Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 3 Vocabulary Terms Material Science
Caricato da
icantdecide0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni2 pagineMaterial science Chapter 3 terms to study and learn for Test Number 1.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoMaterial science Chapter 3 terms to study and learn for Test Number 1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
26 visualizzazioni2 pagineChapter 3 Vocabulary Terms Material Science
Caricato da
icantdecideMaterial science Chapter 3 terms to study and learn for Test Number 1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Key Terms: Chapter 3
allotropic Describing elements capable of having more than one crystal
structure
anisotropic Having properties that vary with direction.
atomic packing factor (APF) The fraction of space in a unit cell filled by
spherical atoms.
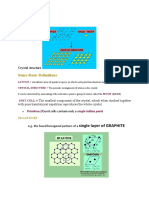
basal plane The top or bottom plane in a crystal. In hexagonal crystals the basal
plane is defined by the atoms placed on the six corners of hexagons. It is normal
to the c axis.
basis The number of atoms or ions on each lattice position.
body-centered cubic (BCC) A cubic structure in which atoms are located in the
corners of the unit cell plus one in the center of the cubic unit cell.
Bragg's law The defining equation of X-ray diffraction, n =2d sin .
close-packed direction A crystallographic direction in a crystal along which
atoms touch.
close-packed plane A crystallographic plane in a crystal on which each atom
contacts six neighbors.
close-packed structures A crystal of a single atom type in which the spherical
atoms are packed as tightly as possible, giving a coordination number of l2 and
an APF of 0.74. HCP and FCC are close-packed structures.
coordination number The number of nearest neighbors that surround an atom
or ion.
crystal lattice The framework on which atoms ate placed in periodic three-
dimensional structures.
diffraction A specific interaction of radiation with materials. Diffraction appears
as reflections from parallel planes and is governed by Bragg's law.
face-centered cubic (FCC) A cubic crystal in which the atoms or ions are
positioned at each corner and in the center of each of the six faces.
families of directions All the equivalent directions in a crystal, which are all the
permutations of the Miller indices of any direction in the family.
families of planes All the equivalent planes in a crystal, which are all the
permutations of the Miller indices of any plane in the family.
hexagonal close-packed (HCP) A crystal that has a regular hexagonal basal
plane and rectangular side planes normal to the basal plane. Individual atoms or
ions are located at each corner of the basal plane and in the center of the basal
plane, and three more atoms are on the midplane, located over the interstices of
the atoms in the basal plane. Each atom has 12 neighbors that touch, giving an
APF of 0.74.
highest-density plane A crystallographic plane with the largest number of atoms
or ions centered on the plane per unit area.
interstices The regions between atoms that are defined by at least four atoms or
ions. Interstices in crystals are usually tetrahedral or octahedral.
isotropic Characterized by properties that are independent of the direction in
which they are measured.
lattice Three-dimensional space-filling repeating pattern on which atoms or ions
are placed to form a crystal.
lattice parameter The lengths of the unit-cell edges.
lattice point One position in the three-dimensional space-filling repeating pattern
that forms a crystal. One or more atoms or ions are placed at each lattice point.
linear density The number of atoms centered on a crystallographic direction per
unit length.
liquid crystal An anisotropic fluid, usually a melt or solution characterized by
molecular alignment.
Miller indices A shorthand for expressing directions and planes in crystals.
octahedral site A position in a crystal defined by six nearest neighbors.
planar density The number of atoms or ions centered on a crystallographic
plane per unit area of the plane.
polycrystalline Describing a solid, usually isotropic, of joined crystals or grains.
polymorphic Describing compounds capable of more than one crystal structure.
simple cubic (SC) A crystal with cubic symmetry in which the atoms or ions are
located at all eight corner positions.
tetrahedral site A position in a crystal defined by four nearest neighbors.
unit cell The smallest representation of a material. In crystals the unit cell is the
smallest patterned collection of atoms or ions that repeats in space.
volumetric density The number of atoms centered in a unit volume of crystal.
Often the volume considered is the unit cell.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocumento40 pagineThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAsif AliNessuna valutazione finora
- 3Documento67 pagine3Louise UmaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3Documento30 pagineLecture 37pnqmtty84Nessuna valutazione finora
- MaterialDocumento2 pagineMaterialAtif AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocumento18 pagineThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAkshay BundhooNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I 2Documento21 pagineUnit-I 2Nivishna RNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic and Ceramic StructureDocumento32 pagineMetallic and Ceramic StructurebasitNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento59 pagineChapter 2Temesgen Zeleke100% (1)
- EMG 1204 Lecture 3Documento15 pagineEMG 1204 Lecture 3James musambakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture1 Electronics and Its ApplicationsDocumento23 pagineLecture1 Electronics and Its Applicationsaribamatloob09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal StructureDocumento7 pagineCrystal StructureSREERAGHAV KNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 3 MatsciDocumento5 pagineHW 3 MatscinoteasytobebooNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallurgy MMS Module 1 and 2Documento245 pagineMetallurgy MMS Module 1 and 2Sahal T YousephNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 - Crystalline Structure of MetalsDocumento25 pagineLecture 2 - Crystalline Structure of MetalsAkerkeMami100% (1)
- Nearly Free ElectronDocumento15 pagineNearly Free ElectronJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento18 pagineLecture 2sgab cANessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal StructureDocumento8 pagineCrystal StructurekdNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3. Basic Concepts of Crystal StructuresDocumento72 pagineUnit 3. Basic Concepts of Crystal StructuresClaresse NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE 301 1stLongExam Chapter3Documento2 pagineMSE 301 1stLongExam Chapter3Ilove PioneeringNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 2 Crystallography and Xray DiffDocumento22 pagineUNIT 2 Crystallography and Xray Diffshaikshafina7107Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline Structures AssignmentDocumento6 pagineCrystalline Structures AssignmentNouman1203Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline Structures: Chemistry For EngineersDocumento62 pagineCrystalline Structures: Chemistry For EngineersRoselyn CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- CrystallographyDocumento39 pagineCrystallographypoornachandhu022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline StructureDocumento23 pagineCrystalline StructureJuvita Hamizah SouminNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureDocumento28 pagineMSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureJansen DomoguenNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureDocumento40 pagineMSE 101 - Lecture 4 - Crystal StructureKate Lynn PabelicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure PPT JntuDocumento118 pagineCrystal Structure PPT JntuKapil Siddhant Devulapalli100% (3)
- Section-A: Some Basic DefinitionsDocumento81 pagineSection-A: Some Basic DefinitionsappliedphyNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of MetalsDocumento29 pagineStructure of Metalsps4haris.ch3534Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Crystalline 1-DikonversiDocumento24 pagineStructure of Crystalline 1-DikonversiAndhika Setyo AdjieNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Crystal StructureDocumento7 pagine2 Crystal StructureyasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Lattices and Structures-1Documento10 pagineCrystal Lattices and Structures-1Watyu Dennis PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Engg Physics R20 - Unit-5Documento18 pagineEngg Physics R20 - Unit-5manchikatlahimanshu.13Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Do Atoms Arrange Themselves To Form Solids?: Crystalline Material: Single CrystalDocumento23 pagineHow Do Atoms Arrange Themselves To Form Solids?: Crystalline Material: Single Crystalmpcd07Nessuna valutazione finora
- MEE1005 Materials Engineering and Technology: Lecture - 3Documento15 pagineMEE1005 Materials Engineering and Technology: Lecture - 3Aashna ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- MEE1005 Materials Engineering and Technology: Lecture - 3Documento15 pagineMEE1005 Materials Engineering and Technology: Lecture - 3Aashna ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structures - Unit IDocumento16 pagineCrystal Structures - Unit Isanjay sNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure - Delivery NotesDocumento35 pagineCrystal Structure - Delivery NotesAninda LahiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State 7 JulyDocumento25 pagineSolid State 7 JulyQwertyNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystalline StructureDocumento8 pagineCrystalline StructureAdeolu AdelekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Lattice - Chemistry LibretextsDocumento3 pagineCrystal Lattice - Chemistry Libretextssafwan shafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Delivery NotesDocumento30 pagineChapter 1 - Delivery NotesSrushtiNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure Notes: 1. Explain The Following Terms BrieflyDocumento12 pagineCrystal Structure Notes: 1. Explain The Following Terms BrieflyNitesh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tushar 1Documento17 pagineTushar 1TUSHAR MISHRA gs2116022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes, Unit 1Documento42 pagineNotes, Unit 1Srisailam ChintuNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State Chemistry (CYT644) : Dr. Sumanta Kumar MeherDocumento40 pagineSolid State Chemistry (CYT644) : Dr. Sumanta Kumar MeherAastha PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Cell Vs Primitive Cell: Symmetry OperationsDocumento48 pagineUnit Cell Vs Primitive Cell: Symmetry OperationsMohammad Anas SaiyedNessuna valutazione finora
- 211 3Documento57 pagine211 3Mada ChohNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento3 pagineUnit 2V V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNessuna valutazione finora
- SMER1Documento80 pagineSMER1Supreeth PremkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal StructureDocumento52 pagineCrystal StructureTausif TausNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT II Crystal - MergedDocumento29 pagineUNIT II Crystal - Mergedsaurb77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)Documento33 paginePhysics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)ch215109152 B.Sc. ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- C2710 Introduction To Solid State Chemistry 2023Documento8 pagineC2710 Introduction To Solid State Chemistry 2023sispulieNessuna valutazione finora
- ChAPTER 2 Crystalline StructuresDocumento38 pagineChAPTER 2 Crystalline StructuresMulatu EMENessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 113E Module 7Documento9 pagineChem 113E Module 7Kenneth John FerrarizNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of MetalsDocumento13 pagineStructure of Metalshammad00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Documento7 pagineAtomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Joseph MuhoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Camp's Biochemistry and Cell Biology by the NumbersDa EverandCamp's Biochemistry and Cell Biology by the NumbersNessuna valutazione finora