Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Breast Cancer and Her2
Caricato da
JimWillis0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
40 visualizzazioni2 pagineA brief overview of Breast Cancer and the importance of HER2, ideal for Medical science students or those interested in HER2 positive Breast Cancer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoA brief overview of Breast Cancer and the importance of HER2, ideal for Medical science students or those interested in HER2 positive Breast Cancer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
40 visualizzazioni2 pagineBreast Cancer and Her2
Caricato da
JimWillisA brief overview of Breast Cancer and the importance of HER2, ideal for Medical science students or those interested in HER2 positive Breast Cancer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
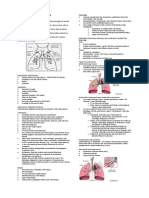
Breast Cancer and HER2
Structure of Normal Breast
The breast is composed of fatty tissue, milk ducts and lobes
o Layers of connective tissue sit between the fatty tissue
and ducts
Nipple and duct opening
The milk ducts are composed of a lumen surrounded by a layer of
simple columnar epithelial cells
o Epithelial cells are surrounded by layer of simple
cuboidal/myoepithelial cells
o Myoepithelial cells are surrounded by basement
membrane
The breast sits atop the ribs and intercostal muscles
How the diagnosis of breast cancer is made
A combined, clinical, imaging and pathological approach (triple approach)
Clinical = investigation of all lumps detected in breast, referral for imaging
Imaging = some types of breast cancer do not lead to palpable lump
o Tumour on x-ray = unusual opaque area
o Calcified lesions on X-ray (little white spots) = may be early sign of breast cancer
Pathological = investigation of withdrawn samples from breast
o Fine needle aspiration
Small thin needle and syringe withdraw sample of cells from lump
Extracts cytological material
o Core biopsy
Needle withdraws a core of lump tissue
Extracts histological material
o Specific diagnosis based on pathological examination
E.g. ductal carcinoma (most common)
Observed tumour cells in a biological specimen invade normal breast tissue
creating a dense fibrous stroma
E.g. Tubular carcinoma
Observed tumour cells form regular tubular structures resembling small ducts
E.g. Mucoid Carcinoma
Cells secrete mucin into the stroma
Tumour grading
o Tubule formation
>75% = 1
10-75% = 2
<10% = 3
o Nuclear pleomorphism
Small uniform cells = 1
Moderate increase in size and variation = 2
Marked variation = 3
o Mitotic count (per10 high power fields)
up to 7 = 1
8 to 14 = 2
15 or more = 3
TMN system = assessing stage of breast cancer (1= T1, N0, M0; 4 = T4, N2, M1)
o Tumour spread
T0 = breast free of tumour
T1 = Lesion <2cm in size
T2 = Lesion 2-5cm
T3 = Skin/ chest wall involved by
invasion
o Lymph Node involvement
N0= No axillary nodes involved
N1= Local nodes involved
N2= Distant nodes involved
o Metastatic spread
M0=No metastases
M1=demonstrable metastases
MX=suspected metastases
Relevance of Testing for HER2 expression
HER2 overexpressed in 25-30% of invasive breast cancers
Dimerisation of HER2 receptors + subsequent phosphorylation of signalling proteins activates
cascade of signalling pathways
HER2+ve normally ER-ve and PR-ve
o Prognosis: HER2 = significantly worse prognosis in node +ve cancer
o Treatment: favourable response to Herceptin (aka Trastuzumab) or Herceptin +
chemotherapy
Herceptin blocks receptor dimeristation between HER family
Prevents extracellular domain cleavage by sheddase enzymes (alternative mode of
activation)
Prevents activation of signalling pathways
o Prevents activation of proliferative genes/ inhibition of pro-
apoptotic genes
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Colo RectalDocumento31 pagineColo RectalAmber CarterNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast Diseases: 1 Historical PerspectiveDocumento14 pagineBreast Diseases: 1 Historical PerspectiveMuhammad IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast Cancer: Faraza Javed M.Phil PharmacologyDocumento23 pagineBreast Cancer: Faraza Javed M.Phil PharmacologyMaheen IdreesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ovarian CA 450918 SHDocumento52 pagineOvarian CA 450918 SH180045Nessuna valutazione finora
- 930708張葳葳65 ADENOMYOSISDocumento55 pagine930708張葳葳65 ADENOMYOSISAnonymous tdqn4roe6RNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines On Testicular Cancer: (Limited Text Update March 2009)Documento18 pagineGuidelines On Testicular Cancer: (Limited Text Update March 2009)PJ CoNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast Cancer: Presented By: Ola NemriDocumento46 pagineBreast Cancer: Presented By: Ola NemriHaitham Ahmed100% (1)
- The Case of A 53 Year Old Menopausal Female From Novaliches, Quezon CityDocumento38 pagineThe Case of A 53 Year Old Menopausal Female From Novaliches, Quezon CityByaruhanga EmmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast CaDocumento35 pagineBreast CaVincent SerNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast CancerDocumento3 pagineBreast Cancerampogison08Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Do You Need To Know About Breast Cancer: DR / Mokhtar Gusmallah Clinical OncologistDocumento26 pagineWhat Do You Need To Know About Breast Cancer: DR / Mokhtar Gusmallah Clinical OncologistjehemirNessuna valutazione finora
- Uterine CancerDocumento10 pagineUterine CancerKristen Leigh MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraDocumento6 pagine3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraCassey Koi FarmNessuna valutazione finora
- Malignant Breast DiseasesDocumento40 pagineMalignant Breast DiseasesDavid MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- CancerDocumento70 pagineCancerapi-3735995100% (1)
- Colon CancerDocumento75 pagineColon Cancershefalika mandremNessuna valutazione finora
- Endometrial NeoplasiaDocumento48 pagineEndometrial NeoplasiaBONI M.WoyessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Abdominal TumorsDocumento27 paginePediatric Abdominal TumorsDlman JamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Breast CaDocumento32 pagineCase Study Breast Caapi-391376321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rectal Ca:: Malueth Abraham, MBCHB ViDocumento32 pagineRectal Ca:: Malueth Abraham, MBCHB ViMalueth AnguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith 2017Documento14 pagineSmith 2017Evelynππ θσυNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast Cancer PresentationDocumento52 pagineBreast Cancer Presentationapi-341607639100% (1)
- Cytomorphology of Canine Transmissible Veneral TumorsDocumento14 pagineCytomorphology of Canine Transmissible Veneral TumorsGanesh DasaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast and Lung CancerDocumento141 pagineBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan On TumorsDocumento19 pagineLesson Plan On TumorsPuneetNessuna valutazione finora
- CarcinomarectumDocumento45 pagineCarcinomarectumHuzefa MemonNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocumento61 pagine11 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDevy Eryn TobingNessuna valutazione finora
- Carcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWDocumento74 pagineCarcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWTowhidulIslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Case6. ERISGRUPtesticularcancerDocumento3 pagineCase6. ERISGRUPtesticularcancerJardee DatsimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Bowel CancerDocumento16 pagineSmall Bowel CancerFauzie MegantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast GSUDocumento48 pagineBreast GSUAbdalla SamatarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung CancerDocumento7 pagineLung CancerClarinda RondainNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast and Lung CancerDocumento141 pagineBreast and Lung CancerabdurehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob CPCDocumento80 pagineOb CPCDonna Meryll Eduave-EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Carcinoma of The Breast - Bailey & LoveDocumento5 pagineCarcinoma of The Breast - Bailey & LoveKeyshia Yazid100% (1)
- Parotid TumorDocumento37 pagineParotid TumorRiyan SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer of The EsophagusDocumento83 pagineCancer of The EsophagusFlaviu Ionuț FaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Oncology NursingDocumento10 pagineOncology NursingMhaii Ameril88% (8)
- All You Have Ever Wanted To Know About Mucoepidermoid CarcinomaDocumento63 pagineAll You Have Ever Wanted To Know About Mucoepidermoid CarcinomaNeeraj TekariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue BookDocumento126 pagineBlue Bookgojo_11Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2.1 Epidemiology Cancer of The Stomach, or Gastric Cancer, Is A Disease in Which StomachDocumento23 pagine1.2.1 Epidemiology Cancer of The Stomach, or Gastric Cancer, Is A Disease in Which StomachMuthu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CANCER ReportDocumento135 pagineCANCER ReportEnzo TimbolNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca MammaeDocumento34 pagineCa MammaedarNessuna valutazione finora
- OncologyDocumento66 pagineOncologyMaria Sofia Stephanie SatoriNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Lesions of The OvaryDocumento7 pagineBenign Lesions of The Ovaryredhasalah665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Uterine / Endometrial Vaginal: Gynae CancersDocumento1 paginaUterine / Endometrial Vaginal: Gynae CancersDavid HosamNessuna valutazione finora
- Who IiDocumento19 pagineWho IiCristián Fernando Cristóbal RoblesNessuna valutazione finora
- Neoplastic Diseases of The OvaryDocumento61 pagineNeoplastic Diseases of The Ovaryea013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Breast Cancer: DR - Syed Alam ZebDocumento51 pagineTreatment of Breast Cancer: DR - Syed Alam ZebSucipto HartonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast CancerDocumento32 pagineBreast CancerSHIVAJINessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosis in Oncology: Dr. Teguh Aryandono Division of Surgical Oncology Faculty of Medicine, GMUDocumento43 pagineDiagnosis in Oncology: Dr. Teguh Aryandono Division of Surgical Oncology Faculty of Medicine, GMUXsar AritamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.uterine Disorders (B.m.a)Documento35 pagine16.uterine Disorders (B.m.a)Jimmy MainaNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgery Oral ExamDocumento46 pagineSurgery Oral ExamM Patel100% (9)
- Colorectal Carcinoma: Samuel Onedes S. Alexander B. A. Denny SetyadiDocumento31 pagineColorectal Carcinoma: Samuel Onedes S. Alexander B. A. Denny SetyadiHeru WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Patologi Tumor Sistim UrogenitalDocumento29 paginePatologi Tumor Sistim UrogenitalSiddiq Blackhell CakepNessuna valutazione finora
- Cervical Cancer: Predominately Squamous Cell CancerDocumento1 paginaCervical Cancer: Predominately Squamous Cell CancerAila CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Salivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentDa EverandSalivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentLisa LicitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementDa EverandNeuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementJordan M. CloydNessuna valutazione finora
- School Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoyDocumento4 pagineSchool Nutritional Status Record: Grade 7 - JoySidNessuna valutazione finora
- Centrifugal ChillerDocumento24 pagineCentrifugal ChillerARUL SANKARANNessuna valutazione finora
- M. Pharm. Pharmaceutics 2011 SyllabusDocumento19 pagineM. Pharm. Pharmaceutics 2011 SyllabusRammani PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- (Handbook) Exchanges ProfileDocumento20 pagine(Handbook) Exchanges ProfileHouda MahfoudiNessuna valutazione finora
- NPD Phase 1Documento2 pagineNPD Phase 1Abdullah ZahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Health-Optimizing Physical EducationDocumento13 pagineModule 3 - Health-Optimizing Physical EducationLazyy TanakaNessuna valutazione finora
- 13th & 14th WK - Oxygen Therapy With VideoDocumento89 pagine13th & 14th WK - Oxygen Therapy With VideoJesus Mario Lopez100% (1)
- Using The Childrens Play Therapy Instrument CPTIDocumento12 pagineUsing The Childrens Play Therapy Instrument CPTIFernando Hilario VillapecellínNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 pagineDaftar PustakaameliaaarrNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeDocumento20 pagineCommon Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeEng Stephen ArendeNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunotherapy A Potential Adjunctive Treatment For Candida - Il e IfnDocumento6 pagineImmunotherapy A Potential Adjunctive Treatment For Candida - Il e IfnLuiz JmnNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Drug Information 2000Documento66 pagineWHO Drug Information 2000Rajib ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis of The Hip and Knee Flowchart PDFDocumento2 pagineOsteoarthritis of The Hip and Knee Flowchart PDFsilkofosNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Examination FormDocumento4 paginePhysical Examination FormDawit KumsaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W6Documento4 pagineDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q4 - W6Bernard Martin100% (1)
- Project Proposal: A. Project Tittle: "Operation Cleanliness"Documento8 pagineProject Proposal: A. Project Tittle: "Operation Cleanliness"Mike Avila100% (1)
- ORCULLO 3NC NCM114 JournalDocumento4 pagineORCULLO 3NC NCM114 JournalDudil GoatNessuna valutazione finora
- Feeding Norms Poultry76Documento14 pagineFeeding Norms Poultry76Ramesh BeniwalNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadDocumento3 pagine11th Bio Zoology EM Official Answer Keys For Public Exam Mhay 2022 PDF DownloadS. TAMIZHANNessuna valutazione finora
- PSC Question BankDocumento9 paginePSC Question BankFaisal qblp100% (29)
- Project ProposalDocumento3 pagineProject ProposalSkrrtt SkrrttNessuna valutazione finora
- KLP 5 - Nutrition Intake and MedicationDocumento4 pagineKLP 5 - Nutrition Intake and MedicationdzakyNessuna valutazione finora
- Standards For Accreditation-Schools - 2010Documento43 pagineStandards For Accreditation-Schools - 2010Nayda Jiménez Pérez100% (1)
- AM LOVE School Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition ReportDocumento4 pagineAM LOVE School Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition ReportLornaNirzaEnriquezNessuna valutazione finora
- BNMHGDocumento34 pagineBNMHGAnonymous lt2LFZHNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - The Generics Act of 1988Documento22 pagine10 - The Generics Act of 1988rhydelNessuna valutazione finora
- Derma GITDocumento48 pagineDerma GITapi-3843372Nessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia Unit 4Documento9 pagineSchizophrenia Unit 4varadarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Essays: 1-Title: Physical FitnessDocumento7 pagineEssays: 1-Title: Physical FitnessMy PcNessuna valutazione finora
- Diet's CardDocumento8 pagineDiet's CardJORGE ATRIANONessuna valutazione finora