Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Format Nota Ringkas
Caricato da
myza_zesty0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
139 visualizzazioni16 paginenota menggunakan format ghani (ump)
Titolo originale
format nota ringkas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentonota menggunakan format ghani (ump)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
139 visualizzazioni16 pagineFormat Nota Ringkas
Caricato da
myza_zestynota menggunakan format ghani (ump)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 16
CHAPTER 1: MATTER
PART A: GHANIS FORMAT
SUBTOPIC:
i. WHAT IS MATTER
ii. STATES OF MATTER
iii. CONCEPT OF DENSITY
SUBTOPIC
MAJOR
POINT
MINOR
POINT
SUPPORTING POINT
1
SUPPORTING
POINT 2
What is
Matter?
Defined as
anything
which has
mass and
occupies
space
Consists of
living things
and non-living
things.
Example of non-living
things:
Air
Water
soil
Example of living
things:
Plants
Animals
Humans
States of
Matter
Solid Properties of
solid
-Retains a fixed volume
and shape
-cannot be compressed
-Does not flow
-Rigid (particles cannot
move)
Particles Model for
solid
Liquid Properties of
liquid
-Occupies the shape of
part of container
-Not easily compressible
-Flows easily
-Particles can move
Particles Model for
liquid
Gas Properties of
gas
- Occupies the shape and
volume of container
- Compressible
- Flows very easily
-Particles can move past
one another
Particles Model for
gas
Concept of
Density
Definition of
Density
-Physical
property of
matter that
describes the
degree of
compactness
of a substance
on how closely
packed the
particles of a
substance are.
-Relationship between
mass and volume of a
substances:
Density = Mass
Volume
Relationship
between
ability to
float and
density
-Buoyancy
refers to the
ability of a
material to
float on water
-An object will sink in a
liquid if the object is
denser than the liquid
-Object which is less
dense will float in a
liquid that is denser.
Sink and float
candle
Applications Boat and
Ship
-Boat and ships
that weigh
thousands of
tonnes can
float on the
water because
inside of the
structure are
empty spaces
that filled with
air.
-This makes
the density of
boat and ship
is less than
density of
water.
Boat that float on the water
Submarine -A submarine
uses ballast
(stability) as a
means of
descending and
ascending
underwater.
-If submarine
rises towards
the surface, a
valve will
opened to
release
compressed air
into tanks
(ascending)
-The air
pushes out
water and
causes the
submarine to
ascend.
Float
-A float helps a
swimmer to
float on the
surface of
water
-The air in the
float makes it
less dense
than water.
PART B: QUESTIONS
Objective questions
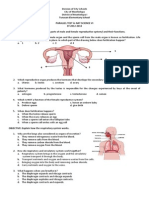
1. What determines the state of matter?
A. Freezing point and boiling point
B. Densities of matter
C. Arrangement of particles
D. Number of particles in matter
2. Water molecules in steam and water molecules in ice differ in term of
A. Size of molecules
B. Densities of molecules
C. Volume of molecules
D. Distance between molecules
Subjective questions
1. Figure 1 shows the arrangement of particles in substances P, Q and S.
P Q S
Figure 1
a) Based on Figure 1, identify the states of P, Q, and S. [3 marks]
b) States two characteristics each for substances P, Q and S. [6 marks]
c) State two examples of substances that have similar characteristics as P, Q and S.
[3 marks]
PART B: ANSWER
Objective questions
1. C arrangement of particles
Matters exist in three states which is solid, liquid and gas. They are differentiate based
on the arrangement of the particles.
2. D distance between molecules
The particles in solids are closely packed together, particles in liquids are not arranged
in regular pattern and less compact, and particles in gas are far apart and not in fixed
pattern.
Subjective questions
1.
a) P:Solid Q: Liquid S: Gas
b) 2 Characteristics of P, Q and S
P (solid) Q (liquid) S (gas)
Has a fixed
volume and
shape
Occupies the
shape of part of
container
Occupies the shape
and volume of
container
Cannot be
compressed
Not easily
compressible
Compressible
Rigid (particles
cannot move)
Particles can
move
Particles can move
past one another
CHAPTER 2 : BIODIVERSITY
PART A : GHANIS FORMAT
SUBTOPIC:
i. DIVERSITY OF LIVING ORGANISMS IN A HABITAT
ii. CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS
SUBTOPIC
MAJOR
POINT
MINOR
POINT
SUPPORTING
POINT 1
SUPPORTING
POINT 2
Diversity of
living
organisms in a
habitat
Definition of
Biodiversity
defined as
different types
of animals and
plants on Earth
Classification
of living
organisms
-based on their
characteristics
-in
classification
used today,
they are
classified into
five main
groups called
kingdom
The 5 main groups:
Animals
Plants
Fungi
Bacteria
Very simple
organisms
Classification
of animals
Vertebrates
-animals with
backbone
-classified into
5 smaller
group with
their own
characteristics
Fish Live in water
have tails and fins
to help them swim
Cold-blooded
Breath through
gills
Most lay eggs
without shells
o Clown
fishes
o Snapper
o Stingrays
o Sea
horses
o Carp
Amphibians Live on both land
and in water
Adults have 4
limbs to jump on
land and swim in
water
Cold-blooded
Young breath
through gills
Adults breathe
through lungs
when on land and
through skin when
in water
Female lay eggs in
water
o Frogs
o Toads
o Newts
Reptiles Most of them live
on land but some
are in water
Have 4 limbs
except for snake
Cold-blooded
Breath through
lungs
Lay eggs on land
and they fertilised
inside females
body
o Lizards
o Tortoises
o Snakes
o Alligators
Birds Live on land
Most them can fly
Warm-blooded
Breath through
lungs
Lay eggs in their
nests and they are
fertilised
internally and
have hard shells
o Owls
o Ducks
o Chickens
o Parrots
o Penguins
o Sparrows
Mammals Most live on land
but some in water
Some fly, some
move on land
Warm-blooded
Breath through
lungs
All mammals
except duck-billed
platypus and ant-
eater, give birth to
live young
o Dolphins
o Rabbits
o Bats
o Squirrels
o Pangolins
o Whales
Invertebrates
-animals
without
backbone
-divided into 2
groups based
on the type of
legs
With jointed
legs
Divided into
3 groups
based on
number of
legs
Three pairs of legs
Butterfly
Beetle
Grasshopper
Butterfly
Four pairs of legs
Scorpion
Spider
Mite
Spider
More than four pair
of legs
Shrimp
Crab
Centipede
Shrimp
Without
jointed legs
-divided into 2
groups based
on their
appearance
Worms-like
invertebrates
Leeches
Earthworms
Clam
Earthworm
Non-worm-like
invertebrates
Jellyfish
Starfish
Snails
Snail
PART B: QUESTIONS
Objective questions
1.
Which of the following animals has the above characteristics?
A. Stingray
B. Platypus
C. Whale
D. Shark
2. Which of the following plants is a non-flowering plant?
A. Maize
B. Sugar cane
C. Coconut tree
D. Pine tree
3. Which of the following is not correct about the similarities between reptiles and
amphibians?
A. Both have moist skin
B. Both are cold-blooded
C. Both breath through lungs
D. Both lay eggs
Warm-blooded
Lives in the sea
Give birth to young
Skin covered with hair
Subjective question
1. J, K, L and M in Figure 1 are four different types of animals.
J K L M
a) Give three characteristics that can be used to classify animals J, K, L and M.
[3 marks]
b) Classify animals J, K, L and M according to their common characteristics by
completing the flow chart below. [10 marks]
Animals
PART B: ANSWER
Objective questions
1. B Platypus
All mammals are Warm-blooded and breathe through lungs. Except for duck-billed
platypus and ant-eater, they give birth to live young.
2. D Pine tree
Flowering plants are plants with flowers. So, here all the three (maize, sugar cane and
coconut tree) do have flowers.
3. A Both have moist skin
Reptiles have dry and scaly skin, while amphibians have loose and moist skin.
Subjective question
1.
a) Three characteristics to classify animals J, K, L and M
vertebrates and invertebrates
with and without joined legs
Cold-blooded or warm-blooded.
b) .
Common characteristics
Invertebrates
Vertebrates
Joined legs
Without
joined legs
Cold-
blooded
Warm
blooded
Scorpions Jelly fish
Fish Cat
Animals
CHAPTER 3 : BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
PART A : GHANIS FORMAT
SUBTOPIC:
i. TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN HUMAN
ii. TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN PLANT
SUBTOPIC
MAJOR
POINT
MINOR
POINT
SUPPORTING
POINT 1
SUPPORTING
POINT 2
Transport
system in
human
-called
human
circulatory
system
-consists of 3
parts
Heart Made up of
cardiac
muscles,
connective
tissues, and
blood vessels
Functions of
the right side
heart is to
collect
deoxygenated
blood from
body and
pump it to
lungs
The left side
of heart
collects
oxygenated
blood from the
lungs and
pumps it out to
the body
Heart is divided
into 4 chamber
Right atrium is
connected to the
vena cava
Left atrium is
connected to the
pulmonary vein
Right ventricle is
connected to the
pulmonary artery
Left ventricle is
connected to the
aorta
Structure of human
heart
Blood
vessels
connect the
heart to each
part of the
body
consists of
three types
-Arteries
-Veins
-Capillaries
Arteries
carry blood away
from the heart
have thick,
muscular and
elastic walls
have small lumens
and do not have
valves
Veins
carry blood back to
the heart
has larger lumen
contain valves that
prevent blood from
flowing back
Capillaries
connects arteries
and veins
does not have
valves
Blood about 45%of
blood is made
up of solids
called blood
cells of
corpuscles
3 kinds of
blood cells
-red blood
cells
-white blood
cells
platelets
Red blood cells
(erythrocytes)
They are
biconcave, disc-
shaped cells
without nucleus.
Contain
haemoglobin
which give the
blood its red colour
White blood cells
(leucocytes)
Play an important
part in the body
immune system to
defend the body
against diseases
Platelets
(thrombocytes)
They are produced
from bone marrow,
nucleus and does
not have definite
shape
Their main job is
to heal wounds
erythrocytes
thrombocytes
Transport
system in
plants
Vascular
tissues
Xylem
Carries water
containing
dissolved
mineral salts
from the
roots to the
leaves
through
osmosis
Phloem
Carries
dissolved
food in the
form of sugar
to all parts of
plants
Cross section of the stem
Transpir-
ation
Process
where water
is loss by
evaporation
from the
leaves of a
plant
Water
escapes from
the spaces
inside the
leaves in
form of
water vapour
and passes
through the
pores called
stoma.
Stoma
Is a single hole or
pole, through
which gases can
enter or leave a
plant leaf
Surrounded by a
pair of cells known
as guard cells
Stoma structure
PART B: QUESTIONS
Objective questions
1. The human circulatory system consists of
I. The heart II. Blood
vessels
III. Lungs
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III.
2. The pulmonary artery differs from the pulmonary vein because it
A. Has seminular valves
B. Has thin muscular walls
C. Carris blood under low pressure
D. Carries deoxygenated blood
3. Which of the following is the characteristic of arteries?
A. Have thick muscular walls
B. Have thin muscular walls
C. Have very thin muscular walls
D. Have walls which is only one cells thick
Subjective Questions
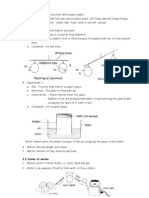
1. Figure 1 shows a cross section of a balsam plant.
Figure 1
a) Wjich part of the balsam plant is the cross section taken? [1 mark]
b) Name the parts labelled P and Q. [1 mark]
c) What is the function of the part labelled P in a plant? [1 mark]
d) What is the function of the labelled Q in a plant? [1 mark]
PART B: ANSWERS
Objective questions
1. A I and II only
Human circulatory system consists of heart, blood and blood vessels.
2. D carries deoxygenated blood.
All arteries deliverosygenated blood to body cells, except for the pulmonary artery
which deliver deoxygenated blood to lungs.
3. A have thick muscular walls.
The arteries are blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. They have
thick, muscular and elastic walls.
Subjective Questions
1. Figure 1 shows a cross section of a balsam plant .
a) Root
b) P : Phloem Q : Xylem
c) i) the P in the figure shows the Phloem which is function to transport water in the
plant
ii) the Q in figure shows the Xylem which is function to transport food in the plant
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reproductive and Respiratory Systems NAT TestDocumento11 pagineReproductive and Respiratory Systems NAT TestKristine BarredoNessuna valutazione finora
- FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding the Basics of ScienceDocumento19 pagineFORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding the Basics of ScienceQQLove92% (13)
- FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding Nature Through Systematic StudyDocumento19 pagineFORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding Nature Through Systematic StudyKhadijah Yusop100% (1)
- Animal ClassificationDocumento7 pagineAnimal ClassificationMohanad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- VI-9-The Living Organisms and Their SurroundingsDocumento19 pagineVI-9-The Living Organisms and Their SurroundingsMusfarNessuna valutazione finora
- Extended Universal Science Class 5 AnsweDocumento28 pagineExtended Universal Science Class 5 Answeastershivani tejpalNessuna valutazione finora
- STEM General Biology2 3-4Documento13 pagineSTEM General Biology2 3-4Jp menorNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 2 Notes (Chapter 1 - Chapter 4)Documento20 pagineScience Form 2 Notes (Chapter 1 - Chapter 4)AmirulNazheefBinZakaria73% (11)
- Science Quiz Bee Levels 1-3Documento7 pagineScience Quiz Bee Levels 1-3El Cruz100% (4)
- Name: Roshini A/P Mohan Krishan Class: 2 KRK 1 Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineName: Roshini A/P Mohan Krishan Class: 2 KRK 1 Subject: ScienceRoshini MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Life Science - Q1 - Week1 - SLK1 - Earth-and-Earth-System - ALFANTADocumento17 pagineEarth and Life Science - Q1 - Week1 - SLK1 - Earth-and-Earth-System - ALFANTACharles Adrian Cabil100% (1)
- Chapter 9Documento7 pagineChapter 9saakittuNessuna valutazione finora
- Beloved TR: Miss RoslinDocumento42 pagineBeloved TR: Miss RoslinBindi Dharod0% (1)
- The Living OrganismsDocumento16 pagineThe Living Organismsmr1977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q Ans The Living Organisms Characteristics and HabitatDocumento5 pagineQ Ans The Living Organisms Characteristics and HabitatSweetandSour CandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Living Things, Their Habitat and AdaptationDocumento5 pagineLiving Things, Their Habitat and AdaptationVIKASYOJANAEduCareNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Animalia - 1Documento13 pagineKingdom Animalia - 1rajeev Kumar guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Must-Know Key Concepts in PSLE ScienceDocumento30 pagineMust-Know Key Concepts in PSLE ScienceClarisa CynthiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nota Sains Tahun 5Documento46 pagineNota Sains Tahun 5mohdfirdaushada100% (2)
- Army Public School Gopalpur: CLASS - 11 Science Subject-Biology SESSION-2020-2021 Animal KingdomDocumento11 pagineArmy Public School Gopalpur: CLASS - 11 Science Subject-Biology SESSION-2020-2021 Animal KingdomAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Origin and Structure of The Earth Planet EarthDocumento4 pagineLesson 1 Origin and Structure of The Earth Planet Earthhellosirpogi0% (1)
- EST Paper 2 - Trial ExamDocumento11 pagineEST Paper 2 - Trial ExamLum Yoke LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6. Vertebrates: 1. Fish 2. Amphibians 3. Reptiles 4. Birds 5. MammalsDocumento27 pagineUnit 6. Vertebrates: 1. Fish 2. Amphibians 3. Reptiles 4. Birds 5. MammalsgenusxyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Jss 1 - Basic ScienceDocumento24 pagineJss 1 - Basic ScienceAyomipo OlorunniwoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 habitat of living 20 Feb 24Documento8 pagine4 habitat of living 20 Feb 24ramasenNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Experiment Group Answers Inserted Envi Sci FinalDocumento6 pagineModule 3 Experiment Group Answers Inserted Envi Sci FinalJillian Kaye OsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Science NotesDocumento21 pagineForm 1 Science NotesVanaja Mani SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- English PutriDocumento3 pagineEnglish PutriRendy DunggioNessuna valutazione finora
- General Science ElementaryDocumento8 pagineGeneral Science ElementaryJademarie Tamaray100% (5)
- Chapter 3: Biodiversity 3.1 The Variety of Living Organisms: Segmented Body Unsegmented BodyDocumento3 pagineChapter 3: Biodiversity 3.1 The Variety of Living Organisms: Segmented Body Unsegmented BodyHeina NadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 1 Notes: 1. Pelicanus Occidentalis ReductionDocumento5 pagineBiology Chapter 1 Notes: 1. Pelicanus Occidentalis ReductionNoor HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Chapter 3 MatterDocumento6 pagineForm 1 Chapter 3 Matterjj9821100% (1)
- The Genre of Science: Genres in CLIL SubjectsDocumento16 pagineThe Genre of Science: Genres in CLIL SubjectsCarme Florit BallesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento33 pagineChapter 1Salma AymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth's Characteristics that Sustain LifeDocumento19 pagineEarth's Characteristics that Sustain LifeVaness Flor Cabug PuyatNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 7 Bio Chap Answer - Key - 3Documento6 pagineClass 7 Bio Chap Answer - Key - 3Laiq Ur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- G7RC23 Science 1.1 - 1.4Documento8 pagineG7RC23 Science 1.1 - 1.4Audree JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet No.1 VertebratesDocumento4 pagineActivity Sheet No.1 VertebratesRaniey MayolNessuna valutazione finora
- JSS1 Basic Science Term 1 NotesDocumento19 pagineJSS1 Basic Science Term 1 NotesFolukeNessuna valutazione finora
- JSS1 Basic Science Term 1 E-Learning NotesDocumento19 pagineJSS1 Basic Science Term 1 E-Learning NotesPeter Omovigho Dugbo100% (1)
- Answer Key ReinforcementDocumento11 pagineAnswer Key ReinforcementMari Cruz Sanchez ÚbedaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Science ElementaryDocumento12 pagineGeneral Science ElementaryShan Taleah RealNessuna valutazione finora
- Reptiles: Diapsid AmniotesDocumento3 pagineReptiles: Diapsid AmniotesJerome AbrigoNessuna valutazione finora
- AGES AND STAGES SCHOOL SCIENCE QUIZ BEE PROPER KinderDocumento6 pagineAGES AND STAGES SCHOOL SCIENCE QUIZ BEE PROPER KinderJhomar Lat100% (1)
- Chapter 3: BiodiversityDocumento2 pagineChapter 3: BiodiversityAlexander Noah A MNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Topic: 1.1 Study Living ThingsDocumento5 pagineBiology Topic: 1.1 Study Living Thingsazizul hasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Question With AnswerDocumento5 pagineBiology Question With AnswerKhairy Iest100% (1)
- Grade 5 New Week 4 Grade 5 12 5 20Documento10 pagineGrade 5 New Week 4 Grade 5 12 5 20habiba buttNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 110 - Ch1Documento34 pagineBio 110 - Ch1محسن الشاطريNessuna valutazione finora
- G7RC Science 1.1 - 1.3Documento6 pagineG7RC Science 1.1 - 1.3Audree JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Characteristics of The Earth and Its SubsystemsDocumento13 pagineEarth Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Characteristics of The Earth and Its SubsystemsBaji C. NaksakNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5. InvertebratesDocumento8 pagineUnit 5. InvertebratesYolanda Fernández VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has ADocumento7 pagineA Vertebrate Is Any Chordate That Has AomariaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Env 107L-4Ecology and EcosystemDocumento14 pagineEnv 107L-4Ecology and EcosystemMomin UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - WS-1Documento6 pagineAnswer Key - WS-1dwolf3639Nessuna valutazione finora
- GED Science Posttest: 38 ItemsDocumento17 pagineGED Science Posttest: 38 ItemsThin Thin ThiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Classification - Ii (Notes)Documento5 pagineKingdom Classification - Ii (Notes)Sanhitha RameshNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification and Properties of Matter QuizDocumento17 pagineClassification and Properties of Matter QuizRhejean BasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Animal Kingdom Phyla CharacteristicsDocumento13 pagineClassification of Animal Kingdom Phyla CharacteristicsAryanNessuna valutazione finora
- CataloguingDocumento143 pagineCataloguingmyza_zestyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions For Win Explorer ErrorDocumento1 paginaSolutions For Win Explorer Errormyza_zestyNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 3 Chapter 1Documento5 pagineForm 3 Chapter 1myza_zestyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz1 CopyrightDocumento2 pagineQuiz1 Copyrightmyza_zestyNessuna valutazione finora
- Diploma in YogaDocumento11 pagineDiploma in YogaMukesh KumawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Pressure - Blood Pressure ChartDocumento3 pagineBlood Pressure - Blood Pressure ChartMahmoud MaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Venous Anomalies - DR RanjithDocumento96 pagineSystemic Venous Anomalies - DR RanjithKhaled S. HarbNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento23 pagineApproach To Cardiovascular DiseasesanjivdasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Surgery in The Adult-3rd EditionDocumento1.729 pagineCardiac Surgery in The Adult-3rd EditionFlorentina Negoita96% (26)
- Updated Second Term Study PackDocumento46 pagineUpdated Second Term Study PackDaveNessuna valutazione finora
- SYBSc Sem 4 Practical No. 16 Aortic ArchesDocumento2 pagineSYBSc Sem 4 Practical No. 16 Aortic ArchesAnkit Nariya100% (1)
- CH 9 Transport in Animals Worksheet 2Documento8 pagineCH 9 Transport in Animals Worksheet 2Mohamed AlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plans For All PDFDocumento32 pagineLesson Plans For All PDFmuzamil shabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Percutaneous Interventional Cardiovascular Medicine - The PCR-EAPCI TextbookDocumento18 paginePercutaneous Interventional Cardiovascular Medicine - The PCR-EAPCI TextbookRanda TabbahNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertensive Vascular DiseaseDocumento5 pagineHypertensive Vascular DiseaseGenoMacaraanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology SLEDocumento27 pagineAnatomy and Physiology SLEMoti Pagador100% (4)
- Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease Madebla Bla BL SimpleDocumento259 pagineEchocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease Madebla Bla BL SimpleStoicaAlexandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunity STPMDocumento2 pagineImmunity STPMjennie0% (1)
- Pulmonary Hipertension PDFDocumento481 paginePulmonary Hipertension PDFRadhiatul AdillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Physiology in An Aquatic EnvironmentDocumento47 pagineHuman Physiology in An Aquatic EnvironmentMARIA CAMILA RENGIFO CAICEDONessuna valutazione finora
- Atrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsDocumento10 pagineAtrial Fibrillation - Geeky MedicsJahangir AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Marcial - Assignment#1Documento5 pagineMarcial - Assignment#1Francois MarcialNessuna valutazione finora
- The Knight: Smoking and HealthDocumento8 pagineThe Knight: Smoking and Health健康生活園Healthy Life GardenNessuna valutazione finora
- 2607 FullDocumento94 pagine2607 FullanindiawNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Module For Science 9 First Quarter: Camarines Norte College IncDocumento24 pagineLearning Module For Science 9 First Quarter: Camarines Norte College IncCrisanto VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 8.Final-GHTF RegulationDocumento27 pagineWeek 8.Final-GHTF Regulationmustafe810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Disease in The Adult: Special ReportDocumento10 paginePathophysiology of Congenital Heart Disease in The Adult: Special ReportLwin ThantNessuna valutazione finora
- Lymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesDocumento9 pagineLymphatic System and Immunity - Seeleys - NotesLol lol100% (2)
- Important Causes of Sudden Cardiac DeathDocumento2 pagineImportant Causes of Sudden Cardiac DeathTausif AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport in Animals 4 QPDocumento13 pagineTransport in Animals 4 QPRehan AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Boardworks As Biology ContentsDocumento19 pagineBoardworks As Biology ContentsStudent 365Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Case Study Homework Week 5Documento4 pagineCardiac Case Study Homework Week 5Study AssistantNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular EmergenciesDocumento2 pagineCardiovascular EmergenciesAli AbdullahiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Diagnosis: Right Ventricular Myocardial Infarction: Clinical MedicineDocumento2 pagineECG Diagnosis: Right Ventricular Myocardial Infarction: Clinical MedicineNadyaindriati96Nessuna valutazione finora