Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Stereochemistry Questions
Caricato da
alyson_lDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Stereochemistry Questions
Caricato da
alyson_lCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Additional Problems
7.16 Assign the conguration of these compounds as R or S:
7.17 Draw the structures of these compounds:
a) (R)-3-Chloro-1-pentene
b) (S)-1-Methyl-2-cyclohexenol
7.18 Determine the number of stereoisomers for these compounds:
b)
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
a)
O
OH
i)
CH
2
Ph
CO
2
H
Phenylalanine
H
2
NH
W
W
W
h)
H
W
W
W
CH
2
CH
2
Cl
HOCH
3 g)
O
X
CH
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
Br
OH
H
f) e)
C
H
H
3
C
X
O
CH
d)
Br
c) C
HCPC
HOCH
2
CH
3
H
b)
CH
3
CO
2
H
a)
CH
3
O
ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 249
Assess your understanding of
this chapters topics with
additional quizzing and
conceptual-based problems at
http://now.brookscole.com/
hornback2
BioLink
Openmirrors.com
7.19 Draw all of the stereoisomers of these compounds:
7.20 Explain whether or not these compounds would rotate plane-polarized light:
7.21 Consider the two enantiomers of this carboxylic acid:
CH
3
CHCOH
O
X W
Cl
i)
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
HOH
h)
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
HOH
g)
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
f)
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
e)
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
H
3
C
d)
Cl
Cl
H
H H
3
C
CH
3
CC
c)
OH
OH
b)
OH
OH
a)
OH
OH
b) CH
3
CHCHCHCHCHCH
3
W
OH
a) CH
3
CHCHCHCH
3
W
OH
d)
OH
c)
O
OH
250 CHAPTER 7 STEREOCHEMISTRY II
Explain whether each of the following statements is true, is false, or cannot be
determined from this information:
a) The enantiomers have the same melting point.
b) The enantiomers have the same boiling point.
c) The enantiomers have the same solubility in water.
d) The enantiomers have the same magnitude of rotation of plane-
polarized light.
e) The enantiomers have the same direction of rotation of plane-
polarized light.
f ) The enantiomers have the same pK
a
.
g) The enantiomers have the same rate of reaction with methanol.
h) The enantiomers have the same pH of an aqueous solution.
i) The enantiomers have the same rate of reaction with (S)-2-butanol.
j) The (R)-enantiomer rotates plane-polarized light in a clockwise
direction.
k) This reaction produces more of the (R)-enantiomer than the (S)-enantiomer.
7.22 Identify these pairs of compounds as identical, structural isomers, enantiomers,
or diastereomers:
i)
h)
g)
f) e)
d)
OH OH
OH OH
c)
OH
OH OH
OH
b)
Cl Cl
a)
Cl
Cl
CH
3
CHCOH
O
X
H
W
Cl
2
HCl C
CO
2
H
H
Cl
H
3
C
C
CO
2
H
H
Cl
H
3
C
ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 251
Openmirrors.com
7.23 Identify these pairs of compounds as identical, structural isomers, enantiomers,
or diastereomers:
7.24 a) A solution of 0.2 g/mL of a compound in a 1 dm cell rotates plane-polarized
light 13.3 at the sodium D line. What is the specic rotation of this
compound?
b) What is the rotation caused by a solution of 0.1 g of this compound in 10 mL
of solution?
c) Suppose a solution of a compound gave a rotation of 160. How could
this rotation be distinguished from one of 200? from one of 520?
7.25 Describe how this amine could be resolved by using this carboxylic acid:
7.26 An unknown compound, X, has the formula C
6
H
12
.
a) Calculate the degree of unsaturation of X.
b) X reacts with H
2
in the presence of a catalyst to form a compound, Y, with
the formula C
6
H
14
. What information does this experiment provide about
the structure of X?
c) X rotates plane-polarized light, but Y does not. Show structures for
X and Y.
CNH
2
CH
3
W
W
H
W
C
Cl
H
3
C
H
CO
2
H
g)
CH
3
CO
2
H
CH
3
CO
2
H
H
2
NH
W
W
W
H C NH
2
f)
O
X
CH
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
O
X
CH
W
W
W
H
H
3
COH e)
O
X
CH
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
CH
3
W
W
W
CH
X
O
HOH
d)
O
X
CH
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
OH
W
W
W
H
HCCH
3
O
X
c)
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HCl
BrH
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HCl
BrH
b)
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HCl
BrH
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HCl
HBr
a)
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
HOH
CH
3
W
W
W
W
W
CH
3
HOH
HOH
252 CHAPTER 7 STEREOCHEMISTRY II
7.27 How many stereoisomers exist for this compound? Assign the relative stabili-
ties of each. Is the methyl group axial or equatorial in the more stable con-
former of the least stable stereoisomer?
7.28 Draw a stereoisomer of this compound that is chiral, and draw two that are not
chiral:
7.29 Many compounds are found as a single stereoisomer in nature even though
they have numerous chirality centers. Determine how many chirality centers
are present in each of the following naturally occurring compounds and how
many stereoisomers are possible for each:
c)
OH
OH
OH
OH
Pancratistatin
(an anticancer drug)
O
NH
O
O
HO
b)
O
HO
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
O
OH
OH
O
Sucrose
(table sugar)
CH
3
O
Alanine
residue
Phenylalanine
residue
(a tripeptide)
Threonine
residue
O CH
2
CHCH
3
W W
Ph OH
W W
W X X
a)
NH
2
CHCNHCHCNHCHCO
2
H
OH HO
CH
3
CH
3
Ph
ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 253
BioLink
Openmirrors.com
Ascorbic acid
(vitamin C)
HO OH
O O CHCH
2
OH
OH
h)
g)
Vitamin D
2
HO
f)
Vitamin E
O
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
HO
PGE
2
(a prostaglandin)
O
HO
CO
2
H
OH
e)
d)
Testosterone
(a steroidal hormone)
OH
O
254 CHAPTER 7 STEREOCHEMISTRY II
7.30 All naturally occurring amino acids have the same relative conguration. All
have the S absolute conguration, except for cysteine, which has the R congu-
ration. Explain.
7.31 Explain whether each of these compounds is chiral or not:
f)
CH
3
O
O
S
..
e)
Ph
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
2
Br
+
NCH
2
CH
3
d)
H
3
C CO
2
H
CH
3
O CO
2
H
c)
H
3
C CH
3
CH
3
O CO
2
H
b)
CCC
H
H
3
C
COH
CH
3
O
X
a)
CCC
H
3
C
H
3
C
CCH
3
H
O
X
CO
2
H
Cysteine
CH
2
SH
C H H
2
N
i)
Apoptolidin
(a potent antitumor agent)
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
OH
OH
H H
OH
HO
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
O
ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS 255
BioLink
Openmirrors.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CH 18 Blood VesselsDocumento30 pagineCH 18 Blood VesselsprocellogirlNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Hoehn Test BankDocumento36 pagineHuman Anatomy Physiology 10th Edition Marieb Hoehn Test Bankdorislanhpr028Nessuna valutazione finora
- (K) Gastroenteritis and Fluid VolumeDocumento1 pagina(K) Gastroenteritis and Fluid Volumeapi-3769252Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFDocumento108 paginePhysiology Comprehensive Exam Pointers PDFRaynalynGimoros100% (1)
- Chapter 013Documento10 pagineChapter 013api-281340024Nessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of AppendixDocumento1 paginaHistology of Appendixalyson_l100% (1)
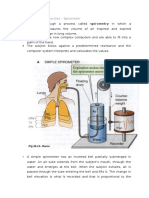
- SpirometerDocumento2 pagineSpirometeralyson_lNessuna valutazione finora
- NOED - Flexible PipesDocumento34 pagineNOED - Flexible PipesZhizhou Wang100% (2)
- Lab Report DETERMINATION OF THE CONCENTRATION OF ACETIC ACID IN VINEGARDocumento27 pagineLab Report DETERMINATION OF THE CONCENTRATION OF ACETIC ACID IN VINEGARP NDNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Lab Technique Notes For The DATDocumento3 pagineOrganic Chemistry Lab Technique Notes For The DATOscar Federico SpadaNessuna valutazione finora
- L 17 Structure and Functions of ProteinsDocumento43 pagineL 17 Structure and Functions of ProteinssNessuna valutazione finora
- The Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionDocumento12 pagineThe Action Potential: Page 1. IntroductionSimón JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymesDocumento19 pagineEnzymesوليد. وفي الروح0% (1)
- Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and ProteinsDocumento55 pagineBiomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and ProteinsBoooooooseNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Term PhysiologyDocumento3 pagine1st Term PhysiologyAbdul QuaiyumNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaDocumento43 pagine1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaGeevee Naganag VentulaNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOC 307 Old Exam 1Documento17 pagineBIOC 307 Old Exam 1Katie RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physiology: First YearDocumento67 pagineGeneral Physiology: First YearGo HellNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Summary Body Fluids and BloodDocumento22 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Summary Body Fluids and BloodKelly Anne BrandNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewDocumento31 pagineBIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewRomo AnthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 70-GuytonDocumento9 pagineChapter 70-Guytonswoljaswol1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medical BiochemistryDocumento264 pagineMedical BiochemistryKarren Taquiqui PleteNessuna valutazione finora
- Epimer of GlucoseDocumento8 pagineEpimer of GlucoseMohammad BaberNessuna valutazione finora
- Ist Year MbbsDocumento3 pagineIst Year MbbsJaved Gaba0% (1)
- Lecture 20 - Carboxylic AcidsDocumento46 pagineLecture 20 - Carboxylic Acidsapi-19824406Nessuna valutazione finora
- PhysiologyDocumento31 paginePhysiologyraza20100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology 2 Lab ManualDocumento129 pagineAnatomy and Physiology 2 Lab ManualMAJEETH மஜீத் TIRUNELVELINessuna valutazione finora
- l08 Metabolism in Liver 2 - Fatty Acid Metabolism (Mod)Documento21 paginel08 Metabolism in Liver 2 - Fatty Acid Metabolism (Mod)Swapnil100% (4)
- Protein Structure and Folding LectureDocumento18 pagineProtein Structure and Folding Lecturemaryscribd241Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasDocumento27 pagineChapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasSheila GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE NOTES For Health Science StudentDocumento211 pagineLECTURE NOTES For Health Science StudentMohsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Biopolymers Structure and PropertiesDocumento78 pagineBiopolymers Structure and PropertiesgautamahujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemDocumento12 pagineChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System蔡旻珊Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionDocumento7 pagineBiochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionTheo SantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Forum AbdDoneDocumento7 pagineAnatomy Forum AbdDoneMedShare100% (1)
- Chapt 05Documento83 pagineChapt 05emmielyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 LipidsDocumento44 pagine3 LipidsSuresh ChovatiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- anatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءDocumento8 pagineanatomy 8 scalp تعلم بذكاءmahmoud ezzeldeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholesterol and Lipoprotein MetabolismDocumento32 pagineCholesterol and Lipoprotein MetabolismBenjamin PrabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Heteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarDocumento20 pagineHeteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarIMDCBiochem67% (6)
- Chapter 7 - Urinary SystemDocumento8 pagineChapter 7 - Urinary Systemapi-19824406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocumento57 pagineRespiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationHanifa AffianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Notes PDFDocumento38 pagineProtein Notes PDFLUi Anne Mateo LatogNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Physiology in Physio-1 On BmeDocumento47 pagineBlood Physiology in Physio-1 On BmeGUIDE ON BIO-MEDICAL ENGINEERING UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM:Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-Large BiomoleculesDocumento24 pagineChapter 5-Large Biomoleculesprehealthhelp100% (4)
- Musculoskeletal PhysiologyDocumento5 pagineMusculoskeletal PhysiologyKhairul IkhwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18 Lippincott BiochemistryDocumento62 pagineChapter 18 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateDocumento24 pagineLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashir100% (1)
- Lecture 5 (Exercise Metabolism)Documento31 pagineLecture 5 (Exercise Metabolism)Helmi RaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry (GREEN)Documento18 pagineBiochemistry (GREEN)BRYAN BALDOMERONessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyGichana ElvisNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry: Molecules of LifeDocumento20 pagineBiochemistry: Molecules of Lifeapi-464344582Nessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocumento60 pagineMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaAmanda PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical BiochemistryDocumento108 paginePractical BiochemistryCindy Nona100% (1)
- Sodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialDocumento4 pagineSodium Potassium Pump and Action PotentialPiyush BhallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Metabolism of Carbohydrates, LipidsDocumento209 pagineModule 3 Metabolism of Carbohydrates, Lipidsninas1112Nessuna valutazione finora
- Textbook Catalogue 2009Documento52 pagineTextbook Catalogue 2009Lippincott Williams and Wilkins- Europe100% (2)
- Composition and Function of Blood ComponentsDocumento17 pagineComposition and Function of Blood ComponentsPrakash Kumar Nayak100% (1)
- Biochemistry 8th EditionDocumento12 pagineBiochemistry 8th EditionxewazixNessuna valutazione finora
- Channels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportDa EverandChannels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportNessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIDa EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Taxol® and its DerivativesDa EverandThe Chemistry and Pharmacology of Taxol® and its DerivativesNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Normal Ranges: Haematology BiochemistryDocumento1 paginaAdult Normal Ranges: Haematology Biochemistryalyson_lNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Normal RangesDocumento1 paginaPaediatric Normal Rangesalyson_lNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Pathology - Further Reading 1) Kartagener's SyndromeDocumento9 pagineCellular Pathology - Further Reading 1) Kartagener's Syndromealyson_lNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalysts Used For PNADocumento3 pagineCatalysts Used For PNAmarviNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic QuestionsDocumento51 pagineOrganic Questionshemab30851Nessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Letters: Aishwarya Devadiga, Vidya Shetty K., M.B. SaiduttaDocumento6 pagineMaterials Letters: Aishwarya Devadiga, Vidya Shetty K., M.B. Saiduttameilandina prillyNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers: Exercise-IDocumento16 pagineAnswers: Exercise-IdivyankNessuna valutazione finora
- GuideDocumento8 pagineGuideMichael A. HackneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Crow PDFDocumento238 pagineCrow PDFAkshayan R100% (1)
- Metabolisme Vitamin, Mineral, Xenobiotic - DR - Zul - RevDocumento63 pagineMetabolisme Vitamin, Mineral, Xenobiotic - DR - Zul - RevM Daffa Abhista ReviansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Decomposition of Soil Organic MatterDocumento3 pagineDecomposition of Soil Organic MatterjuniNessuna valutazione finora
- 典型加速腐蝕實驗方法Documento4 pagine典型加速腐蝕實驗方法Nelly TsaiNessuna valutazione finora
- M1-L2 - Hardness Determination EDTADocumento9 pagineM1-L2 - Hardness Determination EDTAShivika MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- WHP Fine and Specialty Chemicals 154169Documento8 pagineWHP Fine and Specialty Chemicals 154169sanjayshah99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Efficient and Simple NaBH4 Reduction of Esters at Cationic Micellar SurfaceDocumento4 pagineEfficient and Simple NaBH4 Reduction of Esters at Cationic Micellar Surfacemario.micciarelli2313Nessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Basic Magnesium Sulfate Cement in Civil EngineeringDocumento6 pagineApplications of Basic Magnesium Sulfate Cement in Civil EngineeringPrashant GaradNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissolvine GL Technical BrochureDocumento13 pagineDissolvine GL Technical BrochurealejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 1Documento3 pagineActivity 1MANALANG JULIA ALEXISNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A 967 - 01 - Chemical Passivation Stainless Steel PDFDocumento7 pagineAstm A 967 - 01 - Chemical Passivation Stainless Steel PDFElwe SingoloNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid Tablet. ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineTITLE: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid Tablet. Objectivenurrina NadhirNessuna valutazione finora
- Heliyon: N.G. Mbewana-Ntshanka, M.J. Moloto, P.K. MubiayiDocumento8 pagineHeliyon: N.G. Mbewana-Ntshanka, M.J. Moloto, P.K. MubiayijaiemNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements-of-a-Smartphone INFOGRAFIA PDFDocumento1 paginaElements-of-a-Smartphone INFOGRAFIA PDFAna Elena Betancourt BucheliNessuna valutazione finora
- Percent Composition & Hydrates & Empirical FormulasDocumento2 paginePercent Composition & Hydrates & Empirical FormulasConnor BingamanNessuna valutazione finora
- HPTLCDocumento26 pagineHPTLCBhavik NagdaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1,2,4 TriazolesDocumento4 pagine1,2,4 TriazolesRoman RusnacNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Acid:: (A) Mineral Acids (B) Organic Acids 1 (A) Mineral AcidsDocumento5 pagine1 Acid:: (A) Mineral Acids (B) Organic Acids 1 (A) Mineral AcidsAayushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Screen PrintingDocumento7 pagineScreen Printingjennygraceshalini100% (1)
- 34-Mixtures Solutions and CompoundsDocumento3 pagine34-Mixtures Solutions and CompoundsAbdullah JafarNessuna valutazione finora
- MTT AssayDocumento3 pagineMTT AssayRuben Santiago-AdameNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermometric TitrationDocumento4 pagineThermometric TitrationKizzy Anne Boatswain CarbonNessuna valutazione finora
- Photo Electro CatalystDocumento19 paginePhoto Electro CatalystHijab HaiderNessuna valutazione finora