Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Drug Calcu 2014
Caricato da
Paul Anthony LoricaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Calcu 2014
Caricato da
Paul Anthony LoricaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
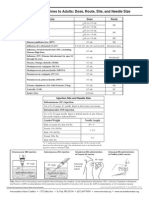
DRUG CALCULATION
CONVERT THE FOLLOWING:
1. 5 teaspoons to mL
9. 8 mg to mcg
2. 3 tablespoons to teaspoon
10.38 oC to oF
3. 7 ounce to mL
11.35.5 oC to oF
4. 6 cups to ounce
12.110 oF to oC
5. 2 glasses to ounce
13.101 oF to oC
6. 7 fluid drams to min
14.
70 lbs to oz
7. 1000 mg to grains
15.
20 min to mL
8. 1/6 grain to grams
SOLVE THE FOLLOWING:
1. A patient has an order for Dexametyhasone (Decadron) 6 mg IV push stat.
Available is a vial of dexamethasone with a concentration of 4 mg/ml. How
many mL does the nurse draw into the syringe to administer the dose?
2. The patient has an order for Cefotaxime (Claforan) 1 gram IV q6h. The
reconstituted vial in the patients medication drawer is labeled with a
concentration of 95 mg/ml. How many milliliters of solution should be added to
the IV bag for the intermittent infusion?
3. The patient has an order for globuride (DiaBeta) 1.25 mg before breakfast and
dinner. Available are 2.5mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse plan to
administer?
4. The patient has an order for lorazepam (Ativan) 0.5 mg IV q6h PRN for
agitation. Available is a vial containing 2 mg/ml. how many ml of solution
should the nurse draw up for injection?
5. A patient has a temperature of 101.2 oF. There is an order for acetaminophen
(Tylenol) 650 mg PO for fever, and 325 mg tablets are available. How many
tablets should the nurse give?
6. A patient complaints of pain in his right lower extremity. The Physician orders
codeine 60 mg and aspirin grains XPO every 4 hours, as needed for pain. Each
1
codeine tablet contains 15 mg of codeine. Each aspirin contains 325 mg of
aspirin. How much codeine and aspirin should be administered by the nurse?
7. A nurse is calculating a patients fluid intake for an 8 hour period. The patient
drank 8 ounce of tea and 4 ounce of orange juice for breakfast, 4 ounce of
water at 10 AM and at 1 PM when taking his medications, and 6 oz of iced tea
at lunch. At 8 AM and again at 2 PM, the patient received his antibiotics
intravenously in 50 mL of normal saline. What is the patients total intake in
milliliters?
8. The physician orders nitroglycerin, 1/150 gr. The medication label reads 0.4 mg
per tablet. The nurse prepares to administer how many tablets to the patient?
9.
A 3 month old has an order for Acetaminophen (Tylenol) suspension 45 mg
PO q4h prn. The product label lists of concentration of 500 mg/mL. After
determining that the dosage is safe, how many mL should the nurse
administer?
10.
The physician orders continuous heparin sodium by IV at 1000 units per
hour. The label on the IV bag reads 500 mL D 5W with 20,000 units of heparin
sodium. How many milliliters per hour are required to administer the correct
dose?
11.
The physician orders continuous heparin regular insulin by IV at 10 units
per hour. The label on the IV bag reads 100 mL NS with 50 units regular insulin.
How many milliliters per hour are required to administer the correct dose?
12.
A physician orders an intravenous (IV) dose of 400,000 units of penicillin G
benzathine (Bicillin). The label on the 10-ml ampule sent from the pharmacy
reads penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin), 300,000 units per milliliter. A nurse
prepares how much medication to administer the correct dose?
13.
Gentamicin sulfate (Garamycin), 80 mg in 100 ml normal saline (NS), is be
administered over 30 minutes. The drop factor is 10 drops per milliliter. A nurse
sets the flow rate at how many drops per minute?
14.
The nurse cares for a client receiving hourly peritoneal dialysis exchanges.
During a one hour exchange, the nurse infuses 2000 ml of dialysate and 1,900
ml of outflow is returned. During the exchange, the client drinks 8 oz of apple
juice, 2 cups of water, and voids 150 ml of urine. Calculate and record the
clients intake in milliliters.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Heart of the Field "Refresher & Nha Certification Quick Notes"Da EverandHeart of the Field "Refresher & Nha Certification Quick Notes"Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsDa EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 - Drug ComputationsDocumento135 pagineLecture 8 - Drug ComputationsAlyssa Audrey CaoagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Calculation WorksheetDocumento3 pagineDrug Calculation WorksheetUmaru DomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication Calculation Practice Problems: Level Ii, Iii and IvDocumento6 pagineMedication Calculation Practice Problems: Level Ii, Iii and IvQueennita100% (7)
- Nursing-Math Practice Set 1 PDFDocumento3 pagineNursing-Math Practice Set 1 PDFSanaz NikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Geriatric Soap NoteDocumento6 pagineGeriatric Soap Noteapi-282282363100% (6)
- Drug Dosage Calculation Test IDocumento6 pagineDrug Dosage Calculation Test Ikarenmcc06142013100% (1)
- Kerry Layne Author Albert Ferro Author 100 Cases in Clinical PharmacologyDocumento249 pagineKerry Layne Author Albert Ferro Author 100 Cases in Clinical Pharmacologyteju100% (3)
- Drug CalculationsDocumento2 pagineDrug CalculationsBern NerquitNessuna valutazione finora
- Med Math Practice TestDocumento2 pagineMed Math Practice TestTad McDowell100% (1)
- Convert Units, Doses, Concentrations Math ProblemsDocumento13 pagineConvert Units, Doses, Concentrations Math Problemstetarwal100% (1)
- Skills Drug ComputationDocumento23 pagineSkills Drug ComputationFreida Michelle BonnitNessuna valutazione finora
- Paramedic Math Practice 2Documento2 pagineParamedic Math Practice 2TherleDregansky100% (1)
- Ethical Decision MakingDocumento28 pagineEthical Decision MakingPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- NUR 207 Drug Dosage Calculation Practice Fall 2020Documento5 pagineNUR 207 Drug Dosage Calculation Practice Fall 2020Francesca LopesNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 05 Pharmacology Test BankDocumento4 pagineCHAPTER 05 Pharmacology Test BankseeryneNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Pre-Test QuestionsDocumento4 pagineMath Pre-Test Questionsgok_addictedNessuna valutazione finora
- InfluenzaDocumento19 pagineInfluenzapppammNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsDocumento14 paginePerioperative Nursing 50 QuestionsPaul Anthony Lorica100% (3)
- 10 Golden Rules For Administering Drug SafelyDocumento5 pagine10 Golden Rules For Administering Drug SafelyAngel EsplenadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamDa EverandPharmacy Calculation Workbook: 250 Questions to Prepare for the NAPLEX and PTCB ExamValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Pharm ReviewDocumento5 paginePharm ReviewChelsea ChanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparing for the Drug Dosage ExamDocumento7 paginePreparing for the Drug Dosage ExamchicktankNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation SeatworkDocumento2 pagineCalculation SeatworkBenedict James BermasNessuna valutazione finora
- NR 324 Med Calculation Practice TestDocumento3 pagineNR 324 Med Calculation Practice TestHilarymaeBoldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Fluids CalculationDocumento23 pagineDrug Fluids CalculationRuby Jane Mansueto - Pague100% (1)
- Other Ethical Schools of ThoughtDocumento56 pagineOther Ethical Schools of ThoughtPaul Anthony Lorica100% (1)
- Calculations Practice TestDocumento13 pagineCalculations Practice TestFrancis VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Nursing CareDocumento124 paginePerioperative Nursing CarePaul Anthony Lorica100% (1)
- HKDocumento5 pagineHKnurseoncervixNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Nurse QuizzesDocumento10 pagineStudent Nurse QuizzesElesis samaNessuna valutazione finora
- Boot CampDocumento190 pagineBoot CampfekaduNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG CALCULATIONS GUIDEDocumento42 pagineDRUG CALCULATIONS GUIDECarl Josef C. GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 106 - DRUG and IVF CALCULATIONS - VIOSDocumento3 pagineNCM 106 - DRUG and IVF CALCULATIONS - VIOSIra Velle ViosNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubrics For Preparing Blood TransfusionDocumento4 pagineRubrics For Preparing Blood TransfusionMARK JOSHUA ALFARONessuna valutazione finora
- OSODROENTDocumento82 pagineOSODROENTAvner TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: - Competency Appraisal 2Documento2 pagineName: - Competency Appraisal 2Matt Joseph CabantingNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Calculations AssignmentDocumento2 pagineDrug Calculations AssignmentDarren RobertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Review ProblemsDocumento3 pagineMath Review ProblemsrailguncannonNessuna valutazione finora
- DosageDocumento24 pagineDosageLes ChiensNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurdr Practice QuestionsDocumento6 pagineNurdr Practice QuestionsSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2 QuizDocumento2 pagineDay 2 QuizAngie MandeoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Practice Problems Group 3Documento2 pagineMath Practice Problems Group 3Lukman Nal 26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Numericals AssignmentDocumento2 pagineNumericals AssignmentAiman SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- NUR 215 Math PracticeDocumento3 pagineNUR 215 Math PracticeSierrah SlaughterNessuna valutazione finora
- IV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityDocumento2 pagineIV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityNicole Chloe OcanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computation DrillsDocumento3 pagineComputation DrillsnicoletbaenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Numerical Assignment With AnswersDocumento3 pagineMaths Numerical Assignment With AnswersAiman SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma 2017 1st GradexamDocumento4 paginePharma 2017 1st GradexamteabagmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DISP-CalculationsWorksheetLab LecDocumento4 pagineDISP-CalculationsWorksheetLab LecRafaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation of Drug Dosages A Work Text 10th Edition Ogden Test Bank DownloadDocumento8 pagineCalculation of Drug Dosages A Work Text 10th Edition Ogden Test Bank Downloadupwindscatterf9ebp100% (26)
- HESI Dosage Calculation Practice ExamDocumento24 pagineHESI Dosage Calculation Practice Exambhilligoss35Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCNRSDosage Calculati 2Documento6 pagineMCNRSDosage Calculati 2Srikanth ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication Calculation QuizDocumento1 paginaMedication Calculation QuizObada DyabNessuna valutazione finora
- Transitions Exam 3Documento17 pagineTransitions Exam 3brittney dolceNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma Calculation ReviewerDocumento4 paginePharma Calculation ReviewerTine GuibaoNessuna valutazione finora
- RN Math WorkSheet Q1 and AnswersDocumento4 pagineRN Math WorkSheet Q1 and Answersshereln.ballNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmaDocumento1 paginaPharmaIrene Soriano BayubayNessuna valutazione finora
- Med Math Practice Rights and ConversionsDocumento4 pagineMed Math Practice Rights and ConversionsShequilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infusion and medication calculations: 38 charactersDocumento6 pagineInfusion and medication calculations: 38 charactersjhonNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWDocumento9 pagineNURSING PHARMACOLOGY REVIEWRia Angely PanagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Dosage Practice QuestionsDocumento2 pagineDrug Dosage Practice QuestionsCelia Seneh GwandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculations Practice TestDocumento13 pagineCalculations Practice TestFrancis VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Pharmacology Dosage CalculationsDocumento9 pagineNursing Pharmacology Dosage Calculationslea mae andoloyNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Drug Computation Problem SamplesDocumento2 pagine2022 Drug Computation Problem SamplesXeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento27 pagineChapter 6yeshi janexo100% (1)
- Math Quiz Week 2Documento2 pagineMath Quiz Week 2johnsonnbrandieNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Calculations: How Many Tablets, Capsules, Suppositories, or mL to AdministerDocumento5 pagineDrug Calculations: How Many Tablets, Capsules, Suppositories, or mL to AdministerJoy HavsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Cal - Practice TestDocumento2 pagineDrug Cal - Practice TestBryan Mae H. DegorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Beneficence & Other PrinciplesDocumento5 pagineBeneficence & Other PrinciplesPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of GNDDocumento42 pagineTheories of GNDPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Ethics Quizs Doc XDocumento1 paginaHealth Ethics Quizs Doc XPaul Anthony Lorica100% (1)
- What Is EthicsDocumento33 pagineWhat Is EthicsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Routes of NutritionDocumento58 pagineRoutes of NutritionPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsDocumento2 pagineTable of Commonly Used IV SolutionsKelly Diane LigosNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastric Lavage and Gavage Nutrition TechniquesDocumento5 pagineGastric Lavage and Gavage Nutrition TechniquesPaul Anthony Lorica100% (1)
- VirtuesDocumento3 pagineVirtuesPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicable Diseases 2012 Student VersionDocumento60 pagineCommunicable Diseases 2012 Student VersionJelaine CENessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition-Definition of TermsDocumento5 pagineNutrition-Definition of TermsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Administering Vaccines To AdultsDocumento1 paginaAdministering Vaccines To AdultsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullets OBDocumento3 pagineBullets OBPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Growth & Development SummarizedDocumento1 paginaTheories of Growth & Development SummarizedJoannaNicoleZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemeriksaan LabDocumento1 paginaPemeriksaan LabYeri HoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Topics and Questions NursingDocumento4 pagineTopics and Questions NursingPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- BulletsDocumento10 pagineBulletsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob Gyne NotesDocumento9 pagineOb Gyne NotesPaul Anthony Lorica100% (1)
- BulletsDocumento18 pagineBulletsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of GrowthDocumento1 paginaTheories of GrowthPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- MS3 Review NotesDocumento11 pagineMS3 Review NotesPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharma MnemonicsDocumento14 paginePharma MnemonicsPaul Anthony LoricaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse OximeterDocumento16 paginePulse OximeterChing Wai Yong100% (1)
- Overview HyperparatiroidDocumento5 pagineOverview HyperparatiroiddyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive Health AssignmentDocumento12 pagineReproductive Health AssignmentRmanojkumar OmanNessuna valutazione finora
- " Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics" "Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics"Documento7 pagine" Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics" "Hypercholesterolemia: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics"kookiescreamNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease Research PaperDocumento6 pagineDisease Research PaperJose PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- Echinacea SPP MonographDocumento2 pagineEchinacea SPP MonographOliver Rathbone100% (1)
- Incomplete Right Bundle-Branch Block: A Developmental Variant Rather Than Conduction AbnormalityDocumento10 pagineIncomplete Right Bundle-Branch Block: A Developmental Variant Rather Than Conduction AbnormalityErol SefchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Success Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes To Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) CourseDocumento11 pagineSuccess Manual and Cheat Sheet Notes To Pass Your Basic Life Support (BLS) CourseanthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Intraocular Foreign BodiesDocumento7 pagineManagement of Intraocular Foreign BodiesdebbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Indriatmi, W. 2018. Ilmu Penyakit Dan Kulit Kelamin. Edisi Ke-7. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran IndonesiaDocumento10 pagineIndriatmi, W. 2018. Ilmu Penyakit Dan Kulit Kelamin. Edisi Ke-7. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran IndonesiaDiza Hanni PertiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Template Continued On Page 2: Dose-Dense Ac (Doxorubicin/Cyclophosphamide) CourseDocumento2 pagineTemplate Continued On Page 2: Dose-Dense Ac (Doxorubicin/Cyclophosphamide) CourseJaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheatsheet PDFDocumento2 pagineCheatsheet PDFJudaeo SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Aloe Vera (Gel) Other Aloe SPP.: Aloe Vera (L.) Burm.f., A. Arborescens Mill. andDocumento3 pagineAloe Vera (Gel) Other Aloe SPP.: Aloe Vera (L.) Burm.f., A. Arborescens Mill. andRiani EkawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynzone TrainingDocumento62 pagineGynzone TrainingMariana PinheiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Norovirus 201309101051579338Documento3 pagineNorovirus 201309101051579338Jeeva maria GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaDocumento30 pagineLaporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaShifa Ali JannatinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypospadias Pathophysiology and Treatment Principles, Not As Recent As We Think.Documento2 pagineHypospadias Pathophysiology and Treatment Principles, Not As Recent As We Think.TI Journals PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- CA125: A Marker for Ovarian Cancer Detection and MonitoringDocumento3 pagineCA125: A Marker for Ovarian Cancer Detection and Monitoringडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxic Megacolon: Daniel M. Autenrieth, MD, and Daniel C. Baumgart, MD, PHDDocumento8 pagineToxic Megacolon: Daniel M. Autenrieth, MD, and Daniel C. Baumgart, MD, PHDGoran TomićNessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Project Rough Draft 1Documento17 pagineSenior Project Rough Draft 1api-405410037Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blood ReportDocumento15 pagineBlood ReportSaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson A 6-WPS OfficeDocumento3 pagineLesson A 6-WPS OfficeRestuNessuna valutazione finora
- Herpes Simplex I and IIDocumento50 pagineHerpes Simplex I and IItummalapalli venkateswara raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Step by Step Lihation of The Internal Iliac ArteryDocumento6 pagineStep by Step Lihation of The Internal Iliac ArteryAkbar PurnadiputraNessuna valutazione finora