineJim Financial ManagementGARUIS MELINessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Working Capital ManagementDocumento16 pagineProject On Working Capital ManagementVineeth VtNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital ManagementDocumento9 pagineWorking Capital ManagementSahil PasrijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cira Renewable Project .2Documento85 pagineCira Renewable Project .2VDRATNAKUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis 29.12.2022 - Amale Pradip GanpatDocumento8 pagineSynopsis 29.12.2022 - Amale Pradip Ganpatarchana bagalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Management Analysis of Yamaha ShowroomDocumento4 pagineCash Management Analysis of Yamaha ShowroomshaileshNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital ManagmentDocumento4 pagineWorking Capital ManagmentKundan kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature ReviewDocumento16 pagineLiterature Reviewধ্রুবজ্যোতি গোস্বামীNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1. Importance of Working Capital ManagementDocumento7 pagine1.1. Importance of Working Capital ManagementShesha Nimna GamageNessuna valutazione finora
- 02working Capital Management - Navdeep Bajwa, SMS, Pbi Uni.Documento85 pagine02working Capital Management - Navdeep Bajwa, SMS, Pbi Uni.Jitin BhutaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Capital Management at Pepsico IndiaDocumento5 pagineWorking Capital Management at Pepsico Indiamahesh_kumar_bNessuna valutazione finora
- M.keerthi Kumari SynopsisDocumento11 pagineM.keerthi Kumari Synopsismr copy xeroxNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to the Nature and Functions of HRM DevelopmentDocumento13 pagineIntroduction to the Nature and Functions of HRM DevelopmentNIKITHAA ASHWINNessuna valutazione finora
- 391711329-Asian-Game-Project-FullDocumento19 pagine391711329-Asian-Game-Project-FullRaj MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Company Profile Text DocumentDocumento12 pagineCompany Profile Text DocumentRaj MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Volvo Working Capital ManagementDocumento108 pagineVolvo Working Capital ManagementRaj MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Study On Recruitment and Selection ProcessDocumento106 pagineStudy On Recruitment and Selection ProcessAnuj Sankaran91% (11)
- Set Depreciation Start Dates Period ControlDocumento5 pagineSet Depreciation Start Dates Period ControlSpandana SatyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Completing The Accounting CycleDocumento26 pagine06 Completing The Accounting CycleKristel Joy Eledia NietesNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy and National DevelopmentDocumento35 pagineStrategy and National DevelopmentelmarcomonalNessuna valutazione finora
- URC 2011 Annual Report HighlightsDocumento146 pagineURC 2011 Annual Report HighlightsMelan YapNessuna valutazione finora
- All About Inflation: Club of Economics and Finance IIT (BHU), VaranasiDocumento16 pagineAll About Inflation: Club of Economics and Finance IIT (BHU), VaranasiShashank_PardhikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarkson QuestionsDocumento5 pagineClarkson QuestionssharonulyssesNessuna valutazione finora
- RMO NO. 44-2016 - DigestDocumento1 paginaRMO NO. 44-2016 - DigestGar La ARNessuna valutazione finora
- Unique Aspects of The Hospitality IndustryDocumento25 pagineUnique Aspects of The Hospitality Industry李曉泉100% (1)
- Renewal Form for CR and CRTEDocumento1 paginaRenewal Form for CR and CRTEMarkyNessuna valutazione finora
- KH Vatec and SamsungDocumento53 pagineKH Vatec and SamsungNicky198Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz in PartnershipDocumento5 pagineQuiz in PartnershipPrincessAngelaDeLeon0% (1)
- Acc101 Mini Exam Review For StudentsDocumento11 pagineAcc101 Mini Exam Review For Studentsjan petosilNessuna valutazione finora
- Adecco India Pvt. LTD.: Payslip For The Month of September 2017Documento1 paginaAdecco India Pvt. LTD.: Payslip For The Month of September 2017Sajal RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- SYbcom Ac Sem3Documento56 pagineSYbcom Ac Sem3Anandkumar Gupta56% (9)
- BIR RULING (DA-545-04) : Atty. Miguel Romualdo T. SanidadDocumento3 pagineBIR RULING (DA-545-04) : Atty. Miguel Romualdo T. SanidadRod Ralph ZantuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tata Vs HyundaiDocumento49 pagineTata Vs HyundaiAnkit SethNessuna valutazione finora
- D8Documento11 pagineD8neo14100% (1)
- Quiz On Other LiabilitiesDocumento14 pagineQuiz On Other Liabilitiesimsana minatozakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts in Federal Taxation 2017 24th Edition Murphy Solutions Manual 1Documento73 pagineConcepts in Federal Taxation 2017 24th Edition Murphy Solutions Manual 1hiedi100% (34)
- Maruti Suzuki Financial StatementDocumento5 pagineMaruti Suzuki Financial StatementMasoud AfzaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Taxation Law Question Bank BALLBDocumento49 pagineTaxation Law Question Bank BALLBaazamrazamaqsoodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sammad Rubber WorksDocumento69 pagineSammad Rubber WorksNabeel Safdar29% (7)
- Financial Analysis of Hòa Phát Group Joint Stock CompanyDocumento36 pagineFinancial Analysis of Hòa Phát Group Joint Stock CompanySang NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing-Review Questions Chapter 13Documento5 pagineAuditing-Review Questions Chapter 13meiwin manihingNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 11 Accounting P1 (English) November 2022 Answer BookDocumento9 pagineGR 11 Accounting P1 (English) November 2022 Answer BookDoryson CzzleNessuna valutazione finora
- Bago City 2012 Budget MessageDocumento3 pagineBago City 2012 Budget MessageAl SimbajonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nestle Maggi Sales Analysis in Indian MarketDocumento60 pagineNestle Maggi Sales Analysis in Indian MarketMohd DilshadNessuna valutazione finora
- FRX2Any v.12.14.01 DEMO MANAGEMENT REPORTDocumento3 pagineFRX2Any v.12.14.01 DEMO MANAGEMENT REPORTkrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Merchandising OperationsDocumento39 pagineMerchandising OperationsRyan Jeffrey Padua Curbano50% (2)
- Financial Management Practices of Small Firms in Ghana:-An Empirical Study. BY Ben K. Agyei-MensahDocumento24 pagineFinancial Management Practices of Small Firms in Ghana:-An Empirical Study. BY Ben K. Agyei-MensahLaylyDwi_RNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesDa EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1631)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (327)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesDa EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (273)
- The Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessDa EverandThe Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (456)
- SUMMARY: So Good They Can't Ignore You (UNOFFICIAL SUMMARY: Lesson from Cal Newport)Da EverandSUMMARY: So Good They Can't Ignore You (UNOFFICIAL SUMMARY: Lesson from Cal Newport)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsDa EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (708)
- Can't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsDa EverandCan't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (382)
- Summary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessDa EverandSummary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Make It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningDa EverandMake It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (55)
- Summary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosDa EverandSummary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (294)
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryDa EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (555)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Summary of Slow Productivity by Cal Newport: The Lost Art of Accomplishment Without BurnoutDa EverandSummary of Slow Productivity by Cal Newport: The Lost Art of Accomplishment Without BurnoutValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Summary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionDa EverandSummary of Supercommunicators by Charles Duhigg: How to Unlock the Secret Language of ConnectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsDa EverandSummary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessDa EverandEssentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (187)
- We Were the Lucky Ones: by Georgia Hunter | Conversation StartersDa EverandWe Were the Lucky Ones: by Georgia Hunter | Conversation StartersNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeDa EverandDesigning Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (61)
- Summary of Bad Therapy by Abigail Shrier: Why the Kids Aren't Growing UpDa EverandSummary of Bad Therapy by Abigail Shrier: Why the Kids Aren't Growing UpValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Book Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck by Mark MansonDa EverandBook Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck by Mark MansonValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (577)
- The 5 Second Rule by Mel Robbins - Book Summary: Transform Your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageDa EverandThe 5 Second Rule by Mel Robbins - Book Summary: Transform Your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (329)
- Steal Like an Artist by Austin Kleon - Book Summary: 10 Things Nobody Told You About Being CreativeDa EverandSteal Like an Artist by Austin Kleon - Book Summary: 10 Things Nobody Told You About Being CreativeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (128)
- Summary of Atomic Habits by James ClearDa EverandSummary of Atomic Habits by James ClearValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (168)
- Crucial Conversations by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler - Book Summary: Tools for Talking When Stakes Are HighDa EverandCrucial Conversations by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler - Book Summary: Tools for Talking When Stakes Are HighValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (97)
- The Whole-Brain Child by Daniel J. Siegel, M.D., and Tina Payne Bryson, PhD. - Book Summary: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing MindDa EverandThe Whole-Brain Child by Daniel J. Siegel, M.D., and Tina Payne Bryson, PhD. - Book Summary: 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)
- Blink by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: The Power of Thinking Without ThinkingDa EverandBlink by Malcolm Gladwell - Book Summary: The Power of Thinking Without ThinkingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (114)
- Summary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursDa EverandSummary of Million Dollar Weekend by Noah Kagan and Tahl Raz: The Surprisingly Simple Way to Launch a 7-Figure Business in 48 HoursNessuna valutazione finora
- Psycho-Cybernetics by Maxwell Maltz - Book SummaryDa EverandPsycho-Cybernetics by Maxwell Maltz - Book SummaryValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (91)