Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Spinning Project Profile Final
Caricato da
Faizan Motiwala67%(3)Il 67% ha trovato utile questo documento (3 voti)
1K visualizzazioni23 pagineThis document provides a project profile for a proposed cotton spinning mill in Ethiopia. It includes the following key details:
- The mill will have an annual spinning capacity of 8,000 tons and be located on 30,000 square meters of land. It is designed to sell 80% of production internationally and 20% domestically.
- Market analysis shows present domestic demand is 25,414 tons annually and is projected to reach 79,760 tons by 2015, leaving 53,902 tons of unsatisfied demand. International demand is projected to leave 1,982,351 tons of unsatisfied demand by 2015.
- The project will require a total investment of 918 million Birr and create 267 jobs.
Descrizione originale:
g
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document provides a project profile for a proposed cotton spinning mill in Ethiopia. It includes the following key details:
- The mill will have an annual spinning capacity of 8,000 tons and be located on 30,000 square meters of land. It is designed to sell 80% of production internationally and 20% domestically.
- Market analysis shows present domestic demand is 25,414 tons annually and is projected to reach 79,760 tons by 2015, leaving 53,902 tons of unsatisfied demand. International demand is projected to leave 1,982,351 tons of unsatisfied demand by 2015.
- The project will require a total investment of 918 million Birr and create 267 jobs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
67%(3)Il 67% ha trovato utile questo documento (3 voti)
1K visualizzazioni23 pagineSpinning Project Profile Final
Caricato da
Faizan MotiwalaThis document provides a project profile for a proposed cotton spinning mill in Ethiopia. It includes the following key details:
- The mill will have an annual spinning capacity of 8,000 tons and be located on 30,000 square meters of land. It is designed to sell 80% of production internationally and 20% domestically.
- Market analysis shows present domestic demand is 25,414 tons annually and is projected to reach 79,760 tons by 2015, leaving 53,902 tons of unsatisfied demand. International demand is projected to leave 1,982,351 tons of unsatisfied demand by 2015.
- The project will require a total investment of 918 million Birr and create 267 jobs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 23
0
Project profile on spinning
1
Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary............................................................................................2
2. Product Description and Application.................................................................3
3. Market Study, Plant Capacity and Production Program...................................3
3.1 Market Study...................................................................................................3
3.1.1 Present Demand and Supply..........................................................................3
3.1.2 Projected Demand.........................................................................................4
3.1.3 Pricing and Distribution.................................................................................7
3.2 Plant Capacity and production capacity..........................................................8
4. Raw Materials and Utilities ..............................................................................9
4.1 Availability and Source of Raw Materials.......................................................9
4.2 Annual Requirement and Cost of Raw Materials and Utilities.....................10
5. Location and Site..............................................................................................11
6. Technology and Engineering..............................................................................11
6.1 Production Process..........................................................................................13
6.2 Machinery and Equipment .............................................................................13
6.3 Civil Engineering Cost.....................................................................................15
7. Human Resource and Training Requirement ...................................................17
8. Financial Analysis..............................................................................................18
8.1 Underlying Assumption....................................................................................18
8.2 Investment.....................................................................................................19
8.3 Production Costs.............................................................................................20
8.4 Financial Evaluation.........................................................................................21
2
1. Executive Summery
This project profile foresees the launching of a conventional cotton spinning mill with
annual spinning capacity of 8000tonnes which is located on 30,000m2 of land in Sebeta
industrial zone.
The plant is designed to sell 80 % of its product to the international market and the
remaining 20 % is for the domestic market.
The present demand for the local market estimated at 25,414 tons per annum. The
Demand is expected to reach at 79,760 tons by the year 2015.The unsatisfied
domestic market within the same year will be 53,902 tones.
It is quite clear that the international yarn market is entirely open for all developing
nations; however, we have determined the unsatisfied demand based on 5 year GTP
(Growth and transformation plan) for textile sector.
Thus the unsatisfied demand for the international market is estimated to be 1,982,351
tons by the year 2015. Hence both the local and foreign market is adequate enough to
accommodate full capacity of the plant.
The project will create employment opportunity for 267 people.
The total investment requirement is estimated at Birr 918,162,386 Birr, out of which
Birr 690,220,478 Birr is required for plant and machinery.
The project is financially feasible that it will reach breakeven point at 18% of the
capacity and has a payback period of 3 years.
3
2. Product description and application
Nowadays, out of the total demand of textile fibers about 70 % is covered by cotton.
Its widespread use is largely due to the ease with which its fibers are spun in to yarn.
Cottons strength, absorbency and capability to be washed and dyed also make it
adaptable to be a considerable variety of textile products.
Cotton yarn count can range from 6 Ne to 160 Ne depending on the end user demand.
Cotton yarns can be employed for both weaving and knitting processes.Furthermore;
cotton yarn can be sold for hand loom weavers as market yarn.
Cotton fiber, which grows in the seed pod of cotton plants, is the only one that is
useful for manufacturing of textiles. Different species of cotton plants produce fiber
of different length. Long staple fibers are spun in to fine, strong yarns, which are then
woven in to better quality fabrics. Cotton yarn can be dyed and printed easily, so that
they are useful for producing woven fabric with a multitude of colors and design.
3. MARKET STUDY AND PLANT CAPACITY
3.1 MARKET STUDY
3.1.1. Past Supply and Present Demand
Ethiopian wear traditional dresses (Ye Habesha Libse) woven by traditional weavers
made from cotton yarn. Such demand for cotton yarn in Ethiopia is met mainly from
local suppliers who spin cotton manually in a very small scale at a household level.
Moreover, currently, large numbers of newly emerging cottage industries (which are
working on diversifying, upgrading and modernizing Ethiopian traditional costumes) are
demanding large amount of cotton yarn as their major input.
The demand for cotton yarn in Ethiopia is currently met through domestic production
though the country was importing some amount in the past to fill the demand gap. The
4
local producers are two spinning plants: Adei Ababa Yarn Factory and Edget Yarn and
Sewing Thread Factor y and integrated textile mills: Akaki, Arbaminch, Awassa,
Kombolcha, Bahirdar, Almeda ,Ayka, Adama,and Dire Dawa textile factories.
The integrated mills produce yarn mainly for the consumption of their own weaving
departments to produce fabrics, while the spinning factories produce exclusively for
the hand loom sector and other consumers of marketed yarn.
Though these major spinning companies in Ethiopia have an annual installed capacity of
37,625 tons of yarn, currently they have an attainable capacity of25, 858 tons per
annum as most of the machineries are obsolete and inefficient.
The domestic production Data of Industrial cotton yarn is shown in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1 Domestic Production and Import of cotton yarn
1
Year(EC)
Domestic production
(In KG) Import (In KG) Total
Growth
Rate(%)
1996 13,774,483 2,342 13,776,825 7.6%
1997 14,812,523 14,534 14,827,057 -16.3%
1998 12,414,339 446 12,414,785 6.1%
1999 13,140,399 31,586 13,171,985 -0.8%
2000 13,033,289 34,745 13,068,034 25.0%
2001 16,291,611 38,219 16,329,830 20.0%
2002 19,549,934 42,041 19,591,974 30.0%
2003 25,414,914 46,245 25,461,159 35.0%
Production of cotton yarn has exhibited a significant growth in the past years. During
recent years the production level increases to about 25,414 tons.
1
Source central statistical Agency
5
Even though the export market is entirely open for developing nations like Ethiopia,
The export demand based on the government yarn export plan has totally unsatisfied
by current production capacity of existing plants.
Table 3.2 Export Market demand plan of cotton yarn
2
Year(EC)
Yarn Export plan
(In KG) Yarn Exported (Kg) Growth Rate (%)
1996 9,900,392 10890431 10.0%
1997 11,000,435 12100479 10.0%
1998 12,222,706 13444977 10.0%
1999 13,580,784 14938862 10.0%
2000 15,089,760 16598736 20.0%
2001 18,862,200 20748420 28.0%
2002 26,197,500 28817250 30.0%
2003 37,425,000 41167500 30.0%
Table 3.1 and 3.2 depicts that the present demand for cotton yarn both locally and
foreign market is quite big that the existing plants are unable to satisfy the cotton
yarn demand both in the country and oversees.
3.1.2. Projected Demand
As revealed by the data set in Table 3.3, cotton yarn consumption had exhibited an
average annual growth of 25% during the years 1996 to 2003. Assuming this growth
trend will increase to 30%, the future demand for cotton yarn is projected to range
from 25,461 tons in year 2003 to 593,193 tons by the year 2015. The unsatisfied local
market demand by the year 2015 is determined to be 567,338 tons assuming that the
2
Source Growth and Transformation plan
6
existing spinning capacity 25,858 tons is remained unchanged for the coming 10 years
as it is shown in table 3.3
Table 3.3 Domestic Market demand Projection
Year(EC)
Projected Demand
(In KG) Existing Capacity(Kg)
Unsatisfied
demand (KG)
2003 25,461,159 25,858,000 -396,841
2004 33,099,507 25,858,000 7,241,507
2005 43,029,359 25,858,000 17,171,359
2006 55,938,166 25,858,000 30,080,166
2007 72,719,616 25,858,000 46,861,616
2008 94,535,501 25,858,000 68,677,501
2009 122,896,151 25,858,000 97,038,151
2010 159,764,997 25,858,000 133,906,997
2011 207,694,496 25,858,000 181,836,496
2012 270,002,845 25,858,000 244,144,845
2013 351,003,698 25,858,000 325,145,698
2014 456,304,807 25,858,001 430,446,806
2015 593,196,250 25,858,002 567,338,248
As revealed by the data set in Table 3.4, cotton yarn export plan had exhibited an
average annual growth of 25% during the years 1996 to 2003. Assuming this growth
trend will increase to 30%, the future export demand for cotton yarn is projected to
range from 37,425 tons in year 2003 to 2,008,209 tons by the year 2015. The
unsatisfied local market demand by the year 2015 is determined to be 1,982,351 tons
assuming that the existing spinning capacity 25,858 tons is remained unchanged for
the coming 10 years as it is shown in table 3.4
Table 3.4 Export Market demand Projection
Year (EC) Projected Demand
Existing Capacity
(In KG)
Unsatisfied demand
(KG)
7
2003 37,425,000 25,858,000 11,567,000
2004 48,688,000 25,858,000 22,830,000
2005 74,772,000 25,858,000 48,914,000
2006 102,176,000 25,858,000 76,318,000
2007 136,077,000 25,858,000 110,219,000
2008 190,507,800 25,858,000 164,649,800
2009 266,710,920 25,858,000 240,852,920
2010 373,395,288 25,858,000 347,537,288
2011 522,753,403 25,858,000 496,895,403
2012 731,854,764 25,858,000 705,996,764
2013 1,024,596,670 25,858,000 998,738,670
2014 1,434,435,338 25,858,000 1,408,577,338
2015 2,008,209,474 25,858,000 1,982,351,474
3.1.3 Pricing and Distribution
The current factory gate price of marketed Cotton yarn is shown on table 3.5
Distribution of yarn to the domestic market is undertaken by long established
wholesalers, most of them located in 'Merkato'.
The product will find its foreign market outlets through the most reputable yarn
marketers to USA and Europe.
The envisaged plant is expected to sell its product to the whole seller at an average
price of 90.5 Birr to both local and foreign market.
Table 3.5 Price distribution
3
3
Source Textile industry development institute
8
Product Mix U/m Current price(Birr) Weight (%)
Reeled yarn Grey Ne 10 kg 64 5%
Reeled yarn Grey Ne 21 kg 75 3%
Conned Yarn Ne 20 kg 94 7%
Conned Yarn Ne 24 kg 80 40%
Conned Yarn Ne 30 kg 105 30%
Conned Yarn Ne 40 kg 125 15%
Average Price/Kg 90.5 100%
.3.2 Plant capacity and production program
3.2.1 Plant capacity
Relaying on the projected data obtained from the market, the spinning mill is
supposed to produce different kinds of yarn counts at a capacity of 25 ton/day. The
machinery technology allows it to produce product mix of ranging from 10Ne to 60Ne.
The spinning mill will work 320 days per annum and 21 days per day in 3 shifts. The
total working days in the year excludes Sundays and public holydays.
The product mix consists of both ring spun yarn and open end yarns at different
factor and counts. In the ring spun yarn categories combed yarn and carded are
inclusive.
3.2.2 Production program
9
The planned capacity cannot be achieved in the establishment year of the spinning
mill. In a period of 2 years, the plan comes to be certain. The integral reasons for
these are gradual build up in labor productivity and fine tuning of machineries. It is
estimated that production starts at 80% plant capacity in the first year and the plant
reaches its full planned capacity at the second year.
Table 3.6 Production Program
Year 1 2 3 4 and above
Capacity Utilization (%) 80 100 100 100
Operation(Tons) 6400 8000 8000 8000
4. Raw Materials and other inputs
4.1 Raw Materials
The main raw material required to produce spun yarn is lint cotton. As well known,
cotton is obtained from local cotton suppliers. Besides, most regions in the country
have the potential to grow cotton having different fines, staple length and color.
Along with cotton, different kinds of materials are used in the manufacturing of
cotton yarn. Among the materials paper cones, plastic bobbins and cops, cans and
plastic bags are very crucial for the spinning process. The total cost of these
packing materials reaches up to 3% of the total cotton cost per annum.
Table 4.1 Raw and Auxiliary materials & costs
4
4
Source Textile industry development institute
10
S/n Description U/M Qty Cost(Birr)
A. Raw material LC FC TC
1 Cotton Fiber Tone 6400 50,000 320,000,000
2 Polyester Fiber
Sub Total 320,000,000
B. Auxiliary material
1 Packing materials Tone 89.6 28,571 2,559,962
2 Jute sack(Bag) Tone 128 10,000 1,280,000
Sub Total 3,839,962
C. Miscellaneous 3,200,000
Sub Total 3,200,000
Total 327,039,962
4.2 Utilities
Electricity, fuel and water are the three major utilities required by the plant. Total
annual cost of major utility items at full operation capacity of the plant is Birr
11,477,067.Details are shown in the table below
Table 4.2 Utilities Requirement
S/N Utility Requirements (Annual) Unit price Cost(Birr)
1 Electricity 10,666,667kwh 0.55 Birr/Kwh 5,866,667
2 Fuel(Diesel Oil) 384000lt 14.50 Birr/lt 5,568,000
3 Water 16000 m3 2.65 Birr/m3 42,400
Total 11,477,067
5. Location and Site
11
Location of the plant is determined on the proximity of raw materials, availability of
infrastructure, availability of skilled man power and distance to potential market
outlet.
In view of this, the envisaged plant will be established in Oromiya regional state at
Sebeta industrial zone.
6. Technology and Engineering
6.1 Production process
Yarn manufacturing process starts with stock cleaning and mixing of ginned cotton.
After removing trash and foreign materials, the chute is transfers for further
process of intense cleaning and mixing to carding. In this condition, the material
becomes in a form of rope called carded sliver.
The carded sliver goes to drawing frames. In these processes the sliver becomes more
even and well blended. Depending on the demand of the production schedule and staple
length of fiber, the sliver obtained from the drawing frame goes to roving frame,
comber machine or open end spinning.
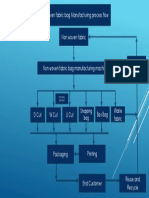
The following chart shows the process flow in the envisaged spinning mill
12
Open End
Combing
Drawing
Cotton mixing
Blow room
Carding
Winding
Combed yarn
Open End Yarn
Drawing
Winding
Ring frame
Carded Yarn
Roving
Ring Frame
Roving
13
6.2 Sources of Technology
Mostly European technologies are better to be considered as source of technology for
establishing spinning mill. Especially, Germany, Switzerland and Italy are the prime
suppliers of yarn manufacturing technology and spinning machines. Among these
machineries Marzoli, Rieter, Trutzchler, Lakshmi and other brands have the reputation
to be the best choice for the source of technology for the spinning plant. For air
conditioning equipments Luwa, Switzerland is chosen.
6.3 Engineering
Machinery and equipment the required cotton spinning machineries and equipments for
the project are listed in the table 6.1
The machinery capacity is selected in a way that it could produce 25 tons/day without
bottle necks along the production line.
The total cost of machinery and equipment is estimated at Birr 690 million, out of
which 685 million Birr will be required in foreign currency.
Air conditioning equipments are needed for production of all preparatory section (such
as blowing room, carding room, roving frame room and ring frame room), pinning section
and yarn finishing sections. Proper air blowing and ducting lines have to be installed for
appropriate operation in the spinning mill.
14
Table 6.1 Machinery and Equipment requirement & Cost for spinning Mill
5
S/N Description Brand Origin U/M Qty
Price(Birr)
U/p(Birr) TC(Birr)
1 Blow room Equipments Trutzchler Germany Set 1 15,102,096 15,102,096
2 High speed card Reiter Swizerland pcs 8 41,588,128 332,705,024
3
High speed Draw Frame
Breaker Reiter Swizerland pcs 3 1,440,873 4,322,620
4
High speed Draw Frame
Finisher Reiter Swizerland pcs 3 1,440,873 4,322,620
5 Roving Frame Sussean Swizerland pcs 4 22,732,630 90,930,520
6 Ring Frame 1000 spindle Reiter Swizerland pcs 13 5,320,524 69,166,812
7 Auto Conner 100spd Murata Japan pcs 7 4,000,000 28,000,000
8 Doublers 120spd Murata Japan pcs 2 2,113,100 4,226,200
9 Twisters 160spd Murata Japan pcs 2 1,536,800 3,073,600
10 Lap former Reiter Swizerland pcs 2 5,306,973 10,613,946
11 comber Reiter Swizerland pcs 4 8,189,260 32,757,040
12
Open end rotor spinning 500
spd Orlicon Germany pcs 3 4,500,000 13,500,000
13 Reeling Toyoda Japan pcs 10 200,000 2,000,000
14 Cotton weighing machine Japan pcs 2 100,000 200,000
15 Spinning Laboratory equipment Uster Swizerland Set 1 4,300,000 4,300,000
16 Steam Generation unit 1 ton/hr Loose Germany pcs 1 500,000 500,000
17 Air conditioning Luwa Swizerland set 1 40,000,000 40,000,000
17 Compressor GA 50 Atlascopco Belgium pcs 3 1,000,000 3,000,000
18 Water treatment Spirox Germany set 1 4,500,000 4,500,000
19 Fire Fighting plant Iveco Italy Set 1 10,000,000 10,000,000
20 Electric power plant Siemens Germany set 1 5,000,000 5,000,000
21
Stand by Electric power
Generator Caterpilar USA pcs 2 500,000 1,000,000
22 Mechanical Workshop Italy set 1 1,000,000 1,000,000
23
Electrical and Electronic
workshop Siemens Italy set 1 1,000,000 1,000,000
24 Miscellaneous set 1 4,000,000 4,000,000
FOB Price 185,371,258 685,220,478
Freight, Insurance, customs &
Bank charges, Material
handling cost 5,000,000 5,000,000
Total CIF Land cost 690,220,478
5
Source Machinery Manufacturers catalogue
15
6.3. Land, building and civil work
As is the same with all other investment activities, there are four main ingredients for the
realization of the project under study and fulfillment of all without exemption of one another
is mandatory. There are capital labor, land and entrepreneur skill. Some amount of capital will
be injected from the pockets of the promoters who also has ample experience and
entrepreneur skill some amount of capital will be injected from the bank
The labor force (i.e. skilled semi skilled and unskilled) is readily available in the labor market
currently operational Institution providing specialized education in specific production or
services machine operation, and the like will be instrumental in the supply of the required labor
force. The only remaining constraint to the realization of the project under study will be land.
The construction and implementation of the project and to the supplemental facilities
indicated in the above section of this paper will required a minimum of 40,000 meter square of
land. The location of the land is already identified to be at Sebeta wereda in Sebeta town
location adjacent to Jimma road which is to the left of the main road. The location is easily
accessible for all sorts of infrastructure including roads transport electricity, telephone line,
water etc.
The regional government of Oromia is already preparing plots in these areas for possible
takeover by perspective investor, and expects to benefit from this opportunity in order to
materialize the project under study..
If the promoter of this project gets the land 12birr/ m2 then the total land cost will be birr
28,800,000 out of this amount 10% down payment birr 2,880,000 will be paid . The remaining
balance will be paid within 40 years after the end of grace period. The total investment cost
for land, building and civil works will be 120 million birr.
16
7. Man power and training requirements
7.1 Man power requirement for operation
Table 7.1 below, shows the list of manpower required along with annual labor cost.
Total manpower needed, including skilled and unskilled labor is 267 persons.
Table 7.1 Man power Requirement of spinning mill and Annual labor cost
S/N Description Req No Monthly salary Annual salary
1 Factory Manager 1 9,000 108,000
2 Secretary 1 3,000 36,000
3 Production and Tech Manager 1 7,500 90,000
4 Production Head 1 6,000 72,000
5 Maintenance head 1 6,000 72,000
6 Shift Leader 4 4,000 192,000
7 Production supervisor 4 3,500 168,000
8 Mechanical maintenance supervisor 1 3,500 42,000
9 Elecrical Supervsor 1 3,500 42,000
10 Machine Operators 171 800 1,641,600
11 Mechanic 10 1,300 156,000
12 Electrician 5 1,300 78,000
13 Doffing gangs 14 600 100,800
14 Quality and Laboratory manager 1 7,500 90,000
15 Process testers 6 2,000 144,000
16 Marketing Manager 1 7,500 90,000
17 Adminstration and Finance manager 1 7,500 90,000
18 Acountant 3 5,000 180,000
19 Clerks 3 1,000 36,000
20 Cashier 1 1,200 14,400
21 Purchasers 1 1,500 18,000
22 Store Keepers 4 1,000 48,000
23 Guard 7 700 58,800
24 Messenger and cleaner 1 600 7,200
25 Driver 3 800 28,800
26 Cleaner 20 600 144,000
Sub Total 3,747,600
Employee Benefit( %) 15% 562,140
Grand Total 267 4,309,740
17
7.2 Man power requirement for Project execution
Table 7.2 below, shows the list of manpower required along with annual labor cost.
Total manpower needed, including skilled and unskilled labor is 40 persons.
Table 7.2 Man power Requirement of spinning mill project
S/N Description Req. No
Monthly
salary/head Annual salary
1 Project Manager 1 15,000 180,000
2 Project Engineer (Civil) 1 10,000 120,000
3 Project Engineer (Mechanical) 1 10,000 120,000
4 Project Engineer (Electrical) 1 10,000 120,000
5 Process Engineer(Textile) 1 10,000 120,000
6 Construction Forman 1 6,000 72,000
7 Electrician 4 4,000 192,000
8 Mechanics and Plumbers 6 4,000 288,000
9 Secretary 1 3,000 36,000
10 Finance and Administration 1 10,000 120,000
11 Accountant 1 7,000 84,000
12 Purchaser 1 5,000 60,000
13 Cashier 1 1,500 18,000
14 Daily Laborer 12 2,000 288,000
15 Driver 1 1,000 12,000
16 Guard 6 1,000 72,000
Sub Total 1,902,000
Employee Benefit( %) 30% 570,600
Grand Total 2,472,600
18
7.3 Training, Design and Consultancy
The total cost required for design, consultancy, training and commissioning is
estimated to be 10 million birr.
Table 7.3 Design, consultancy ,training and test run cost
S/N Description Est. Budget/year(Birr)
1 Engineering, Design & consultancy fee 4,000,000
2 training 2,000,000
3 Commissioning and test run with 10% contingency 4,000,000
4 Total 10,000,000
8. Financial Analysis
8.1 Underlying Assumption
The financial analysis of cotton yarn producing plant is based on the data provided in
the preceding chapters and the following assumptions
A. Construction and Finance
Construction period 1 year
Source of Finance 30% equity and 70% Loan from bank
Tax Holidays 5 years
Bank Interest rate 8.50%
Discount for cash flow 8.50%
Value of Land Based on the lease rate of Oromiya
Spare parts & Repair and Maintenance 5% of the fixed investment
19
B. Depreciation
Building 5%
Machinery and Equipment 10%
Office Furniture 10%
Vehicles 20%
Pre-Production(Amortization) 20%
C. Working Capital(Minimum day of coverage)
Raw Material Local 30 days
Raw Material Foreign 120 days
Factories supplies in stock 30 days
Spare part in stock and Maintenance 60 days
Work in Progress 5 days
Finished Product 20 days
Account receivable 30 days
Cash in Hand 20 days
Accounts payable 30 days
8.2 Investment
The investment cost of the project including working capital is estimated at Birr 918 million.
The owner shall contribute 30% of the finance in the form of equity while the remaining 70%
is to be financed by bank loan.
20
Table 8.1 Total initial investment
Item LC FC Total
Land 2,880,000 2,880,000
Building and Civil Work 118,000,000 118,000,000
Office Equipment 8,000,000 8,000,000
Vehicles 6,000,000 6,000,000
Plant machinery and equipment 690,220,478 690,220,478
Total Fixed investment cost 822,220,478 822,220,478
Pre-Production(Capital Expenditure) 12,472,600 12,472,600
Total initial investment cost 834,693,078 834,693,078
Working capital at full capacity 83469307.8 83,469,308
Total 86,349,308 834,693,078 918,162,386
8.3 Production Cost
The total production cost at full capacity operation is estimated at Birr 514 million.
raw material and utilities accounts for 80%.while repair and maintenance costs 5% of
the raw material cost.
Table 8.2 Production cost at Full capacity
Raw material Requirement Cost
1.Local raw material 408,799,951
2.Foreign raw material
Total 408,799,951
21
Table 8.3 Total Production cost at full capacity
Items Cost
1. Raw Material 408,799,951
2.Utilities 11,477,067
3.Wages and salaries 4,309,740
4.Spares and Maintenance 34511023.9
Factory Cost 459,097,782
5. Depreciation 44,905,544
6.Misclenous 10,300,000
Total Production cost 514,303,326
8.4 Financial Evaluation
I. Profitability
According to the projected income statement (See Annex 1) the project will generate
profit beginning from the second year of operation and increases on wards. The income
statement and other profitability indicators also show that the project is viable.
II. Breakeven Analysis
The breakeven point of the projects is given by the formula:
BEP = Fixed Cost
Sale Variable Cost at full capacity.
The project will break even at 18.5 % of capacity utilization
III. Payback Period
Investment cost and income statement projection are used in estimating the project
payback period. The projects will payback fully the initial investment less working
capital in three years.
22
9. Economic and Social Benefits and Justification
Based on the foregoing presentation and analysis, we can learn that the proposed
project possesses wide range of benefits that complement the financial feasibility
obtained earlier. In general, the envisaged project promotes the socio-economic goals
and objectives stated in the growth and transformation plan of the government.
A. Profit Generation
The project is found to be financially viable and earns on average a profit of Birr
280million per year and Birr 25.2 million within the project life. Such result induces
the project promoters to reinvest the profit which, therefore, increases the
investment magnitude in the country.
B. Tax Revenue
In the project life under consideration, the region will collect about Birr 800 million
from corporate income tax. Such result create additional fund for the government
that will be used in expanding social and other basic services in the region.
C. Employment and Income Generation
The proposed project is expected to create employment opportunity to several
citizens of the country. That is, it will provide permanent employment to 60
professionals as well as support stuffs.
D. Pro Environment Project
The proposed production process is environment friendly.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Microsoft Access Database TemplatesDocumento3 pagineMicrosoft Access Database TemplatesFaizan Motiwala0% (2)
- Stock Sentiment IndicatorDocumento14 pagineStock Sentiment IndicatorNihit VarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- MITC Credit CardDocumento11 pagineMITC Credit CardAbhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Wrigley Gum 21Documento18 pagineWrigley Gum 21Fidelity RoadNessuna valutazione finora
- IIBF - FIMMDA - Certified Treasury Dealer PDFDocumento16 pagineIIBF - FIMMDA - Certified Treasury Dealer PDFAshish mNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance Schedule For Gas Genset - GE JENBACHERDocumento5 pagineMaintenance Schedule For Gas Genset - GE JENBACHERrajputashi92% (12)
- Investment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Leather Garment Making PlantDocumento26 pagineInvestment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Leather Garment Making PlantJohn100% (1)
- Sole PropritorshipDocumento6 pagineSole Propritorshipacharla55490% (1)
- SMEDA Absorbent CottonDocumento22 pagineSMEDA Absorbent CottonManohar Waghela100% (2)
- Gentsshirtsandtrousers PDFDocumento12 pagineGentsshirtsandtrousers PDFwwwaqarNessuna valutazione finora
- Usufruct ReviewerDocumento6 pagineUsufruct ReviewerAizaFerrerEbinaNessuna valutazione finora
- SMEDA Fabric Dyeing & Finishing Unit (Knit Fabric)Documento27 pagineSMEDA Fabric Dyeing & Finishing Unit (Knit Fabric)Nisar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Flow Chart of Garments ManufacturingDocumento3 pagineProcess Flow Chart of Garments ManufacturingMahNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Policy and Strategic ManagementDocumento89 pagineBusiness Policy and Strategic Managementanmol100% (1)
- Plant Layout Group C 2019Documento27 paginePlant Layout Group C 2019Mukarram Ali KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Corpo Second Exam TSN ShortDocumento77 pagineCorpo Second Exam TSN ShortChay GorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Men's Readymade GarmentsDocumento5 pagineMen's Readymade Garmentsmorshed.mahamudNessuna valutazione finora
- PRNCaseStudiesBook PDFDocumento21 paginePRNCaseStudiesBook PDFDiana Teodora ȘtefanoviciNessuna valutazione finora
- Gents T-Shirts: NtroductionDocumento8 pagineGents T-Shirts: Ntroductionharish_kavetiNessuna valutazione finora
- HomeDesignTrendsVol3No2 PDFDocumento158 pagineHomeDesignTrendsVol3No2 PDFAngel VelezNessuna valutazione finora
- Costing For A Spinning Mill PDFDocumento13 pagineCosting For A Spinning Mill PDFyogesh kumawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Corn Flakes Producing PlantDocumento27 pagineInvestment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Corn Flakes Producing PlantTESFALEWATEHE100% (1)
- Textile InternshipDocumento42 pagineTextile InternshipNutukurthi Venkat RamjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Getachew Alewi 2Documento52 pagineGetachew Alewi 2Birhanu Alemu0% (1)
- Spinning MillDocumento6 pagineSpinning MillAnand Arumugam0% (1)
- Surgical Bandages: Profile No.: 35 NIC Code: 21006Documento12 pagineSurgical Bandages: Profile No.: 35 NIC Code: 21006Bhagwan MatreNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Machinery and Their Functions of Apparel Industry PDFDocumento2 pagineList of Machinery and Their Functions of Apparel Industry PDFzeeshan umer100% (1)
- Cotton Yarn Project ProfileDocumento20 pagineCotton Yarn Project ProfilesajidaliyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Report On Spinning Sector of Bangladesh-InitiationDocumento24 pagineResearch Report On Spinning Sector of Bangladesh-InitiationjohnsumonNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Absorbent Cotton Making PlantDocumento29 pagineInvestment Office ANRS: Project Profile On The Establishment of Absorbent Cotton Making Plantabel_kayelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gauze and BandageDocumento25 pagineGauze and BandageGowri SankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Inner FabricsDocumento19 pagineInner Fabricsabel_kayelNessuna valutazione finora
- Sergical Absorbent CottonDocumento11 pagineSergical Absorbent Cottonzeine100% (1)
- A Project On The Spinning Industry of India: BY Deepak Luniya Roll No: 290Documento45 pagineA Project On The Spinning Industry of India: BY Deepak Luniya Roll No: 290deepakluniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonwoven Bags Project Report DubaiDocumento54 pagineNonwoven Bags Project Report Dubaisugaimpax80% (10)
- Pre-Feasibility Study: S O C K S M ANU F Actur I NG UnitDocumento20 paginePre-Feasibility Study: S O C K S M ANU F Actur I NG UnitAbid Bari GorayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorbent Cotton Manufacturing UnitDocumento19 pagineAbsorbent Cotton Manufacturing UnitIbrahim MunirNessuna valutazione finora
- Textile Traning ReportDocumento62 pagineTextile Traning ReportSanjeev Singh0% (1)
- Corrugated Paper BoxDocumento13 pagineCorrugated Paper BoxhibadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Relience Weaving Mills LTDDocumento82 pagineRelience Weaving Mills LTDMuhammad Fahim Khan80% (5)
- Alok IndustriesDocumento37 pagineAlok IndustriesHitesh Kumar100% (1)
- Garment Industry 1Documento28 pagineGarment Industry 1Mega MegalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic RopesDocumento6 paginePlastic RopesSamy VishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ProjectDocumento77 pagineFinal ProjecttrainingandplacementNessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton Ginning Plant OperatorDocumento18 pagineCotton Ginning Plant Operatorsapphire207100% (1)
- Non Woven Bag Word 1Documento11 pagineNon Woven Bag Word 1Bhimsen100% (1)
- Denim Jeans Stitching UnitDocumento25 pagineDenim Jeans Stitching UnitSaad NaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- Lucky TextileDocumento5 pagineLucky TextileSaim Bin RashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandpaper Project ProfileDocumento15 pagineSandpaper Project ProfileTekeba Birhane100% (3)
- The Impact of Energy Crisis On Textile SectorDocumento4 pagineThe Impact of Energy Crisis On Textile SectorAymen SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Report On Gohar TextileDocumento107 pagineInternship Report On Gohar Textilesiaapa60% (5)
- Industrial Attachment On Hams Washing & Dyeing Ltd.Documento103 pagineIndustrial Attachment On Hams Washing & Dyeing Ltd.Jahid Hossain Maruf100% (2)
- Garment Project Profile FinalDocumento36 pagineGarment Project Profile Finalshivling100% (2)
- Project Report On Knit Product DevelopementDocumento46 pagineProject Report On Knit Product Developementoliveahamed100% (1)
- Feasibility Report of New BusinessDocumento10 pagineFeasibility Report of New BusinessFabihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Utkal Non Woven Fabric Bag Manufacturing Process Flow Non Woven FabricDocumento1 paginaUtkal Non Woven Fabric Bag Manufacturing Process Flow Non Woven FabricsatyabannayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Grain Bag Manufacturing Feasibility StudyDocumento53 pagineGrain Bag Manufacturing Feasibility StudyCalvawell MuzvondiwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton Ginning Male-2Documento32 pagineCotton Ginning Male-2Tesfaye DegefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Woven Bags-Project ProfileDocumento6 pagineWoven Bags-Project ProfileBalas43100% (2)
- IshaqTextile MillDocumento14 pagineIshaqTextile MilladeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Relience Weaving Mills LTD 2015Documento30 pagineRelience Weaving Mills LTD 2015haidersarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Training Project of Textile Industry"manjinder Singh"Documento89 pagineSummer Training Project of Textile Industry"manjinder Singh"manjinder1933% (3)
- Topic: "A Study On Productivity Efficiency of Textile Industry of India"Documento5 pagineTopic: "A Study On Productivity Efficiency of Textile Industry of India"Divya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Compiled Thematic AreasDocumento60 pagineCompiled Thematic Areasalene100% (4)
- Internship Report On Concepts of Modern Merchandising Tools and Techniques in Sweater (Woolen & Wool LTD) Industry.Documento130 pagineInternship Report On Concepts of Modern Merchandising Tools and Techniques in Sweater (Woolen & Wool LTD) Industry.RahatSaifNessuna valutazione finora
- Profile On Production of Jute BagsDocumento20 pagineProfile On Production of Jute BagsM A Akad MasudNessuna valutazione finora
- Knitted Fabrics ClothesDocumento16 pagineKnitted Fabrics Clotheskathirvelus9408Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton YarnDocumento29 pagineCotton YarnThomas MNessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton GinningDocumento18 pagineCotton GinningRushlan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Finished LeatherDocumento22 pagineFinished LeatherMartha Getaneh100% (1)
- Cotton Fibre Quality ResearchDocumento11 pagineCotton Fibre Quality ResearchprabhjotseehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cotton YarnDocumento26 pagineCotton YarnAbebaw SirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorbent CottonDocumento27 pagineAbsorbent CottonTrầnChíTrungNessuna valutazione finora
- Custom Tambola Housie Tickets PDFDocumento5 pagineCustom Tambola Housie Tickets PDFFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Post TestDocumento7 paginePre Post TestFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-25 BINGO: Safety First!Documento17 pagine1-25 BINGO: Safety First!Faizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Limiting Factor AnalysisDocumento5 pagineLimiting Factor AnalysisFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- CMA Positions: Dawn Sunday October 11, 2015 - Page 4Documento27 pagineCMA Positions: Dawn Sunday October 11, 2015 - Page 4Faizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jumbo Touch Remote ImDocumento18 pagineJumbo Touch Remote ImFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBE Shedule Quarterly Winter 2015 FinalDocumento1 paginaCBE Shedule Quarterly Winter 2015 FinalFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Et Set 4 Update 14 ScreenDocumento2 pagineEt Set 4 Update 14 ScreenFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ets Ust 3 Update 14 ScreenDocumento2 pagineEts Ust 3 Update 14 ScreenFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chairman's Message: Frequently Asked Questions On The Code of Corporate Governance (Revised)Documento26 pagineChairman's Message: Frequently Asked Questions On The Code of Corporate Governance (Revised)Faizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- LCMPL AdDocumento1 paginaLCMPL AdFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management IsDocumento6 pagineOperations Management IsFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineFormula SheetFaizan Motiwala100% (1)
- Sohail ResumeDocumento2 pagineSohail ResumeFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sohail ResumeDocumento2 pagineSohail ResumeFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Movie ListyDocumento1 paginaMovie ListyFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Human Resource ManagementDocumento34 pagineManaging Human Resource ManagementFaizan MotiwalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Anholt Editorial - Editor's Foreword To The First IssueDocumento8 pagine1.1 Anholt Editorial - Editor's Foreword To The First IssueGabriela EpureNessuna valutazione finora
- AshokaDocumento16 pagineAshokaManjesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AKD ResearchDocumento10 pagineAKD ResearchjibranqqNessuna valutazione finora
- Aslan Corporation BenefitDocumento1 paginaAslan Corporation BenefitMax CevioNessuna valutazione finora
- IFBPDocumento11 pagineIFBPmohanraokp2279Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fins 2624 Quiz 1Documento3 pagineFins 2624 Quiz 1sagarox7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Standalone Financial Results, Limited Review Report For December 31, 2016 (Result)Documento3 pagineStandalone Financial Results, Limited Review Report For December 31, 2016 (Result)Shyam SunderNessuna valutazione finora
- FCCBDocumento20 pagineFCCBHitesh MulaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 4 Intermediate Term FinancingDocumento17 pagineChapter - 4 Intermediate Term FinancingMuhammad D. Hossain Mak33% (3)
- ICE Cotton BrochureDocumento6 pagineICE Cotton BrochureAmeya PagnisNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 1 FMDocumento26 pagineCHAPTER 1 FMZati TyNessuna valutazione finora
- College of St. John - Roxas: Flexible Learning Plan Course Syllabus A.Y 2021-2022Documento6 pagineCollege of St. John - Roxas: Flexible Learning Plan Course Syllabus A.Y 2021-2022Miles SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Itm 11. Interpreneureship With Fundamentals of CooperativeDocumento20 pagineItm 11. Interpreneureship With Fundamentals of Cooperativelaliy palaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- IBPS Clerk Prelimsl Previous PaperDocumento26 pagineIBPS Clerk Prelimsl Previous PapershakthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 For Qawid Fiqqiyah Article PDFDocumento8 pagineChapter 3 For Qawid Fiqqiyah Article PDFkhalidcarabNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical Roller Mill UpgradeDocumento2 pagineVertical Roller Mill UpgradeBülent BulutNessuna valutazione finora
- Margaret A. Cargill Philanthropies - Program Officer, Aging ServicesDocumento6 pagineMargaret A. Cargill Philanthropies - Program Officer, Aging ServicesLars LeafbladNessuna valutazione finora
- PAMI Asia Balanced Fund Product Primer v3 Intro TextDocumento1 paginaPAMI Asia Balanced Fund Product Primer v3 Intro Textgenie1970Nessuna valutazione finora
- Investinournewyork BillionairepandemicprofitDocumento9 pagineInvestinournewyork BillionairepandemicprofitZacharyEJWilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Warren Larsen Chp1 (Principles of Accounting)Documento147 pagineWarren Larsen Chp1 (Principles of Accounting)annie100% (1)