Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
ECON 102 Midterm 2009S1
Caricato da
examkiller0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
87 visualizzazioni8 pagineThere are 18 MC and 3 short-answer / graph questions. Mark your answers next to corresponding numbers provided below.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThere are 18 MC and 3 short-answer / graph questions. Mark your answers next to corresponding numbers provided below.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
87 visualizzazioni8 pagineECON 102 Midterm 2009S1
Caricato da
examkillerThere are 18 MC and 3 short-answer / graph questions. Mark your answers next to corresponding numbers provided below.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
Econ 102: Principles of Macroeconomics
Solution to Midterm V.A (summer)
May 26, 2009
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Total Marks: 100
Students Name: ________________, __________________
(Last) (First)
Student # ________________________
There are 18 MC and 3 short-answer/graph questions. Once you have picked the
correct choices for all the MC questions, please also copy your answers next to
corresponding numbers provided below:
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7. 8.
9. 10. 11. 12.
13. 14. 15. 16.
17. 18.
Marks:
MC Questions: 3 x .. =
Essay Questions: 1. .
2. ...
3.
____________________________
Total Marks:
A. Multiple Choice Questions: Encircle the correct or best answer (54)
1. In which of the following situations is the rest of the world's savings being
used to finance investment in Canada?
(a) Supply exceeds demand.
(b) Exports exceed imports.
(c) Investment exceeds national savings.
(d) Net taxes exceed national savings.
(e) Investment exceeds household savings.
2. An auto company has 10 workers. Each worker can produce a maximum of
either 7 cars or 4 SUVs a day. One day, the company decides to produce 35 cars
and 25 SUVs. This output level is
(a) production efficient because it is on the PPF.
(b) efficient if firms reduce the number of workers.
(c) inside the frontier and so is attainable but inefficient.
(d) outside the frontier and so is unattainable.
3. The price of a local phone call is 15 cents/minute in 2005, the base year. What
is the price of this phone call in 2009 dollars if the CPI is 160 in 2009?
a. 24.0 cents
b. 40.0 cents
c. 20.0 cents
d. 9.0 cents
4. Use the table below to answer the following question.
Government expenditures on goods and
services $400
Wages, salaries, and supplementary labor
income $2,000
Capital consumption $500
Gross investment $200
Personal consumption $2000
Net exports $-100
Indirect taxes $150
Net domestic product equals
(a) $ 2150.
(b) $ 2000.
(c) $ 2600.
(d) $ 2500
5. An economy is at full employment. The money/nominal wage rate is $20 an
hour and the price level is 100. If the money wage rate falls to $16 an hour, then
the AS curve shifts _______________ and the price level where the shifted AS
curve and the potential GDP line intersect is ____________.
a. leftward; 120.
b. rightward; 70.
c. leftward; 70.
d. rightward; 80.
6. A change in any of the following factors except _________ shifts the AD curve.
(a) Expectation about the future.
(b) The money wage rate.
(c) Monetary and fiscal policies.
(d) The state of the world economy.
7. Suppose that an Island economy produces only 2 goods as given below.
Data for 1992 Data for 2006
Item Quantity Price Quantity Price
Bananas 60 10 60 12
Coco-nuts 30 10 40 10
Given that the base year is 1992, what is the CPI for 2006?
(a) 100.5
(b) 113.3
(c) 140.0
(d) 112.5
(e) 100.0
8. Assume cars and SUVs are substitutes in production. If a high world demand
for SUVs increases its price, then the supply curve of cars.
a. remains constant.
b. shifts to the right.
c. shifts to the left.
d. shifts to the left initially and then returns to its original condition.
9. In a country with a working-age population of 30 million, 18 million are
employed, 2 million are unemployed, and 2 million of the employed are working
part-time, half of whom wish to work full-time. The unemployment rate is _____.
(a) 9.1%
(b) 11.1%
(c) 10.0%
(d) 14.3%
(e) 9.0%
10. Indias GDP is measured in Rupees and that of Canada in $. If the current
exchange rate is Rs. 40 ($ 1 = Rs 40) and a similar good that costs $ 1 in Canada
costs Rs. 20 in India, the real GDP of India as measured in terms of Rs and then
converted to $ ________.
a. tends to understate Indias standard of living.
b. tends to overstate Indias standard of living.
c. may understate or overstate Indias standard of living depending upon
the situation.
d. correctly measures Indias standard of living.
11. Given the following production possibility table.
Workers needed to make:
One Car One Ton of Grain
U.S. 8 10
Japan 4 4
a. Japan should export cars and the US grain.
b. Japan should export grain and the US cars.
c. Japan should produce both cars and grain and export to the US.
d. US should produce both and export to Japan.
12. The following figure shows the aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate
supply (SAS), and long-run aggregate supply (LAS) curves for an economy. As
the economy automatically adjusts to long-run equilibrium,
(a) AD shifts leftward.
(b) SAS shifts rightward.
(c) LAS shifts rightward.
(d) SAS shifts leftward.
13. There are no exports or imports in the economy illustrated in the figure
below. When real GDP is equal to Y
a
, aggregate planned expenditure
(a) exceeds real GDP and real GDP will fall.
(b) is less than real GDP and real GDP will fall.
(c) is equal to real GDP and real GDP will neither rise nor fall.
(d) exceeds real GDP and real GDP will rise.
(e) is less than real GDP and real GDP will rise.
14. Which of the following does not affect aggregate demand?
a. Exchange rate.
b. Monetary policy.
c. Expected future income.
d. Technological change.
e. Fiscal Policy.
15. The recent decrease in GST from 6% to 5% by the present Conservative
government is expected to
a. shift the AS curve to the right.
b. shift the AD curve to the right.
c. shift the AS curve to the left.
d. shift the AD curve to the left.
16. Suppose that investment decreases by $15 billion. If the multiplier is 3, and
the aggregate supply curve is positively sloped. In the short run, equilibrium real
GDP will
(a) not be affected.
(b) decrease by less than $45 billion.
(c) a decrease by $45 billion.
(d) increase by less than $45 billion.
(e) decrease by more than $45 billion.
17. When the Canadian price level rises with the foreign price levels remaining
the same ________.
(a) Canadian exports increase and the AD curve shifts rightward.
(b) Canadian exports decrease, Canadian imports increase, and the AD
curve shifts leftward.
(c) Canadian exports decrease, Canadian imports increase, and there
is a movement up along the AD curve.
(d) Canadian firms' profits increase and the AD curve shifts rightward.
18. If AE = 100 + 0.7Y and Y = 300, then unplanned inventories deplete by
(a) 10 units.
(b) 300 units.
(c) 333.33 units.
(d) 100 units.
(e) none as the economy is in equilibrium.
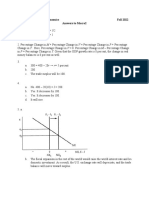
B. In the case of graph question(s), please draw self-explanatory and well-
labeled graph(s) (i.e., showing the mechanisms for curve shift, if any, reasons
for such shift and the results) and avoid extra verbal explanations. (46)
1. Suppose Canadian economy is in full employment level. What happens to
Canadian real GDP in the short run when
(a) the government of Canada cuts the sales tax rate from 6% to 5%? In this
case, also illustrate the economys (natural) tendency to come back to the
full employment level. (8)
Real GDP
GDP Deflator
AS
AD'(cut in sales
tax leads to rise in
C)
Potential GDP
AD
Y
1
Y
2
P
1
AS' (due to higher money
wage rate caused by
inflationary gap)
P
2
SR equilibrium
LR eqlbm
P
3
(b) Canada develops a new (production) technology. (6)
Real GDP
GDP Deflator
AS
AD
LAS
AS' (due to new tech,
the cost of production
f ll )
Y
1
Y
2
P
1
LAS' (due to new tech.
potential GDP increases)
2. An island economy produces only lobsters and crabs as given below.
In 2007 In 2008
Lobsters: Q = 100, P = $20. Q = 110, P = $25.
Crabs: Q =25, P = $25. Q = 40, P= $30
a. Calculate the real GDP in 2007 (the base year) and 2008 using Statistics
Canadas new method. (10)
.
GDP in 2007 Prices:
GDP
07
=100x20+25x25 =$2625
GDP
08
=110x20+40x25 =$3200
% change in GDP from 2007 to 2008 =(3200 2625)/2625 =21.90%
GDP in 2008 Prices:
GDP
07
=100x25+25x30 =$3250
GDP
08
=110x25+40x30 =$3950
% change in GDP from 2007 to 2008 =(3950 3250)/3250 =21.54%
Average % change in GDP from 2004 to 2005 =21.72%
Real GDP
07
(base year) =$ 2625
Real GDP
08
=1.2172 x 2625 =$ 3195.15
b. Calculate the GDP deflator in 2008 and interpret your result. (4)
GDP deflator =(Nominal GDP
08
/Real GDP
08
) x 100 =395000/3195.15 =123.62
The average prices in 2008 are 23.62% higher than those in 2007 (the base year).
Alternative: The nominal GDP in 2008 gives the overestimation of real production in that
year by the same % increase in price (relative to base year), which is 23.62%.
3. In an economy, autonomous consumption is $200 billion, the marginal
propensity to consume c = 0.8, investment is $200 billion, government
expenditure is $150 billion, export is $50 billions and imports M = 0.2Y. The
marginal tax rate = 10%.
(a) Calculate the equilibrium real GDP, Y, of this economy. (4 marks)
(b) If the government increases expenditure by $100 billion, calculate the new
equilibrium Y? (4 marks)
(c) Calculate the size of the expenditure multiplier. (4marks)
(d) Draw a diagram illustrating your results. (6 marks)
(a) AE = C + I + G + X M = 200 + 0.8(1 0.1)Y +200 + 150 + 50 0.2Y
= 600 + 0.52Y
At equilibrium, AE = Y
600 + 0.52Y = Y
0.48Y = 600 Y* = $1250
(b) New AE = 700 + 0.52Y
At new equilibrium, new AE = Y Y** = $1458.33
(c) Expenditure Multiplier = 1/(1 slope of AE) = 1/(1 0.52) = 2.083.
(Alternative: Multiplier = Y/G = (Y** - Y*)/G = (1458.33 1250)/100 = 2.083)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ECON 102 Midterm1 SampleDocumento5 pagineECON 102 Midterm1 SampleexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 203 W16 Final Exam Version 1Documento15 pagineEcon 203 W16 Final Exam Version 1givemeNessuna valutazione finora
- FIN201 Quiz 1 FA 2022Documento8 pagineFIN201 Quiz 1 FA 2022Nguyễn Đức MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam!!!!Documento22 pagineSample Exam!!!!kbond93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theory Multiple ChoiceDocumento82 pagineTheory Multiple ChoiceAlessioMartucciNessuna valutazione finora
- 203 Sample Midterm2Documento16 pagine203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ - Practice Exam 2Documento8 pagineEcon - Practice Exam 2John DoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam1Answers 1Documento6 pagineExam1Answers 1Ай МөлдирNessuna valutazione finora
- w10 112 v1Documento22 paginew10 112 v1Rusty ButlerNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 102 Midterm 2012W2Documento7 pagineECON 102 Midterm 2012W2examkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Questions For Test 2 Key 2012Documento10 pagineReview Questions For Test 2 Key 2012Zeke MerchantNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 203 S16 Final Exam Version 1Documento15 pagineEcon 203 S16 Final Exam Version 1givemeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Exam Solutions FAPM Economics Feb 2016Documento11 pagineMock Exam Solutions FAPM Economics Feb 2016MbusoThabetheNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics & Accounting ExerciseDocumento9 pagineMacroeconomics & Accounting ExerciseM.Y FauzanNessuna valutazione finora
- CB2402 Problem Set 1 16-17ADocumento13 pagineCB2402 Problem Set 1 16-17AMatthew ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECN204 Mid 2013WDocumento17 pagineECN204 Mid 2013WexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- MT 2016Documento9 pagineMT 2016Ismail Zahid OzaslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final 2017Documento9 pagineFinal 2017Ismail Zahid OzaslanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 MidtermDocumento4 pagine2021 MidtermatiquesbNessuna valutazione finora
- PracticeMCQECO401 PDFDocumento42 paginePracticeMCQECO401 PDFSyed ShoaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Past Midterm February Econ 295Documento11 paginePast Midterm February Econ 295Teodor SaucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Macroeconomics Midterm 2013Documento19 pagineMacroeconomics Midterm 2013Daniel Welch100% (1)
- Final Exam - 2019 SpecialDocumento12 pagineFinal Exam - 2019 SpecialLiz zzzNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Fall FinalsDocumento12 pagine2019 Fall FinalsmeganyaptanNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 203 PRactice Final 2016Documento15 pagineEcon 203 PRactice Final 2016BOOMERBADNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Final Winter 2014Documento38 paginePractice Final Winter 2014Locklaim CardinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Macroeconomics: Answer The Following Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento23 pagineChapter 1: Introduction To Macroeconomics: Answer The Following Multiple Choice QuestionsThuý NgaNessuna valutazione finora
- EKO201E Sample 2Documento9 pagineEKO201E Sample 2Kadir Y. DemirNessuna valutazione finora
- MacroDocumento7 pagineMacroraveen007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 - KTEE203.1Documento11 pagineAssignment 1 - KTEE203.1Hà ChiếnNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ exam+1+VADocumento13 pagineEcon exam+1+VABlackBunny103Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 2013-02 Second Midterm ExamDocumento11 pagineECO 2013-02 Second Midterm ExamRyan BekinfieldNessuna valutazione finora
- 18e Key Question Answers CH 28Documento3 pagine18e Key Question Answers CH 28Mustafa KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Paper For MA Economics Entrance 2012Documento18 pagineQuestion Paper For MA Economics Entrance 2012ARUPARNA MAITYNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro PracticeDocumento32 pagineMacro PracticecholoNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Two Springl 2012Documento6 pagineMidterm Two Springl 2012Zahra Ahmed AlfarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco2004s 2014 Test 2Documento6 pagineEco2004s 2014 Test 2Kiran DesrajNessuna valutazione finora
- HMW 5-nh1Documento6 pagineHMW 5-nh1Teagan BurkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz MCQDocumento27 pagineQuiz MCQkartik100% (1)
- Assignment 05Documento21 pagineAssignment 05Harris AzharNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 2 - MergedDocumento43 pagineProblem Set 2 - MergedSamantha Marie RebolledoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 Introduction To Economics - EditedDocumento8 pagineAssignment 3 Introduction To Economics - EditedLAIBA WAHABNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Spring - Econ 312 - Practice Problem Set 2Documento16 pagine2011 Spring - Econ 312 - Practice Problem Set 2hami619Nessuna valutazione finora
- F22 Macro TermTest TF MCDocumento8 pagineF22 Macro TermTest TF MCjefferyliu791Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2Documento21 pagineCH 2Geoffroy ElmiliardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 1311 AS - AD & Business Cycles QuizDocumento6 pagineEcon 1311 AS - AD & Business Cycles QuizHaifa Al-humayydNessuna valutazione finora
- 201 - Winter08 - Final Solutions PDFDocumento13 pagine201 - Winter08 - Final Solutions PDFpenusilaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Midterm - SolutionDocumento6 pagine2022 Midterm - SolutionwannafadedNessuna valutazione finora
- Use The Table Below To Answer The Following QuestionDocumento9 pagineUse The Table Below To Answer The Following QuestionexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- 201 Final Fall 2013 V1aDocumento11 pagine201 Final Fall 2013 V1aJiedan HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 202 - Assignment 3-Section III-No Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineECON 202 - Assignment 3-Section III-No Answer KeyArodwenNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro AssignmentDocumento17 pagineMacro AssignmentImran UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty / Dept: Subject Number: Subject NameDocumento9 pagineFaculty / Dept: Subject Number: Subject Namevanessa8pangestuNessuna valutazione finora
- Clep Macroecon Q PrintDocumento15 pagineClep Macroecon Q PrintJeong Gyun Kang100% (1)
- Study Questions 1 (GDP)Documento7 pagineStudy Questions 1 (GDP)Syed Karim100% (1)
- Problems and Possibilities of the Us EconomyDa EverandProblems and Possibilities of the Us EconomyNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Economics: A Simplified Detailed Edition for Students Understanding Fundamentals of MacroeconomicsDa EverandMacro Economics: A Simplified Detailed Edition for Students Understanding Fundamentals of MacroeconomicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionDa EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- One Year of Living with COVID-19: An Assessment of How ADB Members Fought the Pandemic in 2020Da EverandOne Year of Living with COVID-19: An Assessment of How ADB Members Fought the Pandemic in 2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eco100y1 Wolfson Tt4 2013wDocumento11 pagineEco100y1 Wolfson Tt4 2013wexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT220 Midterm PracticeDocumento13 pagineSTAT220 Midterm PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 101 Final Practice1Documento32 pagineECON 101 Final Practice1examkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Mgeb02 FinalDocumento4 pagineMgeb02 FinalexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC302 Midterm 2010FDocumento3 pagineSSC302 Midterm 2010FexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT112 Midterm1 PracticeDocumento18 pagineSTAT112 Midterm1 PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco100 Furlong Tt2 2014sDocumento10 pagineEco100 Furlong Tt2 2014sexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco100y1 Wolfson Tt2 2012fDocumento12 pagineEco100y1 Wolfson Tt2 2012fexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco100y1 Wolfson Tt3 2013wDocumento13 pagineEco100y1 Wolfson Tt3 2013wexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH263 Mid 2009FDocumento4 pagineMATH263 Mid 2009FexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH115 Exam1 2013W PracticeDocumento10 pagineMATH115 Exam1 2013W PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam1 Hendrix PracticeDocumento6 pagineSTAT110 Exam1 Hendrix PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Eco100 Furlong Tt3 2014sDocumento5 pagineEco100 Furlong Tt3 2014sexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH150 Midterm1 2009springDocumento8 pagineMATH150 Midterm1 2009springexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT111 Final PracticeDocumento3 pagineSTAT111 Final PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT111 Exam2 PracticeDocumento11 pagineSTAT111 Exam2 PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Final 2009spring PracticeDocumento5 pagineSTAT110 Final 2009spring PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT111 Exam1 PracticeDocumento5 pagineSTAT111 Exam1 PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam3 2009F Version ADocumento4 pagineSTAT110 Exam3 2009F Version AexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam2 2009F PracticeDocumento6 pagineSTAT110 Exam2 2009F PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam2 2013spring Edwards PracticeDocumento3 pagineSTAT110 Exam2 2013spring Edwards PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam1 2009F Version BDocumento6 pagineSTAT110 Exam1 2009F Version BexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam2 2009FDocumento6 pagineSTAT110 Exam2 2009FexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT110 Exam3 2009F PracticeDocumento2 pagineSTAT110 Exam3 2009F PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT1100 Exam3 LaurelChiappetta PracticeDocumento4 pagineSTAT1100 Exam3 LaurelChiappetta PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT1100 Exam2 LaurelChiappetta PracitceDocumento4 pagineSTAT1100 Exam2 LaurelChiappetta PracitceexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT1100 Final LaurelChiappetta PracticeDocumento10 pagineSTAT1100 Final LaurelChiappetta PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT0200 Final 2009spring Pfenning PracticeDocumento13 pagineSTAT0200 Final 2009spring Pfenning PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT1100 Exam1 LaurelChiappetta PracitceDocumento5 pagineSTAT1100 Exam1 LaurelChiappetta PracitceexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT102 Midterm2 PracticeDocumento9 pagineSTAT102 Midterm2 PracticeexamkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Companies in Vapi GujaratDocumento9 pagineTop Companies in Vapi GujaratNimesh C VarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enter Pen Eur ShipDocumento7 pagineEnter Pen Eur ShipMuskan Rathi 5100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Investment and Portfolio AnalysisDocumento6 pagineInvestment and Portfolio AnalysisMuhammad HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalamba Games - 51% Majority Stake Investment Opportunity - July23Documento17 pagineKalamba Games - 51% Majority Stake Investment Opportunity - July23Calvin LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 Assignment Apex ChemicalsDocumento4 pagineWeek 2 Assignment Apex ChemicalsSunita Chaudhary0% (1)
- HR Practices in Automobile IndustryDocumento13 pagineHR Practices in Automobile IndustryNEENDI AKSHAY THILAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Industries: Growth and Problems of Major Industries 1. Iron & Steel 2. Cotton Textiles 3. Cement 4. Sugar 5. PetroleumDocumento10 pagineIndustries: Growth and Problems of Major Industries 1. Iron & Steel 2. Cotton Textiles 3. Cement 4. Sugar 5. PetroleumvidhipoojaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Essential Business Strategy ToolsDocumento30 pagine5 Essential Business Strategy ToolsrlwersalNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Business Processes: © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallDocumento20 pagineOverview of Business Processes: © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice HallCharles MK ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Inmon vs Kimball Data Warehouse ApproachesDocumento3 pagineInmon vs Kimball Data Warehouse ApproachesDeepanshu KatariaNessuna valutazione finora
- S 5 Bba (HRM)Documento2 pagineS 5 Bba (HRM)Anjali GopinathNessuna valutazione finora
- NABARD financing pattern analysisDocumento9 pagineNABARD financing pattern analysisFizan NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM Industry LandscapeDocumento26 pagineCRM Industry LandscapeAdityaHridayNessuna valutazione finora
- Workday Glossary of TermsDocumento27 pagineWorkday Glossary of Termsnaimenim100% (1)
- Joint Cost Allocation Methods for Multiple ProductsDocumento17 pagineJoint Cost Allocation Methods for Multiple ProductsATLASNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Estimation ProcurementDocumento21 pagineCost Estimation ProcurementEng-Ahmed BaasaayNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking License ApplicationDocumento22 pagineBanking License ApplicationFrancNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Environment AnalysisDocumento9 pagineBusiness Environment AnalysisHtoo Wai Lin AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Retail ManagementDocumento40 pagineRetail Managementij 1009Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Social Entrepreneurship Can Drive Economic GrowthDocumento8 pagineHow Social Entrepreneurship Can Drive Economic GrowthAadhavan ParthipanNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Corporate FinanceDocumento13 pagineMCQ Corporate FinancesubyraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Team 6 - Pricing Assignment 2 - Cambridge Software Corporation V 1.0Documento7 pagineTeam 6 - Pricing Assignment 2 - Cambridge Software Corporation V 1.0SJ100% (1)
- How Monetary Policy Impacts Inflation in KenyaDocumento46 pagineHow Monetary Policy Impacts Inflation in KenyaNjoguNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Cash Equivalents Reviewer2Documento9 pagineCash Cash Equivalents Reviewer2anor.aquino.upNessuna valutazione finora
- New-Doing: How Strategic Use of Design Connects Business With PeopleDocumento53 pagineNew-Doing: How Strategic Use of Design Connects Business With PeopleHernán Moya ArayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Costing By-Product and Joint ProductsDocumento36 pagineCosting By-Product and Joint ProductseltantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Cycle of A Service Business-Step 3-Posting To LedgerDocumento40 pagineAccounting Cycle of A Service Business-Step 3-Posting To LedgerdelgadojudithNessuna valutazione finora
- Deed of Conditional Sale of Motor VehicleDocumento1 paginaDeed of Conditional Sale of Motor Vehicle4geniecivilNessuna valutazione finora
- Agribusiness Development Program Starts HereDocumento6 pagineAgribusiness Development Program Starts Herepriya singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Dedicated Freight Corridor in India - India Freight CorridorDocumento9 pagineDedicated Freight Corridor in India - India Freight CorridorThe United IndianNessuna valutazione finora