Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Year Six Mathematics Curriculum Specifications
Caricato da
wahid_730 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
590 visualizzazioni5 pagine1.1. Name and write numbers up to seven digits. 1.2. Multiply up to six-digit numbers with a one-digit number. 1.3. Solve mixed operations problems involving addition and subtraction. 1.4. Identify the place value of the digits in any whole number of up to 7 digits..
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documento1.1. Name and write numbers up to seven digits. 1.2. Multiply up to six-digit numbers with a one-digit number. 1.3. Solve mixed operations problems involving addition and subtraction. 1.4. Identify the place value of the digits in any whole number of up to 7 digits..
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
590 visualizzazioni5 pagineYear Six Mathematics Curriculum Specifications
Caricato da
wahid_731.1. Name and write numbers up to seven digits. 1.2. Multiply up to six-digit numbers with a one-digit number. 1.3. Solve mixed operations problems involving addition and subtraction. 1.4. Identify the place value of the digits in any whole number of up to 7 digits..
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
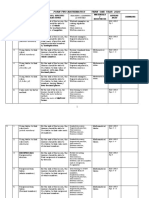
YEAR SIX MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM SPECIFICATIONS
N Topic Learning Learning Outcome Wee
o. Area k
1. Whole 1.1 1.1.1 Name and write numbers up to seven 1
Number Numbers Up digits
s To Seven 1.1.2 Determine the place value of the digits in
Digits any whole number
of up to seven digits.
1.1.3 Writing numbers in extended notation.
1.1.4 Express whole numbers in decimals of a 2
million and vice
versa. Limit decimal terms up to 3 decimal
places.
1.1.5 Express whole number in fractions of a
million and vice versa.
Limit decimal terms up to 3 decimal
places.
1.1.6 Compare number values up to seven 3
digits.
1.2 Basic 1.1.7 Round off numbers to the nearest tens,
Operations hundreds and
With thousands.
Numbers Up 1.1.8 Round off numbers to the nearest ten
To Seven thousands, hundred 4
Digits thousands and millions.
1.2.1 Add any two to five numbers to 9 999 999.
1.2.2 Subtract one number from bigger number 5
less than
10 000 000.
1.2.3 Subtract successively from a bigger
number less than
10 000 000.
1.2.4 Multiply up to six-digit numbers with a
one-digit number. 6
1.2.5 Multiply up to six-digit numbers with a
two-digit number.
1.2.6 Multiply up to six-digit numbers with 10,
100 and 1 000.
1.2.7 Divide numbers of up to seven digits by a
one-digit number.
1.3 Mixed 1.2.8 Divide numbers of up to seven digits by 7
Operations 10, 100 and 1 000.
With 1.2.9 Divide numbers of up to seven digits by
Numbers Up two-digit number.
To Seven 1.2.10 Solve addition problems involving
Digits numbers up to seven
digits.
1.2.11 Solve subtraction problems involving
numbers up to seven
digits.
1.2.12 Solve multiplication problems involving
numbers up to
seven digits.
1.2.13 Solve division problems involving
numbers up to seven
digits.
1.3.1 Compute mixed operations problems
involving addition and
multiplication.
1.3.2 Compute mixed operations problems
involving subtraction
and division.
1.3.3 Compute mixed operations problems
involving brackets.
1.3.4 Solve problems involving mixed operations
on numbers of up
to seven digits.
2. Fraction 2.1 Addition 2.1.1 Add three mixed numbers with the same
s of Fractions denominator of up to
10.
2.1.2 Add three mixed numbers with the
different denominator of 8
up to 10.
2.1.3 Solve problems involving addition of
mixed numbers.
N Topic Learning Learning Outcome Wee
o. Area k
2.2 2.2.1 Subtract involving three mixed numbers
Subtraction with the same denominator of up to 10.
of Fractions 2.2.2 Subtract involving three mixed numbers
with different denominators of up to 10.
2.2.3 Solve problems involving subtraction of
mixed numbers.
9
2.3 2.3.1 Multiply mixed numbers with a whole
Multiplicatio number. The whole number component of a mixed
n of number is limited to three digits. The denominator of the
Fractions fractional part of the mixed number is limited to less than
10.
2.4 Division 2.4.1 Divide fractions with a whole number.
of Fractions Denominators for the dividend is limited to less than 10.
The divisors is limited to less than 10 for both the whole
number and fraction.
2.4.2 Divide fractions with a fraction.
Denominators for the dividend is limited to less than 10.
The divisors is limited to less than 10 for both the whole
number and fraction.
10
2.4.3 Divide mixed number with a whole
number. Denominators for the dividend is limited to less
than 10. The divisors is limited to less than 10 for both the
whole number and fraction.
2.4.4 Divide mixed number with a fraction.
Denominators for the dividend is limited to less than 10.
The divisors is limited to less than 10 for both the whole
number and fraction.
3. Decimal 3.1 Mixed 3.1.1 Add and subtract three to four decimal 10
s Operations numbers of up to 3 decimal places involving
With decimals numbers only.
Decimals 3.1.2 Add and subtract three to four decimal
numbers of up to 3 decimal places involving
whole numbers and decimal numbers.
4. Percent 4.1 4.1.1 Convert mixed numbers to percentage. To
age Relationship relate mixed numbers to percentages, the numbers have
Between to viewed as fractions. Mixed numbers have to be
converted to improper fractions first, to give meaning to
Percentage, the relationship mixed numbers with percentages. Decimal
Fraction and numbers to values is limited to less tahn 10 and to two
Decimal. decimal places only. 11
4.1.2 Convert decimal numbers of value more
than 1 to percentage. To relate mixed numbers to
percentages, the numbers have to viewed as fractions.
Mixed numbers have to be converted to improper fractions
first, to give meaning to the relationship mixed numbers
with percentages. Decimal numbers to values is limited to
less tahn 10 and to two decimal places only.
4.1.3 Find the value for given percentage of a
quantity.
4.1.4 Solve problems in real context imvolving
relationships between percenrage, fractions and
decimals. Solve problems in real life involving
percentage calculation of income and expenditure,
savings, profit and loss, discount, dividend or interest,, tax,
commission, etc.
5. Money 5.1 Money 5.1.1 Perform mixed operations with money up
Up To RM10 to a value of RM10 million. Mixed operations exercise
Million may also include brackets. Discuss problems involving
various situations such as savings, income, expenditure,
investments, cost price, selling price, profit, loss and
discount. 12
5.1.2 Solve problems in real context involving
computation of money. Mixed operations exercise
may also include brackets. Discuss problems involving
various situations such as savings, income, expenditure,
investments, cost price, selling price, profit, loss and
discount.
6. Time 6.1 Duration 6.1.1 Calculate the duration of an event
between months.
6.1.2 Calculate the duration of an event
between years. 13
6.1.3 Calculate the duration of an event
between dates.
6.1.4 Compute time period from situations
expressed in fractions of duration.
6.1.5 Solve problem in real context involving
computation of time duration.
N Topic Learning Learning Outcome Wee
o. Area k
7. Length 7.1 7.1.1 Compute length from a situation 13
Computatio expressed in fraction. The term fraction includes
n Of Length mixed numbers.
7.1.2 Solve problem in real context involving
computation of length. Problem involving
computation of length may also include measuring,
conversion of units and/or calculation of length. The scope
of units of measurement for length involves cm, m and km.
Teacher guides pupils to solve problems following Polya’s
four-step model of,
i. Understanding the problem
ii. Devising a plan
iii. Implementing the plan
iv. Looking backs
8. Mass 8.1 8.1.1 Compute mass from a situation expressed 14
Computatio in fraction. The term fraction includes mixed numbers.
n Of Mass 8.1.2 Solve problem in real context involving
computation of mass. Problem involving computation
of mass may also include measuring, conversion of units
and/or calculation of mass. The scope of units of
measurement for mass involves g and kg.
Teacher guides pupils to solve problems following Polya’s
four-step model of,
i. Understanding the problem
ii. Devising a plan
iii. Implementing the plan
iv. Looking back
9. Volume 9.1 9.1.1 Compute volume of liquid from a situation 14
of Computatio expressed in fraction. The term fraction includes
Liquid n Of Volume mixed numbers.
of Liquid 9.1.2 Solve problem in real context involving
computation of volume of liquid. Problem involving
computation of volume of liquid may also include
measuring, conversion of units and/or calculation of
volume of liquid. The scope of units of measurement for
volume of liquid involves m and .
10 Shape 10.1 Two 10.1.1 Find the perimeter of a two-dimensional 15
. and Dimensional composite shape of two or more quadrilaterals
Space Shapes and trangles. Quadrilaterals is limited to squares and
rectangles, and triangles to right-angled trangles.
10.1.2 Find the area of two-dimensional
composite shape of two or more quadrilaterals
and trangles. Quadrilaterals is limited to squares and
rectangles, and triangles to right-angled trangles.
10.1.3 Solve problems in real context involving
calculation of perimeter and area of two-
dimensional shapes.
11 Shape 11.1 Three 11.1.1 Find the surface area of a three- 16
. and Dimensional dimensional composite shape of two or more
Space Shapes cubes and cuboids. Only cubes and cuboids used to
form composite 3-D shapes.
11.1.2 Find the volume of a three-dimensional
composite shape of two or more cubes and
cuboids. Only cubes and cuboids used to form composite
3-D shapes.
11.1.3 Solve problems in real context involving
calculation of surface area and volume of a
three-dimensional shapes.
12 Data 12.1 12.1.1 Calculate the average of up to five 17
. Handlin Average numbers. The value of averages is limited to three
g decimal places.
12.1.2 Solve problems in real contexts involving
average. Include compound units for calculation of
average when dealing with money and time.
12.2
Organising 12.2.1 Construct a pie chart from a given set of
And data.
Interpreting 12.2.2 Determine the frequency, mode,
Data range,mean, maximum and minumum value
from a pie chart.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mathematics Yearly Plan Y5Documento12 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan Y5skppasir0% (1)
- Yearly Maths Plan for Year 6 Covers Fractions, Decimals & MoreDocumento4 pagineYearly Maths Plan for Year 6 Covers Fractions, Decimals & MorealisetanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5)Documento8 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5)mhdimNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan Yr 5Documento10 pagineYearly Plan Yr 5kupcai_powerNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan Maths 4sklpDocumento8 pagineYearly Plan Maths 4sklpAfifa SafferNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6)Documento4 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6)jackquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan Y4Documento14 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan Y4skppasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving math skills up to 1,000,000Documento4 pagineImproving math skills up to 1,000,000Syahrir AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT 2020 DLP Mathematics Year 3 KSSR SemakanDocumento15 pagineRPT 2020 DLP Mathematics Year 3 KSSR SemakanMohammad FalakhuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT & Plan-J Math Year 5Documento30 pagineRPT & Plan-J Math Year 5yp87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : 1.1 Numbers To 1 000 000 DetermineDocumento9 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 5) : 1.1 Numbers To 1 000 000 Determinecikgu F100% (1)
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6)Documento5 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 6)cikgu FNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT 2021 DLP Mathematics Year 3 KSSR SemakanDocumento17 pagineRPT 2021 DLP Mathematics Year 3 KSSR SemakanYEEMA A/P MOHGAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Peta Minda HSP Tahun 5 (Kump 3)Documento12 paginePeta Minda HSP Tahun 5 (Kump 3)Mariah Binti Mohd YassinNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT 2020 Mathematics Year 4 KSSR SemakanDocumento13 pagineRPT 2020 Mathematics Year 4 KSSR SemakanThulasi VasiNessuna valutazione finora
- SCHEME OF WORK p6 Term 1Documento3 pagineSCHEME OF WORK p6 Term 1KimAyraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)Documento12 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year 4)cikgu F100% (1)
- BW - Mathematics 2Documento6 pagineBW - Mathematics 2Remelyn Monares Dela Cruz IINessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan Mathematics DLP Year 4 2020: Learning Area Content Standard Learning StandardDocumento12 pagineYearly Plan Mathematics DLP Year 4 2020: Learning Area Content Standard Learning StandardSilvens Siga SilvesterNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Mat Year 6Documento6 pagineRPT Mat Year 6Kayalvile Vijaya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Year3 Mat HSPDocumento8 pagineYear3 Mat HSPAbu SuffianNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT 2021 Math Year 5 KSSR (Revised 2017) : Week Content Standard Learning Standard NoteDocumento16 pagineRPT 2021 Math Year 5 KSSR (Revised 2017) : Week Content Standard Learning Standard NotemarziahNessuna valutazione finora
- Year3 Mat HSPDocumento8 pagineYear3 Mat HSPmala78Nessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 2 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishDocumento116 pagineGRADE 2 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishnoviNessuna valutazione finora
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocumento8 pagineBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterEnteng ODNessuna valutazione finora
- School Template Q1 Summative Assessment Results - XLSX - MathDocumento6 pagineSchool Template Q1 Summative Assessment Results - XLSX - MathJaremie AyonkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan Mathematics Year 2Documento8 pagineYearly Plan Mathematics Year 2sklongsebanganNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesoon Plan 2Documento4 pagineLesoon Plan 2La RaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyDocumento13 pagineRancangan Tahunan Math Tahun 5 2012 MS Excell Shared by AzyTravis MonroeNessuna valutazione finora
- RPH Math DLP Year 2Documento24 pagineRPH Math DLP Year 2Raymond McdonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Pn. Rafidah Binti Abd. Ghafar SK Dato' Haji ZainuddinDocumento10 paginePrepared By: Pn. Rafidah Binti Abd. Ghafar SK Dato' Haji ZainuddinRafidah N RithauddenNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 1 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus)Documento108 pagineGRADE 1 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus)noviNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheme of Work For Year 4 Mathematics Weeks Learning Area / Learning Objective Learning OutcomesDocumento18 pagineScheme of Work For Year 4 Mathematics Weeks Learning Area / Learning Objective Learning OutcomesLoh Tzen HiakNessuna valutazione finora
- Budget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterDocumento8 pagineBudget of Work in Mathematics 2 (K To 12) 1 TO4 QuarterLea Garcia MagsinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Week/ Date Topic Content/ Skill Learning Outcomes RemarksDocumento5 pagineWeek/ Date Topic Content/ Skill Learning Outcomes RemarksSHALINI A/P MURUGAN -Nessuna valutazione finora
- MT Yearly Plan Year 6Documento6 pagineMT Yearly Plan Year 6Saiful AsrulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesoon Plan 2.PntDocumento4 pagineLesoon Plan 2.PntLa RaNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Matematik DLP 2023 Tahun 3Documento16 pagineRPT Matematik DLP 2023 Tahun 3SITI SARAH BINTI YUSUF MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersDocumento3 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersRamziah BongsuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionDocumento27 pagine2007 Mathematics Standards by ProgressionElaine EricksonNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT 2021 DLP Math Year 5 KSSR SemakanDocumento16 pagineRPT 2021 DLP Math Year 5 KSSR SemakanShalini SuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- SK Suri Math RPT Year 4Documento14 pagineSK Suri Math RPT Year 4MUHAMMAD KHAIRIZAM BIN JASRI MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Three) Sekolah Kebangsaan Bandar Baru Salak TinggiDocumento9 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Three) Sekolah Kebangsaan Bandar Baru Salak TinggickapotNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Mate DLP THN 3 2022-2023Documento22 pagineRPT Mate DLP THN 3 2022-2023rashiden denNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 RPT 2021 DSKP KSSR Semakan 2017 Mathematics Year 3 v4Documento38 pagine03 RPT 2021 DSKP KSSR Semakan 2017 Mathematics Year 3 v4leeks70Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Mathematics Scheme of Work for Year 5Documento22 pagineYearly Mathematics Scheme of Work for Year 5Thanaletchumy RamesamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersDocumento3 pagineMathematics Yearly Plan (Year Six) : 1. Whole NumbersAdemizan AhadNessuna valutazione finora
- Rpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Documento27 pagineRpt&Plan-j Math Year 4Kee SekKhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mate Ma Tics Yearly Plan For Year 4Documento26 pagineMate Ma Tics Yearly Plan For Year 4Lawrence Ming GanyaNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Math DLP Year 3 2022Documento21 pagineRPT Math DLP Year 3 2022NOOR FARISHA BINTI NASIR MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 5 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishDocumento20 pagineGRADE 5 - Indonesia and Cambridge Combined (Syllabus) - EnglishnoviNessuna valutazione finora
- ListDocumento5 pagineListLa RaNessuna valutazione finora
- SK AYER KEROH, MELAKA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3Documento15 pagineSK AYER KEROH, MELAKA YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICS (DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMME) KSSR YEAR 3marina75% (4)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6Da EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Casa Del Niño Montessori School of Roxas San Rafael, Roxas, Isabela Curriculum Map Mathematics 10 GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10Documento8 pagineCasa Del Niño Montessori School of Roxas San Rafael, Roxas, Isabela Curriculum Map Mathematics 10 GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10Schievvie AbanillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Volume of 3D Shapes: Calculating the Volumes of Cuboids, Pyramids, Cylinders, Spheres and Composite 3D ShapesDocumento9 pagineVolume of 3D Shapes: Calculating the Volumes of Cuboids, Pyramids, Cylinders, Spheres and Composite 3D ShapesClever RatNessuna valutazione finora
- Area and Simultaneous EquationsDocumento3 pagineArea and Simultaneous EquationsAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Theory 1 (Moment Area Method)Documento38 pagineStructural Theory 1 (Moment Area Method)acurvz2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Caita Powercopy, CatalogDocumento161 pagineCaita Powercopy, Catalogmmk_worldNessuna valutazione finora
- Java Lab ManualDocumento50 pagineJava Lab ManualRishi PandyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CLAT Maths Quiz 43: Key and ExplanationsDocumento7 pagineCLAT Maths Quiz 43: Key and ExplanationsPooja DiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Math g4 m3 Full ModuleDocumento590 pagineMath g4 m3 Full ModuleNorma AguileraNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Measuring VolumeDocumento8 pagineStudent Exploration: Measuring VolumeGabriel LouimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding Area Between CurvesDocumento22 pagineFinding Area Between CurvesMark Lester RealNessuna valutazione finora
- Kartografi, Generalisasi, Interpolasi PDFDocumento16 pagineKartografi, Generalisasi, Interpolasi PDFDanu LarasatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module CARE Paper1@Set1Documento2 pagineModule CARE Paper1@Set1Hayati Aini AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- IBPS PO 16-19 MergedDocumento165 pagineIBPS PO 16-19 MergeddfsdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Papers ImoDocumento11 paginePast Papers ImoUsman ⊆ SubhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Form 2 2020 Schemes of WorkDocumento30 pagineMathematics Form 2 2020 Schemes of Worktinomuda100% (1)
- Refresher MathDocumento4 pagineRefresher MathJocel palganNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook Ebook PDF Primary and Middle Years Mathematics Teaching Developmentally PDFDocumento42 pagineEbook Ebook PDF Primary and Middle Years Mathematics Teaching Developmentally PDFkeith.cowley538100% (33)
- TCS1Documento100 pagineTCS1api-3832274Nessuna valutazione finora
- Area and vectors geometry problemsDocumento17 pagineArea and vectors geometry problemsjonathanyewNessuna valutazione finora
- MA02 June 2022Documento28 pagineMA02 June 2022Vedant DasNessuna valutazione finora
- VoronoiDocumento42 pagineVoronoiturtle42012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pythagoras Past Paper QuestionsDocumento36 paginePythagoras Past Paper Questionslc.amnaarifNessuna valutazione finora
- Spring Modelling Approach For Evaluation and Design of Tension Loaded Anchor Groups in Case of Concrete Cone FailureDocumento18 pagineSpring Modelling Approach For Evaluation and Design of Tension Loaded Anchor Groups in Case of Concrete Cone FailureNavneet RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics GS 4Documento215 paginePhysics GS 4HackerzillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Cheat Sheet 4 2d Shapes FormulasDocumento2 pagineGeometry Cheat Sheet 4 2d Shapes Formulascheruma100% (1)
- Adv Ex 0405 TrigonometryDocumento6 pagineAdv Ex 0405 Trigonometryau angelNessuna valutazione finora
- Screenshot 2024-02-12 at 1.03.08 PMDocumento7 pagineScreenshot 2024-02-12 at 1.03.08 PMranjan.vaneeNessuna valutazione finora
- C++ programs to solve maths and logic problemsDocumento3 pagineC++ programs to solve maths and logic problemssiddhant bhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Valuation Report of Sushila Gopali and Manoj Gopali FinalDocumento21 pagineValuation Report of Sushila Gopali and Manoj Gopali FinalSkyline100% (1)
- 2022 Term 2 Final ExamDocumento19 pagine2022 Term 2 Final ExamRyan MASSEYNessuna valutazione finora