Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Acls Tachi
Caricato da
ratnawkCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Acls Tachi
Caricato da
ratnawkCopyright:
Formati disponibili
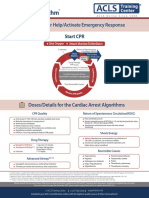
Wide (>0.
12 sec)
Unstable
Irregular Regular
12
8
6
Narrow
Symptoms Persist
Stable
1
ACLS Tachycardia
With Pulses
3
Is patient stable?
Unstable signs include altered
mental status, ongoing chest pain,
hypotension or other signs of shock
Note: rate-related symptoms
uncommon if heart rate <150/min
During Evaluation Treat contributing factors:
Secure, verify airway
and vascular access
when possible
Consider expert
consultation
Prepare for
cardioversion
- Hypovolemia - Toxins
- Hypoxia - Tamponade/cardiac
- Hydrogen ion (acidosis) - Tension pneumothorax
- Hypo-/hyperkalemia - Thrombosis (coronary or
- Hypoglycemia pulmonary)
- Hypothermia - Trauma (hypovolemia)
2005 ECC Guidelines
2
Assess and support ABCs as needed
Give oxygen
Monitor ECG (identify rhythm), blood pressure, oximetry
Identify and treat reversible causes
11
Irregular Narrow-Complex
Tachycardia
Probable atrial fibrillation or
possible atrial flutter or MAT
(multifocal atrial tachycardia)
Consider expert consultation
Control rate (eg, Diltiazem,
-Blockers; use -blockers
with caution in pulmonary
disease or CHF)
7
Attempt vagal maneuvers
Give Adenosine 6 mg rapid IV
push, if no conversion, give 12
mg rapid IV push; may repeat
12 mg dose once
5
Establish IV access
Obtain 12-lead ECG
(when available or rhythm
strip)
Is QRS narrow (<0.12 sec)?
4
Perform immediate
synchronized cardioversion
Establish IV access and give
sedation if patient is
conscious; do not delay
cardioversion
Consider expert consultation
If pulseless arrest develops,
see Pulseless Arrest Algorithm
WIDE QRS*:
Is Rhtyhm Regular?
Expert consultation
advised
13
If Ventricular
Tachycardia or
uncertain rhythm
Amiodarone
150mg IV over 10 min
Repeat as needed to
maximum dose of
2.2 g/24 hours
Prepare for elective
synchronized
cardioversion
If SVT with aberrancy
Give Adenosine
(go to box 7)
14
If Atrial Fibrillation with
aberrancy
See irregular Narrow-
Complex Tachycardia
(Box 11)
If pre-excited Atrial
Fibrillation (AF + WPW)
Expert consultation
advised
Avoid AV nodal
blocking agents (eg,
Adenosine, Digoxin,
Diltiazem, Verapamil)
Consider antiarrythmic
(eg, Amiodarone
150 mg IV over 10 min)
If recurrent polymorphic
VT, seek expert
consultation
If torsades de pointes,
give Magnesium
(load with 1-2 g over
5-60 min, then infusion)
9
If rhythm converts,
probable reentry SVT
(reentry Supraventricular
Tachycardia):
Observe for recurrence
Treat recurrence with
Adenosine or longer-
acting AV nodal blocking
agents (eg, Diltiazem,
-blockers)
10
If rhythm does NOT convert,
possible Atrial Flutter,
ectopic Atrial Tachycardia,
or Junctional Tachycardia:
Control rate (eg, Diltiazem,
-blockers; use -blockers with
caution in pulmonary disease
or CHF)
Treat underlying cause
Consider expert consultation
*Note: if patient becomes
unstable, go to Box 4.
Regular Irregular
Converts Does Not Convert
NARROW QRS*:
Is Rhythm Regular?
Does rhythm
convert?
Note: Consider
expert consultation
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- History Paper 2 IB Study GuideDocumento6 pagineHistory Paper 2 IB Study Guidersuresh1995100% (4)
- The Christian Life ProgramDocumento28 pagineThe Christian Life ProgramRalph Christer MaderazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hepatic Vein FlowDocumento14 pagineHepatic Vein FlowJORGENessuna valutazione finora
- AP WindowDocumento13 pagineAP WindowHugo GonzálezNessuna valutazione finora
- Asymetry Analysis of Breast Thermograma Using Automated SegmentationDocumento8 pagineAsymetry Analysis of Breast Thermograma Using Automated Segmentationazazel17Nessuna valutazione finora
- HR Recruiter Interview Question & AnswerDocumento6 pagineHR Recruiter Interview Question & AnswerGurukrushna PatnaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Jataka Tales - The Crane and The CrabDocumento5 pagineJataka Tales - The Crane and The Crabshahrajan2k1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Life Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementDocumento40 pagineLife Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementRuki HartawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast and Lung CancerDocumento141 pagineBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 BIRADS Mammography ReportingDocumento20 pagine02 BIRADS Mammography ReportinglPiNGUSlNessuna valutazione finora
- Pacing Week PresentationsDocumento54 paginePacing Week PresentationsjoejenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- CARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDocumento54 pagineCARDIAC CYCLE New For StudentDavi DzikirianNessuna valutazione finora
- CA Breast New ChangedDocumento72 pagineCA Breast New Changedbenak shivalingappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Braunwald Lecture Series #2Documento33 pagineBraunwald Lecture Series #2usfcards100% (2)
- 5 Steps To Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocumento2 pagine5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretationjosh082572Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocumento29 pagineElectrical Axis: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramMihaela PrisacaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Pacing CombinedDocumento54 pagineBasics of Pacing CombinedMichael Susanto100% (1)
- HBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnDocumento35 pagineHBP C315HIS Implant Procedure-eLearnRichiNessuna valutazione finora
- DR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made EasyDocumento66 pagineDR K Chan - Ecg For SVT Made Easyapi-346486620Nessuna valutazione finora
- MapseDocumento6 pagineMapseRaul GascueñaNessuna valutazione finora
- RV Dysfunction - Assessment by EchocardiographyDocumento52 pagineRV Dysfunction - Assessment by EchocardiographyNag Mallesh RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento33 pagineCoronary Artery DiseaseAlma Rifa'Ana LiskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cme Atrial FibrillationDocumento43 pagineCme Atrial FibrillationAlex Matthew100% (1)
- Start CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorDocumento2 pagineStart CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorFelicia ErikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementDocumento48 pagineAortic Stenosis:: Updates in Diagnosis & ManagementCuca PcelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart BlocksDocumento6 pagineHeart BlocksMark Hammerschmidt100% (1)
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentDocumento54 pagineDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentadela_97line100% (2)
- Study of Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Malformations by EchocardiographyDocumento23 pagineStudy of Pediatric Congenital Cardiac Malformations by EchocardiographyRana Abd AlmugeethNessuna valutazione finora
- Diastolic DysfunctionDocumento6 pagineDiastolic DysfunctionMarina SecureanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Atrial Septial DefectDocumento22 pagineAtrial Septial DefectJulie MckinneyNessuna valutazione finora
- M-Mode Echocardiography: John N. Hamaty D.O. SJHGDocumento37 pagineM-Mode Echocardiography: John N. Hamaty D.O. SJHGhirsi200518Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac SarcoidosisDocumento13 pagineCardiac SarcoidosisEmeric Jorge Macedo VendezuNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed PH.D Pharmacology and ToxicologyDocumento79 pagineAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed PH.D Pharmacology and ToxicologyPrasan Bhandari100% (1)
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Detection, Significance and TreatmentDocumento27 pagineLeft Ventricular Hypertrophy: Detection, Significance and TreatmentKudor Szabadi ZoltánNessuna valutazione finora
- EkgDocumento67 pagineEkgFendi Rafif Dad'sNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Documento24 pagineMechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Malar MannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic Root FinalDocumento82 pagineAortic Root FinalMustafa KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecg Pathology 02Documento95 pagineEcg Pathology 02Andi MP Manurung100% (1)
- Austin Journal of Clinical CardiologyDocumento15 pagineAustin Journal of Clinical CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- BradyarrthmiaDocumento73 pagineBradyarrthmiaKuba ArebaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular SonographerDocumento2 pagineVascular Sonographerapi-121643740Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prosth ValvesDocumento74 pagineProsth ValvesRavi ZoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology 2020Documento113 pagineCardiology 2020Fatima ShoukatNessuna valutazione finora
- Acls 2015Documento9 pagineAcls 2015Andy PrasetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- HUTTDocumento25 pagineHUTTdrdj14100% (1)
- Simple Office SpirometryDocumento42 pagineSimple Office SpirometryRoberto Merza III100% (4)
- Pediatric Cardiology LectureDocumento87 paginePediatric Cardiology LectureMena HashemNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis and Management of The Neonate With Critical Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento35 pagineDiagnosis and Management of The Neonate With Critical Congenital Heart Diseasemotzco0% (1)
- MVR CabgDocumento57 pagineMVR CabgRoshani sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of The AortaDocumento48 pagineDiseases of The AortaYibeltal AssefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Perioperative ArrhythmiasDocumento51 pagineManagement of Perioperative ArrhythmiasAbhishek LonikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest X - Ray InterpretationDocumento147 pagineChest X - Ray InterpretationFcsieka FcseikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Catheter Directed Thrombolysis: Gan Dunnington M.D. Stanford Vascular Conference 9/12/05Documento25 pagineCatheter Directed Thrombolysis: Gan Dunnington M.D. Stanford Vascular Conference 9/12/05Pratik SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 PrimerDocumento51 pagineTemporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 Primerwaqas_xsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultrasound EchocardiographyDocumento3 pagineUltrasound EchocardiographyDr. MLKNessuna valutazione finora
- DELNIDODocumento32 pagineDELNIDOsarwansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- HEARTDocumento14 pagineHEARTNag Mallesh RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Workout Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDocumento27 pagineECG Workout Flashcards: Atrial ArrhythmiasDima HabanjarNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging AnatomyDocumento7 pagine3 Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Anatomyjefaturaimagenologia Hospital NogalarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Congestive Heart Failure: Dr. Irwan, SPJPDocumento115 pagineChronic Congestive Heart Failure: Dr. Irwan, SPJPMuhammad Arief Budiman YSNessuna valutazione finora
- 439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG BasicsDocumento34 pagine439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG BasicsjpoutreNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrients 13 00411Documento8 pagineNutrients 13 00411ratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- Informatorium COVID-19 Indonesian FDA (English Version) EditDocumento137 pagineInformatorium COVID-19 Indonesian FDA (English Version) EditratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- The Risk of Spinal Haematoma Following Neuraxial Anaesthesia or Lumbar Puncture in Thrombocytopenic IndividualsDocumento11 pagineThe Risk of Spinal Haematoma Following Neuraxial Anaesthesia or Lumbar Puncture in Thrombocytopenic IndividualsratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- Saudi J Anaesth 2013 7 4 480 481Documento2 pagineSaudi J Anaesth 2013 7 4 480 481ratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- Zero Skin Contact Protocol.: Re-IntroducingDocumento19 pagineZero Skin Contact Protocol.: Re-IntroducingratnawkNessuna valutazione finora
- SuratiDocumento2 pagineSuratiTariq Mehmood TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Management A Focus On Leaders Plus 2014 Mymanagementlab With Pearson Etext Package 2 e Annie MckeeDocumento24 pagineSolution Manual For Management A Focus On Leaders Plus 2014 Mymanagementlab With Pearson Etext Package 2 e Annie MckeeAnnGregoryDDSemcxo100% (90)
- Jackson Et Al 2019 Using The Analytical Target Profile To Drive The Analytical Method LifecycleDocumento9 pagineJackson Et Al 2019 Using The Analytical Target Profile To Drive The Analytical Method LifecyclerbmoureNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesDocumento7 pagineCBSE Class11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesRoy0% (1)
- 5909 East Kaviland AvenueDocumento1 pagina5909 East Kaviland Avenueapi-309853346Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Consensual SpankingDocumento21 pagineAdult Consensual Spankingswl156% (9)
- Dermatome, Myotome, SclerotomeDocumento4 pagineDermatome, Myotome, SclerotomeElka Rifqah100% (3)
- ECON266 Worksheet 8Documento4 pagineECON266 Worksheet 8Oi OuNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurolinguistic ProgrammingDocumento9 pagineNeurolinguistic ProgrammingMartin MontecinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Satya Prakash Tucker Chief Secretary To GovernmentDocumento1 paginaSatya Prakash Tucker Chief Secretary To Governmentmass1984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad MedinaceliDocumento3 pagineLolita Enrico Vs Heirs of Spouses Eulogio Medinaceli and Trinidad Medinacelichatmche-06Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Week in My CountryDocumento2 pagineA Week in My CountryAQhuewulland Youngprincess HokageNarutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Note NegligenceDocumento15 pagineExam Note Negligenceengyi96Nessuna valutazione finora
- My Pitch p2Documento16 pagineMy Pitch p2api-477556951Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paleontology 1Documento6 paginePaleontology 1Avinash UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Language Processing Projects: Build Next-Generation NLP Applications Using AI TechniquesDocumento327 pagineNatural Language Processing Projects: Build Next-Generation NLP Applications Using AI TechniquesAnna BananaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asher - Bacteria, Inc.Documento48 pagineAsher - Bacteria, Inc.Iyemhetep100% (1)
- 2009-Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyDocumento37 pagine2009-Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyLeticia Bonancio CerqueiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Iml601 Week 4 AbsDocumento69 pagineIml601 Week 4 AbsNur Nazurah NordinNessuna valutazione finora
- NHÓM ĐỘNG TỪ BẤT QUY TẮCDocumento4 pagineNHÓM ĐỘNG TỪ BẤT QUY TẮCNhựt HàoNessuna valutazione finora
- 479f3df10a8c0mathsproject QuadrilateralsDocumento18 pagine479f3df10a8c0mathsproject QuadrilateralsAnand PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Ila 0306Documento11 pagineIla 0306Hong ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Second ConditionalDocumento1 paginaSecond ConditionalSilvana MiñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Trigonometric FunctionDocumento34 pagineBasic Trigonometric FunctionLony PatalNessuna valutazione finora