Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
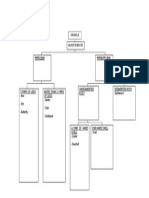
Chapter 1 - Standard Form
Caricato da
Shu Hui OoiTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 1 - Standard Form
Caricato da
Shu Hui OoiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 1 - Standard Form
Positive Number
Single numbers
Example: 12 100
0.003 023
Standard form,
A 10
n
with 1 A 10
and n an integer.
Example: 1.21 10
4
3.023 10
-3
Level of accuracy required
Significant figures (sig. fig)
Example: 1000 (1 sig. fig)
200.0 (4 sig. fig)
0.0023 (2 sig. fig)
0.0310 (3 sig. fig)
Round off to a given number of significant figures.
Example:
2.7 10
4
540 (correct to 3 sig. fig)
= 1.458 10
7
= 1.46 10
7
(correct to 3 sig. fig)
Chapter 2 Quadratic Expressions
and Equations
Two linear expressions
(mx + p)(nx + q)
Example:
(x - 1)(x + 4)
(3x + 2)(5x + 1)
Quadratic expressions
ax
2
+ bx + x, a 0
Highest power of unknown is 2
Example: x
2
+ 3x - 4
Factorisation
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0
(mx + p)(nx + q) = 0
mx + p = 0 or nx + q = 0
x = -
x = -
Trial and improvement method
Substitute values of x into
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0.
Check whether they satisfy the
equation.
Quadratic equations
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0, a 0
Example:
3x
2
- 16x + 5 = 0
Solution for quadratic equations
Trial and improvement method
Factorization
Roots of a quadratic equation are values
that satisfy the equation.
Chapter 3 Sets
Element ()
An object in a
set
n(A): number of
elements in set
A
Union (AB)
Consists of all the
elements in set A
or set B or both
Equal sets (A = B)
All the elements of set A are
elements of set B and vice
versa.
Venn diagram
Representation
of sets using
geometrical
diagrams
Sets
A group or
collection of
objects
Defined by
using
descriptions or
set notations
Intersection (AB)
Consists of all the
elements which
belong to both set
A and set B
Operations on sets
Complement of set A (A)
Consists of all the elements in
universal set than are not
found in A.
Universal set ()
Consists of all the elements
under discussion
Subset (A B)
All the elements of set A are
found in set B
Empty set ( or {})
A set which does not have any
elements.
Chapter 4 Mathematical Reasoning
Statement
A statement is a sentence that is either true or false but not both simultaneously.
Example:
8 2 = 16 4 2 = 3 4x + 5
Statement is true Statement is false Not a statement
Quantifiers [All or Some]
Quantifiers are used to indicate the number of
cases there are in a statement.
All indicates each and every one.
Some indicates at least one or several.
Implication
If p, then q. (p q)
p is the antecedent. q is the consequent.
Converse of p q is q p.
p if and only if q (p q) means
p q and q p
Deduction is the process of making specific
conclusion based on a given general
statement.
Induction is the process of making a general
conclusion based on given specific cases.
Argument
An argument is made up of premises and a
conclusion.
Make a conclusion based on two premises for
argument:
Form I
All A are B.
C is A.
C is B.
Form II
If p, then q.
p is true.
q is true
Form III
If p, then q.
Not q is true.
Not p is true.
Operations
Negate a statement by placing Not or
No. Trust table for statement p and ~p
p ~p
True False
False True
Combine two statements with the word
and.
Combine two statements with the word
or. Truth table for statements p and q
and p or q.
p q p and q p or q
True True True True
True False False True
False True False True
False False False False
May not
be true
Not p
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Beep Recording SheetDocumento1 paginaBeep Recording SheetLuccyanNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Engineering Bicol University Legazpi CityDocumento2 pagineCollege of Engineering Bicol University Legazpi CityCyrus Mozart Magno BritanicoNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Math - LM U4M11 PDFDocumento606 pagine8 Math - LM U4M11 PDFMark Jefferson Borromeo50% (4)
- AngahDocumento27 pagineAngahAddeen_Angah_5088Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 03Documento9 pagineMCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 03Kasaijja AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ignou Mca Mcs-013 Solved Assignment 2011Documento15 pagineIgnou Mca Mcs-013 Solved Assignment 2011Meera Sukhesh100% (1)
- Real Numbers and Their PropertiesDocumento31 pagineReal Numbers and Their PropertiesFaist Name Last NameNessuna valutazione finora
- Real No.s 1Documento10 pagineReal No.s 1Sayak ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- DM Unit II CH 1finalDocumento91 pagineDM Unit II CH 1finalKhaja AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Mit18 100af20 Lec Full2Documento92 pagineMit18 100af20 Lec Full2apostolosNessuna valutazione finora
- Inclusion ExclusionDocumento5 pagineInclusion ExclusionsaiNessuna valutazione finora
- AlgebraDocumento114 pagineAlgebraMay Perez Oruene Fombo-HartNessuna valutazione finora
- Number Theory Chap ReviewDocumento5 pagineNumber Theory Chap ReviewWazer WifleNessuna valutazione finora
- CSC331 Week 1 Topic ADocumento54 pagineCSC331 Week 1 Topic AfrankjamisonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Inequalities, Circles, and LinesDocumento87 pagine1 - Inequalities, Circles, and LinesBaui KojiNessuna valutazione finora
- FPM NotesDocumento98 pagineFPM NotesJake Bennett-WoolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Random Variables: Chapter 1 - Part 1Documento26 pagineRandom Variables: Chapter 1 - Part 1jcheonNessuna valutazione finora
- SSLC Maths FormulaeDocumento22 pagineSSLC Maths Formulaekarunakaran09100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Preliminaries: Economics Calculus 1Documento92 pagineChapter 1: Preliminaries: Economics Calculus 1RedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento64 pagineChapter 1s12340077Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Slides 01Documento30 pagineLecture Slides 01georgNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Math and Probability TheoryDocumento133 pagineDiscrete Math and Probability TheoryninjatronNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 10 Formula BookletDocumento24 pagineClass 10 Formula Bookletmayukhsarkar100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proof TechnologyDocumento7 pagineProof TechnologyLokesh GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Tripos Part IADocumento7 pagineMathematical Tripos Part IAjivasumanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento63 pagineChapter 1AnasSalahatNessuna valutazione finora
- TD2 LogicDocumento2 pagineTD2 LogichadNessuna valutazione finora
- SETLecture 5Documento26 pagineSETLecture 5Rezwan Ahmed TuhinNessuna valutazione finora
- Divisibility & Prime NumbersDocumento10 pagineDivisibility & Prime NumbersmhussainNessuna valutazione finora
- File File Class 10 1634634464 1638865876Documento18 pagineFile File Class 10 1634634464 1638865876Meer JishanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ps 1 SolDocumento3 paginePs 1 SolPang XsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 01Documento28 pagineChapter 01Lee DickensNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Class X Subject - Maths No. of Classes Teaching and Learning ActivitiesDocumento6 pagineLesson Plan Class X Subject - Maths No. of Classes Teaching and Learning ActivitiesSudhir IshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- OUTPOT in Modern WorldDocumento9 pagineOUTPOT in Modern WorldDimpleNessuna valutazione finora
- Dania - 22 - 12363 - 1-Lecture 2 Coordinate System-Fall 2015Documento34 pagineDania - 22 - 12363 - 1-Lecture 2 Coordinate System-Fall 2015erwin100% (1)
- Chapter5 - Induction and RecursionDocumento30 pagineChapter5 - Induction and RecursionDao Xuan DatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Real Number SystemDocumento6 pagineThe Real Number Systemana rosemarie enaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Problems in Discrete Mathematics: 1 Using Mathematical InductionDocumento5 pagineSample Problems in Discrete Mathematics: 1 Using Mathematical InductionStoriesofsuperheroesNessuna valutazione finora
- DivisibilityDocumento4 pagineDivisibilityDebbie Marie VerzosaNessuna valutazione finora
- BII Algebra Lecture 1Documento25 pagineBII Algebra Lecture 1Mrinmoy BanikNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sparkcharts Algebra IDocumento4 pagineThe Sparkcharts Algebra IMuhammad Fariz Mohamed Zain88% (8)
- Come104 Lecture 4Documento32 pagineCome104 Lecture 4Abdullah Al-DimashkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Tripos Part IADocumento7 pagineMathematical Tripos Part IAChristopher HitchensNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics NewDocumento27 pagineMathematics NewKumar SandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)Documento23 pagineBasic Principles of Enumeration (Lecture Notes) (David G. Wagner) (Z-Library)ishimweinesolgaNessuna valutazione finora
- PGCE Secondary Mathematics Pre-Interview Task: 1 Dividing by FractionsDocumento8 paginePGCE Secondary Mathematics Pre-Interview Task: 1 Dividing by Fractionsjfpowell100% (1)
- Basic Structures Sets, Functions Sequences, and SumsDocumento34 pagineBasic Structures Sets, Functions Sequences, and Sumsnguyên trần minhNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic, Sets, and Proofs: David A. Cox and Catherine C. Mcgeoch Amherst CollegeDocumento7 pagineLogic, Sets, and Proofs: David A. Cox and Catherine C. Mcgeoch Amherst CollegePritam GainNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th Class Mathematics Full Book Definitions PDF q3jDocumento10 pagine11th Class Mathematics Full Book Definitions PDF q3jAhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- S 5 SolDocumento4 pagineS 5 SolEric ParkerNessuna valutazione finora
- FX 12 SolDocumento7 pagineFX 12 SolJeremieNessuna valutazione finora
- Set TheoryDocumento19 pagineSet TheoryplycionNessuna valutazione finora
- Sets and FunctionsDocumento12 pagineSets and FunctionsShkidt IsaacNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis II Lecture NotesDocumento85 pagineAnalysis II Lecture NotesChandan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- H5Documento5 pagineH5Nuno MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Aut2014 (Final) SolDocumento23 pagineMidterm Aut2014 (Final) SolErico ArchetiNessuna valutazione finora
- MT2116 Enc 3Documento21 pagineMT2116 Enc 3Andion AdikristianNessuna valutazione finora
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDa EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (8)
- Stencils, Mobiles, Cards & More. Colorado, United States: ShambhalaDocumento1 paginaStencils, Mobiles, Cards & More. Colorado, United States: ShambhalaShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lamp IranDocumento1 paginaLamp IranShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics PresentationDocumento10 pagineMathematics PresentationShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics PresentationDocumento10 pagineMathematics PresentationShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics PresentationDocumento10 pagineMathematics PresentationShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento11 paginePresentation 1Shu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- ReferencesDocumento1 paginaReferencesShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- User ManualDocumento4 pagineUser ManualShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Refer AnceDocumento1 paginaRefer AnceShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento1 paginaIntroductionShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
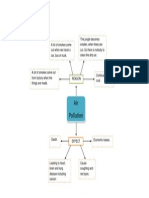
- Mind MapDocumento1 paginaMind MapShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Numb ER Topic Pag E: 2 Objective 4 Information 5 Discussion 9 Conclusion 10 References 11Documento1 paginaNumb ER Topic Pag E: 2 Objective 4 Information 5 Discussion 9 Conclusion 10 References 11Shu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind MapDocumento1 paginaMind MapShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference: Tan Yin Toon, Loh Wai Teng, Tan On Tin. (2011) - Success Chemistry SPM. Shah Alam: Oxford FajarDocumento1 paginaReference: Tan Yin Toon, Loh Wai Teng, Tan On Tin. (2011) - Success Chemistry SPM. Shah Alam: Oxford FajarShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- With Legs Without Legs: AnimalsDocumento1 paginaWith Legs Without Legs: AnimalsShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- New Correlation Between Height and Arm SpanDocumento4 pagineNew Correlation Between Height and Arm SpanShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Numb ER Topic Pag E: 2 Objective 4 Information 5 Discussion 9 Conclusion 10 References 11Documento1 paginaNumb ER Topic Pag E: 2 Objective 4 Information 5 Discussion 9 Conclusion 10 References 11Shu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- DiscussionDocumento1 paginaDiscussionShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1 Upper Boundary and Class IntervalDocumento16 pagine6.1 Upper Boundary and Class IntervalShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- With Legs Without Legs: AnimalsDocumento1 paginaWith Legs Without Legs: AnimalsShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- ConclusionDocumento1 paginaConclusionShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- CeramicDocumento2 pagineCeramicShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
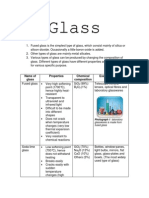
- GlassDocumento2 pagineGlassShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- I. 3815 (Correct To 2 Sig. Fig) 3800: 1.1 Significant FigureDocumento11 pagineI. 3815 (Correct To 2 Sig. Fig) 3800: 1.1 Significant FigureShu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Straight Line Gradient (M)Documento10 pagineThe Straight Line Gradient (M)Shu Hui OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems On LCM & HCFDocumento4 pagineProblems On LCM & HCFArif WaitsNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesDocumento19 pagineCAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesAndre MaxwellNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 01 Limits (Solutions)Documento5 pagineExercise 01 Limits (Solutions)ECoUFNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Painlevé Property, Test and Analysis1 (R Conte & M Mussette)Documento7 pagineIntroduction To The Painlevé Property, Test and Analysis1 (R Conte & M Mussette)Jason UchennnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton Raphson ExerciseDocumento2 pagineNewton Raphson Exercisek yong100% (1)
- Amch1: Mathematics Iii: 1. Partial Differentiation and Partial Differential EquationDocumento2 pagineAmch1: Mathematics Iii: 1. Partial Differentiation and Partial Differential EquationAnonymous 70lCzDJv100% (1)
- Periodical Test - TLE 10 2nd GradingDocumento9 paginePeriodical Test - TLE 10 2nd GradingLOVELY DELA CERNANessuna valutazione finora
- Junior Mathematical Challenge: Thursday 30 April 2020Documento4 pagineJunior Mathematical Challenge: Thursday 30 April 2020Add UpNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Algebra Review PDFDocumento16 pagineGeometry Algebra Review PDFangel anne marie jabianNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 4733 Class Notes: Kinematic Singularities and JacobiansDocumento9 pagineCS 4733 Class Notes: Kinematic Singularities and JacobiansNoor Nabi MujahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Functions MCR3U Unit 8 (May 2015)Documento18 pagineDiscrete Functions MCR3U Unit 8 (May 2015)Shanaz ParsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg 9.1 PacketDocumento5 pagineAlg 9.1 PacketAN NGUYENNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Analysis Semester 1 Final ReviewDocumento10 pagineMath Analysis Semester 1 Final ReviewmayanbNessuna valutazione finora
- On A Mixed Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityDocumento6 pagineOn A Mixed Arithmetic-Geometric Mean InequalityMelek GüngörNessuna valutazione finora
- Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 5th Edition Beecher Solutions ManualDocumento36 paginePrecalculus A Right Triangle Approach 5th Edition Beecher Solutions Manuallawerslowbackplpy100% (30)
- Mathematics Class 4Documento202 pagineMathematics Class 4nirmalv100% (1)
- Maxwell's Equations in Arbitrary Coordinate SystemDocumento12 pagineMaxwell's Equations in Arbitrary Coordinate SystemMuhammad AzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Mathematics (041) (Standard)Documento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Mathematics (041) (Standard)ShrikantNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Chapter 1 Sequences and Series (Student Copy)Documento57 pagine2022 Chapter 1 Sequences and Series (Student Copy)Alice DuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Basiccalculus g11 Q3mod1 Functionslimitsand-continuity-V4Documento72 pagineFinal Basiccalculus g11 Q3mod1 Functionslimitsand-continuity-V4Benice GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 120 Past Exam QuestionsDocumento199 pagineMath 120 Past Exam Questions19cerena03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Explore: Identify If The Following Are Well-Defined. Write WD If Well-Defined and ND If NotDocumento3 pagineExplore: Identify If The Following Are Well-Defined. Write WD If Well-Defined and ND If NotjejejeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 2 Properties of Circles NotesDocumento10 pagine4 2 Properties of Circles Notesapi-276774539Nessuna valutazione finora
- ImplicitDocumento4 pagineImplicitMulangira MulangiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Related Rates ABDocumento26 pagine2019 Related Rates ABArebeeJayBelloNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 03 Runge-Kutta 2nd Order MethodDocumento11 pagine08 03 Runge-Kutta 2nd Order MethodJohn Bofarull GuixNessuna valutazione finora
- Wazwaz IEch 3 S 2 S 3 P 8Documento1 paginaWazwaz IEch 3 S 2 S 3 P 8honey fatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti, NoidaDocumento8 pagineNavodaya Vidyalaya Samiti, Noida9A RN10 Harmandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora