Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Forming Process NO.2
Caricato da
Muhammed I'zwanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Forming Process NO.2
Caricato da
Muhammed I'zwanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
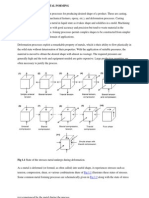
Overview of Metal Forming Overview of Metal Forming
F i /B lk D f ti Forming/Bulk Deformation
Forming/Bulk Deformation Processes Forming/Bulk Deformation Processes
are those processes in which
material is plastically deformed to mater al s plast cally deformed to
the desired shape and size.
Metal Forming Metal Forming
Metal forming includes a large group of
manufacturing processes in which plastic
deformation is used to change the shape of metal
work pieces work pieces
Plastic deformation: a permanent change of
shape, i.e., the stress in materials is larger than shape, i.e., the stress in materials is larger than
its yield strength
Usually a die is needed to force deformed metal Usually a die is needed to force deformed metal
into the shape of the die
Metal Forming
Metal with low yield strength and high ductility
is in favor of metal forming s n favor of metal form ng
One difference between plastic forming and
metal forming is
Plastic: solids are heated up to be polymer melt Plastic: solids are heated up to be polymer melt
Metal: solid state remains in the whole process Metal: solid state remains in the whole process
Metal Forming
Metal forming is divided into: (1) bulk and (2) sheet
g
Bulk: (1) significant deformation
(2) massive shape change
(3) surface area to volume of the work is small (3) surface area to volume of the work is small
Sheet: Surface area to volume of the work is large Sheet: Surface area to volume of the work is large
Characteristics of Forming Processes
1.Equipment expensive because of the large forces q p p g
involved.
2.Large capital expenditure because of heavy presses
and dies and dies.
3.Suited for a large number of parts only.
4 P d ti t i f t 4.Production rate is fast.
5.Advantage of near net-shape forming.
Categories of Forming Categories of Forming
Cold Working Cold Working
- Performed at room temperature or slightly
above
- Minimum or no machining usually required,
net shape or near-net shape process
Hot Working
- Performed at above re-crystallization rform at a o r crysta zat on
temperature (temperature at which new
strain-free grains are formed by annealing)
M hi i i d - Machining required
Cold Working vs. Hot
k ( ) Working (Advantages)
Cold Working Hot Working Cold Working Hot Working
Better accuracy,
closer tolerances
Shape of part can be
significantly altered closer tolerances significantly altered
Better surface
finish
Lower force and power
required
Strain hardening
increases strength &
hardness
No strengthening of part
occurs advantageous in case
when part is subsequently hardness when part is subsequently
processed by cold forming
No heating of work Metals that usually fracture in
required (less total
energy)
cold working can be hot
formed
Friction in Metal Forming
In most metal forming processes friction is
Friction in Metal Forming
In most metal forming processes, friction is
undesirable:
Metal flow is retarded
Forces and power are increased
Wears tooling faster
Metalworking lubricants are applied to tool-
k i t f i f i ti work interface in many forming operations
to reduce harmful effects of friction
Forming/Bulk Deformation Forming/Bulk Deformation
Types of Forming Types of Forming
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Metal Forming ProcessDocumento19 pagineMetal Forming ProcessragulnarayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFDocumento62 pagineLecture 7 - Manufacturing Processes - Metal and Sheet Forming, Bulk Deformation Processes - DR Bilal Ahmad PDFjawad khalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Metal Forming ProcessesDocumento103 pagineChapter 3 Metal Forming Processesdagimawgchew777Nessuna valutazione finora
- MFG II 3182 Chapter 1Documento58 pagineMFG II 3182 Chapter 1Naol EmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal FormingDocumento80 pagineMetal FormingIbrahim Mehkri100% (1)
- Unit-I Chapter-1 Introduction and Concepts: by Ravichandran G Assistant Professor Dept. of Mech - Engg. CUFE, BengaluruDocumento38 pagineUnit-I Chapter-1 Introduction and Concepts: by Ravichandran G Assistant Professor Dept. of Mech - Engg. CUFE, BengaluruRavichandran GNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento113 pagineChapter 4girma workuNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal FormingDocumento80 pagineMetal Formingashok PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Deformation Processes in Metal WorkingDocumento83 pagineBulk Deformation Processes in Metal WorkingMr-Mk MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Casting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingDocumento44 pagineCasting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingRaj PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal FormingDocumento53 pagineMetal Forming4058AMAN ANANDNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal Forming & Shaping Processes: Topic 3Documento37 pagineMetal Forming & Shaping Processes: Topic 3afnanhananyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IIIDocumento167 pagineUnit IIIJG MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento7 pagineUntitledKondwani NguletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Engineering Forming: Chapter 3: MetalDocumento98 pagineManufacturing Engineering Forming: Chapter 3: MetalnunuNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Stress or True StressDocumento7 pagineFlow Stress or True StressRajshekar NagarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Process 1 2Documento70 pagineManufacturing Process 1 2MD Al-Amin100% (1)
- Unit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationDocumento77 pagineUnit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationAkash akNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingDocumento6 pagineBulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingAbdulfattah TawfiqNessuna valutazione finora
- MP Lecture Unit 3 FormingDocumento21 pagineMP Lecture Unit 3 Formingaakash sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14.1 To 14.4,14.6Documento20 pagineChapter 14.1 To 14.4,14.6Lhekha RaviendranNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Unit 2 - Metal Forming ProcessesDocumento27 pagine6 Unit 2 - Metal Forming ProcessesAditya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- We Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesDocumento6 pagineWe Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesConnor WalshNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal Forming: Fig 1.1 Fig 1.2Documento116 pagineFundamentals of Metal Forming: Fig 1.1 Fig 1.2gazabzabarNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-2 (1) MPDocumento70 pagineUnit-2 (1) MPVishvas SinghhNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal Working ProcessesDocumento191 pagineMetal Working Processesss2mrattriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 32 - Introduction To Metal FormingDocumento23 pagineLecture 32 - Introduction To Metal Formingkunal gargNessuna valutazione finora
- U 4 P 1 MetalformingprocessesDocumento82 pagineU 4 P 1 MetalformingprocessesAbhinandan ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Metal Forming ProcessDocumento10 pagineReport On Metal Forming Processorangeideas7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Working & Cold WorkingDocumento34 pagineHot Working & Cold Workingavutu_kunduruNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocumento34 pagine6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesMaida NurhidayahNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocumento34 pagine6 - Bulk Deformation ProcessesZack MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Dies - Unit 4Documento149 pagineDesign of Dies - Unit 4210 SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Deformation ProcessesDocumento71 pagineBulk Deformation ProcessesHavenesh HaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocumento9 pagineFundamentals of Metal FormingGeorge CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Blanking & Piercing (Handout)Documento50 pagineBlanking & Piercing (Handout)banana100% (1)
- Forming Process ReportDocumento4 pagineForming Process ReportAqib ZamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocumento33 pagineChapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingMuhammad Qasim QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 CH3 MacJul19 PDFDocumento115 pagine03 CH3 MacJul19 PDFNabilah MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Deformation Processes: RollingDocumento17 pagineBulk Deformation Processes: RollingEthan DanielsNessuna valutazione finora
- HVFDocumento23 pagineHVFFRANCIS THOMASNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal Forming: Fig 1.1 Fig 1.2Documento54 pagineFundamentals of Metal Forming: Fig 1.1 Fig 1.2jainvikram8498Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cold and Hot ForgingDocumento6 pagineCold and Hot ForgingAnonymous vvO0nZWflrNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Documento93 pagineManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)beila.amu.22Nessuna valutazione finora
- EMG 4102 Lecture 2Documento5 pagineEMG 4102 Lecture 2MaxwellNessuna valutazione finora
- Metals FormingDocumento34 pagineMetals FormingBilisuma SeyoumNessuna valutazione finora
- ForgingDocumento52 pagineForgingRavichandran G100% (1)
- L5-Fundamentals of Metal CastingDocumento22 pagineL5-Fundamentals of Metal CastingKhayrulIslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal Forming: RollingDocumento26 pagineFundamentals of Metal Forming: RollingamitNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocumento37 pagineFundamentals of Metal FormingDeepak LambaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsDocumento13 pagine4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsHussein SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: Chapter 3: Metal Forming and Shaping ProcessesDocumento22 pagineAssignment: Chapter 3: Metal Forming and Shaping ProcessesIrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 1 MPTDocumento28 pagineCH 1 MPTmolla biyadgieNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing TechnologyDocumento46 pagineManufacturing TechnologyMuthu BaskaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento60 pagineLecture 1Ishtiaq AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- L5 - Ta201p (05.07.2021)Documento84 pagineL5 - Ta201p (05.07.2021)quick winnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Process - Module2.0Documento33 pagineManufacturing Process - Module2.0Fiza KamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Documento111 pagineManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)AlemNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Metal WorkingDocumento59 pagineFundamentals of Metal WorkingRaghu SNessuna valutazione finora
- Lukisan Unjuran OrtografikDocumento1 paginaLukisan Unjuran OrtografikMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Switchcraft 712aDocumento2 pagineSwitchcraft 712aAlexandruStratilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Price List For Peninsular Malaysia Effective From 10: UMW Toyota Motor SDN BHD (60576-K) January 2019Documento1 paginaPrice List For Peninsular Malaysia Effective From 10: UMW Toyota Motor SDN BHD (60576-K) January 2019نور العصمةNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 1 Amal PDFDocumento1 paginaHomework 1 Amal PDFMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Key MathTypeDocumento3 pagineProduct Key MathTypeMuhammed I'zwan55% (11)
- Product Key MathTypeDocumento3 pagineProduct Key MathTypeMuhammed I'zwan55% (11)
- Homework 1 AmalDocumento1 paginaHomework 1 AmalMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- ch4 2Documento15 paginech4 2Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistencias Codigo Colores PDFDocumento2 pagineResistencias Codigo Colores PDF'Cesar Guel81% (16)
- DownloadForMac SanDiskSecureAccessV3.0Documento1 paginaDownloadForMac SanDiskSecureAccessV3.0Gherca OvidiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Facility Natural-Gas PipingDocumento19 pagineFacility Natural-Gas Pipinglutfi awnNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Carry WeightDocumento15 pagineHuman Carry WeightMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Img 20170610 0001Documento1 paginaImg 20170610 0001Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- SanDisk SecureAccessV3.0 QSG PDFDocumento25 pagineSanDisk SecureAccessV3.0 QSG PDFAnonymous SX8ODClMeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohd Nasrull Abd RahmanDocumento37 pagineMohd Nasrull Abd RahmanMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Robo-Sloth: A Rope-Climbing RobotDocumento10 pagineRobo-Sloth: A Rope-Climbing RobotmatitotbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3 Signal Conditioning CircuitDocumento26 pagineChap 3 Signal Conditioning CircuitMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- ASTABOT QuickStartGuide (V1.02)Documento16 pagineASTABOT QuickStartGuide (V1.02)Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- TTL CmosDocumento28 pagineTTL CmosMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- ASTABOT QuickStartGuide (V1.02)Documento16 pagineASTABOT QuickStartGuide (V1.02)Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 29/10/2013 12:07:35 PM C:/Users/USER/Documents/amri/eagle/test - SCH (Sheet: 1/1)Documento1 pagina29/10/2013 12:07:35 PM C:/Users/USER/Documents/amri/eagle/test - SCH (Sheet: 1/1)Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rancangan InstruksionalDocumento6 pagineRancangan InstruksionalMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Combinational Logic Using NAND and NORDocumento16 pagineCombinational Logic Using NAND and NORJaismeer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Proper Use of PA System: Staycation 2008 Staycation 2008Documento9 pagineProper Use of PA System: Staycation 2008 Staycation 2008Muhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- PIC16F84A DataSheetDocumento88 paginePIC16F84A DataSheetEmanueleNessuna valutazione finora
- Mpasm /mplink Picmicro Mcu Quick ChartDocumento0 pagineMpasm /mplink Picmicro Mcu Quick ChartArturo Velazquez MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter05 FinalDocumento55 pagineChapter05 FinalMuhammed I'zwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Uber Strategy TeardownDocumento44 pagineUber Strategy Teardownskouti9100% (3)
- Ls Pu BackgroundDocumento5 pagineLs Pu BackgroundRolando Cruzada Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Axial Piston Fixed Motor AA2FM Series 6x: AmericasDocumento30 pagineAxial Piston Fixed Motor AA2FM Series 6x: AmericasKaian OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Hydrant - WikipediaDocumento9 pagineFire Hydrant - WikipediaVaibhav SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Alufusion Eng TrocalDocumento226 pagineAlufusion Eng TrocalSid SilviuNessuna valutazione finora
- Stone MasonaryDocumento23 pagineStone MasonarypurvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ispmach 4000V/B/C/Z Family: FeaturesDocumento100 pagineIspmach 4000V/B/C/Z Family: Featuresjose morenoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.9. How To Send SSL-Encrypted EmailDocumento3 pagine6.9. How To Send SSL-Encrypted EmailJoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Character SheetDocumento2 pagineCharacter SheetBen DennyNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A BW WorkspaceDocumento8 pagineWhat Is A BW Workspacetfaruq_Nessuna valutazione finora
- ASHRAE - HVAC Noise and Vibration ControlDocumento93 pagineASHRAE - HVAC Noise and Vibration Controlmnt6176100% (3)
- Townsend Labs Sphere L22 Microphone System User GuideDocumento59 pagineTownsend Labs Sphere L22 Microphone System User GuideGuillermoMazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjustment of Conditions: Contents: Procedure Adjustment Methods Country-Specific Methods in Austria and SwitzerlandDocumento41 pagineAdjustment of Conditions: Contents: Procedure Adjustment Methods Country-Specific Methods in Austria and Switzerlandtushar2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Philips New Pricelist July 2022Documento3 paginePhilips New Pricelist July 2022PravinNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Checks On Linde Reach Stacker Heavy TrucksDocumento2 pagineOil Checks On Linde Reach Stacker Heavy TrucksmliugongNessuna valutazione finora
- 9-4130 - Loose Stepper MotorDocumento2 pagine9-4130 - Loose Stepper MotorarasNessuna valutazione finora
- Trafo Manual ABBDocumento104 pagineTrafo Manual ABBMarcos SebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Runner BrochureDocumento4 pagineLight Runner Brochureguruprasad19852011Nessuna valutazione finora
- ITC-1000F User Manual: All-Purpose Temperature ControllerDocumento10 pagineITC-1000F User Manual: All-Purpose Temperature Controllerdavid panahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambar SuspensiDocumento1 paginaGambar SuspensiMashiro HikariNessuna valutazione finora
- HRSG Design and Operation On Unit Reliability and Remaining LifeDocumento74 pagineHRSG Design and Operation On Unit Reliability and Remaining LifeNisal PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - Rigid Pavement ManualDocumento24 pagine01 - Rigid Pavement ManualTsegawbeztoNessuna valutazione finora
- Savitha S. Panikar, PH.DDocumento4 pagineSavitha S. Panikar, PH.Diboorose7Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Dark WebDocumento23 pagineThe Dark Webnoussa100% (1)
- Os Se VB Mis SadDocumento336 pagineOs Se VB Mis SadMuhammad Sikandar DarNessuna valutazione finora
- FKB Stories Who Takes The Train - en PDFDocumento19 pagineFKB Stories Who Takes The Train - en PDFJaione IbarguengoitiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Divinity Original Sin 2 GrenadesDocumento2 pagineDivinity Original Sin 2 Grenadesbeans54Nessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation JigDocumento16 pagineRegulation JigMichaelZarateNessuna valutazione finora
- Logitech Mouse M505 ManualDocumento2 pagineLogitech Mouse M505 ManualbmmanualsNessuna valutazione finora
- Rahul Soni BiodataDocumento2 pagineRahul Soni BiodataRahul SoniNessuna valutazione finora