Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Structure and Function of The Cell
Caricato da
Irene Quimson0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni17 paginexx
Titolo originale
Structure and Function of the Cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni17 pagineStructure and Function of The Cell
Caricato da
Irene Quimsonxx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 17
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
All Materials Cmassengale
I. All Organisms are Made of Cells
A. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function
B. The cell is the smallest unit that can still carry on all life processes
C. Both unicellular (one celled) and multicellular (many celled) organisms are composed of
cells
D. Before the 17
th
century, no one knew cells existed
E. Most cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye
F. In the early 17
th
century microscopes were invented & cells were seen for the 1
st
time
G. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, a Dutchman, made the 1
st
hand-held microscope & viewed
microscopic organisms in water & bacteria from his teeth
Leeuwenhoek's microscope consisted simply of:
A) a screw for adjusting the
height of the object being
examined
B) a metal plate serving as the
body
C) a skewer to impale the object and rotate it
D) the lens itself, which was spherical
H. In 1665, an English scientist named Robert Hooke made an improved microscope and
viewed thin slices of cork viewing plant cell walls
I. Hooke named what he saw "cells"
J. In the 1830s, Matthias Schleiden (botanist studying plants) &
Theodore Schwann (zoologist studying animals) stated that all living things were made of
cells
K. In 1855, Rudolf Virchow stated that cells only arise from pre-existing cells
L. Virchows idea contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation (idea that nonliving things
could give rise to organisms)
M. The combined work of Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow is known as the Cell Theory
Schwann Schleiden Virchow
II. Principles of the Cell Theory
A. All living things are made of one or more cells
B. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in organisms
C. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells
III. Cell Diversity
A. Not all cells are alike
B. Cells differ in size, shape, and function
C. The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a microscope
D. Bacterial cells are some of the smallest cells & are only visible with a microscope
E.coli Bacterial Cells
E. Cells need surface area of their cell membrane large enough to adequately exchange
materials with the environment (wastes, gases such as O
2
& CO
2
, and nutrients)
F. Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area & their volume
G. Small cells have more surface area for their volume of cytoplasm than large cells
H. As cells grow, the amount of surface area becomes too small to allow materials to enter &
leave the cell quickly enough
I. Cell size is also limited by the amount of cytoplasmic activity that the cells nucleus
can control
J. Cells come in a variety of shapes, & the shape helps determine the function of the cell
(e.g. Nerve cells are long to transmit messages in the body, while red blood cells are disk
shaped to move through blood vessels)
IV. Prokaryotes
A. Prokaryotic cells are less complex
B. Unicellular
C. Do not have a nucleus & no membrane-bound organelles
D. Most have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane & a single,
looped chromosome (genetic material) in the cytoplasm
E. Include bacteria & blue-green bacteria
F. Found in the kingdom Monera
V. Eukaryotes
A. More complex cells
B. Includes both unicellular & multicellular organisms
C. Do have a true nucleus & membrane-bound organelles
D. Organelles are internal structures in cells that perform specific functions
a. Nucleus
b.
Chloroplast
c. Golgi
d.
Mitochondria
E. Organelles are surrounded by a single or double membrane
F. Entire eukaryotic cell surrounded by a thin cell membrane that controls what enters &
leaves the cell
G. Nucleus is located in the center of the cell
H. The nucleus contains the genetic material (DNA) & controls the cells activities
I. Eukaryotes include plant cells, animal cells, fungi, algae, & protists
J. Prokaryotes or bacteria lack a nucleus
K. Found in the kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae, & Animalia
VI. Cell Membrane
A. Separates the cytoplasm of the cell from its environment
B. Protects the cell & controls what enters and leaves
C. Cell membranes are selectively permeable only allowing certain materials to enter or leave
D. Composed of a lipid bilayer made of phospholipid molecules
E. The hydrophilic head of a phospholipid is polar & composed of a glycerol & phosphate
group and points to the aqueouscytoplasm and external environment.
F. The two hydrophobic tails are nonpolar point toward each other in the center of the
membrane & are composed of two fatty acids
G. When phospholipids are placed in water, they line up on the waters surface with their
heads sticking into the water & theirtails pointing upward from the surface.
H. The inside of the cell or cytoplasm is an aqueous or watery environment & so is
the outside of the cell. Phospholipid "heads" point toward the water.
I. Phospholipid "tails" are sandwiched inside the lipid bilayer.
J. The cell membrane is constantly breaking down & being reformed inside living cells.
K. Certain small molecules such as CO
2
, H
2
O, & O
2
can easily pass through the phospholipids
VII. Membrane Proteins
A. A variety of protein molecules are embedded in the cells lipid bilayer.
B. Some proteins called peripheral proteins are attached to the external & internal surface of
the cell membrane
C. Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins are embedded & extend across the entire cell
membrane. These are exposed to both the inside of the cell & the exterior environment.
D. Other integral proteins extend only to the inside or only to the exterior surface.
E. Cell membrane proteins help move materials into & out of the cell.
F. Some integral proteins called channel proteins have holes or pores through them so
certain substances can cross the cell membrane.
G. Channel proteins help move ions (charged particles) such as Na
+
, Ca
+
, & K
+
across the cell
membrane
H. Transmembrane proteins bind to a substance on one side of the membrane & carry it to
the other side. e.g. glucose
I. Some embedded, integral proteins have carbohydrate chains attached to them to serve
as chemical signals to help cells recognize each other or for hormones or viruses to attach
VIII. Fluid Mosaic Model
A. The phospholipids & proteins in a cell membrane can drift or move side to side making
the membrane appear "fluid".
B. The proteins embedded in the cell membrane form patterns or mosaics.
C. Because the membrane is fluid with a pattern or mosaic of proteins, the modern view of
the cell membrane is called the fluid mosaic model.
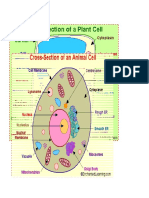
IX. Internal Cell Structure & Organelles of Eukaryotes
A. Cytoplasm includes everything between the nucleus and cell membrane.
B. Cytoplasm is composed of organelles & cytosol (jellylike material consisting of mainly
water along with proteins.
C. Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotes do not
D. Mitochondria are large organelles with double
membranes where cellular respiration (breaking down glucose to getenergy) occurs
1. Energy from glucose is used to make ATP or adenosine triphosphate
2. Cells use the ATP molecule for energy
3. More active cells like muscle cells have more mitochondria
4. Outer membrane is smooth, while inner membrane has long folds called cristae
5. Have their own DNA to make more mitochondria when needed
E. Ribosomes are not surrounded by a membrane & are where proteins are made in the
cytoplasm (protein synthesis)
1. Most numerous organelle
2. May be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER (endoplasmic reticulum)
F. Endoplasmic reticulum are membranous tubules & sacs that transport molecules from one
part of the cell to another
1. Rough ER has embedded ribosomes on its surfaces for making proteins
2. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes & helps break down poisons, wastes, & other toxic chemicals
3. Smooth ER also helps process carbohydrates & lipids (fats)
4. The ER network connects the nucleus with the cell membrane
G. Golgi Apparatus modifies, packages, & helps secrete cell products such as proteins and
hormones
1. Consists of a stack of flattened sacs called cisternae
2. Receives products made by the ER
H. Lysosomes are small organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes to digest materials for the
cell
1. Single membrane
2. Formed from the ends of Golgi that pinch off
3. Found in most cells except plant cells
I. Cytoskeleton consists of a network of long protein tubes & strands in the cytoplasm to
give cells shape and helps move organelles
1. Composed of 2 protein structures --- microtubules, intermediate filaments, &
microfilaments
2. Microfilaments are ropelike structures made of 2 twisted strands of the protein
actin capable of contracting to cause cellular movement (muscle cells have many
microfilaments)
3. Microtubules are larger, hollow tubules of the protein called tubulin that maintain cell
shape, serve as tracks for organelle movement, & help cells divide by forming spindle fibers
that separate chromosome pairs
Cytoskeleton Element General Function
Microtubules
Move materials within the cell
Move the cilia and flagella
Actin Filaments Move the cell
Intermediate Filaments Provides mechanical support
J. Cilia are short, more numerous hair like structures made of bundles of microtubules to
help cells move
1. Line respiratory tract to remove dust & move paramecia
Cross section of Cilia & Flagella
K. Flagella are long whip like tails of microtubules bundles used for movement (usually 1-3 in
number)
1. Help sperm cells swim to egg
L. Nucleus (nuclei) in the middle of the cell contains DNA (hereditary material of the cell) &
acts as the control center
1. Most cells have 1 nucleolus, but some have several
2. Has a protein skeleton to keep its shape
3. Surrounded by a double layer called the nuclear envelope containing pores
4. Chromatin is the long strand of DNA in the nucleus, which coils during cell division to
make chromosomes
5. Nucleolus (nucleoli) inside the nucleus makes ribosomes & disappears during cell division
M. Cell walls are nonliving, protective layers around the cell membrane in plants, bacteria, &
fungi
1. Fungal cell walls are made of chitin, while plant cell walls are made of cellulose
2. Consist of a primary cell wall made first and a woody secondary cell wall in some plants
N. Vacuoles are the largest organelle in plants taking up most of the space
1. Serves as a storage area for proteins, ions, wastes, and cell products such as glucose
2. May contain poisons to keep animals from eating them
3. Animal vacuoles are smaller & used for digestion
O. Plastids in plants make or store food & contain pigments to trap sunlight
1. Chloroplast is a plastid that captures sunlight to make O
2
and
glucose during photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll
a. Double membrane organelle with an inner system of membranous sacs called thylakoids
b. Thylakoids made of stacks of grana containing chlorophyll
2. Other plastids contain red, orange, and yellow pigments
3. Found in plants, algae, & seaweed
X. Multicellular Organization
A. Cells are specialized to perform one or a few functions in multicellular organisms
B. Cells in multicellular organisms depend on each other
C. The levels of organization include:
Cells --> Tissues --> Organs --> Systems --> Organism
D. Tissues are groups of cells that performs a particular function (e.g. Muscle)
E. Organs are groups of tissues working together to do a job (e.g. heart, lungs, kidneys,
brain)
F. Systems are made of several organs working together to carry out a life process (e.g.
Respiratory system for breathing)
G. Plants have specialized tissues & organs different from animals
1. Dermal tissue forms the outer covering of plants
2. Ground tissue makes up roots & stems
3. Vascular tissue transports food & water
4. The four plant organs are the root, stem, leaf, & flower
H. Colonial organisms are made of cells living closely together in a connected group but
without tissues & organs (e.g. Volvox)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Becker's USMLE Step 1 - Lecture NotesBiochemistry, Genetics (2013) (UnitedVRG)Documento278 pagineBecker's USMLE Step 1 - Lecture NotesBiochemistry, Genetics (2013) (UnitedVRG)Gps Pandette100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Module 1 Q1Documento20 pagineGeneral Biology 1 Module 1 Q1Katana Mist100% (2)
- Salient Features of Notarial LawDocumento5 pagineSalient Features of Notarial LawIrene Quimson100% (1)
- POLITICAL LAW TO CRIMINAL LAWDocumento2 paginePOLITICAL LAW TO CRIMINAL LAWdayaners88% (16)
- Animal Nutrition CIE IGCSE 0610 PPQDocumento12 pagineAnimal Nutrition CIE IGCSE 0610 PPQcharbie galNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Custodial InvestigationDocumento11 pagineWhat Is Custodial InvestigationIrene Quimson100% (4)
- What Is Custodial InvestigationDocumento11 pagineWhat Is Custodial InvestigationIrene Quimson100% (4)
- Constructive Dismissal - 2016Documento9 pagineConstructive Dismissal - 2016Irene Quimson100% (1)
- Chapter 2Documento7 pagineChapter 2Kaness MathzNessuna valutazione finora
- Original PDF Nutrition From Science To You 4th Edition PDFDocumento41 pagineOriginal PDF Nutrition From Science To You 4th Edition PDFjose.martinez439100% (32)
- Examining Immune System ResponsesDocumento18 pagineExamining Immune System Responseswhitewave25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Chromosome Mitosis Meiosis Review WorksheetDocumento4 pagineChromosome Mitosis Meiosis Review Worksheetapi-331662907Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocumento19 pagineCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (1)
- IB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsDocumento5 pagineIB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsTiffani Choy100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Documento20 pagineGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1Pril Gueta100% (2)
- 2004 Rules on Notarial Practice ApprovedDocumento20 pagine2004 Rules on Notarial Practice ApprovedirditchNessuna valutazione finora
- MNEMONICS IN LABOR LAWSDocumento108 pagineMNEMONICS IN LABOR LAWSdavaounionNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocumento4 pagineCell Parts and FunctionsRonald AzoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid Catabolism: Refer To Chapter 23, Stryer, 5e and Chapter 18, Lehninger, 4eDocumento17 pagineAmino Acid Catabolism: Refer To Chapter 23, Stryer, 5e and Chapter 18, Lehninger, 4elylasherliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Claims Case Made SimpleDocumento21 pagineSmall Claims Case Made SimpleIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Claims Case Made SimpleDocumento21 pagineSmall Claims Case Made SimpleIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET - Biology - Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento38 pagineNEET - Biology - Cell Structure and Functionknlsinha67% (3)
- Notes On Cell OrganellesDocumento11 pagineNotes On Cell Organellesapi-241062194Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Introduction To CellsDocumento7 pagineNotes On Introduction To Cellsapi-241062194Nessuna valutazione finora
- Angelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Documento7 pagineAngelyn M. Morales Beed A-1Angelyn MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocumento8 pagineUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Elizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedDocumento14 pagineElizondo Cell Theory and Cell Organelles-UpdatedRahanie Gadungan PajijiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structures WorksheetDocumento2 pagineCell Structures WorksheetCharlene BarcelonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DelacruzDocumento46 pagineCell DelacruzKylamae BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 4Documento6 pagineAP Biology Outline - Chapter 4Omar Lopez100% (1)
- Structure and Function of CellDocumento11 pagineStructure and Function of CellWoobin RealNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 CellsDocumento19 pagineChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNessuna valutazione finora
- The CellDocumento14 pagineThe CellDaniel NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocumento14 pagineKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellDocumento11 pagineAS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellJosebeth CairoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Membrane and Its FunctionsDocumento6 pagineThe Cell Membrane and Its FunctionsMark Kenneth CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Sheet Formative AssessmentDocumento4 pagineAnswer Sheet Formative Assessmentapi-328130455Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alpah Term ss2 Biology e - NoteDocumento39 pagineAlpah Term ss2 Biology e - NoteSamuel BiyamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocumento4 pagineDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Structure and FunctionsDocumento39 pagineThe Cell Structure and Functionsjeremiah oseniNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocumento4 pagineClass 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesneilNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell - Structure and Functions PDFDocumento3 pagineCell - Structure and Functions PDFmaya__scribd100% (1)
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDocumento4 pagineChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellmzunl254760% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFDocumento5 pagineThe Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFmanoharrish3Nessuna valutazione finora
- General BiologyDocumento14 pagineGeneral BiologybonNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Questions of Cell - The Unit of LifeDocumento9 pagineImportant Questions of Cell - The Unit of LifeAyush DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21Documento10 pagineBiology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21fahad darNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal and Plant CellDocumento8 pagineAnimal and Plant CellSamar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Outline: ELL Tructure and UnctionDocumento5 pagineChapter Outline: ELL Tructure and Unctionrommel benamir100% (1)
- General BiologyDocumento23 pagineGeneral BiologyPereyra Faith AngeliqueNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell: Life's Fundamental Building BlockDocumento8 pagineThe Cell: Life's Fundamental Building BlockQadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Function and The ComponentsDocumento5 pagineCell Function and The ComponentssalisongloNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 BioDocumento5 pagineCH 6 BioedwarddameNessuna valutazione finora
- Задания (строение)Documento12 pagineЗадания (строение)D1chuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Documento10 pagineThe Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Justin RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles 2Documento13 pagineCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science NotesDocumento8 pagineChapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science Notesdeepti jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Class DiscussionDocumento3 pagineLesson 2 Class DiscussionBABY NICOLE ARELLANONessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocumento2 pagineCell Parts and FunctionsMian Nakahara0% (1)
- Earth Life Science Module 5Documento15 pagineEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNessuna valutazione finora
- CELLS For Class8Documento15 pagineCELLS For Class8cbseiscNessuna valutazione finora
- Edible Plant CellDocumento4 pagineEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organelles in Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 pagineOrganelles in Animal and Plant CellsDr.CharinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular StructureDocumento11 pagineCellular StructureHannah Barahan ArgotaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Cell The Unit of Life - .Documento10 pagineNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Cell The Unit of Life - .susilmaji92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocumento5 pagineRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsArpit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Bio 1Documento8 pagine9 Bio 1Amisha SenapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fundamental Unit of Life1678869792(2)Documento5 pagineThe Fundamental Unit of Life1678869792(2)rayan kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SYLLABUS: Discovery of Cell, Modern Cell Theory, A Prokaryotic Cell, Unicellular and Multicellular Organism, Level ofDocumento12 pagineSYLLABUS: Discovery of Cell, Modern Cell Theory, A Prokaryotic Cell, Unicellular and Multicellular Organism, Level ofVijay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell and TissueDocumento10 pagineCell and TissueCarl SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Intro To CellDocumento6 pagineChapter 1 Intro To CellrexartoozNessuna valutazione finora
- CELL_CLASSIX_SESSION3_MADE_BY_PURNIMA__SHARMA_1Documento7 pagineCELL_CLASSIX_SESSION3_MADE_BY_PURNIMA__SHARMA_1jeetjyoti787Nessuna valutazione finora
- Second DivisionDocumento10 pagineSecond DivisionIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Promissory NoteDocumento1 paginaPromissory NoteIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Executive DepartmentDocumento8 pagineExecutive DepartmentIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneously With The Commission of The Fraud. Thus, Under Article 315, Paragraph 2 (D) ofDocumento2 pagineSimultaneously With The Commission of The Fraud. Thus, Under Article 315, Paragraph 2 (D) ofIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- BuCor tomato paste purchaseDocumento6 pagineBuCor tomato paste purchaseIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- SsDocumento7 pagineSsIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- To Make Out A Case of Unlawful Detainer Under Section 1Documento10 pagineTo Make Out A Case of Unlawful Detainer Under Section 1Irene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- I Min Love With My Fake Boyfriends BrotherDocumento141 pagineI Min Love With My Fake Boyfriends BrotherJayeM25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Dispute Resolution: ArbitrationDocumento1 paginaAlternative Dispute Resolution: ArbitrationIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultDocumento1 paginaRule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocumento1 paginaRepublic of The PhilippinesIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- BNDocumento5 pagineBNIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Expanded Jurisdiction of Cam and JDRDocumento5 pagineThe Expanded Jurisdiction of Cam and JDRliljoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultDocumento1 paginaRule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultDocumento1 paginaRule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Dispute ResolutionDocumento1 paginaAlternative Dispute ResolutionIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Memo NDocumento15 pagineMemo NIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Obillos Et Al vs. CIR/CA: MoneyDocumento2 pagineObillos Et Al vs. CIR/CA: MoneyIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Gospel 1Documento5 pagineGospel 1Irene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultDocumento1 paginaRule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultDocumento1 paginaRule 55. Default Default Judgment: Ntering A EfaultIrene QuimsonNessuna valutazione finora
- PROTEINDocumento41 paginePROTEIN2BSN19Manuel, Rhadalie V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acid DegradationDocumento57 pagineAmino Acid DegradationUjjwal YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis Part 3Documento12 pagineGlycolysis Part 3Rishav BajoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell anatomy and divisionDocumento4 pagineCell anatomy and divisionMarielle SaymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Polakof Et Al, 2012, Review GlucoseDocumento31 paginePolakof Et Al, 2012, Review GlucosecarolinaBTRNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam1 2011 PDFDocumento8 pagineExam1 2011 PDFMasterYsterNessuna valutazione finora
- (20493614 - Endocrine Connections) How Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists WorkDocumento13 pagine(20493614 - Endocrine Connections) How Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists WorkEka RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mutation PresentationDocumento22 pagineMutation PresentationJoanne GodezanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Biosensors: Detection Using Biological ComponentsDocumento11 pagineIntroduction to Biosensors: Detection Using Biological Componentsdeepak guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lipids NotesDocumento4 pagineLipids NoteskatNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of SNP and CAPS Markers Application in Genetic Research in Wheat and BarleyDocumento5 pagineComparison of SNP and CAPS Markers Application in Genetic Research in Wheat and BarleyAlangelico Ortiz San PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Extraction of White Onion: Group 5Documento25 pagineDNA Extraction of White Onion: Group 5CHELSEA BERNARDINE MANALONessuna valutazione finora
- Biol 243 Tert Assignment w19Documento3 pagineBiol 243 Tert Assignment w19rtm haiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Guideline TBDocumento128 pagineGuideline TBChest X RayNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazingly Versatile: Gateway Recombination Cloning TechnologyDocumento8 pagineAmazingly Versatile: Gateway Recombination Cloning Technologymike kakundaNessuna valutazione finora
- Elisa - PCR - Electrophoresa: Dr. Malayana R Nasution, SPPKDocumento30 pagineElisa - PCR - Electrophoresa: Dr. Malayana R Nasution, SPPKfgrehNessuna valutazione finora
- Scoring Rubric Dna RnaDocumento2 pagineScoring Rubric Dna RnaHisoka RyugiNessuna valutazione finora
- The structure of the small intestine allows digestion and absorptionDocumento24 pagineThe structure of the small intestine allows digestion and absorptionHana ElattarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio NoteDocumento5 pagineBio NoteErikNessuna valutazione finora
- Martin Shkreli COVID-19 PlanDocumento11 pagineMartin Shkreli COVID-19 PlanAustin DeneanNessuna valutazione finora
- Transgenic Plants For Production of EnzymesDocumento17 pagineTransgenic Plants For Production of Enzymeslaidydy10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions ManualDocumento12 pagineVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions ManualDavidWardrcobi100% (14)
- ATP Production Through Tissue RespirationDocumento28 pagineATP Production Through Tissue RespirationSheldon MillerNessuna valutazione finora
- Weekly Plan3 - TNDocumento37 pagineWeekly Plan3 - TNABDULGAFFAR MNessuna valutazione finora