Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B - SAS Functional Description For CCR Rev1
Caricato da
kytongTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B - SAS Functional Description For CCR Rev1
Caricato da
kytongCopyright:
Formati disponibili
We reserve all rights in this document and in the information contained therein.
Reproduction, use or disclosure to third parties without express authority is strictly forbidden.
Copyright 2013 ABB
FORMOSA HA TINH STEEL CORPORATION
FORMOSA CHEMICALS & FIBRE CORPORATION ENG. & UTILITY DIVISION
Document Code : AHS-PS32-1402-B
CUSTOMER :
FORMOSA CHEMICALS & FIBRE CORP.
PROJECT :
HA-THINH STEEL PLANT PROJ ECT VIETNAM
220KV SUBSTATIONS
B 2013-07-04 SL SL SL
Rev Date Prepared /
Revised
Checked Approved Note / Detail of Revision
Prepared :S.Lemmerann Based on : / Replaces :
AHS-PS32-1402-A
Sep.PL same No.
Without separ. PL
Scale : Doc.Type : Format :
Sep. PL anoth. No.
NA A4
Checked :S.Lemmermann Responsible department : PSSA-P Title :
SAS functional description for CCR
Approved : M.Gnter Take over department : NA Language :
EN
R
e
v
i
s
i
o
n
:
1 2013-07-04/SL No Sheets :
34
ABB Switzerland Ltd.
Document Number : 1KHF334933
Sheet No :
1
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved.
Customer doc. no.
-
Based on -
Customer
FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Prepared Lemmermann 2012-01-07
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Approved M.Gnter 2012-01-07
Order
16234
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Ref.
des.
-
Resp. dept.
PSSA-P
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
1
ABB Switzerland Ltd 1KHF334933 EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Main contractor ABB CH - PSSS
Order 16234
Plant Ha Thinh Steel Plant - PPCCR
Equipment Substation Automation - mSCADA
Title SAS functional description for CCR
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
2
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Index
1. Preface ....................................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Contents of this document .............................................................................................. 3
1.2 Target group of readers .................................................................................................. 3
1.3 Definitions and Abbreviations ......................................................................................... 3
2. Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Scope of this document .................................................................................................. 5
2.2 Application Area ............................................................................................................. 5
2.3 System Description ......................................................................................................... 6
3. System Architecture ................................................................................................................. 8
3.1 System Hierarchy ........................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Communication system to PMS, EC and EVN Control Center (on hold by
customer) ...................................................................................................................... 11
4. Functional Description ........................................................................................................... 12
5. Hardware and Software Components ................................................................................... 13
5.1 Front End ...................................................................................................................... 13
5.2 Operator Workstation ................................................................................................... 15
5.3 Engineering Notebook .................................................................................................. 17
5.4 Training Workstation ..................................................................................................... 17
5.5 Simulation Workstation ................................................................................................. 18
5.6 Gateway ....................................................................................................................... 22
5.7 Video wall ..................................................................................................................... 23
5.8 Ethernet Switch ............................................................................................................ 23
5.9 Peripheral devices ........................................................................................................ 24
7. Appendix: Fiber Optic Cable Specification .......................................................................... 27
7.1 Fiber Optic Components ............................................................................................... 27
7.2 Standard Wavelengths ................................................................................................. 28
7.3 Fiber Optic Standards ................................................................................................... 28
7.4 Fiber Optic Cables inside cubicles ............................................................................... 29
8. Revision ................................................................................................................................... 33
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
3
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
1. Preface
1.1 Contents of this document
The purpose of this Document is to describe the implemented functions of the SAS station
mentioned in the first page of this document. All pictures and examples, which are shown,
are of general manner, but cover all the needs.
1.2 Target group of readers
This functional description is intended for customer to see which functions are
implemented in his SCMS system, where to find it and how to use it.
1.3 Definitions and Abbreviations
The following table is a list of abbreviations and acronyms used in this document. Product
names are not taken into this list.
ACP Application Communication Protocol
CD-ROM Compact disk - read only memory
CE Certified standard: The device conforms to the
directive 89/336/EWG on the approximation of the
law of the member states of the European
Community relating to electromagnetic compatibility.
COM Serial interface
CPU Central processor unit
DCS Digital Control System
DDE Dynamic Data Exchange
DOI Double Operating Interlock
FBS Fall-Back Switch
FUPLA Function Plan Programming Language for the ABB
IEDs
GIS Gas Insulated Switchgear
GPS Global Positioning System
HSB Hot Stand-By
IED Intelligent Electronic Device
IP Ingress Protection standard IEC60529
ISA Industrial Standard Architecture
LDC Load Dispatch Centre
LAN Local Area Network
MicroSC
ADA Pro
Version of the base software, on which the SAS
application is developed
HMI Man machine program for ABB IEDs
MMI
MMS Manufacturing Message Specification
ISO 9506-1 and ISO 9506-2
NCC Network Control Centre
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
4
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
NIC Network Interface Card
NV Network Variable
ODBC Open Database Communication/Connectivity
OLE Object Linking and Embedding
OPC OLE for Process Control
PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association
PC-NET Communication software for personal computers
RAM Random Access Memory
RAS Remote Access Service
RCC Remote Control Centre
RDBMS Relational Database Management System
RTU Remote Terminal Unit
SA Substation Automation
SAS Substation Automation System
SCIL Supervisory Control Implementation Language
SQL Structured Query Language
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol
TCS Tap change Control and Supervision
UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply
PPCCR Power Plant Control Center Room
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
5
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
2. Introduction
2.1 Scope of this document
The Substation Automation System (SAS) functional description presents the design,
functions, features and facilities of the SAS system.
This functional description is intended to provide an overview of the functions which are
implemented in the SA system. For more detailed information and specifications, consult
the Data Sheets of the relevant product. The software or hardware described in this
document is furnished under a license and may be used, copied, or disclosed only in
accordance with the terms of such license.
SAS built in PPCCR is a mirrored system of the 4 substations ESP01, ESP02, ESM01
and ESH01. Means that functionality will be same as in local Micro SCADA system
Therefore this document will reference at several points to functional descriptions of local
Micro SCADA at substations.
Project specific pictures will be submitted for approval at detail engineering phase for
substations ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01 as appendix.
2.2 Application Area
The substation automation system SAS600 Series is designed for controlling and
monitoring the primary and secondary equipment of a substation. Typical applications are
substations for power utilities on
distribution,
sub-transmission,
high-voltage transmission
extra high voltage transmission
new installations and refurbishment of existing substations
gas and air-insulated switchgear
The SAS600 series solutions for substation automation are based on and fully compliant
with IEC61850. They provide the communication and integration of ABB's bay control and
bay protection solutions (BCS6xx and BPS6xx), all the station level functions and as an
option the remote link to e.g. a network control center.
The SAS provides an extensive range of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
(SCADA) functions.
Control and supervision of switching devices, transformers, etc.
Bay and station interlocking
Current, voltage, frequency and power measurement
Alarm functions, storage and evaluation of events
Time synchronization of the system
User management
Disturbance recording and evaluation
Serial connection to all numerical relays
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
6
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
2.3 System Description
The SAS600 series are state-of-the art solutions based on IEC61850 for operation under
electrical conditions present in high-voltage substations, follow the latest engineering
practice, ensure long-term compatibility requirements and continuity of equipment supply
and the safety of the operating staff.
The system is designed in such a way that personnel without any background knowledge
in microprocessor-based technology are able to operate the system easily after having
received some basic training.
Cubicles that incorporate the control, monitoring and protection functions provide self-
monitoring, signaling and testing facilities, measurement as well as memory functions,
event recording and disturbance recording. The basic control functions are derived from a
modular standardized and type-tested software library.
Maintenance, modification or extension of components does not cause a shut down of the
whole substation automation system. Self-monitoring of single components, modules and
communication is incorporated to increase the availability and the reliability of the system
and minimize maintenance.
Protection and control devices are freely adaptable to the required application
functionality.
The SAS conforms fully to the IEC61850 standard and has a decentralized architecture
consisting of the following main hardware components:
Application server and Human Machine Interface (HMI)
Managed switched fiber-optic Ethernet LAN in a fault tolerant ring architecture
Gateway for remote communication to Remote Control Centre (RCC) and / or
National control Center (NCC), communicating for example on IEC 60870-5-101
protocol
Dot matrix printer (DMP) for alarms and events
Laser printer for printing graphics and reports
GPS receiver per station to synchronize the time of SAS including the IEDs.
IEDs for bay and station protection
IEDs for bay control and monitoring
Disturbance Recorder (DR) evaluation workstation
Multi-Meters and energy meters for measurement report
The basic functions / features of a Substation Automation System are listed below:
Supervision and control of switching devices, transformers, tap changers and other
controllable primary equipment
Local as well as remote control of the substation switching devices
Safety checks, station and bay interlocking
Time synchronization of the SA system
Current, voltage, frequency and power measurement
System supervision of the secondary and station level devices
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
7
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Alarm functions, storage and evaluation of events, blocking lists
Time scheduled activities
User management
Optional advanced functions provided in the SAS are:
Trend recording and storage
Measurement reports
IED parameterization
Disturbance recording, upload and analysis
Trip counter table
Dynamic busbar coloring
Perform auto electrical billing calculation
The above in this chapter describes in general the possible features of SAS600 series,
which will be implemented in ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01. SAS built in PPCCR is
a mirrored system of the 4 substations. Means that functionality will be same as in local
Micro SCADA system Therefore this document will reference at several points to
functional descriptions of local Micro SCADA at substations.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
8
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
3. System Architecture
3.1 System Hierarchy
This chapter will explain system hierarchy between local Micro SCADA at the 4 substations
ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01. For system hierarchy within the substation please refer to
document:
AHS-PS32-2406 SAS Functional description - ESP01
AHS-PS32-2406 SAS Functional description - ESP02
AHS-PS32-3406 SAS Functional description - ESM01
AHS-PS32-4406 SAS Functional description - ESH01
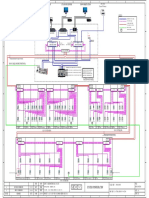
Fig. 3.1-1: System Hierarchy
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
9
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
The system architecture of the PPCCR SAS as shown above (Fig. 3.1-1) is designed in a manner
which facilitates different hierarchical levels:
EVN Control Center
PMS
Energy Center
PPCCR
ESP01 back up of PPCCR
Local Micro SCADA at Substations
These are described in detail below.
Control and monitoring of all 4 substations is only possible in PPCCR and ESP01 back up of
PPCCR. Monitoring function between substation will be realized via remote desktop application
with Micro SCADA viewer access.
3.1.1 EVN Control Center
EVN Control Center A0 & A1 have only switching authority (in parallel) via gateway for CB, DS, ES
HSES in AA2.D1.
EVN Control Center A0 & A1 have only switching authority (in parallel) for CB, DS, ES HSES for
generator feeder (D2.Q09, D2.Q11, D2.Q12, D2.Q19, D2.Q20) in AA2.D2.
Following signals shall be provided for all feeders of AA2.D1 and AA2.D2
Measurement
o Busbar: kV, Hz
o Generator feeder: MW, Mvar, high-limit control (MW), low-limit control
(MW)
o Transformer feeder (220/220kV & 220/35kV): MW, Mvar, kV, A
o Transmission line: Mw, Mvar, kV, A
o Power Plant total active power, total reactive power
Alarm signals
Control mode indication (station & bay level)
Tap Changer indication (tap, raise, lower, faulty)
Operation mode of IED (faulty, healthy, testmode)
Protection Trip & Alarm (Mechanical Protection & numerical protection)
ES/DS/CB position (double point)
Communication protocol is IEC 60870-5-101 slave.
3.1.2 Power Management System (PMS)
PMS requirements (only applicable for ESP01 and ESP02):
Analogue signals from ESP01 & ESP02 to PMS system:
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
10
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Feeder kW/T (via transducer 4 to 20mA) for all 220kV Feeder and 35kV outgoing
feeder exclude capacitor.
Main bus (BB1A, BB1B, BB2A, BB2B of AA2.D2) frequency and voltage (via
transducer 4 to 20mA)
Binary signals from ESP01 & ESP02 to PMS system:
220kV Lockout relay (86) operated (2 dry contact)
220kV and 35kV CB and DS status On and Off (1 dry contact per object/status)
Main bus (BB1A, BB1B, BB2A, BB2B of AA2.D2) 81U1 (1 dry trip contact), 81U2
(1 dry trip contact), 81O1 (1 dry trip contact), 27 (1 dry trip contact),
Binary signals from PMS System to ESP01 and ESP02:
Load shedding: 1 dry contact for tripping on TC1 and 1 dry contact for alarm to
BCU/Micro SCADA) for =AA2.D2.Q21 =AA2.D2.Q22
Load shedding: 35kV Feeder (ESP01/ESP02): 1 dry contact for tripping on TC1
and 1 dry contact for alarm to BCU/Micro SCADA)
Dynamic breaking: 1 dry contact for tripping on TC1 and 1 dry contact for alarm to
BCU/Micro SCADA) for =AA2.D2.D2.Q09, =AA2.D2.D2.Q11, =AA2.D2.D2.Q12,
=AA2.D2.D2.Q19, =AA2.D2.D2.Q20
Signals shall be hardwired directly to PMS panel.
No communication protocol provided. One spare LAN Card port (RJ45) will be reserved at
Gateway 1 and Gateway 2.
3.1.3 Energy Center (EC) (on hold by customer)
Energy Center has no control authority. EC will only receive measurement values collected by
metering equipment.
Communication protocol is Modbus TCP/IP & IEC 60870-5-104.
3.1.4 Power Plant Control Center Room (PPCCR)
PPCCR has control authority of ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01, if local Micro SCADA at
substation is set to Remote Control commands can be issued to OLTC, earthing switch,
disconnector and circuit breakers. PPCCR will receive same signals as local Micro SCADA
substation.
Signals, commands and measurement values are mirrored from local Micro SCADA at substation
to PPCCR.
3.1.5 ESP01 back up of PPCCR
ESP01 back up of PPCCR has control authority of ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01, if local
Micro SCADA at substation is set to Remote Control and if there is no communication between
PPCCR and ESP01 back up of PPCCR. In that case authority control needs to be set manually to
active at ESP01 back up of PPCCR and same functionality of PPCCR applies.
Signals, commands and measurement values are mirrored from local Micro SCADA at substation
to ESP01 back up of PPCCR.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
11
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
3.2 Communication system to PMS, EC and EVN Control Center (on hold by customer)
This is a communication software package / HW providing gateway services for routing the data
flow between the process and network control systems. The data transfer usually involves protocol
conversion. It also handles system coordination tasks, such as dynamic assignments of the control
command authorities. A variety of protocols for connecting upper level systems are supported.
For EC Modbus TCP/IP and for EVN Control Center IEC 60870-5-101 slave is assigned.
3.2.1 Station Level
The components at PPCCR are Front End Computers, Workstations, Gateways, printers, master
clock for synchronization and video wall system. These are connected together via an Ethernet
LAN utilizing the TCP/IP protocol.
A dedicated GPS master clock is provided for the synchronization of the entire system. This master
clock is independent of the station computers and gateways, and it synchronizes all devices via the
station bus.
The communication gateway enables communication to the next higher level system, for data and
information exchange with PMS, EC and EVN Control Center.
In order to increase the reliability, local Hot-Standby workstation located in ESP01 is dedicated as
backup system of main control system in CCR.
Additional an engineering workstation laptop including docking station is foreseen, which can be
used at PPCCR or any of the 4 substations for engineering work. Laptop needs to be connected to
certain station or bay level LAN switches (or directly to IED) for engineering and maintenance
work.
3.2.2 Station Level LAN
The Ethernet based on IEEE 802.3 (CSMA/ CD) and OSI TCP/IP is used to interconnect the
subsystems (ESP01, ESP02, ESM01, ESH01) of superior system at PPCCR. Front End computer,
workstations, communication units (routers, repeaters) and print servers are connected to the local
area network (LAN) with a communication speed of 100 or 1000Mbit/s depending on the device
speed.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
12
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
4. Functional Description
Micro SCADA in PPCCR is only a mirrored application of local Micro SCADA systems of
substations ESP01, ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01. Therefore, please refer to documents:
AHS-PS32-2406 SAS Functional description - ESP01
AHS-PS32-2406 SAS Functional description - ESP02
AHS-PS32-3406 SAS Functional description - ESM01
AHS-PS32-4406 SAS Functional description - ESH01
for detailed information of following topics:
System Overview
Software Description
Process Database
Overview
Process object function
Process object types
Data processing
Report Database
System objects
Base tools
Application Engineering
System Functions
Station HMI
Login and User Management
Monitor Layout
Time Synchronization
Control Authority handling
Station Local/Remote control
Bay Local/Remote control
Basic Monitoring and Control Functions
Colors and Symbols
Busbar and line colors
Symbol Colors
Symbols for Switching Objects
Process Displays Level
Level 1: Overall Single Line Picture
Level 2: Single Line Picture
Level 3: Bay View Picture
System Self Supervision
Event List
Alarm List
Blocking List
Control Concept
Select before operate
Synchrocheck bypass and interlocking bypass
Measurement presentation
Advanced Monitoring and Control Functions
Trends and Process Value Measurements
Parameter setting in IEDs
Busbar Coloring
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
13
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5. Hardware and Software Components
5.1 Front End
5.1.1 Redundant Station Computer
The redundant station computers contain the supervisory and control functions. The station
computers are high-profile pre-tested industrial PCs running under the Windows 2003 operating
system and the MicroSCADA application software. The redundant station computers work in a hot
standby configuration. During normal operation, the standby station computer mainly works as a
second workplace. The mutual supervision of the station computers and the database shadowing is
performed via the redundant station LAN. In the event that the hot station computer fails, the standby
station computer takes over the process control immediately. Getting all actual process data at any
time via the IEC61850 bus supports the actuality of data. Also manual changes in the database of
the hot station computer, e.g. pictures or limit values, are automatically copied to the standby station
computer. In order to communicate with the IEDs using the IEC61850 protocol for each bus segment,
one LAN card in each station computer is required. The redundant station computers also serve as
redundant operator/engineering workstations.
5.1.2 Hot standby Station Computer
The two Front End computer base systems are working in a hot standby configuration. The hot
system performs the communication tasks to the process and to the printer.
The hot standby concept is based on data shadowing of disk-resident data as well as RAM-resident
data between the two base systems. The entity subject to shadowing is the application of Micro
SCADA. In case of
Failure of the hot station computer
Failure of the hot application
Failure of the communication between the hot and stand-by PC
Failure of communication between hot station computer and local Micro SCADA at ESP01,
ESP02, ESM01 and ESH01
a take-over will take place meaning that the application receiving the shadowed data in stand-by
mode will become hot and the application activities are started. The stand-by application is an
identical copy of the hot application both in respect of disk data and in respect of RAM-resident data.
Data is shadowed on event basis, i.e. during the run-time only changed data items are shadowed.
Temporary disk and RAM resident-data such as picture and report caches, printer spools, execution
states and monitor states are not shadowed. At start-up, a complete copy is made from the hot
application to the stand-by application. The shadowing is fully symmetric meaning that the application
may be shadowed in both directions in turn. Take-over may also be initiated manually. After a take-
over, the shadowing will automatically start in the reversed direction when the system detects that
the failed station computer is available.
The interconnected station computers are connected with a TCP/IP link with a bit rate of 1000 Mbit/s.
5.1.3 System startup
The station computers are always running and it is usually not allowed to shut them down.
After a power loss they are starting up automatically:
Operating system Windows 2008 Server will start.
MicroSCADA and its applications will start.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
14
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
The station computer, which comes up first, will take over the hot state
The Terminal connections to the application data of the actual running hot station computer will be
done and the operator will be asked for his MicroSCADA username and password.
The operator will only be able to operate from the SAS according his user authorization level.
5.1.4 Front End Software
Item Description Remark
1 Windows 2008 Server R2 64bit Base
2 Print Key Base
3 Internet Explorer Base
4 Adobe Reader Base
5 Obermeier Base
6 mSCADA Professional Base
7 Terminal server (open licence) Base
5.1.5 Front End Hardware
The Front-End computer is provided with monitor, keyboard and mouse. It is mainly used for
operating of the SAS.
Item Description Detail
1 Industrial PC 19-inch slide-in
2 Housing 7-slot slide-in housing ATX for 19-inch
racks, 4 rack units
3 Slots all for full-length plug-in cards
3 PCI Express x1
3 PCI slots
1 PCI Express x16
4 Front flap Lockable
5 Card holders
6 Protection class IP60 when operating
7 Operating temperature 055 C
8 Weight of the basic
configuration
17.0 kg (37.5 lbs)
9 Dimensions 483 x 177 x 500 mm / 19" x 7" x 19.5" (W x
H x D)
10 Processor
2nd Generation Intel Core i7, 2.1 GHz,
4 cores (TC3: 80)
11 Motherboard ATX motherboard for 2nd Generation Intel
Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 or Celeron
12 RAM 4 GB DDR3 RAM
13 Graphic adapter Integrated inside the Intel processor: 1
DVI-I
1 DVI-D
1 Display Port connector
2 of 3 connectors useable at same time
14 Dual Ethernet adapter On-board with 2 x 10/100/1000BASE-T
connector
1 Dual Port Gigabit-Ethernet-PC network
cards, PCI-Express-x1-Bus
15 RAID on-board SATA RAID 1 controller, Intel
Rapid Storage Technology
16 Hard disk 1. 3-inch, 500 GB
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
15
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
2. 3-inch, 320 GB
17 Serial ports 4xRS232 1 of these RS232 ports are led
out with 9-pin D-sub connectors; 14 USB
2.0, 4 of these USB ports are led out at the
rear side and 2 are behind the front flap
18 Keyboard socket PS/2
19 Mouse socket PS/2
20 Power Supply Redundant
100240 V AC (50/60Hz) full range power
supply
5.2 Operator Workstation
The operator workstation is provided with monitor, keyboard and mouse. It is mainly used for
operating of the SAS. The operator workstation knows, which station computer is the hot base
system, and the data will be fetched from there. The process pictures shown on the operator
workplace are stored in the front-end computers. The operator workstation calls the picture from
the actual running hot base system.
5.2.1 Operator Workstation Software
Item Description Remark
1 Windows 7 Base
2 Print Key Base
3 Internet Explorer Base
4 Adobe Reader Base
5.2.2 Operator Workstation Hardware
Item Description Detail
1 Industrial PC 19-inch slide-in
2 Housing 7-slot slide-in housing ATX for 19-inch
racks, 4 rack units
3 Slots all for full-length plug-in cards
3 PCI Express x1
3 PCI slots
1 PCI Express x16
4 Front flap Lockable
5 Card holders
6 Protection class IP60 when operating
7 Operating temperature 055 C
8 Weight of the basic
configuration
17.0 kg (37.5 lbs)
9 Dimensions 483 x 177 x 500 mm / 19" x 7" x 19.5" (W x
H x D)
10 Processor Intel Celeron 1.6 GHz, 2 Core (TC3: 50)
11 Motherboard ATX motherboard for 2nd Generation Intel
Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 or Celeron
12 RAM 4 GB DDR3 RAM
13 Graphic adapter Integrated inside the Intel processor: 1
DVI-I
1 DVI-D
1 Display Port connector
2 of 3 connectors useable at same time
14 Dual Ethernet adapter On-board with 2 x 10/100/1000BASE-T
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
16
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.2:2 OWS installed in Front End Cubicle
Item Description Detail
1 Industrial PC ATX-Midi Tower
2 Processor IIntel Core2 Quad Processor Q9400
(6M Cache, 2.66 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB)
3 Motherboard Intel Q35 and ICH9 DO supporting
800/1066/1333 MHz FSB
Supports dual core and quad core process
with 45nm processing
Dual channel DDR2 667/800 SDRAM up to
8 GB
PCIe x 16 slot for external VGA card
Supports 4 PCI and 2 PCIe x1
1 parallel (SPP/EPP/ECP)
2 PS/2
Supports 6 SATA II and software RAID 0, 1,
5, 10
Built in with dual GbE controllers
support optional TPM module
4 RAM 4GB DDR2 800MHz RAM
5 Graphic adapter Chipset integrated VGA controller
6 LAN Card Network Card 1x 10/100-RJ45, 1x 100-ST,
PCI
7 DVD/CD Writer CD-DVD-RW Drive, 20X IDE
DVD+/-RW DL
8 Hard disk 500GB SATA Harddisk
3.5" SATA 7KRPM
9 Serial ports 4 USB 2.0 ports on rear
4 serial ports (3 of RS-232, 1 of RS-
232/422/485)
10 Keyboard socket PS/2
11 Mouse socket PS/2
12 Power Supply 450W AC-DC ATX Power Supply
5.2:2 Desktop OWS
connector
1 Dual Port Gigabit-Ethernet-PC network
cards, PCI-Express-x1-Bus
15 RAID on-board SATA RAID 1 controller, Intel
Rapid Storage Technology
16 Hard disk 3-inch, 500 GB
17 Serial ports 4xRS232 1 of these RS232 ports are led
out with 9-pin D-sub connectors; 14 USB
2.0, 4 of these USB ports are led out at the
rear side and 2 are behind the front flap
18 Keyboard socket PS/2
19 Mouse socket PS/2
20 Power Supply 100240 V AC (50/60Hz) full range power
supply
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
17
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.3 Engineering Notebook
The engineering notebook is provided with docking station, keyboard and mouse. It is mainly used
for engineering of the SAS but could also be used in the same manner as the operator workstation.
The engineering workstation knows, which front-end computer is the hot base system, and the data
will be fetched from there. The process pictures shown on the engineering workplace are stored in
the front-end computers. The engineering notebook calls the picture from the actual running hot base
system.
5.3.1 Engineering Notebook Software
Item Description Remark
1 Windows 7 Base
2 Print key Base
3 Internet Explorer Base
4 Adobe Reader Base
5 Microsoft Office Professional
5.3.2 Engineering Notebook Hardware
5.4 Training Workstation
On a separate workstation as build mSCADA application will be installed. All data points will be set
to fictive. Real time data update is not possible.
With this training workstation the staff will be able to train the mSCADA handling. Commands can
be issued and object feedback (open/close) will be simulated. Busbar coloring and event-list
update is activated. Blocking and Interlocking conditions will not be realized.
Item Description Detail
1 Docking Station Sony VGP-PRS30 500 GB Hard disk
2 Laptop Sony SVS1313C5E
Processor Intel CoreTM i7-3540M, 3
GHz
Keyboard US
RAM 8 GB 1333 MHz DDR3L-
SDRAM
Display 33.7cm LCD
Resolution 1366x768 Intel GPU
Graphic card Intel HD Graphics 3000
Hard disk 500 GB Serial ATA (7200
U/Min)
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
18
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.5 Simulation Workstation
5.5.1 Definition of the network size for licensing
Medium size
Number of primary substations <15
Number of MV/LV subst.(load points) <1000
Number of switching devices <2000
5.5.2 Implemented functions
Base System (Topology Management)
Network Analysis
General Extensions
HSB support
HSB support means that DMS 600 can always use the active MicroSCADA Pro SYS 600 server in
SCADA interface. DMS 600 is using one MS SQL Server database and database servers are not
redundant.
5.5.3 The substation parts/voltage levels that are connected to DMS 600 system:
220 kV network and outgoing 35 kV feeders to load points like e.g. 35/6 kV transformers.
Totally 124 ( 32 + 60 + 32 ) outgoing feeders. Each feeder is having only one load point e.g. 35/6
kV transformer.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
19
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.5.4 Overview of Network Analysis
Network analysis functions offer load flow and fault current calculations and
over-current protection analysis of radially operated and meshed networks. The generators are
taken into account during the network analysis. Additionally, the distributed generators and
capacitors are taken into account in the load flow calculations. The protection analysis function can
analyze definite time-delay and inverse time type overcurrent relays. Also the medium voltage
fuses are taken into account during protection analysis. The solid earthed networks and networks
earthed via resistor are supported in the protection analysis.
Network analysis is used to define the electrical state of the distribution network in a Real-time or
simulated network topology using network calculations, i.e. the load flow and fault current
calculations. Calculations can also use measurement data provided by MicroSCADA. Manually
updateable measurements can be used to model the separate load point, load of border switch or
backup feeder. Load estimation means the correction of the feeders and substations loads
calculated using static load data such that the loads of the feeders approximate the current
measurement of the feeder from MicroSCADA. The electrical state of the network can then be
calculated as accurate as possible.
The following network data is needed for calculation purposes during network analysis in WS:
Distribution network data.
1. Electrical properties of conductors.
2. Switching state of the network.
3. Load data for load flow calculation.
4. Relay data for protection analysis.
Load data is needed for the load flow calculation. Load data can be entered and edited by using
the load info forms, which are available for MV/LV substations. Relay data is used in protection
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
20
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
analysis. It can be changed via the circuit breaker data forms. Load and relay data is saved as a
part of the network database. The electrical properties of conductors are also stored in the network
database.
During simulations in DMS 600 WS, the relay settings, load calculation methods, and network
topology can be changed. The load forecasting starts automatically every hour. It creates dynamic
load curves for feeders and provides also short-term (1 hour to 1 week) load forecasts for
secondary substation loads. The calculation uses the latest MicroSCADA measurements).
Additionally, Load Estimation using available hourly current or P and Q measurements from
SCADA can be used to improve the network analysis accuracy and to form short-term forecasts for
secondary substation loads for radial feeders.
The network topology is automatically updated and networks analysis executed after every
switching state change, if the feature is not disabled by settings. Network calculation results can be
seen as colors in the network window, reflecting voltage drops, detection ability for short-circuit,
three-phase short-circuit capacity, detection ability of earth fault and load levels. The results are
shown as selected in the viewing settings. Warning level and alarm level colors are used in
presenting network analysis results when the calculated values exceed the corresponding settings
for the limits.
The representation of the calculation result depends on the user-defined settings. The switching
state of a distribution network is changed periodically to keep the network near optimal state. Load
changes, maintenance and service tasks together with fault situations also cause a need for
changes in the switching state. All switching actions can be checked beforehand by using the
simulation of WS. After changing the switching state, network analysis can be used to determine
the electrical state of the distribution network with the changed network topology. In order to
analyze the settings of protection relays or the influence of the network analysis settings (for
example load modeling), changes to this data are made and analysis executed again.
5.5.5 Meshed network analysis
In meshed network analysis all the networks having a voltage level under the defined transmission
voltage level are included in the MV network and analyzed. The primary transformers that have
one nominal voltage above the transmission voltage level are used as feeding points having the
defined busbar voltage as nominal voltage. The nodes of node type 'Feeding point' can be used in
the transmission network for topology analysis but the transmission network is not analyzed for
load flow or fault currents. However, radial or meshed sub-transmission network can be included in
network analysis. For example, one or several 400/220 kV primary transformers can be used as
feeding points for 220 kV network when transmission voltage level is set to over 220 kV but less
than 400 kV. Naturally, other primary transformers are used to transform the voltage to medium
voltage levels.
After a change in network and/or switching state data, the meshed network load flow and
maximum short-circuit current calculation for the whole included network is automatically
performed, if this is defined by the settings and the time interval from the last calculation has
elapsed.
5.5.6 Meshed network load flow calculation
The meshed network load flow for the whole MV network is calculated using a modified Newton-
Raphson algorithm. The meshed network load flow cannot use voltage measurements at primary
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
21
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
substations to set busbar voltages. The nominal voltages of the network are directly used to
transform the feeding busbar voltage to lower voltage levels.
The load flow is calculated for the total network even if it consists of several isolated islands. An
isolated island is a part of the network fed by one or several feeding primary transformers but
isolated from the rest of the network. The islands can be connected to each other but isolated by
an open switch.
The load flow supports generators where generators are producing active power and reactive
power by regulating the reactive power produced. These generators can be connected to the
network model using a 'block transformer', which is modeled in the network model as a
transformer, but getting the power from the generator. Primary transformer tap changer positions
are given for the calculation. Calculation is not solving possible new tap changer positions after
possible tap changer control actions.
A current measurement, an active power (P) measurement, or a reactive power (Q) measurement
connected to a generator node that is connected to Generator Block Transformer affects the
meshed network load flow calculation results in loop calculation of WS.
As a result of the meshed network load flow analysis the node voltages and power flows of line
sections are calculated and used in network voltage drops and load levels coloring.
5.5.7 Ha Thinh implementation
EVN feeding network is modeled as a 440/220 kV transformer being the only slack (reference)
node where P and Q are freely changing. Power plants are modeled as generators where P and Q
are known. In real-time mode P and Q is received from SCADA measurement and in simulation
mode P and Q can be modified manually (based on the previous SCADA measurements). When
network is disconnected from EVN network a virtual primary transformer must be switched to
network to provide a slack node and power balance difference can be seen from the loads of this
transformer. This way load shedding needs in island operation mode can be simulated. No stability
analysis is included in the calculations.
DMS 600 Installation:
DMS 600 is installed on a separate server computer having both network database server and
DMS600 software for network analysis, simulation and network maintenance. On MicroSCADA Pro
SYS 600 computers the SCADA integration components of DMS 600 are installed.
DMS600 functionality is limited to 220kV voltage level of ESP01, ESP02, ESH01, ESM01 and
35kV voltage level outgoing feeders of ESP01, ESP02, ESH01.Only load points within above
mentioned feeders are considered for DMS600. Any other load points are excluded from modeling
(out of scope).
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
22
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.6 Gateway
The Gateway is configured as Hot-Hot System. Signals will be sent via modem to A0 control center
and A1 control center via IEC 60870-5-101 slave. To PMS and Engineering center used protocol is
Modbus TCP/IP
5.6.1 Gateway Software
Item Description Remark
1 Windows 2008 Server R2 64bit
2 Print Key
3 Internet Explorer
4 Adobe Reader
5.6.2 Gateway Hardware
The Front-End computer is provided with monitor, keyboard and mouse. It is mainly used for
operating of the SAS.
Item Description Detail
1 Industrial PC 19-inch slide-in
2 Housing 7-slot slide-in housing ATX for 19-inch
racks, 4 rack units
3 Slots all for full-length plug-in cards
3 PCI Express x1
3 PCI slots
1 PCI Express x16
4 Front flap Lockable
5 Card holders
6 Protection class IP60 when operating
7 Operating temperature 055 C
8 Weight of the basic
configuration
17.0 kg (37.5 lbs)
9 Dimensions 483 x 177 x 500 mm / 19" x 7" x 19.5" (W x
H x D)
10 Processor
2nd Generation Intel Core i7, 2.1 GHz,
4 cores (TC3: 80)
11 Motherboard ATX motherboard for 2nd Generation Intel
Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 or Celeron
12 RAM 4 GB DDR3 RAM
13 Graphic adapter Integrated inside the Intel processor: 1
DVI-I
1 DVI-D
1 Display Port connector
2 of 3 connectors useable at same time
14 Dual Ethernet adapter On-board with 2 x 10/100/1000BASE-T
connector
3 Dual Port Gigabit-Ethernet-PC network
cards, PCI-Express-x1-Bus
15 RAID on-board SATA RAID 1 controller, Intel
Rapid Storage Technology
16 Hard disk 1. 3-inch, 500 GB
2. 3-inch, 320 GB
17 Serial ports 4xRS232 1 of these RS232 ports are led
out with 9-pin D-sub connectors; 14 USB
2.0, 4 of these USB ports are led out at the
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
23
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
5.7 Video wall
The video wall system will be supplied with 12 46inch monitors (brand AUO) and one video wall
controller. On each screen one picture can be shown. Facility to extend pictures over several
monitors to have one big picture is provided.
Fig. 5.7-1: 12 46inch screen video wall
5.7.1 Video wall Hardware
5.8 Ethernet Switch
The Station Level LAN is built by using managed Ethernet Switches. Those switches have the
advantage that they do not need any configuration there for they also can easily be replaced by
any unmanaged switch.
rear side and 2 are behind the front flap
18 Keyboard socket PS/2
19 Mouse socket PS/2
20 Power Supply Redundant
100240 V AC (50/60Hz) full range power
supply
Item Description Detail
1 Video wall controller 4U IPC chassis
Windows 7 Professional 64-bit
RGB: 640x480,800x600,1024x768,
1280x1024, 1600x1200,1920x1080 DVI-I:
640x480,800x600, 1024x768, 1280x1024,
1600x1200,1920x1080 HDMI: 1080P,
720P, 576P
Power Input 100~240V AC
2 Screen AUO
46" Measured Diagonally
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
24
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Item Description Detail
1 Unmanaged Ethernet switch ABB AFS675
5.9 Peripheral devices
5.9.1 Event Printer
A matrix line printer with integrated printer server is provided for printing the events. It is connected
to the station automation system through the station level LAN. Events are printed out
spontaneously as they are acquired in the database. Each event contains the following information
e.g. according to ANSI or ISO standards.
Event date and time (17.01.2002 - 20 35 25, 087 <dd.mm.yyyy - hh mm ss,ms>)
Name of the event object (A03 Q0 - <bay name / circuit breaker>)
Descriptive text (CB Open command - <description of the event>)
State or value of the object (EXECUTED - <status>).
5.9.2 Hardcopy Printer
Two color laser printer are provided as hardcopy printer. These printer offer high resolution for data
reports with graphics, tables, curves and process picture snapshot. The color laser printer may be
connected directly to a specific user or shared in the system when connected directly to the
separate station level LAN.
Item Description Detail
1 Epson AcuLaser C1100 DIN A4
color laser printer
2 Epson AcuLaser C9200N DIN A3
color laser printer
5.9.3 Monitor
In order to provide the optimal solution within an EMI-critical environment, LCD color monitors are
used. LCD monitors have a very low start-up current when switched on. This reduces the demands
on the Power Inverter. Standard size is 24", bigger sizes are available as an option.
5.9.4 Ethernet Firewall
An industrial Ethernet Firewall/VPN-Router will be used. The Industrial Ethernet Firewall is the link
between secure network cells and the unsecured outside word. In this function as a link, the
Industrial Ethernet Firewall protects the security-sensitive cell from undesired data traffic along the
connection to the outside world.
Item Description Detail
1 Ethernet Firewall/VPN-Router AFF650
5.9.5 Station Level Cubicle
The cubicle satisfies protection class IP54 according to EN60529.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
25
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Fig. 5.6.5-1: Layout for Front End Cubicle
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
26
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Fig. 5.6.5-2: Layout for Front End Cubicle
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
27
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
7. Appendix: Fiber Optic Cable Specification
7.1 Fiber Optic Components
7.1.1 Fiber Cabling Overview
To better understand fiber performance and operational specifics, we must first look to the
fiber cable for a good basis of understanding.
All fiber optic cables consist of three layers:
1. Core - An extremely thin single strand of glass or high quality plastic. This single strand
is layer that carries the data.
2. Cladding - Another layer of glass with a slightly different index of refraction from the
core. This slight difference can either allow light energy out from the core or keep the
majority of energy within the core (via reflections).
3. Jacket - Usually the last outer layer of plastic intended to protect the core and the
cladding. The composition of this layer greatly depends on the intended installation
Fig. 7.1-1 Fiber Optic Cable Construction
7.1.2 Fiber Optic Transceiver
A fiber optic transceiver is simply a transmitter receiver pair. A transceiver is tasked with
transmitting and receiving data (1s and 0s). A fiber optic transceiver accomplishes this
task by either turning the light source on or off.
7.1.3 Multi-Mode Communication Links
Multi-mode communication links are generally the most common. When forming a multi-
mode link, one must use multi-mode transceivers as well as multi-mode cabling.
Multi-mode fiber cable is generally specified as two numbers such as 62.5/125m or
50/125m. This implies a core size of 62.5m in diameter and a cladding size of 125m.
62.5/125m cabling is generally the most popular, followed by 50/125m. For historical
reasons 62.5/125m cabling has a large install base, but generally 50/125m cabling is
recommended for all new installations to allow for an upgrade path to gigabit (and beyond)
speeds.
Multi-mode is called such because the light used to transmit the data actually travels
multiple paths within the core. The fiber cable is designed with a core/cladding index
difference to keep the majority of light energy within the fiber so that it bounces around.
At the other end of the fiber, a data signal is composed of both the light that took straight
paths through the center of the core as well as the light beams that bounced around. This
phenomenon is called modal dispersion and is the primary characteristic that limits multi-
mode link distances.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
28
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
7.1.4 Single-Mode Communication Links
Single-mode communication links are less common than multi-mode links, but are quickly
gaining ground when longer link distances (> 3 km) are required. When constructing a
single-mode link, one must use single-mode transceivers with single-mode cabling.
Single-mode fiber is also specified as two numbers such as 9/125 m. This implies a core
of just 9m, and a cladding 125m in diameter. 9/125m Cabling is generally the most
common, followed by 8/125m.
The whole idea behind a single-mode link path is that light carrying the data travels a
single path. Light energy that strays away from the center path leaves the core and
become trapped in the cladding due the properties of single-mode cabling. Because
almost all the light received at the opposite end travels approximately the same path,
modal dispersion (or timing jitter) is no longer a factor. The primary distance-limiting factor
for single-mode links is signal power (or amplitude).
7.2 Standard Wavelengths
Fiber optic transceivers generally use four wavelengths (analogous to colors) of light. The
following is a table for reference only, as links should be designed with fiber standards in
mind as opposed to wavelengths of light.
Fig. 7.2-1 Fiber Optic Wavelengths
7.3 Fiber Optic Standards
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) is one of the most widely
recognized standards body in the world. The IEEE has had a large involvement
developing electrical and communications standards including fiber optic communications.
The following table lists several of the industry accepted IEEE fiber optic standards:
Fig. 7.3-1 IEEE Fiber Optic Standards
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
29
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
7.4 Fiber Optic Cables inside cubicles
This chapter defines the characteristics of the Fiber Optic Cables which are in the scope
of ABB and that will be installed inside cubicles.
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
30
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
31
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
32
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
Copyright 2011 ABB. All rights reserved. ABB 2012
Title
SAS functional description for CCR
Customer FCFC Eng. & Utility Division
Project
Ha Thinh Steel Plant
Order 16234
Doc. no. Language Rev.
Sheet
33
ABB Switzerland Ltd
1KHF334933
EN 1
No. sheets
33
Print: 4/07/2013 File: 1KHF334933 - AHS-PS32-1402-B- SASfunctional description for CCRrev1.docm; Rev. 1
8. Revision
Rev. Page (P)
Chapt. (C)
Description Date Dept./Init.
0
- First Issue
2013-01-11 / SL
1 6-7, 2.3
8-9, 3.1
9, 3.1.1
9, 3.1.2
9, 3.1.3
9, 3.2
12, 5.1.2
16, 5.3.1
16, 5.3.2
16, 5.4
16, 5.5
18, 5.7
18, 5.7.1
24-27, 7.4
Customer comments 2013-04-09 and week 17
2013. Changes highlighted in blue
2013-05-14 / SL
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Substation - Project List: SR - No. Project Title Customer Consultant End Client Scope of WorkDocumento7 pagineSubstation - Project List: SR - No. Project Title Customer Consultant End Client Scope of WorksunjeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ky 7 LDocumento59 pagineKy 7 LIbrahim IslamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ut Relay PanelDocumento25 pagineUt Relay PanelPamela BradleyNessuna valutazione finora
- 220kV Da Bac - TEL, SER, FR, FL, TN48, INV Panel Drawing - R7Documento200 pagine220kV Da Bac - TEL, SER, FR, FL, TN48, INV Panel Drawing - R7Văn Ngọc NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- YN1M303223 CDA - 110kV - Line Trafo - CRP 2018 01 19 CST en PDFDocumento85 pagineYN1M303223 CDA - 110kV - Line Trafo - CRP 2018 01 19 CST en PDFTukaram PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- 4a1fn3 6se7134+l08Documento31 pagine4a1fn3 6se7134+l082003vinay100% (1)
- TKT-CM-01-OM-1060-I-R1-O&M Manual - Control & Monitoring System PDFDocumento144 pagineTKT-CM-01-OM-1060-I-R1-O&M Manual - Control & Monitoring System PDFThái Đức NhơnNessuna valutazione finora
- n59 Srep1 Ach Arc Rev ADocumento1 paginan59 Srep1 Ach Arc Rev AedemmikeNessuna valutazione finora
- SMART Control Bujagali - DCS System Architecture Rev D PDFDocumento1 paginaSMART Control Bujagali - DCS System Architecture Rev D PDFBlažević JosipNessuna valutazione finora
- Rtu - SasDocumento19 pagineRtu - SasNitin KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1KHW000890 en NSD570Documento562 pagine1KHW000890 en NSD570jckrishnah100% (1)
- WI-NG-6460-002-36 Work Instruction-230kV and 380kV XLPE Cables Rev00Documento7 pagineWI-NG-6460-002-36 Work Instruction-230kV and 380kV XLPE Cables Rev00MohamedElmahdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen First Sync Procedure - Rev01Documento12 pagineGen First Sync Procedure - Rev01O P Sridharan PerumalNessuna valutazione finora
- TSF12 09 02 Hail 1150 P10 2Documento9 pagineTSF12 09 02 Hail 1150 P10 2Arif MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- IRTU and IGW User Manual Eng Rev2 0Documento190 pagineIRTU and IGW User Manual Eng Rev2 0Bear DguNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb 61850 Sas GeneralDocumento33 pagineAbb 61850 Sas GeneralantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- AHS-KRS-30-BUB - DC-UPS2 - 00E652A3 - RedCorrex PDFDocumento24 pagineAHS-KRS-30-BUB - DC-UPS2 - 00E652A3 - RedCorrex PDFArchiford NdhlovuNessuna valutazione finora
- E38000744 D334 - HIDD C03 400kV Cable Feeder Local and Remote Reactor - REV 0 - 2017-11-13 PDFDocumento164 pagineE38000744 D334 - HIDD C03 400kV Cable Feeder Local and Remote Reactor - REV 0 - 2017-11-13 PDFSatish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 220kV Sicam Panel 2 (BOP) PDFDocumento23 pagine220kV Sicam Panel 2 (BOP) PDFAnonymous SWz3bgcUNessuna valutazione finora
- Ne02 Sas ArchitectureDocumento5 pagineNe02 Sas ArchitectureApoorva BhushanNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Description of The Digital Turbine GovernorDocumento20 pagineTechnical Description of The Digital Turbine GovernorLe Hoang HaoNessuna valutazione finora
- PH12-3H-76-40-T002 - Rev ADocumento27 paginePH12-3H-76-40-T002 - Rev ABalakrishnan KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens AG: Circuit Diagram Energy Management - Medium Voltage & SystemsDocumento170 pagineSiemens AG: Circuit Diagram Energy Management - Medium Voltage & SystemsEdciel EbuenNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection Overview Station Transformer CCPDocumento1 paginaProtection Overview Station Transformer CCPJorge Andres PavónNessuna valutazione finora
- K02ELBD005016P0Documento16 pagineK02ELBD005016P0KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Schema ELECDocumento133 pagineSchema ELECMeyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation: Order No.: Customer: Equipment: Converter Type: Document: 3BHS213774E01 ACS 1000 WDocumento73 pagineInstallation: Order No.: Customer: Equipment: Converter Type: Document: 3BHS213774E01 ACS 1000 WBastian ParedesNessuna valutazione finora
- CRP OhlDocumento75 pagineCRP OhlRachmad Ady SetiawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Exchange Between Power Plant - Substation &Documento16 pagineSignal Exchange Between Power Plant - Substation &Nasiruddin Abdullah HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- IEC61850 ProtocolDocumento24 pagineIEC61850 ProtocolDevas ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synchro TactDocumento36 pagineSynchro Tactbuianhtuan1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Telecom System Design Document Rev-ADocumento18 pagineTelecom System Design Document Rev-ARashad SarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1200 403 R7 New Al QumriyahDocumento187 pagine1200 403 R7 New Al QumriyahNadeem Qureshi100% (1)
- PT. PLN (Persero) : Schematic Diagram of ZDT Line Differential Relay GD StadionDocumento23 paginePT. PLN (Persero) : Schematic Diagram of ZDT Line Differential Relay GD StadionendriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- GCP - Technintegral - Rev00 - 21.07.2021Documento60 pagineGCP - Technintegral - Rev00 - 21.07.2021edwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel Construction - Remote End - Rev-A - 03.06.2013Documento4 paginePanel Construction - Remote End - Rev-A - 03.06.2013ADE mrtNessuna valutazione finora
- SYS500 System Management 844Documento198 pagineSYS500 System Management 844mathew227Nessuna valutazione finora
- Water - Plant Rev03Documento51 pagineWater - Plant Rev03Tarek KhafagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tor1-22015mv001 r8 MV-VFD Elect Drawings 220-Er-015 260kw Referencial Abb RockwellDocumento22 pagineTor1-22015mv001 r8 MV-VFD Elect Drawings 220-Er-015 260kw Referencial Abb Rockwellsareluis30Nessuna valutazione finora
- DNF7 Selection Manual in SCHNEIDERDocumento12 pagineDNF7 Selection Manual in SCHNEIDERsayeem bikashNessuna valutazione finora
- Visio-C System Overview JEC PAS V2-0Documento5 pagineVisio-C System Overview JEC PAS V2-0باسم العوفيNessuna valutazione finora
- UPSDocumento28 pagineUPSAdetunji TaiwoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ban Ve Nhi Thu DCL Alstom 123 - S2daDocumento15 pagineBan Ve Nhi Thu DCL Alstom 123 - S2datuantz206Nessuna valutazione finora
- INPSNM-SA04 Substation Automation With IEC61850-Rev-BDocumento1 paginaINPSNM-SA04 Substation Automation With IEC61850-Rev-BMichael Parohinog GregasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ae1172 Efa020 81mky01 116111 00Documento1 paginaAe1172 Efa020 81mky01 116111 00Mayur GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator Control Panel XX MW: Wiring Diagram, Outline, Terminal Block List, and BOMDocumento6 pagineGenerator Control Panel XX MW: Wiring Diagram, Outline, Terminal Block List, and BOMashraf abdelrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- TJ01 NN VD LG010SG20001 Is1 PDFDocumento6 pagineTJ01 NN VD LG010SG20001 Is1 PDFNiño DioknoNessuna valutazione finora
- 32 Mva Power Expansion Pt. Bekaert: B For Approval FADocumento23 pagine32 Mva Power Expansion Pt. Bekaert: B For Approval FAaditya agasiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 545 398aDocumento78 pagine3 545 398aezze72x5058Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gw1300174.Pg011 34.5kv Control Panel c6Documento33 pagineGw1300174.Pg011 34.5kv Control Panel c6Nick CorrosivesnareNessuna valutazione finora
- M.V. Anil Kumar Kumar: Summary: Work HistoryDocumento3 pagineM.V. Anil Kumar Kumar: Summary: Work HistoryNarendra LakkojuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hamidullah Siddiqui PresentationDocumento35 pagineHamidullah Siddiqui PresentationrjchpNessuna valutazione finora
- Comet Gland CatalogueDocumento12 pagineComet Gland CataloguePrabhudatta KarNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Cable Schedule (A) - Armoured Cable, (F) - Flexible Cable, (S) - Cable With Screen. KWPCL/DRG/CS/018 Rev. 1 Sheet 1 of 3Documento3 pagineControl Cable Schedule (A) - Armoured Cable, (F) - Flexible Cable, (S) - Cable With Screen. KWPCL/DRG/CS/018 Rev. 1 Sheet 1 of 3ARIJIT KUNDUNessuna valutazione finora
- CE-429149 Protection Cubicle F71 RevBDocumento74 pagineCE-429149 Protection Cubicle F71 RevBMuhammad NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Drawings For MV Switchgear Unigear Zs3.2: Ampliacion Se Sur WSPDocumento4 pagineDrawings For MV Switchgear Unigear Zs3.2: Ampliacion Se Sur WSPfrankrosseliNessuna valutazione finora
- Connection Cable SelectionDocumento258 pagineConnection Cable SelectionGiovanni TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- 3bl61719aaaapbzza 08 enDocumento152 pagine3bl61719aaaapbzza 08 enRajesh PalandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Service Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryDa EverandEngineering Service Revenues World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNessuna valutazione finora
- Multifunctional Generator Rotor Protection Relay PDFDocumento16 pagineMultifunctional Generator Rotor Protection Relay PDFSurachat SannokNessuna valutazione finora
- MR-JE Troubleshoot AlarmDocumento18 pagineMR-JE Troubleshoot AlarmHiren PotdarNessuna valutazione finora
- PZ1000 Protección de LíneaDocumento16 paginePZ1000 Protección de Líneagusfaj100% (1)
- C&S DMPR PDFDocumento19 pagineC&S DMPR PDFDipankar Chakraborty100% (1)
- 1MDS06004 en en REL 100 RELZ 100 Numerical Line Protection TerminalDocumento8 pagine1MDS06004 en en REL 100 RELZ 100 Numerical Line Protection TerminalRuhuluruj100% (1)
- Circuit Breaker GTSDocumento31 pagineCircuit Breaker GTScpandey01_688066930Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento13 pagineUnit 1engshimaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Symmetrical Faults On 3 Phase SystemDocumento11 pagineSymmetrical Faults On 3 Phase SystemChelle Mendoza EslavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Short-Circuit Calculations - The Easy WayDocumento3 pagineShort-Circuit Calculations - The Easy WaymshahidshaukatNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of International Regulations For Connections of Wind Turbines To The NetworkDocumento7 pagineComparison of International Regulations For Connections of Wind Turbines To The NetworkjomoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Manual T4900CRDocumento36 pagineInstallation Manual T4900CRmayNessuna valutazione finora
- Compact 80-1250Documento356 pagineCompact 80-1250rocketvtNessuna valutazione finora
- DDPSMVol 2Documento22 pagineDDPSMVol 2LawrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant and Transmission System Protection CoordinationDocumento35 paginePower Plant and Transmission System Protection CoordinationMichael Parohinog GregasNessuna valutazione finora
- Step2000 Busway-Siemens PDFDocumento96 pagineStep2000 Busway-Siemens PDFMokr AchourNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018-19 Latest Iot CS, Is, Ece Projects AbstractsDocumento33 pagine2018-19 Latest Iot CS, Is, Ece Projects AbstractsIgeeks Technologies,BangaloreNessuna valutazione finora
- TP48300-A-N07A3 Maintenance Guide (V100R001 - 04)Documento53 pagineTP48300-A-N07A3 Maintenance Guide (V100R001 - 04)SamirTam0% (1)
- Lecture Presentaion On Generator, Transformer, Motor and Transmission Line ProtectionDocumento44 pagineLecture Presentaion On Generator, Transformer, Motor and Transmission Line Protectionzeeshanraja100% (1)
- S and PDocumento43 pagineS and PPrathap VuyyuruNessuna valutazione finora
- A Modelling of 440 KV Ehv Transmission Line Faults Identified and Analysis by Using Matlab SimulationDocumento8 pagineA Modelling of 440 KV Ehv Transmission Line Faults Identified and Analysis by Using Matlab Simulationnag500055Nessuna valutazione finora
- NaceCare TTB6652 Troubleshoot Err CodesDocumento1 paginaNaceCare TTB6652 Troubleshoot Err CodesNestor Marquez-DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Farm Protection Using An IEC 61850 Process Bus ArchitectureDocumento16 pagineWind Farm Protection Using An IEC 61850 Process Bus Architecture1453hNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplifier PDFDocumento46 pagineAmplifier PDFvladareanucatalindanNessuna valutazione finora
- 579 081 PDFDocumento78 pagine579 081 PDFJohanAndrésVillarrealNessuna valutazione finora
- Vansco VMM Diagnostics Rev 6 - CUBEXDocumento27 pagineVansco VMM Diagnostics Rev 6 - CUBEXHector Sepulveda Orellana100% (3)
- 7SR242 Duobias Complete Technical ManualDocumento384 pagine7SR242 Duobias Complete Technical ManualAnonymous wl7fgzivPNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE - IEC - Comparison-OLD of Power TransformerDocumento8 pagineIEEE - IEC - Comparison-OLD of Power TransformerJohn Philip ErquizaNessuna valutazione finora
- A3 14 (SC) 01 (B)Documento184 pagineA3 14 (SC) 01 (B)bpd21Nessuna valutazione finora