Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
LH
Caricato da
reacharunkTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
LH
Caricato da
reacharunkCopyright:
Formati disponibili
APPENDIX
A-2l
Weatherproof fittings, Usually with threaded cast-iron hubs to make water-tight
joints. For some systems fiber or cement-asbestos conduit, either buried direct in-
ground or encased in concrete, is used instead of steel conduit. Open overhead wiring
is widely used principally for reasons of economy. All conductors used for overhead
wiring should have type WP insulation. The current-carrying capacities are greater
for conductors in air, because of better heat dissipation. Various wiring methods
are listed below with their most common applications:
Open conductors on insulators
Flood lighting
Festoon lighting
Advertising spot lighting
Highway lighting
[Bridges, tunnels, and underpasses
t>-
-j j. i j -i
JStreet lighting
Rigid steel conduit
L
? ,
I
1 rathe signals
(Flood lighting
Fiber conduit:
Class
J
in concrete
\
Street u hti
Class II direct burialj
Parkway cables:
Nonmetallic sheathed cable (Street lighting
{Airport lighting
Steel-taped sheathed cable (Flood lighting
Wiring for Bridge, Tunnel, and Underpass Lighting
For bridges, tunnels, and underpasses, wiring fixtures are the weatherproof type
with guards and wires generally run in conduit. All wires installed in these conduits
should have moisture-resisting insulation type RW, TW, or rubber and lead sheathed.
On bridges considerations should be given to vibration and all long vertical runs
should have the conductors supported at frequent intervals in junction boxes.
Where it is impractical to drain a conduit to the junction box, special drainage provi-
sions should be made at low points.
Wiring for Floodlighting and Sign Lighting
Floodlighting and sign lighting frequently are installed with open wiring. Flood-
lights are mounted on crossarms or poles and often are arranged with bushing-type
terminals to connect to open wires. The principal problems of this type of wiring are
clearances between wires, buildings, and other obstructions, and because of the
long runs frequently encountered, maintainance of proper socket voltage. The
matter of safe clearances is well defined in Article 730 of the National Electrical
Code and Part 2 of the National Electrical Safety Code. Wire size should be large
enough to ensure proper utilization voltage, which in sports lighting sometimes is
specified as 10 per cent over normal. (See Section 12.)
High-wattage floodlights may require separate circuits. In automobile parking
lots and on buildings rigid conduit systems generally are required. A parking lot
usually will have conduits run underground to floodlight standards. These standards
are often steel pipe, and underground conduits terminate just above ground level
in the standard. Signs often are so constructed that conduit can terminate directly
in the body of the sign. Some signs have complete fuse panels built into the sign body
and only a feeder of proper capacity is required to the sign. Care should be taken to
adhere to the provisions of Article 600 of the National Electrical Code which requires
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- General Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsuranceDocumento19 pagineGeneral Terms and Conditions of The Pzu NNW (Personal Accident Insurance Pzu Edukacja InsurancereacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1464)Documento1 paginaEn (1464)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- Prospekt BGF PDFDocumento150 pagineProspekt BGF PDFreacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1459)Documento1 paginaEn (1459)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1458)Documento1 paginaEn (1458)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- Mate The: (Fig. - VrouldDocumento1 paginaMate The: (Fig. - VrouldreacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1451)Documento1 paginaEn (1451)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- The The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesDocumento1 paginaThe The Jamb The Name Much The: Tlio CL - AssesreacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- And Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atDocumento1 paginaAnd Rome.: in Front of The Prostyle Existed atreacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1386)Documento1 paginaEn (1386)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1383)Documento1 paginaEn (1383)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1382)Documento1 paginaEn (1382)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1376)Documento1 paginaEn (1376)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1374)Documento1 paginaEn (1374)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- En (1372)Documento1 paginaEn (1372)reacharunkNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- A9-1&2 SL03,04-Street Lighting Feeder Pillar Detail-A9-1Documento1 paginaA9-1&2 SL03,04-Street Lighting Feeder Pillar Detail-A9-1amirul aizadNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Quarter 3rd Summative Test and 4th PT TLE 10Documento2 pagine3rd Quarter 3rd Summative Test and 4th PT TLE 10JC Samar EsbietoNessuna valutazione finora
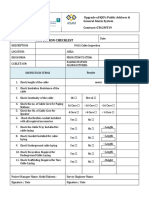
- Cable Inspection Check ListDocumento1 paginaCable Inspection Check ListNuman Saleem88% (8)
- Ignition Transformer For MS5001Documento3 pagineIgnition Transformer For MS5001Chidiebere Samuel OkogwuNessuna valutazione finora
- Registration of Electrical ContractorsDocumento69 pagineRegistration of Electrical ContractorsKevin NdetiNessuna valutazione finora
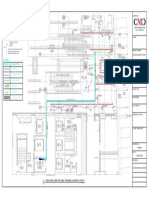
- Escalator Lobby MF Trunking and Conduit LayoutDocumento1 paginaEscalator Lobby MF Trunking and Conduit LayoutrbelduaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elect WorkDocumento34 pagineElect WorkNath YauNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTRICALDocumento1 paginaELECTRICALPetForest Ni JohannNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary ActivityDocumento69 paginePreliminary ActivityRonel Adarlo100% (1)
- Legends: General Notes and Specification:: Electrical Lighting Layout Electrical Power LayoutDocumento1 paginaLegends: General Notes and Specification:: Electrical Lighting Layout Electrical Power LayoutEme DumlaoNessuna valutazione finora
- C-Summary Report-66 KV Shikarpur PSS-Gujarat-2020-21Documento2 pagineC-Summary Report-66 KV Shikarpur PSS-Gujarat-2020-21ddhruvalpNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Ii MCB and ElcbDocumento26 pagineUnit-Ii MCB and ElcbArshad MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- DSR Elec 2022 PDFDocumento155 pagineDSR Elec 2022 PDFShivam50% (2)
- Ebnv.e34997 - Conduit Fittings For Use in Hazardous LocationsDocumento6 pagineEbnv.e34997 - Conduit Fittings For Use in Hazardous Locationsjuan martinNessuna valutazione finora
- Price List Amst Plate SPHC 1,8mm Elp EmailDocumento14 paginePrice List Amst Plate SPHC 1,8mm Elp EmailBaharuddin AbubakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cable SizingDocumento10 pagineCable SizingAhmed MagdyNessuna valutazione finora
- P17 Tempra Pro: Reliably Versatile - . .Documento14 pagineP17 Tempra Pro: Reliably Versatile - . .Laura CallejasNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Storey Load ScheduleDocumento17 pagineTwo Storey Load ScheduleChristian Benedict SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Caterpillar 322 Electrical System 15c16945Documento9 pagineCaterpillar 322 Electrical System 15c16945laura100% (54)
- ABD AC 6kV Switchgear - Signal Cabin St. Cilebut Rev.00.00Documento91 pagineABD AC 6kV Switchgear - Signal Cabin St. Cilebut Rev.00.00Nicodemus Ervino MandalaNessuna valutazione finora
- MUL ACS880 01 R1 R3 QIG H ScreenDocumento104 pagineMUL ACS880 01 R1 R3 QIG H ScreenMarcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cable Current Carrying CapacitiesDocumento3 pagineCable Current Carrying Capacitiessaqib ghouriNessuna valutazione finora
- 311 Ebd 4000 - 1Documento1 pagina311 Ebd 4000 - 1Angel Lazarte DueñasNessuna valutazione finora
- Star Delta BomDocumento7 pagineStar Delta BomEr.AROCKIA STEPHAN VSGNessuna valutazione finora
- 33kV Slash 22kVDocumento192 pagine33kV Slash 22kVShashi Kant ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Elecrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii: Competencies Interpret Technical Drawing and PlanDocumento12 pagineElecrical Installation and Maintenance NC Ii: Competencies Interpret Technical Drawing and PlanSharon AmigleoNessuna valutazione finora
- Appliance ClassesDocumento2 pagineAppliance ClassesGomzalez Bin GembozNessuna valutazione finora
- QuotationDocumento2 pagineQuotationMahmoud Sadaka SafiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Tools Inspection ChecklistDocumento4 paginePower Tools Inspection ChecklistRuzaini Mohamed100% (1)
- Grounding For SunPower AC Modules With SunPower InvisiMount Residential Mounting System 518393 RevADocumento5 pagineGrounding For SunPower AC Modules With SunPower InvisiMount Residential Mounting System 518393 RevAEric WilsonNessuna valutazione finora