Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Retsimp 2013
Caricato da
ijudoptoCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Retsimp 2013
Caricato da
ijudoptoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
01/08/2014
1
Biological Optics & Retinoscopy
Introduction & Principles
Introduction
Retinoscopy - an objective measure to
determine refractive error
Retinoscope illuminates the eye and we
observe the light reflected from retina
Refractive components of the eye influences
the way the light is reflected i.e. reflex
Introduction
Refraction and final Rx are usually from the
combination of objective measurement
(retinoscopy) and refinement with subjective
refraction
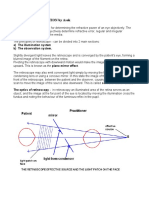
Principles of Retinoscopy
When light enters the patients eye, cornea
and crystalline lens focus (converge) the light
and an image is formed on the retina (fovea)
Important term: Conjugates*
The position of the image can be determined if
the position of the object is known, and vice versa
and both of them are conjugates
Ametropia
The far point is not at infinity
Further divided into:
Spherical ametropia (myopia & hyperopia)
Aspherical ametropia (astigmatism)
01/08/2014
2
Reflex Analysis:
Spherical Refractive Error
Principles
Illuminate patients retina with light from
retinoscope, and observe the reflected light
With regards to the location of the far point, if
the patient is
Emmetropic: reflected light is parallel
Hyperopic: reflected light is divergent
Myopic: reflected light is convergent
What does it all mean?
If the patients far point is behind the
retinoscope (the peephole)
WITH movement is observed
If the far point is in front of the retinoscope
AGAINST movement is observed
In real life,
We can only observe the movements of the
reflex (with/against)
We cannot really observe if the far point is behind
or in front of the peephole
Based on the reflexs movement, we can
deduce that if
AGAINST far point is in front of the retinoscope
WITH far point is behind the retinoscope
If a positive lens is placed in front of an
emmetropic patients eye,
The retina will conjugate with the dioptric
distance of the positive lens, and no movement is
observed (neutral)
The lens is known as working distance lens
E.g. If a +1.50DS is used, the retinoscopist should
perform the examination at 67cm away (why?)
Working distance lens
Movement of reflex (with working distance lens)
Emmetrope
No movement, NEUTRAL
Retinoscope is at the far point, ie, infinity
Hyperope
WITH movement
Far point is behind the retinoscope
Myope
AGAINST movement
Far point is in front of the retinoscope
01/08/2014
3
Video
Working distance &
Working distance lens
Any working distance can be used when
performing retinoscopy
Need to consider:
Brightness of the reflected light from the retina
Access to patient
Distance error when choosing a working distance
The Power of the WD Lens?
If the working distance is too small, eg. 25cm
Brighter retinal reflex, but larger distance error
If the working distance is too large eg. 100cm
Dimmer retinal reflex but smaller distance error
Usually working distance of 67cm or 50cm is
used
Neutral zone
Reflex characteristics
Speed
Fast when approaching neutral
Slow when far from neutral
Brightness
Bright when approaching neutral
Dim when far from neutral
Width
Wide when approaching neutral
Narrow when far from neutral
Neutral zone
There is a zone (not a point) where neutral
reflex can be observed
Inside the neutral zone: there is a confusion
whether the movement is WITH or AGAINST
01/08/2014
4
Handling the Retinoscope
Right hand/Right eye examines patients
right eye
Left hand/Left eye examines patients left
eye
Look through peephole with one eye
Handling the Retinoscope
Hold with one hand
Change the streak orientation only
Ambidexterity (skill) & the ability to suppress
the unused eye is very important
Align the retinal reflex with pupil
Retinoscopes head rests on brow or spectacles
Model eye
Simulation is achieved by changing the length
of the model eye
Increase length: simulate myopia
Decrease length: simulate hyperopia
To simulate high spherical Rx (using trial
lenses), use:
positive lens: __________
Negative lens: _________
Retinoscopy:
Neutralising Astigmatism
Astigmatism
Meridian: 1 to 180 deg
Two meridians are usually 90 deg from each
other
Regular astigmatism (meridians 90 and 180 deg)
Oblique astigmatism e.g. 45 and 135 deg
Irregular astigmatism principal meridians are not 90
deg from each other
With the Rule (WTR)
Axis of the ve cyl lens is at 180 deg
Against the Rule (ATR)
Axis of the ve cyl lens is at 90 deg
Type of Astigmatism
Simple hyperopic
Compound hyperopic
Simple myopic
Compound myopic
Mixed
01/08/2014
5
Reflex of an Astigmatic Eye
Neutralising Astigmatism
Techniques
Minus-cyl technique
Neutralise least minus or most plus meridian first
Plus-cyl technique
Neutralise most minus or least plus meridian first
Minus-cyl technique is most commonly used
However you can opt to do any one of them but
must be aware of the advantages and
disadvantages
Two ways of neutralising
Using spherical lenses only
Neutralise both meridians using spherical lenses
of different power
Transpose the findings into sph-cyl
Using spherical and cylindrical lenses
MOST PLUS or LEAST MINUS meridian is
neutralised first using spherical lens
The other meridian is neutralised using MINUS
cylindrical lens
Neutralising with sph-cyl lens
for Hyperopic eye
Neutralising with sph-cyl lens
for Myopic eye
01/08/2014
6
Summary: Minus-cyl Technique
Minus cyl Technique
To obtain the spherical power of the first
meridian:
Neutral meridian with most plus or least minus
first
Reflex at second meridian
Must be against movement
Neutralise second meridian with ve cyl lens, with
axis parallel to streak orientation
Determining Position of Cylinder Axis
Four ways to determine position of a cyls axis:
Break phenomena
Streak width
Reflex intensity
Reflex skewness
Use enhanced light to observe (sleeve is in
midway position)
All four phenomena are observed
simultaneously
Break and width
Easiest to observe when the cylindrical refractive
error is high
Skew and intensity
Easiest to observe when the cylindrical refractive
error is low
Retinoscopy on Human Eye
Dr. Mohd Izzuddin Hairol
UKM 2013
01/08/2014
7
Refraction
Fixation target
Must not cause the eye to accommodate, i.e. non-
accommodative target
E.g. spot light at 6 metres away
Fogging lens
the eye must relax so must use positive lenses
Usually the power of the working distance lens
(+1.50DS or +2.00DS) is enough to fog the eye place
WDLs before both eyes
DO NOT occlude the non-tested eye
Refraction
The position and alignment of the eyes are
important to get accurate results
WDL power must match the examiners working
distance
If not will cause errors in the final spherical power
Alignment with patients visual axis
If not will cause errors in the final cylindrical power
Patients fixation of the target must not be
blocked
Refraction
Use your right eye (and right hand) to examine
patients right eye, vice versa
Start examination with the RE followed by the
LE (do NOT take out lenses from the RE when
examining LE)
Minus Cyl Technique
Neutralise MOST PLUS or LEAST MINUS first
This is the spherical power for the first meridian
Reflex observed at the second meridian
Must be against
Neutralise the second meridian with minus cyl
lens
Axis of lens is aligned with the orientation of the
retinoscopes streak
Retinoscopy (without WDL)
Retinoscopy can be done without WDL
E.g. when using lens rack
Or to reduce the light reflex from trial lenses
Final power = spherical lens power to achieve
neutrality WDL power
Retinoscopy: Sources of Errors
If there is a marked difference in the final Rx
between objective and subjective refractions,
it could be due to
Neutral point misinterpretation
Retinoscopists technique
Confusing and irregular reflex
Spherical aberrations
Scissor movement
01/08/2014
8
Retinoscopists Techniques
Errors could be due to incorrect working distance
or misalignment of visual axis
Incorrect working distance causes an error in final
spherical correction
Make sure that your working distance and WDL match
Misalignment of visual axis (off-axis) causes an
error in final cylindrical correction
Make sure retinoscope is in line with patients
corresponding visual axis
Irregular reflexes
Sometimes reflexes can be irregular and confusing
Different movements seen at the pupils centre and
periphery
E.g. WITH movement at the centre and AGAINST
movement at the periphery when approaching neutrality
Spherical aberrations especially with larger pupils
Occurs when pupils are naturally large or when using
cycloplegic agents
To overcome: neutralise reflex movement seen at the
centre of the pupil only
Common problems
Reflex is hard to see when patient has smaller
pupils
E.g. elderly patients
To overcome: change to a shorter working
distance
Make sure that the new working distance matches
the WDL used
When reflex is observed with correcting lenses,
change working distance back to 50 cm or 67 cm
to minimise distance error
Common problems
Dull reflex
could be due to
Cloudy media e.g. cataract
High refractive error
To overcome
Cloudy media: change to a shorter working distance
High refractive error: try using high +ve or ve lenses
until a clear reflex is observed, or use the convergent
beam
Convergent beam (verifying AGAINST)
If a patient is a high myope, an AGAINST
movement is sometimes hard to observe
Use convergent beam to verify
With a convergent beam (sleeve in UP position), a
reversal of movement is observed i.e. WITH if a
patient is a myope
If WITH movement is observed with a convergent
beam
Patient is definitely a myope
Change sleeve back to divergent and neutralise as usual
High refractive errors
Difficult to judge reflex when refractive error
is high
Dull reflex is observed
Place high plus or high minus trial lens before
patients eye e.g. +5.00DS or -5.00DS, and observe
the reflex
If with +5.00DS, WITH movement is observed
continue adding plus lenses until neutral
If with -5.00DS, AGAINST movement is observed
continue adding minus lenses until neutral
01/08/2014
9
High refractive errors
If dull reflex is still observed with +5.00 DS or -
5.00DS
Try using lenses with higher power, e.g. +8.00DS or -
8.00DS
Reflex in uncorrected eyes with high refractive
errors sometimes looks neutral (as if there is a
full reflex and no movement is observed)
To differentiate:
Reflex must be bright with fast movement
Move forward, and reflex must be WITH. If not/does not
change the reflex observed earlier was not neutral.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Retinoscope & RetinosDocumento41 pagineRetinoscope & RetinosMiriam Mwangi100% (1)
- Submitted By: Sadia Qasim Submitted To: Mam Sania Aslam Subject: Management of Refractive Error HESC19113023 Bs Optometry 5ADocumento14 pagineSubmitted By: Sadia Qasim Submitted To: Mam Sania Aslam Subject: Management of Refractive Error HESC19113023 Bs Optometry 5AŠadïįaQasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Retinos PDFDocumento83 pagineRetinos PDFPaulo Gan100% (2)
- Retinoscopy by AzmatDocumento29 pagineRetinoscopy by AzmatMazhar Ali ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- RetinosDocumento60 pagineRetinosnickno1100% (1)
- Retinoscopy and Its Principles: Presenter: DR - Rasika Thakur Moderator: DR - Monica Samant MR - Kunal KishorDocumento67 pagineRetinoscopy and Its Principles: Presenter: DR - Rasika Thakur Moderator: DR - Monica Samant MR - Kunal KishorHenok BirukNessuna valutazione finora
- Retinoscopy: Scissors Movement Is Corrected With A Combination of Spherical and CylindricalDocumento3 pagineRetinoscopy: Scissors Movement Is Corrected With A Combination of Spherical and CylindricalgerryajunNessuna valutazione finora
- OPT 2083 Clinical Studies I: L8 Subjective RefractionDocumento36 pagineOPT 2083 Clinical Studies I: L8 Subjective RefractionDjbr MohNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismDocumento187 pagineDr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismVan KochkarianNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Skills Week 1Documento3 pagineClinical Skills Week 1Aishah SiddiqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mri MachineDocumento16 pagineMri Machineمحمد المدنيNessuna valutazione finora
- Accommodation - 2016Documento48 pagineAccommodation - 2016mariekenaw21Nessuna valutazione finora
- RefraksiDocumento42 pagineRefraksiGalihNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of RetinosDocumento51 pagineFundamentals of RetinosJelshan BawogbogNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraction 2Documento47 pagineRefraction 2RuDy RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraction: DR Intan Dwi Rahayu SPMDocumento52 pagineRefraction: DR Intan Dwi Rahayu SPMlaksonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Daa Objective RefractionDocumento56 pagineDaa Objective RefractiondwindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive DisorderDocumento39 pagineRefractive Disorderalvi kamal fikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Squint Evaluation 1Documento69 pagineSquint Evaluation 1rucha kacha100% (2)
- Refractive Errors (Najla) - 1Documento74 pagineRefractive Errors (Najla) - 1Muhammad LukmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive DisorderDocumento38 pagineRefractive DisorderfaustinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aphakia Vs Contact LensDocumento77 pagineAphakia Vs Contact LensSiva LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect OphthalmosDocumento8 pagineIndirect OphthalmosAnumeha JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pemeriksaan ObejktifDocumento12 paginePemeriksaan ObejktifMuhammad FadhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive Disorders Blok VisualDocumento27 pagineRefractive Disorders Blok Visualmuhammad ajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics of The EyeDocumento19 pagineOptics of The EyeObansa JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Baghdad University College of Medicine Ophthalmology DepartmentDocumento20 pagineBaghdad University College of Medicine Ophthalmology DepartmentMariam QaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pembahasan Pemicu 1Documento56 paginePembahasan Pemicu 1CcNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Devices-Physio Eye PresentationDocumento37 pagineMedical Devices-Physio Eye PresentationPharmacy Admission ExpertNessuna valutazione finora
- BV Exam2Documento33 pagineBV Exam2Andrew CoatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive ErrorsDocumento38 pagineRefractive ErrorszahraaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurDocumento56 pagineDr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurGideon IrwandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ophthalmoscopy: Moderater:Dr Bharti NigamDocumento38 pagineOphthalmoscopy: Moderater:Dr Bharti NigamAkansha RastogiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-History and Examination Part 2Documento27 pagine6-History and Examination Part 2AmrNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical SystemDocumento23 pagineOptical SystemluckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eye Exam: Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOMDocumento30 pagineEye Exam: Charlie Goldberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine, UCSD SOMDuhita Pramesthi Hayuningtyas100% (1)
- Introduction To Eye TrackingDocumento20 pagineIntroduction To Eye TrackingRahul Kumar100% (1)
- Sense of VisionDocumento34 pagineSense of VisionqqqqqNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDocumento8 pagineAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraction: Dr. Boyke Sisprihattono, SPMDocumento53 pagineRefraction: Dr. Boyke Sisprihattono, SPMPurnomo Ponco NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Acuity and Refraction Disorders: Eka Sutyawan Dept of Ophthalmology Udayana UniversityDocumento40 pagineVisual Acuity and Refraction Disorders: Eka Sutyawan Dept of Ophthalmology Udayana UniversityIda Ayu Prama YanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Gondar Cmhs Department of Optometry: BV and Clinical NeurologyDocumento36 pagineUniversity of Gondar Cmhs Department of Optometry: BV and Clinical NeurologyGetenet shumetNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Measurement of Lens PowerDocumento58 pagine02 Measurement of Lens PowerEye KnowledgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Light & Eyes: - Vision Begins When Light Comes Into The Eye - LightDocumento31 pagineLight & Eyes: - Vision Begins When Light Comes Into The Eye - LightfouadNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariDocumento25 pagineRefraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariBayu AdityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of VA, Refr Errors, Visual HandicapDocumento14 pagineMeasurement of VA, Refr Errors, Visual HandicapTaiwo IfedolapoNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.refractive DisorderDocumento38 pagine8.refractive DisorderRushdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect OphthalmosDocumento44 pagineIndirect Ophthalmosshar_s85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical RefractionDocumento46 pagineClinical RefractionMuhammed Abdulmajeed100% (1)
- Retinoscope 1Documento13 pagineRetinoscope 1Rimi Sree DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Refraksi YennyDocumento72 pagineRefraksi Yenny1910096Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocumento52 pagineOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Refraction Technique: Retinoscopy: Aao ReadingDocumento57 pagineObjective Refraction Technique: Retinoscopy: Aao ReadingKhairunnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Useful For Fixation and FoggingDocumento12 pagineUseful For Fixation and FogginganggastavasthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomicroscope - 2nd YearDocumento11 pagineBiomicroscope - 2nd Yearhelen paytonNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Objective RefractionDocumento11 pagine12 - Objective RefractionSumon SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Refractive ErrorsDocumento17 pagine3 - Refractive ErrorsF ParikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Ocular Examination: F. Francis Ma. L. Cid, MDDocumento62 pagineOcular Examination: F. Francis Ma. L. Cid, MDroacruzmdNessuna valutazione finora
- Amblyopia: Glomarie Hope A. Paquera Danica Ilah M. SincoDocumento39 pagineAmblyopia: Glomarie Hope A. Paquera Danica Ilah M. SincoJan IrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsDa EverandVisual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Algorithm For Random Dot StereogramsDocumento22 pagineAlgorithm For Random Dot Stereogramsijudopto100% (1)
- ECVP 2012 Supplement AbstractsDocumento275 pagineECVP 2012 Supplement AbstractsijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Toolbox For PsychologyDocumento7 pagineMatlab Toolbox For PsychologyijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Avian Sensory Systems: Sensory World Similar To Ours, That of Other Primates, Primarily VisualDocumento30 pagineAvian Sensory Systems: Sensory World Similar To Ours, That of Other Primates, Primarily VisualijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Age of ResearchDocumento4 pagineThe Age of ResearchijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Progressive Lens Optics - Part 2Documento10 pagineProgressive Lens Optics - Part 2ijudopto100% (1)
- Notes On Progressive LensesDocumento9 pagineNotes On Progressive LensesijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Iras GTDocumento8 pagineIras GTijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelli-Robson & ETDRS Score Sheet & InstructionsDocumento8 paginePelli-Robson & ETDRS Score Sheet & InstructionsPaul H Artes100% (3)
- Effects of Refractive Error On Detection Acuity and Resolution Acuity in Peripheral VisionDocumento10 pagineEffects of Refractive Error On Detection Acuity and Resolution Acuity in Peripheral VisionijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- J Physiol 1968 Campbell 551 66Documento16 pagineJ Physiol 1968 Campbell 551 66ijudoptoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony MDS-JE640 Service ManualDocumento66 pagineSony MDS-JE640 Service ManualDavid MackenzieNessuna valutazione finora
- AFL Service Provider SolutionsDocumento410 pagineAFL Service Provider Solutionsgirish_patkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Objectives in Lighting Design: Visual Performance Physiological Conditions Visual QualityDocumento24 pagineKey Objectives in Lighting Design: Visual Performance Physiological Conditions Visual QualityErwin SyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization Techniques in Material ScienceDocumento8 pagineCharacterization Techniques in Material ScienceSandeep NagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary ProcessingDocumento93 pagineBinary ProcessingNguyễn Thanh LiêmNessuna valutazione finora
- Exceptional Performance - Delivering A High-Resolution Image in A Slim 4.8 MM DiameterDocumento2 pagineExceptional Performance - Delivering A High-Resolution Image in A Slim 4.8 MM DiameterWesam Fh WfhNessuna valutazione finora
- LangauzeDocumento2 pagineLangauzeSwapnil SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 7 Physics Past HSC QuDocumento25 pagineMod 7 Physics Past HSC Quhello thereNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 1st Edition Cowan Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineMicrobiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 1st Edition Cowan Solutions Manualduongnujl33q100% (24)
- 7 Sci10 Reflection of Light On Plane MirrorsDocumento13 pagine7 Sci10 Reflection of Light On Plane Mirrorsrica maeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mirror Equation Worksheet KeyDocumento3 pagineMirror Equation Worksheet Keyminyoongles agustDNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual SokiaDocumento44 pagineManual SokiaFrancisco Alberto Peraza HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- AR 94 - EUSO Balloon - Underflight - JINST 2018 13 P05023Documento19 pagineAR 94 - EUSO Balloon - Underflight - JINST 2018 13 P05023cettina.maccaroneNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamron SP - 350mm f5.6 06b - 500mm f8 55b - Manual PDFDocumento20 pagineTamron SP - 350mm f5.6 06b - 500mm f8 55b - Manual PDFHank MarvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Ali Akbar - Resume ICP OES Dan ICP MSDocumento5 pagineMuhammad Ali Akbar - Resume ICP OES Dan ICP MSrifqi bambangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat Lighting 2022Documento25 pagineCat Lighting 2022yanuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Flame PhotometryDocumento7 pagineFlame PhotometryHussain RizviNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.1 IlluminationDocumento14 pagine16.1 Illuminationjuri bukhamseenNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure Panalex 2Documento2 pagineBrochure Panalex 2Ahmed NourNessuna valutazione finora
- !!trends in Pharmaceutical Analysis and Quality Contro - 2022 - TrAC Trends in AnaDocumento14 pagine!!trends in Pharmaceutical Analysis and Quality Contro - 2022 - TrAC Trends in AnaMostafa AfifyNessuna valutazione finora
- Oratorium Lighting Proposal Jesus ZuluagaDocumento0 pagineOratorium Lighting Proposal Jesus ZuluagaJesus David ZuluagaNessuna valutazione finora
- New FInalDocumento5 pagineNew FInalSai PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Reddot - DocterDocumento41 pagineReddot - DocterPeter DavidsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pentero 900: The Next GenerationDocumento19 paginePentero 900: The Next GenerationHermanto YuliusNessuna valutazione finora
- B.E CSE Full Time Curriculam-2010 PDFDocumento135 pagineB.E CSE Full Time Curriculam-2010 PDFJai SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio G11-5Documento34 pagineBio G11-5BataricitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive Erorrs LPDocumento12 pagineRefractive Erorrs LPSusmita SawardekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Type Designation Code: For Photoelectric SensorsDocumento33 pagineType Designation Code: For Photoelectric SensorsNabtronics FlukeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Nonlinear Refractive Index of Pure and Alloy Metallic Nanoclusters in Silica GlassDocumento6 pagineFast Nonlinear Refractive Index of Pure and Alloy Metallic Nanoclusters in Silica Glassalich500Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ray OpticsDocumento7 pagineRay OpticsArchana RachelNessuna valutazione finora