Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
QMS Audit - Checklist - IsO 9001 - 2008
Caricato da
Rizaldi Djamil0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
239 visualizzazioni27 pagineAudit Checklist
Titolo originale
QMS Audit_Checklist - IsO 9001_2008
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAudit Checklist
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
239 visualizzazioni27 pagineQMS Audit - Checklist - IsO 9001 - 2008
Caricato da
Rizaldi DjamilAudit Checklist
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 27
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
INTRODUCTION
Page 1 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
What auditors should look for:
__ the items listed in these headings
__ that the ISO requirement is met
__ that the requirement is met in the manner described in the organization's documentation
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
4.0 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Page 2 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
4 Quality Management System
4.1 General requirements
Does the organization establish, document, implement, maintain
and continually improve a Quality Management System (QMS) in
accordance with ISO 9001 : 2008 with due consideration given
to:
a) identification of processes needed for the QMS and their
application throughout the system;
b) determination of sequence and interaction of these
processes
c) determination of criteria and methods required to ensure
effective operation and control of these processes;
d) availability of resources and information required to support
the operation and monitoring of processes;
e) measurement, monitoring and analysis of the processes;
f) implementation of action to achieve planned results and
continual improvement.
Has the organization established a system to control outsourced
processes that can affect product conformity?
4.2 Documentation requirements
4.2.1 General
a) Is there a documented quality policy and documented
quality objectives?
b) Is there a documented quality manual?
c) Has the organization established documented procedures
for:
Control of documents;
Control of quality records;
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
4.0 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Page 3 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Internal Audit;
Control of non-conformity;
Corrective action;
Preventive action.
d) Has the organization established some type of
documentation and controls for:
A QMS
Documents required to ensure the effective operation and
control of its processes.
The output of planning
The quality policy
The quality manual
Planning of the realization process
Inputs relating to product requirements
Outputs of the design and/or development process
Design or development changes
Results of review of changes and subsequent follow up
actions
Purchasing documents
Legal and regulatory requirements, existing and new
e) Has the organization established a system for quality
records
4.2.2 Quality Manual
Has a Quality Manual been established and maintained?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
4.0 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Page 4 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Does the Quality Manual include:
a) scope of QMS;
aa) details of exclusion to Section 7.0 with justification;
b) documented procedures or reference to them;
c) description of the sequence and interaction of the processes
included in the QMS relevant to the organization activities.
4.2.3 Control of documents
Has a documented procedure been established to control all
documents (including documents defined as Quality Records)
required for the QMS?
Does the procedure include controls for:
a) approval of documents for adequacy prior to issue;
b) review, update, as necessary and re-approve documents;
c) to identify changes and the current revision status of
documents;
d) to ensure that relevant versions of applicable documents are
available at points of use;
e) to ensure that documents remain legible, readily identifiable
and retrievable;
f) to ensure that documents of external origin are identified
and their updating and distribution controlled;
g) to prevent the unintended use of obsolete documents, and
to apply suitable identification to them if they are retained for
any purpose.
4.2.4 Control of records
Has a documented procedure been established for the
identification, storage, retrieval, protection, retention time and
disposition of quality records?
Are quality records subjected to control?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
4.0 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Page 5 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Has the organization identified quality records to the extent
required to provide evidence of conformance to requirements
and of effective operation of the QMS?
Check control of records for the following:
Results of management review
Records of education, experience, training and qualification
Results of review of product requirements and subsequent
follow-up actions
Results of design and/or development review and
subsequent follow-up actions
Results of design and/or development verification and
subsequent follow-up actions
Results of design and/or development validation and
subsequent follow-up actions
Results of design and/or development changes and
subsequent follow-up actions
Results of supplier evaluations and follow-up actions
Unique identification of the product, when traceability is a
requirement
Unique identification of customer property
Results of calibration for measurement and monitoring
devices
Authority responsible for release of the product
Are there recorded evidences of compliance for the following, as
applicable:
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
4.0 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Page 6 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Customer property that is lost, damaged or otherwise
unsuitable for use reported to the customer;
Process validation records;
Basis of calibration in the absence of traceable national or
international standards;
Recording audit results
Follow-up audit actions including reporting of verification
results
Proposed release of nonconforming product to customer if
required
Results of corrective action taken;
Results of preventive action taken.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
5.0 MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY
Page 7 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
5 Management Responsibility
5.1 Management Commitment
Is there evidence of involvement by top management towards
development and improvement of the QMS through the
following:
a) initiation of action/measures to communicate to the
organization the importance of meeting regulatory and legal
requirements as applicable to the product offered?
aa) initiation of action/measures to communicate to the
organization the importance of meeting customer
requirements?
b) establishment of a quality policy?
c) establishment of quality objectives?
d) conduct by top management of Management Reviews of the
QMS?
e) review by top management of resource requirements
including having measures in place to collect data on
resource needs and provide timely resources to achieve
quality objectives?
5.2 Customer focus
Does top management have methodologies to ensure that
customer needs and expectations are determined through their
QMS, and these are converted into requirements and fulfilled
with the aim of achieving customer satisfaction?
Are obligations related to product, including legal and regulatory
requirements identified and measures established to fulfill the
same?
5.3 Quality policy
Has top management established a Quality Policy?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
5.0 MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY
Page 8 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Is the Quality Policy signed by top management?
a) is the Quality Policy appropriate to the purpose of the
organization?
b) does the Quality Policy include a statement of commitment
to meeting requirements, customer satisfaction and to
continual improvement of the QMS?
c) does the Quality Policy provide a framework for establishing
and reviewing quality objectives?
d) is the Quality Policy communicated and understood at
appropriate levels in the organization?
e) are mechanisms established for review by top management
of the continuing suitability of the Quality Policy?
f) is the Quality Policy controlled?
5.4 Planning
5.4.1 Quality objectives
Are quality objectives established by top management at
relevant functions and levels within the organization?
Do the objectives include relevant objectives to meet product
requirements?
Are the objectives measurable to ensure efficiency and
effectiveness of the organization?
Are the objectives consistent with the Quality Policy including
commitment to continual improvement?
5.4.2 Quality Management System planning
Is the output of quality planning documented?
Does quality planning include:
i) the processes related to the QMS as detailed in Sections
4.1 and 4.2.2a
ii) assessment of resources needed;
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
5.0 MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY
Page 9 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
iii) continual improvement of the QMS.
Are changes to quality plans and planning methodology
controlled?
When changes are initiated, is the integrity of the QMS
maintained during the change process?
5.5 Responsibility, authority, and communication
5.5.1 Responsibility and authority
Has top management identified functions and interrelationships
to facilitate effective quality management?
Has top management defined and communicated to the
organization the responsibilities and authorities of those involved
in the effective operation of the QMS?
5.5.2 Management representative
Has top management appointed a member(s) as Management
Representative(s) with responsibility and authority to:
a) ensure that the processes of the QMS are established,
implemented and maintained.
b) report to management on the performance of the QMS,
including needs for improvement.
c) promote awareness of customer requirements throughout
the organization.
5.5.3 Internal communication
Does the organization ensure communication at various levels
and functions regarding the processes of the QMS and their
effectiveness?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
5.0 MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY
Page 10 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
5.6 Management review
5.6.1 General
Does top management review the QMS to ensure its continuing
suitability, adequacy and effectiveness?
Are the review intervals planned?
Do reviews include assessing opportunities for improvement?
Do reviews include the need for changes to the QMS, quality
policy, and/or quality objectives?
5.6.2 Review input
Does review input include current performance and improvement
opportunities related to:
a) results of audits;
b) customer feedback;
c) process performance and product conformance;
d) status of corrective and preventive actions;
e) follow-up action from earlier management reviews;
f) changes that could affect the QMS, including the quality
policy and quality objectives;
g) recommendations for improvement
5.6.3 Review output
Does output from management review include actions related to:
a) improvement of the QMS and its processes;
b) improvement of product related to customer requirements;
c) resource needs.
Are results of the management review recorded
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
6.0 RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Page 11 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
6 Resource Management
6.1 Provision of resources
Does the organization have methods to determine and provide
resources needed to:
a) implement and improve the processes of the QMS and
b) address customer satisfaction by meeting requirements.
Are the resources allocated on time?
6.2 Human resources
6.2.1 General
Are personnel assigned with responsibilities that are defined in
the QMS competent on the basis of:
applicable education;
training;
skills;
experience.
6.2.2 Competence, awareness, and training
Are competency needs identified for personnel performing
activities affecting product quality?
Is training provided to satisfy the competency needs?
Are the effectiveness of the training evaluated and follow-up
action initiated?
Does the organization ensure that its employees are aware of
the relevance and importance of their activities and how they
contribute to the achievement of quality objectives?
Are records of education, experience, training and qualifications
maintained?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
6.0 RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Page 12 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
6.3 Infrastructure
Have the facilities needed to achieve the conformity of product
been identified and provided including:
a) work space and associated facilities;
b) equipment, hardware and software;
c) supporting services.
Are the facilities maintained to achieve conformity of product?
6.4 Work environment
Has the work environment suitable for process operations and
product conformity been identified?
Does the organization manage human and physical factors of
the work environment needed to achieve conformity of product?
Are records documenting management of the work environment
maintained?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 13 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
7 Product Realization
7.1 Planning of product realization
Has the organization determined the following, as appropriate, in
planning the processes for realization of product:
a) quality objectives for the product, project or contract;
b) the need to establish processes and documentation and
provide resources and facilities specific to the product;
c) verification and validation activities and the criteria for
acceptability;
d) the records that are necessary to provide confidence of
conformity of the processes and resulting product.
Is the planning of the realization processes consistent with other
planning requirements of the organizations QMS and
documented (see 4.1)?
Are there any exclusions on the requirements in section 7.0 and
are they defined in the Quality Manual (4.2.2) with justification?
7.2 Customer related processes
7.2.1 Determination of requirements related to the product
Are processes established to determine requirements for the
product including:
a) customer requirements, including availability, delivery and
support;
b) requirements not specified by the customer but necessary
for intended or specified use;
c) regulatory and legal requirements related to the product;
d) additional requirements determined by the organization.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 14 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
7.2.2 Review of requirements related to the product
Does the organization review customer requirements and
organizational requirements prior to commitment to supply a
product?
Are stages of review (submission of a tender, acceptance of
contract or order) established?
Does the review process ensure that:
a) product functional and performance requirements are
defined;
b) contract or order requirements differing from those
previously expressed are resolved;
c) the organization has the ability to meet defined
requirements.
Where no documented statement of requirements is provided,
are requirements confirmed before acceptance;
Does the review process ensure that changes to product
requirements are communicated to relevant staff in the
organization?
When changes are accepted, are amendments made to relevant
documentation?
Are the results of review and subsequent follow-up actions
recorded? (4.2.4)
7.2.3 Customer communication
Are arrangements for communication identified and implemented
relating to:
a) product information;
b) inquiries, contract or order handling, including amendments;
c) customer feedback, including customer complaints.
7.3 Design and development
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 15 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
7.3.1 Design and development planning
Does the organization plan and control design and/or
development of the product?
Does the design and/or development planning determine:
a) stages of design and/or development;
b) review, verification and validation activities appropriate to
each design and/or development stage;
c) responsibilities and authorities for design and/or
development activities.
Does the organization manage interfaces between different
groups involved in design and/or development to ensure
effective communication and clarity of responsibilities?
Are the design and/or development planning output updated, as
appropriate, as the design and/or development progresses?
7.3.2 Design and development inputs
Are inputs relating to product requirements defined, documented
and reviewed for adequacy?
Does the design and/or development input include:
a) functional and performance requirements
b) applicable regulatory and legal requirements;
c) applicable information derived from similar design and/or
development;
d) any other requirements essential for design.
Are all incomplete, ambiguous or conflicting requirements
identified during review and resolved?
7.3.3 Design and development outputs
Does the organization document design output in a manner that
enables verification against the design and/or development
inputs?
Does the design and/or development output:
a) meet the design input requirements;
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 16 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
b) provide appropriate information for production and service
operations;
c) contain or reference product acceptance criteria;
d) define the characteristics of the product that are essential to
its safe and proper use.
Are all design and/or development output approved prior to
release?
7.3.4 Design and development review
Does the organization identify suitable stages for systematic
reviews of design and/or development to:
a) evaluate the ability to fulfill requirements;
b) identify problems and propose follow-up actions.
Do representatives of functions affected by, or involved in, the
design and/or development stage(s) participate in reviews?
Are the results of review and subsequent follow-up actions
recorded?
7.3.5 Design and development verification
Are design and/or development verification performed to ensure
the output meets the design and/or development inputs?
Are the results of verification and subsequent follow-up actions
recorded?
7.3.6 Design and development validation
Is the design and/or development validation performed to
confirm that resulting product is capable of meeting the
requirements of intended use?
Where it is impractical to perform full validation prior to delivery
or implementation, does the organization perform partial
validation to the extent applicable?
Are results of validation and subsequent follow-up actions
recorded?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 17 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
7.3.7 Control of design and development changes
Are processes established to identify, document and control
design changes?
Is the affect of changes evaluated on constituent parts and
delivered products?
Are all design and/or development changes verified and
validated, as appropriate, and approved before implementation?
Are the results of review of changes and subsequent follow-up
actions documented?
7.4 Purchasing
7.4.1 Purchasing process
Does the organization control its purchasing processes to ensure
purchased product conforms to requirements?
Does the type and extent of control exercised by the organization
depend upon the effect on subsequent realization processes and
their output?
Does the organization evaluate and select suppliers based on
their ability to supply product in accordance with the organization
requirements?
Are criteria for selection and periodic evaluation of suppliers
defined?
Are the results of evaluation and subsequent follow-up actions
recorded?
7.4.2 Purchasing information
Has the organization defined what constitutes a purchasing
document?
Do purchasing documents contain information describing the
product to be purchased, including, where appropriate,:
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 18 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
a) requirements for approval of: Product Processes
Procedures Equipment
b) requirements for qualification of personnel
b) QMS requirements
Do the purchasing processes ensure the adequacy of specified
requirements in the purchasing documents prior to their release
to the supplier?
7.4.3 Verification of purchased product
Has the organization identified and implemented the activities
necessary for verification of purchased product?
Does the organization specify the intended verification
arrangements and method of product release, as part of the
purchasing information?
7.5 Production and service provision
7.5.1 Control of production and service provision
Does the organization control production and service operation
through:
a) the availability of information that specifies the
characteristics of the product;
b) where necessary, the availability of work instructions;
c) the use and maintenance of suitable equipment;
d) the availability and use of measuring and monitoring
devices;
e) the implementation of monitoring and measurement
activities;
f) the implementation of defined processes for release,
delivery and applicable post-delivery activities.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 19 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
7.5.2 Validation of processes for production and service
provision
Has the organization identified production and service processes
that require validation?
Are the processes validated to demonstrate their ability to
achieve planned results?
Are the validation criteria defined and include, as applicable:
a) review and approval of processes;
b) review/qualification of equipment and personnel;
c) use of defined methods and procedures;
d) requirements for records;
e) revalidation.
7.5.3 Identification and traceability
Where appropriate, does the organization identify the product
throughout production and service operations?
Is the status of the product identified with respect to
measurement and monitoring?
Where traceability is a requirement, is the unique identification of
the product controlled and recorded? (4.2.4)
7.5.4 Customer property
Are processes established to exercise care with customer
property while it is under the organizations control or being used
by the organization?
Do the control processes include controls for intellectual
property?
Does the process address the following:
Verification Protection Maintenance
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 20 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Does the process ensure that occurrence of any customer
property that is lost, damaged or otherwise found to be
unsuitable for use are recorded and reported to the customer?
7.5.5 Preservation of product
Are methods and controls established to preserve conformity of
product with customer requirements during internal processing
and delivery to intended destination?
Do the methods and controls include:
Identification Handling Packaging
Storage Protection
Are the controls extended to constituent parts of a product?
7.6 Control of monitoring and measuring devices
Has the organization identified the measurements to be made
and the measuring and monitoring devices required to ensure
conformity of product to specified requirement?
Are the measuring and monitoring devices used and controlled
to ensure that measurement capability is consistent with the
measurement requirements?
Where applicable, are the measuring and monitoring devices:
a) calibrated or verified at specified intervals or prior to use,
against measurement standards traceable to international or
national standards;
aa) calibrated or verified where, if calibration standards do not
exist, the basis for calibration or verification is recorded
(4.2.4);
b) adjusted or readjusted as necessary;
c) identified to enable calibration status to be determined;
d) safeguarded from adjustments that would invalidate the
calibration;
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
AUDIT CHECK LIST
7.0 PRODUCT REALIZATION
Page 21 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
e) protected from damage and deterioration during handling,
maintenance, and storage?
Are records of the results of calibration and verification
maintained (4.2.4)?
When equipment does not conform to requirements, have the
validity of previous results been re-assessed and recorded?
For equipment out of calibration was corrective action taken on
the equipment and affected product?
Was software used for measuring and monitoring of specified
requirements validated prior to use?
Is software used for measuring and monitoring of specified
requirements re-validated periodically?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 22 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
8 Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement
8.1 General
Has the organization established plans to implement the
monitoring, measurement, analysis, and improvement processes
needed to:
a) demonstrate conformity of product;
b) ensure conformity of the QMS
c) continually improve the effectiveness of the QMS
Has the organization determined the need for, and use of,
applicable methodologies including statistical techniques?
8.2 Monitoring and measurement
8.2.1 Customer satisfaction
Has the organization determined methodologies for obtaining
information on customer satisfaction and/or dissatisfaction?
Are the methodologies sufficient to measure performance of the
QMS?
8.2.2 Internal audit
Has a documented procedure been established that includes:
responsibilities of the parties;
requirements for planning the audit;
requirements for conducting the audit;
definition of audit criteria, scope, frequency and methods;
selection of auditors ensuring audit independence;
recording results of the audit (audit evidence);
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 23 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
analyzing audit evidence against audit criteria (audit
Observations).
reporting results to management (audit conclusions).
Are audits planned in the form of an audit program, taking into
consideration:
status and importance of the processes and areas to be
audited;
results of previous audits.
Is the internal audit process adequate to determine whether the
QMS:
Conforms to the requirements of this international standard;
Conforms to the QMS requirements established by the
organization;
Has been effectively implemented and maintained.
Have audits been planned and conducted according to the
procedure?
Does management take timely corrective action on deficiencies
found during the audit?
Are follow-up actions part of the audit process?
Do follow-up actions include:
verification of the implementation of corrective action;
reporting of verification results.
8.2.3 Monitoring and measurement of processes
Are suitable methods established for measurement and
monitoring of those realization processes necessary to meet
customer requirements?
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 24 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Do the methods confirm the continuing ability of each process to
satisfy intended purpose?
When planned results are not achieved, is corrective action
taken?
8.2.4 Monitoring and measurement of product
Has the organization established appropriate stages to measure
and monitor product characteristics?
Is there evidence to confirm that product characteristics meet the
requirements for the product?
Is the evidence of conformity with the acceptance criteria
documented?
Do the measurement and monitoring records indicate the
authority responsible for release of the product? (4.2.4)
Are product/service delivery effected after all the specified
activities have been satisfactorily completed, unless otherwise
approved by a relevant authority and/or the customer.
8.3 Control of non-conforming product
Has a documented procedure been established to define the
processes involved in control of nonconformity?
Do the processes ensure that product that does not conform to
requirements is identified and controlled to prevent unintended
use or delivery?
Do the processes identify responsibilities and authorities for
dealing with non-conformities?
Do the processes identify the methods for:
a) eliminating the non-conformity;
b) authorizing the non-conformitys use, release or acceptance;
c) precluding the non-conformitys original intended use or
application.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 25 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Is corrected nonconforming product subject to re-verification to
demonstrate conformity to the requirements?
Do the processes ensure that appropriate corrective action is
initiated when non-conforming product is detected after delivery
or use has started?
Does the organization report concessions obtained from the
customer, the end user, regulatory body or other body regarding
the proposed correction of non-conforming product?
8.4 Analysis of data
Does the organization determine, collect and analyze
appropriate data to determine the suitability and effectiveness of
the QMS and to identify improvements that can be made?
Does the data include those generated by measuring and
monitoring activities and other relevant sources?
Does the data used for analysis provide information on:
a) customer satisfaction and/or dissatisfaction;
b) conformance to customer requirements;
c) characteristics of process, product and their trends;
cc) opportunities for preventive action;
d) suppliers.
8.5 Improvement
8.5.1 Continual improvement
Does the organization plan and manage processes necessary
for the continual improvement of the QMS.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 26 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Does the organization use the following information to facilitate
continual improvement of the QMS:
Quality Policy Quality Objectives
Audit Results Analysis of Data
Corrective and Preventive Action Management Review
Are there objective evidences of continual improvement with
involvement of top management?
8.5.2 Corrective action
Has the organization established a documented procedure for
corrective action with defined requirements for:
a) reviewing non-conformities (including customer complaints);
b) determining the causes of non-conformity;
c) evaluating the actions needed to ensure that non-
conformities do not recur;
d) determining and implementing the corrective action needed;
e) recording results of action taken;
f) reviewing of corrective action taken.
Are corrective actions taken to eliminate causes of non-
conformities effective in preventing recurrences?
8.5.3 Preventive action
Has the organization established a documented procedure for
preventive action with defined requirements for:
a) identifying potential non-conformities and their causes;
b) evaluating the need for action to prevent occurrence;
c) determining and implementing preventive action needed;
d) recording results of action taken;
e) reviewing preventive action taken.
ISO 9001 : 2008 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
CONVERSION/GAP ANALYSIS CHECK LIST
8.0 MEASUREMENT ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
Page 27 of 53 Flo Samuels Services, 510-733-3174, e-mail: flosamuels@msn.com Rev: 8/02/2008, Version 1
Supporting Document(s)/Pages Observations
Are preventive action taken to eliminate causes of potential non-
conformities effective in preventing occurrences?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 01 ISO 9001-2015 Transition Checklist C 01 Rev ADocumento4 pagine01 ISO 9001-2015 Transition Checklist C 01 Rev Avikkas vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Checklist ISO 9001:2015Documento25 pagineAssessment Checklist ISO 9001:2015Arati GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Manual: UncontrolledDocumento23 pagineQuality Manual: UncontrolledSiddhartha SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 13485:2016Documento17 pagineChecklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 13485:2016Gonzalo MazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q# ISO 9001:2015 Clause Audit Question Audit Evidence: 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibility and AuthoritiesDocumento1 paginaQ# ISO 9001:2015 Clause Audit Question Audit Evidence: 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibility and AuthoritiesHosay100% (2)
- Bizmanualz ISO 90012015 Quality Procedures SampleDocumento7 pagineBizmanualz ISO 90012015 Quality Procedures SampleSamsung Joseph0% (1)
- Melbourne Quality Procedure ManualDocumento61 pagineMelbourne Quality Procedure Manualsurangaguna100% (1)
- Internal Audit Checklist: System & Process Compliance AuditingDocumento7 pagineInternal Audit Checklist: System & Process Compliance AuditingEl BieNessuna valutazione finora
- Cracking the Case of ISO 9001:2015 for Manufacturing: A Simple Guide to Implementing Quality Management in ManufacturingDa EverandCracking the Case of ISO 9001:2015 for Manufacturing: A Simple Guide to Implementing Quality Management in ManufacturingNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting For MaterialsDocumento40 pagineAccounting For MaterialsAngel Alejo Acoba100% (1)
- ISO 9001-2008 Internal Audit ChecklistDocumento16 pagineISO 9001-2008 Internal Audit Checklistkashifbutty2k100% (1)
- Quality Management - ISO 9001 - 2015 Mandatory Documented Information - Documents and RecordsDocumento6 pagineQuality Management - ISO 9001 - 2015 Mandatory Documented Information - Documents and RecordsSithanandan GanapathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume. ShyamDocumento3 pagineResume. Shyamsunder2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- RLOC Equipment Integrity PolicyDocumento10 pagineRLOC Equipment Integrity PolicyMohammed ZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 9000 and Total Quality: The Relationship: Introduction To Quality Management Tell 26Documento25 pagineIso 9000 and Total Quality: The Relationship: Introduction To Quality Management Tell 26Anin Asmoro100% (1)
- Quality Audit Check ListDocumento1 paginaQuality Audit Check ListCandice Hurst100% (1)
- Quality Management System Software A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandQuality Management System Software A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
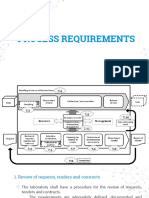
- ISO 17025 Process RequirementsDocumento29 pagineISO 17025 Process Requirementsdinesh171989Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorDocumento36 pagineCH 2 Cost Concepts and BehaviorYunita LalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Review How To Rev1Documento23 pagineManagement Review How To Rev1tony sNessuna valutazione finora
- MGT1116E Lecture 1. Introduction To Quality ManagementDocumento25 pagineMGT1116E Lecture 1. Introduction To Quality ManagementCẩm MiiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Document?: Tips On ISO 9001 Quality Management System DocumentationDocumento5 pagineWhat Is A Document?: Tips On ISO 9001 Quality Management System DocumentationMohammad Jaid AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Final AssignmentDocumento6 pagineFinal Assignmentmhk665Nessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001 2008 Audit ChecklistDocumento20 pagineISO 9001 2008 Audit ChecklistTorres EnriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001 2008 Quality ManualDocumento38 pagineISO 9001 2008 Quality ManualWillyanto Lee100% (1)
- Make Buy Special Order TutorialDocumento5 pagineMake Buy Special Order TutorialMickel Alexander100% (1)
- Concept of QA & QCDocumento16 pagineConcept of QA & QCVidit OberoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrective and Preventive ActionDocumento3 pagineCorrective and Preventive ActionmurugesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Common TS16949 Audit Findings - Perry JohnsonDocumento48 pagineCommon TS16949 Audit Findings - Perry Johnsontehky63Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ungraded Exercises Chapter 4-6Documento20 pagineUngraded Exercises Chapter 4-6lana del reyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality-Plan Iso10005 DemoDocumento9 pagineQuality-Plan Iso10005 DemoJamie dobbins0% (1)
- Revised Auditing TechniquesDocumento42 pagineRevised Auditing Techniquessaurabh choudhary100% (2)
- Quality AssuranceDocumento14 pagineQuality AssuranceNagaraj SridharNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure 01 - Control of Documents and RecordsDocumento6 pagineProcedure 01 - Control of Documents and Recordssuhara hussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Vendor CertificationDocumento5 pagineVendor CertificationAliqahwashNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Job Order CostingDocumento6 pagineProblem Job Order CostingAlan Carlo Galvez100% (1)
- Symbiosis Production OperationsManagementDocumento344 pagineSymbiosis Production OperationsManagementvrushali100% (1)
- Quality Manual 9001-2008 Elsmar 1Documento13 pagineQuality Manual 9001-2008 Elsmar 1luis miguel perez cruzNessuna valutazione finora
- BRC Agents and Brokers StandardDocumento70 pagineBRC Agents and Brokers StandardSYju EliasNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide For Quality System Manual Internal Audit: ApprovedDocumento9 pagineGuide For Quality System Manual Internal Audit: ApprovedMan Peatman ManpeatmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Supplier Quality Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandSupplier Quality Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Initial Audit PlanDocumento2 pagineInitial Audit PlanJamil VoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic FormingDocumento11 paginePlastic FormingAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- ERP NotesDocumento14 pagineERP NotesGaurav DodwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001 Audit & Gap Analysis ChecklistDocumento54 pagineISO 9001 Audit & Gap Analysis Checklisttauqeer25100% (3)
- ISO 9001 Internal Audit ChecklistDocumento14 pagineISO 9001 Internal Audit ChecklistEsterNTNessuna valutazione finora
- Conformity AssessmentDocumento15 pagineConformity AssessmentMaruan MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Checklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 9001-2015 PDFDocumento12 pagineChecklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO 9001-2015 PDFΠερικλής ΣδραβόπουλοςNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO/IEC 17021-1:2015 Requirement Matrix: Authority: Director of Accreditation Effective: 2015/06/16Documento6 pagineISO/IEC 17021-1:2015 Requirement Matrix: Authority: Director of Accreditation Effective: 2015/06/16Mohamed Abbas100% (1)
- SAP Ariba Solutions and SAP S4HANA The Path To Procurement TransformationDocumento2 pagineSAP Ariba Solutions and SAP S4HANA The Path To Procurement TransformationJose SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Blank Audit ChecklistDocumento5 pagineBlank Audit ChecklistWildan RadistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Plan QuestionnaireDocumento1 paginaAudit Plan QuestionnaireImi Zaboss100% (1)
- As IA Checklist Sec7 5Documento5 pagineAs IA Checklist Sec7 5Randy Wee AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Documented InformationDocumento5 pagineDocumented InformationFaridi Mohamed BasriNessuna valutazione finora
- As Iso 10015-2006Documento25 pagineAs Iso 10015-2006АлексейNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Approach A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandProcess Approach A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Control of Nonconforming ProductsDocumento2 pagineControl of Nonconforming ProductsPrince Moni100% (1)
- Nonconformity Report TemplateDocumento2 pagineNonconformity Report TemplateMohammad Hadoumi Saldan100% (1)
- ISO 19011 2011 Is A Management System Auditing StandardDocumento19 pagineISO 19011 2011 Is A Management System Auditing StandardPrashanthPrashanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Bizmanualz ISO 9001 QMS Policies and Procedures SampleDocumento8 pagineBizmanualz ISO 9001 QMS Policies and Procedures SampleallukazoldyckNessuna valutazione finora
- QSP6 1 Risks Preview PDFDocumento3 pagineQSP6 1 Risks Preview PDFCentauri Business Group Inc.100% (4)
- QMS Manual Update TarasimaDocumento25 pagineQMS Manual Update TarasimasahadatNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing The Procurement PlanDocumento8 pagineAuditing The Procurement PlannarendraidealNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001 Internal Audit QuestionsDocumento4 pagineISO 9001 Internal Audit QuestionsLee Leeuss100% (1)
- APG InternalAudit2015 PDFDocumento4 pagineAPG InternalAudit2015 PDFBulmaro SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Haccp& FSMSDocumento3 pagineHaccp& FSMSSelvamani RamanNessuna valutazione finora
- DCC and QMS Coordinator - HandoutDocumento17 pagineDCC and QMS Coordinator - HandoutRaymond PalisocNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 SCP Remote or Virtual Audit Checklist Rev 0 PDFDocumento3 pagine04 SCP Remote or Virtual Audit Checklist Rev 0 PDFQueenie Gallardo AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- CPA Compliance ChecklistDocumento25 pagineCPA Compliance ChecklistFizz FirdausNessuna valutazione finora
- LQMS-SIP Checklist Final v1 - Jan 12 2016 PDFDocumento48 pagineLQMS-SIP Checklist Final v1 - Jan 12 2016 PDFrasimc9475Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Pages - MIS IntroductionDocumento5 pagine3 Pages - MIS IntroductionRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Library Management System SynopsisDocumento3 pagineLibrary Management System SynopsisieeexploreprojectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Surveyor Comment - 2 Pages - Health Information Management SystemDocumento2 pagineSurveyor Comment - 2 Pages - Health Information Management SystemRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Reason For Decertification ISO 9001Documento12 pagineThe Reason For Decertification ISO 9001Rizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Blood Bank - A Simple Management System ApproachDocumento4 pagineThe Blood Bank - A Simple Management System ApproachRizaldi Djamil100% (1)
- 3 Pages Description of Mstering Management SystemDocumento3 pagine3 Pages Description of Mstering Management SystemRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Payroll Management System SynopsisDocumento4 paginePayroll Management System SynopsisShashi Shekar KnNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Simple Pages of Content Management SystemDocumento3 pagine3 Simple Pages of Content Management SystemRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Pages Assessment Material For Procurement and Operations ManagementDocumento12 pagine11 Pages Assessment Material For Procurement and Operations ManagementRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Material - Performance Management System - AgendaDocumento1 paginaPresentation Material - Performance Management System - AgendaRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Guidelines For Project Operation Management - A Sample From UNDocumento2 pagineSimple Guidelines For Project Operation Management - A Sample From UNRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Simple Pages - Introduction To CommunicationDocumento2 pagine2 Simple Pages - Introduction To CommunicationRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Approach of Production and Operation Management - Less PagesDocumento2 pagineSimple Approach of Production and Operation Management - Less PagesRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Plan GuidelinesDocumento5 pagineMarketing Plan Guidelinesv04hannaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Simple Pages - Sample For JOB DESCRIPTION of HR CoordinatorDocumento3 pagine3 Simple Pages - Sample For JOB DESCRIPTION of HR CoordinatorRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- New Ground - Non-Traditional Sectors Benefitting From Project ManagementDocumento3 pagineNew Ground - Non-Traditional Sectors Benefitting From Project ManagementRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Moss Management Agreement NewDocumento2 pagineMoss Management Agreement NewRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Pages - Basic Lecture On HR MANAGEMENTDocumento8 pagine7 Pages - Basic Lecture On HR MANAGEMENTRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Stratagic Marketing Plan - A Sample IntroductionDocumento4 pagineStratagic Marketing Plan - A Sample IntroductionRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Pages - Introduction To Performance ManagementDocumento4 pagine4 Pages - Introduction To Performance ManagementRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Pages - Simple Introduction To Performance ManagementDocumento2 pagine2 Pages - Simple Introduction To Performance ManagementRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Page - Guideline of Marketing ManagementDocumento1 pagina1 Page - Guideline of Marketing ManagementRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Page of Statement Audit - Simple ExampleDocumento1 pagina1 Page of Statement Audit - Simple ExampleRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Page Audit Observation - A Sample ReportDocumento1 paginaSingle Page Audit Observation - A Sample ReportRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Pages Sample of HR Management OutlineDocumento3 pagine3 Pages Sample of HR Management OutlineRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample of Audit Plan - Short and Simple ApproachDocumento2 pagineSample of Audit Plan - Short and Simple ApproachRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Page Sample of Sylabus of Information SecurityDocumento4 pagine4 Page Sample of Sylabus of Information SecurityRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample of Internal Audit Program Fo Is Admin & AccessSecurityDocumento10 pagineSample of Internal Audit Program Fo Is Admin & AccessSecurityRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Pages of Basic Information Security ConceptsDocumento8 pagine7 Pages of Basic Information Security ConceptsRizaldi DjamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Security and IT GovernanceDocumento6 pagineInformation Security and IT GovernanceSreekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical MeetDocumento7 pagineTechnical MeetsameertutejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Supplier Relationship ManagementDocumento2 pagineAssignment Supplier Relationship Managementeeit_nizam100% (1)
- Home Appliances - GujranwalaDocumento10 pagineHome Appliances - GujranwalaMohtasim Kamran MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Grupo de Procesos PMBOKDocumento12 pagineGrupo de Procesos PMBOKEduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Concept, Terminologies and BehaviorDocumento8 pagineCost Concept, Terminologies and BehaviorANDREA NICOLE DE LEONNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Business Management John SchorrDocumento4 pagineIntegrated Business Management John Schorrunknown139Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vendor Managed Inventory - Project ReportDocumento11 pagineVendor Managed Inventory - Project ReportTauheedalHasan100% (2)
- MRP ExerciseDocumento3 pagineMRP ExerciseAbdelrahman El-OrbanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of ProcessDocumento35 pagineDesign of Processsujeetleopard100% (1)
- Purchase: Purchasing Refers To A Business or OrganizationDocumento15 paginePurchase: Purchasing Refers To A Business or OrganizationBhargav LabishettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignemnt 1-Winter2023Documento2 pagineAssignemnt 1-Winter2023Omotara YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Jurnal BelaniaDocumento12 pagine17 Jurnal BelaniaHilary sbnNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship ReportDocumento12 pagineInternship ReportChandrasekar ChithambaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Subrat Bordoloi ResumeDocumento3 pagineSubrat Bordoloi ResumeSachin SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Apparel Manufacturing Process: Assignment - 2Documento8 pagineApparel Manufacturing Process: Assignment - 2LAVANYA KOTHANessuna valutazione finora