Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Previous IB Exam Essay Questions
Caricato da
Czesława KoniecznaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Previous IB Exam Essay Questions
Caricato da
Czesława KoniecznaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Previous IB Exam Essay Questions: Unit 1
Use these model essay question responses to prepare for essay questions on your in class tests, as well as the IB
Examination, Paper 2. These questions have appeared on recent IB examinations, exactly as shown below. Following
each question is the markscheme answer which was used to evaluate student answers on the examination paper.
1. Discuss possible exceptions to cell theory. 4 marks
skeletal muscle fibers are larger/have many nuclei/are not typical cells
fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells
unicellular organisms can be considered acellular
because they are larger than a typical cell/carry out all functions of life
some tissues/organs contain large amounts of extracellular material
e.g. vitreous humor of eye/ mineral deposits in bone/ xylem in trees/other example
statement of cell theory/all living things/most tissues are composed entirely of true cells
2. Explain how the surface are to volume ratio influences cell sizes. 3 marks
small cells have larger ratio (than larger cells)/ratio decreases as size increases
surface area/membrane must be large enough to absorb nutrients/oxygen/substances needed
surface area/membrane must be large enough to excrete/pass out waste products
need for materials is determined by (cell) volume
cell size is limited (by SA/Volume ratio)/cells divide when they reach a certain size
reference to diffusion across/through membrane/surface area
3. Outline differentiation of cells in a multicellular organism. 4 marks
differentiation is development in different/specific ways
cells carry out specialized functions/become specialized
example of a differentiated cell in a multicelluar organism
cells have all genes/could develop in any way
some genes are switched on/expressed but not others
position/hormones/cell-to-cell signals/chemicals determine how a cell develops
a group of differentiated cells is a tissue
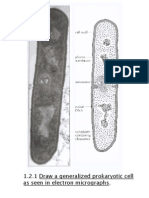
4. Draw a labelled diagram showing the structure of a prokaryotic cell 6 marks
cell wall shown clearly and labelled
cell surface membrane shown thinner than and adjacent to cell wall and labelled
cytoplasm shown with no nucleus present and labelled
ribosomes shown free in the cytoplasm and labelled
loop of DNA shown in the cytoplasm/nucleoid and labelled as DNA
plasmid shown as a small loop and labelled
slime capsule shown as a layer outside the cell wall and labelled
mesosome shown as a membrane invagination and labelled
flagellum shown and labelled (reject if shown with microtubules)
5. Draw a labelled diagram to show the organelles which are found in the cytoplasm of plant cells. 6 marks
Award 1 mark for each of the following structures accurately drawn and labelled
rough endoplasmic reticulum
free ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
mitochondrion
chloroplast
vacuole
nucleus
lysosome
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
6. State one function of each of the following organelles: lysosome, Golgi apparatus, rough endoplasmic
reticulum, nucleus, mitochondrion. 5 marks
lysosome: hydrolysis/digestion/break down of materials (macromolecules)
Golgi apparatus: synthesis/sorting/transporting/secretion of cell products
rough endoplasmic reticulum: site of synthesis of proteins (to be secreted)/ intracellular transport of
polypeptides to Golgi apparatus
nucleus: controls cells activities/mitosis/replication of DNA/transcription of DNA (to RNA)/directs protein
synthesis
mitochondrion: (aerobic) respiration/generates ATP
7. Draw a labelled diagram showing the ultra-structure of an animal cell as seen in an electron
micrograph. 6 marks
Award 1 mrak for each of the following structure clearly drawn and labelled correctly. Award marks for labelled
eukaryotic structures, then deduct 1 mark per labelled prokaryotic structure shown, e.g. mesosome, cell wall.
nuclear membrane/nucleus (with nuclear membrane shown double with pores)
ribosomes (free or attached to ER)
endoplasmic reticulum/ ER
plasma/cell membrane (reject if shown as a double line)
mitochondria (shown with inner and outer membrane)
Golgi (apparatus)
lysosomes
8. Distinguish between the structure of plant and animal cells. 6 marks
Award 1 mark per difference plant cells
have cell walls, animals do not
have plastids/ chloroplasts, animals do not
have a large central vacuole, animals do not
store starch, animal cells store glycogen
have plasmodesmata, animal cells do not
animal cells
have centrioles, plant cells do not
have cholesterol in the cell membrane, plant cells do not
plant cells are generally have a fixed shape/ more regular whereas animal cells are more rounded
9. Using a table, compare the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5 marks prokaryotic
cells eukaryotic cells
DNA naked/loop of DNA associated with protein/histones/nucleosomes/DNA in chromosomes
location of DNA in cytoplasm/nuceloid/no nucleus within a nucleus/nuclear membrane
membrane bound organelles none present
ribosomes 70S 80S
plasma membrane same structure within both groups
cell wall peptidoglycan/not cellulose/not chitin cellusose/chitin/not peptidoglycan
respiratory structures mesosomes/no mitochondria mitochondria
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Kami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsDocumento7 pagineKami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsMaxwell Modeste0% (2)
- Telekom Design - Design Thinking DoingDocumento71 pagineTelekom Design - Design Thinking DoingNitha LarazshatyNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnification QuestionsDocumento4 pagineMagnification QuestionsOmaimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution Bio Question QSDocumento64 pagineEvolution Bio Question QSKristinKrapp100% (1)
- 2.3 Carbohydrates and Lipids Assignment Key PDFDocumento4 pagine2.3 Carbohydrates and Lipids Assignment Key PDFKalpana ParikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 Biology Midterm HLDocumento31 pagineGrade 11 Biology Midterm HLSaima SyedaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-SDocumento5 pagine6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-Sapi-502781581Nessuna valutazione finora
- Previous IB Exam Essay QuestionsDocumento58 paginePrevious IB Exam Essay QuestionsDah Lin J91% (11)
- Basic SketchingDocumento62 pagineBasic SketchingRyan Risley98% (46)
- Bloody Easy Coagulation SimplifiedDocumento24 pagineBloody Easy Coagulation SimplifiedIlyasHasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - Cells: Previous IB Exam Essay Questions: Unit 2Documento4 pagineTopic 2 - Cells: Previous IB Exam Essay Questions: Unit 2ROWENA100% (2)
- Ecology QuestionsDocumento31 pagineEcology QuestionsBosco785Nessuna valutazione finora
- As Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Documento21 pagineAs Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Charity Owo100% (1)
- 2.3 Carbohydrates and LipidsDocumento42 pagine2.3 Carbohydrates and LipidsHelena GlanvilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions Topic 1.4 IB BiologyDocumento12 paginePractice Questions Topic 1.4 IB BiologySamantha DAIRONessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell TheoryDocumento65 pagineIntroduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell Theoryelvira sta.mariaNessuna valutazione finora
- DP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFDocumento6 pagineDP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFSaima SyedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Exchange Structured Questions IBDocumento9 pagineGas Exchange Structured Questions IBJohn Osborne100% (1)
- IB Biology Cells 2010Documento13 pagineIB Biology Cells 2010tr4l100% (1)
- IB BIOLOGY TOPIC 1 QuestionsDocumento3 pagineIB BIOLOGY TOPIC 1 QuestionsSarah Mason100% (1)
- Topic 1 TestDocumento11 pagineTopic 1 Testrania samirNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 5 Notes: 2 Describe The Structure of Chloroplasts in Relation To Their Role in PhotosynthesisDocumento15 pagineTopic 5 Notes: 2 Describe The Structure of Chloroplasts in Relation To Their Role in PhotosynthesisCam J BaileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure ReviewDocumento7 pagineAtomic Structure ReviewKinal PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology HL FlashcardsDocumento22 pagineBiology HL FlashcardsTiegan Blake100% (1)
- Chapter 2- Jnu Techniques in Cell and Molecular Biology - 複本Documento40 pagineChapter 2- Jnu Techniques in Cell and Molecular Biology - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuNessuna valutazione finora
- SL Biology Syllabus NotesDocumento52 pagineSL Biology Syllabus NotesRyel MuchunkuNessuna valutazione finora
- IB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawDocumento33 pagineIB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawSchuyler Huff100% (1)
- 12 Cellular Communication-SDocumento5 pagine12 Cellular Communication-SadaNessuna valutazione finora
- As Practical BookletDocumento46 pagineAs Practical BookletAndreea Maria PavelNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion Questions Ib TEST PDFDocumento8 pagineDigestion Questions Ib TEST PDFDaniela Duran80% (5)
- DNA Structure and Repliation, Transcription and Replication and PhotosynthesisDocumento67 pagineDNA Structure and Repliation, Transcription and Replication and Photosynthesisdiahema100% (1)
- Biology Edexcel IAL Unit 6 January 2022Documento24 pagineBiology Edexcel IAL Unit 6 January 2022Teresa OnfhthNessuna valutazione finora
- EDEXCEL A Level Protein SynthesisDocumento29 pagineEDEXCEL A Level Protein SynthesisKesithan AnandarashNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05Documento190 pagineBiology Unit 1 Edexcel Jan 96-June 05api-3729563100% (2)
- 4 Data-Style Questions On Plant BiologyDocumento13 pagine4 Data-Style Questions On Plant BiologyJohn Osborne100% (2)
- Unit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Documento38 pagineUnit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Olivia Panterka Vainilla100% (2)
- CHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsDocumento7 pagineCHPT 15 Genetics Practice ProblemsFatimah AliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelDocumento11 pagineSummary Notes - Topic 6 Microbiology, Immunity and Forensics - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelsalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology AQA Chapter 1 Questions and AnswersDocumento18 pagineBiology AQA Chapter 1 Questions and Answersmahamed100% (1)
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthDocumento40 pagineEdexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthEshalNessuna valutazione finora
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocumento8 pagineAs Chemistry Unit 1 NoteshamzazzNessuna valutazione finora
- IB2 Topic 1 Sept 23 - RevisionDocumento13 pagineIB2 Topic 1 Sept 23 - RevisionMr_superbNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 Membrane Transport (53 Marks) : MarkschemeDocumento20 pagine1.4 Membrane Transport (53 Marks) : Markschemelayal hashem0% (2)
- Meiosis Lab 211Documento8 pagineMeiosis Lab 211Tracy LykaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis LabDocumento9 pagineMeiosis Labpeter103958Nessuna valutazione finora
- CAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 7: Transport in PlantsDocumento6 pagineCAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 7: Transport in PlantsOtniel Dita NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- C 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsDocumento4 pagineC 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- Honors Chemistry Study Guide For Semester I Final ExamDocumento2 pagineHonors Chemistry Study Guide For Semester I Final ExamBilal QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocumento4 pagineOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis QuestionsDocumento2 pagineDiffusion and Osmosis QuestionsAlfred MwayutaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution-Classification-Mixed-Questions 1Documento12 pagineEvolution-Classification-Mixed-Questions 1JinnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Edexcel Unit 3b NotesDocumento10 pagineBio Edexcel Unit 3b NotesBd Tuntuni100% (3)
- Unit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Documento17 pagineUnit 1 Cell Biology Practice 1: (72 Marks)Rita LimNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Biology Exam QuestionsDocumento8 pagineA2 Biology Exam QuestionseyhethNessuna valutazione finora
- Ib Bio Questions Digestion WansDocumento19 pagineIb Bio Questions Digestion WansShreya DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 A2 Biology With Stafford Workbook Answers NewDocumento17 pagineUnit 6 A2 Biology With Stafford Workbook Answers NewThaai Rodriguez100% (1)
- IB Biology Notes Prokaryotic CellsDocumento4 pagineIB Biology Notes Prokaryotic CellsayushfmNessuna valutazione finora
- HL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingDocumento192 pagineHL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingFaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 1 Edexcel Notes - 15 Pages: Circulatory SystemsDocumento20 pagineBiology Unit 1 Edexcel Notes - 15 Pages: Circulatory SystemsSara EmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyDocumento55 pagineUnit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyMaha NaserNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Notes Biology AqaDocumento94 pagineUnit 5 Notes Biology Aqa李超然Nessuna valutazione finora
- IB HL Biology Notes Cell MembranesDocumento12 pagineIB HL Biology Notes Cell MembranesayushfmNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic Review 1Documento26 pagineTopic Review 1Sameer UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Zuzanna KoniecznaDocumento82 paginePortfolio Zuzanna KoniecznaCzesława KoniecznaNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Bull Style GuideDocumento14 pagineRed Bull Style GuideCzesława KoniecznaNessuna valutazione finora
- CellsDocumento11 pagineCellsCzesława KoniecznaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hitlervsmao Consolidation of PowerDocumento1 paginaHitlervsmao Consolidation of PowerCzesława KoniecznaNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Mutation Type Associated With SNPs of Black Skinned and White Skinned Snails (Archachatina Marginata) in The Rainforest Zone of NigeriaDocumento6 pagineEvaluation of Mutation Type Associated With SNPs of Black Skinned and White Skinned Snails (Archachatina Marginata) in The Rainforest Zone of NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycogen MetabolismDocumento11 pagineGlycogen MetabolismShruti MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- ExpProInNeu (Ne PDFDocumento299 pagineExpProInNeu (Ne PDFanurag_kapila3901100% (1)
- B1.2 Proteins Slides SL&HLDocumento50 pagineB1.2 Proteins Slides SL&HLraya dawodNessuna valutazione finora
- GeneDx Variant Classification Process June 2021Documento4 pagineGeneDx Variant Classification Process June 2021Liza HavengaNessuna valutazione finora
- PKB-immunology - II AntigensDocumento42 paginePKB-immunology - II AntigensSounak MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-4 GENE THERAPYDocumento65 pagineUnit-4 GENE THERAPYPratanu KayetNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper I MCQ's PhysiologyDocumento32 paginePaper I MCQ's PhysiologyMadhu RauniyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin, Diversity and Genome Sequence of Mango (Mangifera Indica L.)Documento14 pagineOrigin, Diversity and Genome Sequence of Mango (Mangifera Indica L.)Dummy MailNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Worksheet 2Documento5 pagineMitosis Worksheet 2Kaylee LewisNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocumento15 pagineA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Watson and CrickDocumento3 pagineWatson and Crickapi-282293385Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Exercise On Protein MetabolismDocumento4 paginePractice Exercise On Protein MetabolismRodriguez MiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimuliDocumento12 pagineCellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimulialaboudimuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Article 1407Documento12 pagine2019 Article 1407Paviliuc RalucaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antigen & Antibody: Dr. Hasina Banu Assistant Professor Dept - of Microbiology Ipgme&RDocumento48 pagineAntigen & Antibody: Dr. Hasina Banu Assistant Professor Dept - of Microbiology Ipgme&Rbook keedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzimologia KanekoDocumento28 pagineEnzimologia KanekoKatty Urbano OrdoñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Microbiological Methods: SciencedirectDocumento7 pagineJournal of Microbiological Methods: Sciencedirectfrancis3ndourNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantification of Demodex Folliculorum by PCR in RosaceaDocumento6 pagineQuantification of Demodex Folliculorum by PCR in RosaceaRoxana SurliuNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationDocumento29 pagineImmunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationBassem AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIDocumento53 pagine19 SYNTHESIS OF ADRENALINEADRENERGIC RECEPTORS by COL AZMAT ALIAhmed YTNessuna valutazione finora
- AGR514 Chapter 3Documento60 pagineAGR514 Chapter 3Muhamad Afif Abdul FatahNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento9 pagineUntitledmisilpiyapiyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 Cell Cycle - QuestionsDocumento6 pagineLecture 3 Cell Cycle - Questions中华雅思王Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Thomas M Devlin DownloadDocumento23 pagineTest Bank For Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Thomas M Devlin DownloadMeganGomezpizb100% (17)
- Principles of Wound HealingDocumento28 paginePrinciples of Wound HealingRafael BagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision For BioDocumento7 pagineRevision For BioJustt MeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ono Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDocumento8 pagineOno Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDaisuke OnoNessuna valutazione finora