Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge Flow
Caricato da
sfwongCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
2.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge Flow
Caricato da
sfwongCopyright:
Formati disponibili
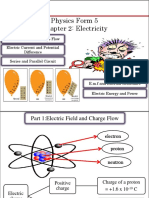
Analysing Electric Fields and Charge
Flow
By Ms Nurul Ain Mat Aron
state the relationship between electron flow and electric current
define electric current
describe an electric field
sketch electric field lines showing the direction of the field
describe the effect of an electric field on a charge
solve problems involving electric charge and current
Objectives
Electric Charge, Q
There are two type of electric charge which are
a) Positive charge (+)
b) Negative charge (-)
An electron has a negative charge and a proton has a positive
charge
The charge on a single electron is -1.6 x 10
-19
C
The charge on a single a proton is +1.6 x 10
-19
C
The unit is
coulomb or C
Electric Charge, Q
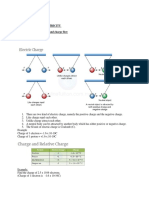
A body is:
a) Neutral, if it has equal number of positive and negative charges.
b) Negative charged, if it has more negative than positive charges
c) Positive charged, if it has more positive than negative charges
Recall:
12 protons
12 neutrons
Magnesium atom
12 electrons
2+
10 electrons
Magnesium ion
Electric Charge, Q
Examples
An object that is positively charges contains all protons and no electrons
FALSE
An object that is negatively charges could contain only electrons with no
accompanying protons
FALSE
Like charges repel, unlike charges attract
Electric Charge, Q
Like charges repel
Electric Charge, Q
unlike charges attract
Stationary electric charges are known as static electricity
Static Electricity
Static electricity is the accumulation of electrical charges on the surface of a
material
Static electricity is usually caused when certain materials are rubbed
against each other
The process causes electrons to be pulled from the surface of one material
and relocated on the surface of the other material.
The material that loses electrons ends up with an excess of positive (+)
charges. The material that gains electrons ends up an excess of negative ()
charges on its surface.
Electric current consists a flow of electrons. The more charges that flow
through a cross section within a given time, the larger is the current.
Therefore, an electric current is define as the rate of flow of charge
Electric Current, I
The amount of charge, Q flowing through any conductor is given by:
Electric Current, I
Q = It
A B
When free electrons move through the wire from A to B, and the electric
currents flows from B to A
I
A fuse wire will blow if the current flowing through it exceeds 5.0A for
a time of 80ms.
a) What is the quantity of electric charge that has passed through
the fuse wire in 80ms?
b) How many electrons have passed through the fuse wire in that
time, given that the charge on 1 electron is 1.6 x 10
-19
C
Problem 1
Answer: 0.40 C and 2.5 x 10
18
Electric Current, I
A charge of 600 C flows through a metal conductor in every 5 minutes.
What is the electric current in the conductor?
Problem 2
Electric Current, I
An electric current of 3.2mA flows through a bulb for 4 minutes.
Determine
a) The electric charge
b) The number of electrons
(the charge in an electrons, e = 1.6 x 10
-19
C)
Problem 3
Electric Current, I
An electric field is a region in which an electric charge experience a
force.
An electric field can be represented by field lines drawn in certain
pattern. The direction of the field is indicated by arrows on the lines.
Electric Field
The lines of force are directed outwards for a positive charge
and inwards for a negative charge.
Electric Field
The strength of the electric field is indicated by how close the field lines
are to each other. The closer the field lines, the stronger the electric field
in that region.
Electric Field
Electric Field
Electric Field
Electric Field
The Effect of an Electric Field
The ball will still remain stationary. This is because the force exert on the
ball by the positive plate is equal to the force exerted on it by the negative
plate.
A ping-pong ball coated with a Conducting Material
The Effect of an Electric Field
If the ping pong ball is displaced to the right to touch the positive plate, it
will then be charged with positive charge and will be pushed towards the
negative plate
A ping-pong ball coated with a Conducting Material
The Effect of an Electric Field
A ping-pong ball coated with a Conducting Material
When the ping pong ball touches the negative plate, it will be charged with
negative charge and will be pushed towards the positive plate. This process
repeats again and again, causes the ping pong ball oscillates to and fro
continuously between the two plates.
The Effect of an Electric Field
Spreading of a Candle Flame
The Effect of an Electric Field
Spreading of a Candle Flame
The heat of the candle flame removes electrons from the air
molecules around it, and therefore ionised the molecule.
The Effect of an Electric Field
Spreading of a Candle Flame
If the candle is placed in between 2 plates connected to a power supply,
the positive ions will be attracted to the negative plate while the negative
ions will be attracted to the positive plate.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ELECTRICITY CHARGE AND FIELDDocumento8 pagineELECTRICITY CHARGE AND FIELDKek Siang MingNessuna valutazione finora
- F 5 C 2Documento14 pagineF 5 C 2jalrizal7Nessuna valutazione finora
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Da EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Nessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricityDocumento200 pagineElectricityNurul FadhilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 2: ElectricityDocumento18 paginePhysics Form 5 Chapter 2: ElectricitySharvinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Electricity 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocumento14 pagineChapter 7 Electricity 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowvaaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 7: Electricity (Part 1) : 7.1 Electric Field and Charge FlowDocumento7 pagineChap 7: Electricity (Part 1) : 7.1 Electric Field and Charge Flowanandraj govindarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Phyf5 Chap2Documento76 paginePhyf5 Chap2Mohd AzlanNessuna valutazione finora
- PKP Lesson 7.1 Electric Fields & Charge Flow (BM)Documento5 paginePKP Lesson 7.1 Electric Fields & Charge Flow (BM)Mazanizam Bin AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Electricity: Van de Graaff Generator & Electric FieldsDocumento7 pagineForm 5 Chapter 2 Electricity: Van de Graaff Generator & Electric Fieldskhangsiean890% (1)
- Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocumento23 pagineElectric Charge and Coulomb's Lawjitin999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Electricity (Form 5)Documento28 pagineChapter 2 - Electricity (Form 5)kcnjojo88% (16)
- Electric ChargeDocumento34 pagineElectric Chargeglaizamaeodinario5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity LectureDocumento59 pagineElectricity LectureTanuj GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutron: Electric Charge and The Atomic Theory of MatterDocumento3 pagineNeutron: Electric Charge and The Atomic Theory of MatterGabriela AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocumento64 pagineElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismFe DNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Documento53 pagineGeneral Physics 2 (Electric Charge and Electric Field)Ronnel MacadangdangNessuna valutazione finora
- AP CH 15-TeacherDocumento36 pagineAP CH 15-TeacherOnur YavuzcetinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Electricity - Static ChargesDocumento4 pagineChapter 7: Electricity - Static ChargesJin TangNessuna valutazione finora
- Question NoDocumento19 pagineQuestion NoAnimesh GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes ElectricityDocumento17 pagineNotes ElectricityPinki NegiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 ElectricityDocumento61 pagineChapter 2 ElectricityNor ShuhadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Properties of Fundamental ParticlesDocumento30 pagineElectric Properties of Fundamental Particlesgloria11111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeDocumento19 pagineElectrostatics: 18.1 Electric ChargeManishKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics - Direct Current PDFDocumento76 pagineElectrostatics - Direct Current PDFRita UmutoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity at HomeDocumento10 pagineElectricity at HomeWilliam HaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 2 Quarter 3Documento35 paginePhysics 2 Quarter 3Aaron Justin BeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- JPN Pahang Electricity Guide Form 5 Chapter 7Documento61 pagineJPN Pahang Electricity Guide Form 5 Chapter 7Liayana Che AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Week 1 To Week 6Documento225 paginePhysics Week 1 To Week 6kenmakozume5074Nessuna valutazione finora
- 24 - Electricity and MagnetismDocumento97 pagine24 - Electricity and MagnetismAM - 12CA 812699 Louise Arbour SSNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceDocumento53 pagineElectrostatics Is The Study of Stationary Electric Charges and All The Effects They ProduceNo PainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)Documento61 pagineChapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)Izawati AmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideDocumento60 pagineChapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideLawrence HiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 22 PhysicsDocumento2 pagineChapter 22 Physicsapi-261669796Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 - Electric ChargeDocumento16 pagineUnit 3 - Electric ChargerajudevisNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Documento33 pagineElectric Charges and Fields:Chapter 1Maryam MehekNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 5 Physics ElectricityDocumento35 pagineForm 5 Physics ElectricityAnonymous Kx8TAybnXQNessuna valutazione finora
- Lectures Physics 2Documento354 pagineLectures Physics 2Uranium PlatinumNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1-Electric FieldDocumento33 pagineChapter 1-Electric FieldThông LêNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 4.0 Electricity and ElectromagnetismDocumento80 pagineSection 4.0 Electricity and Electromagnetismgarikaishumba2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsDocumento21 pagineElectrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsSONY SAB HDNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricityDocumento25 pagineElectricityWeb BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts of ElectricityDocumento229 pagineBasic Concepts of ElectricityDaniel QuarteyNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTROSTATICS KEY CONCEPTSDocumento15 pagineELECTROSTATICS KEY CONCEPTSNARRAYANAN ARNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Quantities - Free Exam AcademyDocumento19 pagineElectrical Quantities - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity and Magnetism NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Exercise 1Documento17 pagineElectricity and Magnetism NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Exercise 1Shashwat MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy CHP 1 NotesDocumento33 paginePhy CHP 1 Notesayaan ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity (Note)Documento9 pagineElectricity (Note)Cally ChewNessuna valutazione finora
- G-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CDocumento35 pagineG-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CEmnet SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Genereal Physics 2Documento65 pagineGenereal Physics 2joshua tejadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric ChargesDocumento15 pagineElectric Chargesarjunr1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Junior PhysicsDocumento9 pagineJunior PhysicsVishesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Ch 20 Forces Charges Electric FieldsDocumento5 paginePhysics Ch 20 Forces Charges Electric FieldsMarah AlsurkhyNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocumento32 pagine7.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowTaner YenerNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 TestrDocumento5 pagine14 TestrΧρίστος ΠαπαναστασίουNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Static ElectricyDocumento26 pagine17 Static ElectricyDoraemonNessuna valutazione finora
- Electic Charge, Electric Fields & ElectrostaticsDocumento55 pagineElectic Charge, Electric Fields & Electrostaticscrizel in nameNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 2 LAS Quarter 3Documento428 pagineGeneral Physics 2 LAS Quarter 3Dkaye GorospeNessuna valutazione finora
- AlgebraDocumento2 pagineAlgebrasfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Power and IndicesDocumento2 paginePower and IndicessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Problems - GRAPHSDocumento3 pagineTopic 1 Problems - GRAPHSsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocumento1 paginaPolynomial and Rational FunctionssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus 3 - Vector Equation ExercisesDocumento4 pagineCalculus 3 - Vector Equation ExercisessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento2 pagineProblems On Trigonometric FunctionssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Derivatives-Related RatesDocumento3 pagineApplications of Derivatives-Related RatessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Maths Differentiation and IntegrationDocumento3 pagineAdd Maths Differentiation and IntegrationsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Limits: Prepared by Janice Wong SFDocumento4 pagineLimits: Prepared by Janice Wong SFsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: Circles: Diagram 1Documento15 pagineChapter 3: Circles: Diagram 1Nabilah YusofNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH1034 Calculus I IntegrationDocumento4 pagineMATH1034 Calculus I IntegrationsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercises On IntegrationsDocumento2 pagineExercises On IntegrationssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento2 pagineProblems On Trigonometric FunctionssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento2 pagineProblems On Trigonometric FunctionssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.2 (Part 1) Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldDocumento14 pagine3.2 (Part 1) Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 - Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocumento12 pagine4.1 - Understanding Thermal EquilibriumsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorDocumento28 pagine3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorsfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento2 pagineProblems On Trigonometric FunctionssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics F4Documento45 paginePhysics F4Maheswaren MahesNessuna valutazione finora
- Peka Form 5 (Ohm's Law)Documento3 paginePeka Form 5 (Ohm's Law)sfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Forces and Pressure - ExercisesDocumento5 pagine3.1 Forces and Pressure - ExercisessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3 Analysing Series and Parallel CircuitsDocumento16 pagine2.3 Analysing Series and Parallel CircuitssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.7 Electromagnetic WavesDocumento13 pagine1.7 Electromagnetic WavessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysing the Relationship between Current, Potential Difference and ResistanceDocumento14 pagineAnalysing the Relationship between Current, Potential Difference and ResistancesfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Introduction To Physics - Understanding PhysicsDocumento7 pagine1.1 Introduction To Physics - Understanding PhysicssfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocumento24 pagine1.6 Sound WavessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 Introduction To Physics - Understanding Base and Derived Quantities (Part 1)Documento21 pagine1.2 Introduction To Physics - Understanding Base and Derived Quantities (Part 1)sfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocumento24 pagine1.6 Sound WavessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.6 Sound WavesDocumento24 pagine1.6 Sound WavessfwongNessuna valutazione finora
- Bundel Soal Kimia TPBDocumento210 pagineBundel Soal Kimia TPBElen Mustika100% (1)
- U-5 - 2022 - Tecnologías de Tratamientos - BDocumento39 pagineU-5 - 2022 - Tecnologías de Tratamientos - BSimón OsésNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser Cutting Process - A Review: June 2014Documento6 pagineLaser Cutting Process - A Review: June 2014cesarNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Source Drain DopingDocumento6 pagineImpact of Source Drain DopingjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Problem Mod 3 CPCDocumento6 pagineSample Problem Mod 3 CPCAman PratikNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahaa One RMC: Er - Nanthakumar Boomi Textile MillsDocumento19 pagineMahaa One RMC: Er - Nanthakumar Boomi Textile MillsMAHAA ONE RMC RAMASAMY MNessuna valutazione finora
- General ChemistryDocumento44 pagineGeneral ChemistrySUSANA, NIÑA FELIZ C.100% (1)
- Lintels and ArchesDocumento49 pagineLintels and Arches18 Architects50% (2)
- 00-H-0008 Air-Cooled Water ChillersDocumento14 pagine00-H-0008 Air-Cooled Water Chillershabibansari2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- TranslateDocumento9 pagineTranslateWira AdjieNessuna valutazione finora
- Alina Dawood - QS - Long AssignmentDocumento11 pagineAlina Dawood - QS - Long AssignmentK AndreNessuna valutazione finora
- Slurry Shield AdditivesDocumento8 pagineSlurry Shield AdditivesfabiodbdbNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotechnical Engineering QuantumDocumento274 pagineGeotechnical Engineering QuantumRitik SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DPW G2 Multi Pole Spec SheetDocumento2 pagineDPW G2 Multi Pole Spec SheetlNessuna valutazione finora
- Tube To Tubesheet Weld Joint Design & Welding Qualifications MicroDocumento21 pagineTube To Tubesheet Weld Joint Design & Welding Qualifications MicroSiva baalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sodra Green - Safety Data SheetDocumento2 pagineSodra Green - Safety Data Sheetibrahim sanlıNessuna valutazione finora
- HUMITECHDocumento1 paginaHUMITECHtimNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC20091118133046Documento5 pagineIEC20091118133046SEANMNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Chloride Content in Reinforced ConcreteDocumento7 pagineCritical Chloride Content in Reinforced ConcreteAshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocumento5 pagineMechanics of Materials Beer 7th Edition Solutions Manualjosephpetersonjaczgqxdsw100% (45)
- EngineeringDocumento208 pagineEngineeringvins4u100% (1)
- 260.equipment For Decentralized Cold Pressing of Oil SeedsDocumento40 pagine260.equipment For Decentralized Cold Pressing of Oil SeedsJhon SyalfiandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculating Electrical Load and Wire SizingDocumento7 pagineCalculating Electrical Load and Wire SizingMarcelo CondinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A-6 PDFDocumento1 paginaAstm A-6 PDFFrank Berrios GarcesNessuna valutazione finora
- Physico-chemical characteristics of corrosion scales in old iron pipesDocumento9 paginePhysico-chemical characteristics of corrosion scales in old iron pipesGustavo Alejandro GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Housekeeping & Accommodation StudiesDocumento15 pagineHousekeeping & Accommodation StudiesCaleb MukaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Corona Treater: Operation and MainenanceDocumento34 pagineCorona Treater: Operation and MainenanceJUAN RODRIGUEZNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13Documento30 pagineCH 13Laurertan TavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas and Oil - ExploitationDocumento12 pagineGas and Oil - ExploitationAnonymous puv25NQenNessuna valutazione finora
- Defects / Imperfections in Crystalline MaterialsDocumento41 pagineDefects / Imperfections in Crystalline Materialsjayant thakareNessuna valutazione finora