Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bio 7.4
Caricato da
zwindows123456789Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bio 7.4
Caricato da
zwindows123456789Copyright:
Formati disponibili
151
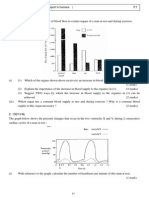
1. 1991/I/5b
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of removing cotyledons on the growth of bean
seedlings. 500 bean seeds were soaked in water for 24 hours. They were then divided into 5 batches (A to E)
and allowed to germinate. 4 batches of these germinating seedlings had their cotyledons removed at
different stages of the germination. At the end of 8 weeks, all the plants were collected, dried in an oven and
weighed to obtain the dry weight. The results are shown in the table below :
Batch Treatment Average dry
weight (per plant)
after 8 weeks
A
B
C
D
E
Cotyledons not removed
Cotyledons removed on the 4
th
day of germination
Cotyledons removed on the 7
th
day of germination
Cotyledons removed on the 10
th
day of germination
Cotyledons removed on the 13
th
day of germination
4.3 g
0.7 g
1.8 g
4.0 g
4.3 g
(i) Give ONE reason why soaking the seeds in water is necessary for germination. (1 mark)
(ii) (1) What is meant by dry weight ? (1 mark)
(2) Why is dry weight preferred to fresh weight in the interpretation of the results of this
experiment ? (Note: Fresh weight refers to the weight of the plants freshly collected.)
(2 marks)
(iii) Why was a large sample size of seeds (100 per batch) used in this experiment ? (1 mark)
(iv) Describe the effect on the growth of bean seedlings of the removal of the cotyledons
(1) on the 4
th
day of germination.
(2) on the 13
th
day of germination. (2 marks)
(v) From your knowledge of the functions of cotyledons, explain the effect of each of the above cases
mentioned in (iv). (3 marks)
2. 1993/I/2c
In order to study the conditions necessary for seed germination, a student designed three experimental
set-ups (A, B and C). These set-ups were put under the sun as shown below :
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 7.4 Growth and development | P.1
152
(i) What conclusion(s), if any, can be drawn by comparing the results in
(1) set-ups A and B only ?
(2) set-ups B and C only ?
Explain how you arrive at your answer. (5 marks)
(ii) Give two reasons why the condition studied in (i) (1) is important in seed germination. (4 marks)
(iii) After one week, there was a decrease in the dry mass of the seeds in set-up B. Explain why this
occurred. (2 marks)
3. 1995/I/2c
The diagrams below show the longitudinal section of a young root and two types of cells taken from it :
(i) Using letters in the diagram, state the region where the following can be found :
(1) cell type 1
(2) cell type 2 (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 7.4 Growth and development | P.2
153
(ii) (1) Name the process occurring in cell type 1 as shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
(2) What is the significance of this process in the root ? (2 marks)
(iii) Explain how cell type 2 is structurally adapted to its function. (3 marks)
4. 1997/I/3b
The diagrams below show the different stages of development of a germinating mung bean seed :
(i) (1) With reference to stages 1 and 2, what tropic response is demonstrated by the radicle ?
(1 mark)
(2) What is the significance of this tropic response to the plant ? (2 marks)
(ii) With reference to the diagrams, deduce, with reasons, two functions of the cotyledons. (4 marks)
(iii) If an excessive amount of chemical fertilizer is added to the soil at stage 7, the seedling will wilt
after several hours. Explain this phenomenon. (4 marks)
5. 2004/I/1b
The diagram below shows a section of a seed :
(i) (1) Name structure A. (1 mark)
(2) What organs will A develop into during seed germination ? (2 marks)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 7.4 Growth and development | P.3
154
(ii) During germination, amylase activity is detected in region B. Explain the importance of amylase
activity to the growth of the seedling. (4 marks)
(iii) The dry mass of the seedling decreases in the initial stage of germination but starts to increase after
one week. Explain the increase in dry mass of the seedling in the later stage. (3 marks)
6. 2006/I/10a
In a study of the growth of mung bean seedlings, two samples of mung bean seeds were grown under the
same conditions except that one sample was kept in daylight while the other in darkness. The same number
of seedlings was collected from each group every 6 days. The average dry mass of the seedlings of each
group was determined and the results are shown below:
Average dry mass of seedlings (g) Time of growth (day)
In daylight In darkness
0 0.81 0.80
6 0.65 0.65
12 0.57 0.52
18 0.79 0.41
(i) Explain the change in the average dry mass of the seedlings in both daylight and dark conditions
from day 0 to day 12. (3 marks)
(ii) From day 12 to day 18, how do the seedlings grown in daylight differ from those grown in the dark
in terms of the change in the average dry mass? Account for this difference. (4 marks)
(iii) Suggest why the dry mass of seedlings was measured instead of the fresh mass in this study.
(1 mark)
HKCEE BIOLOGY | 7.4 Growth and development | P.4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2Documento10 pagine2005 AL Chemistry Paper 2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 1.1Documento4 pagineEcon 1.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- NSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IIDocumento20 pagineNSS Chemistry Part 6 Microscopic World IISabrina WongNessuna valutazione finora
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIDocumento21 pagineNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IIFelix YueNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - QDocumento11 paginePlane Geometry + Coordinate Geometry - Qzwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- NSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - IDocumento36 pagineNSS Chemistry Part 13 Industrial Chemistry - Izwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Econ 1.2Documento1 paginaEcon 1.2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1Documento1 paginaHkcee Biology - 8.4 Genetic Engineering - P.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- As & GS - Q PDFDocumento12 pagineAs & GS - Q PDFPeter ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 8.2Documento10 pagineBio 8.2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1Documento10 pagineHkcee Biology - 7.3 Sexual Reproduction in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 5.4Documento3 pagineBio 5.4zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 8.1Documento2 pagineBio 8.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1Documento1 paginaHkcee Biology - 7.1 Types of Cell Division - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 6.4Documento3 pagineBio 6.4zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 8.3Documento3 pagineBio 8.3zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- HKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1Documento6 pagineHKCEE BIOLOGY - 7.2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 6.1Documento6 pagineBio 6.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 6.2Documento3 pagineBio 6.2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 5.1Documento5 pagineBio 5.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 5.2Documento6 pagineBio 5.2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 5.3Documento3 pagineBio 5.3Michelle ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1Documento7 pagineHkcee Biology - 4.5 Gas Exchange in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1Documento13 pagineHkcee Biology - 4.6 Transport in Humans - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 4.2Documento13 pagineBio 4.2zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 4.4Documento8 pagineBio 4.4zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 3.1Documento7 pagineBio 3.1zwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1Documento5 pagineHkcee Biology - 4.1 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants - P.1irisyyy27Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Past PaperDocumento6 pagineBio Past Paperzwindows123456789Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-02) - RM - BotanyDocumento3 pagineConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-02) - RM - BotanyNancy RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Reproduction Knowledge OrganiserDocumento2 paginePlant Reproduction Knowledge OrganiserSarah KKCNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th STD Bio-Botany Video LinksDocumento3 pagine12th STD Bio-Botany Video Linksnaina10691Nessuna valutazione finora
- Herbarium PDFDocumento47 pagineHerbarium PDFArifaa NovianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis Paper: What Is FlowerDocumento5 pagineSynthesis Paper: What Is Flowercristhel joyNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocumento33 pagine02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsAlyssa Grace BayagNessuna valutazione finora
- Root Identification ManualDocumento247 pagineRoot Identification ManualCatarina GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesDocumento21 paginePlant Structure Adaptations and ResponsesPheby Alfimay Natysya PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Seed Garden SampleDocumento9 pagineThe Seed Garden SampleChelsea Green PublishingNessuna valutazione finora
- Petit Seminaire ST Leon Kabgayi B.P: 66 Gitarama (Muhanga) Covid-19 Holiday'S Evaluations-JulyDocumento2 paginePetit Seminaire ST Leon Kabgayi B.P: 66 Gitarama (Muhanga) Covid-19 Holiday'S Evaluations-JulyWilly LandryNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Gen Bot LecDocumento3 pagineLesson 1 - Gen Bot LecYoko DeangNessuna valutazione finora
- Sansevieria Stuckyi As A Potted Plant Martin Aarseth-Hansen Et AlDocumento6 pagineSansevieria Stuckyi As A Potted Plant Martin Aarseth-Hansen Et AlAl LaiusNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Sheet Milestone 3Documento2 pagineWork Sheet Milestone 3smnchauke3672Nessuna valutazione finora
- XI CH - 06 Anatomy of Flowering Plants - 220605 - 233239Documento17 pagineXI CH - 06 Anatomy of Flowering Plants - 220605 - 233239Annu BaijalNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Wood' - An Anatomical Re-Definition: DendrochronologiaDocumento5 pagineWhat Is Wood' - An Anatomical Re-Definition: DendrochronologiaZakiah UslinawatyNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport System in PlantDocumento16 pagineTransport System in PlantAbu-Omar50% (4)
- Breeding in CrossandraDocumento31 pagineBreeding in Crossandravijjumandula50% (4)
- Sinidu Final LastDocumento20 pagineSinidu Final LastAnonymous RCOlt3gNessuna valutazione finora
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocumento8 pagineInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1Documento10 pagineBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1andra100% (34)
- A Review On Controversial Aspect of Goks PDFDocumento10 pagineA Review On Controversial Aspect of Goks PDFMSKCNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocumento8 pagineChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Plant Breeding AGS127 PDFDocumento92 pagineFundamentals of Plant Breeding AGS127 PDFNikhil SherawatNessuna valutazione finora
- GR 10 Assign 2Documento8 pagineGR 10 Assign 2KhensaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Illustrated Guide To Horticultural WeedsDocumento39 pagineIllustrated Guide To Horticultural WeedsBryana100% (1)
- SrikayaDocumento4 pagineSrikayaForAcademicPurposesNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Macerated Plant MaterialsDocumento4 paginePreparation of Macerated Plant MaterialsBilal Ahmad Formanite0% (1)
- Biology 3rd QTR Activities 1Documento7 pagineBiology 3rd QTR Activities 1Mark Laurence MasellonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Names For Plants A-Z 2017Documento21 pagineScientific Names For Plants A-Z 2017Kathy DunsterNessuna valutazione finora
- Teks Cerita STEMDocumento5 pagineTeks Cerita STEMGanthimathi PanirselvamNessuna valutazione finora