Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fdi in Retail
Caricato da
jhapushkarjhaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fdi in Retail
Caricato da
jhapushkarjhaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
F D I IN RETAIL
0
NAMES KAARTHIKA
DOLA SAHA
VIKAS JOSHI
GAURAV RAJ
JAIDEO KUMAR
SUBJECT - BUSINESS PERSPECTIVES
PROJECT TOPIC-FDI IN REATAIL
FACULTY NAME- VENKATESH G.
FACULTY SIGNATURE-
DATE OF SUBMISSION 21/11/12
F D I IN RETAIL
0
TITLE OF PROJECT REPORT
In the partial fulfillment of post graduate
program in business perspectives.
SUBMITTED BY
NAME OF INSTITUTE
F D I IN RETAIL
0
CONTENTS:
. INTRODUCTION
. ANALYSIS
FDI CONCEPT
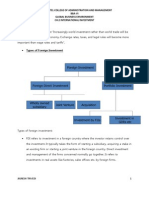
TYPES OF FDI
FDI-ADVANTAGES Vs DISADVANTAGES
FDI PROCEDURES IN INDIA
CURRENT INDIAN FDI LIMITS
FDI TREND IN INDIA
GLOBAL FDI TREND
FDI CASE STUDIES COKE AND IBM
FDI IN INDIA A REALITY CHECK
FDI IN INDIA FUTURE POTENTAIL
FDI INDIA VS OTHERS COMPARISON
. SUGGESTIONS & RECOMMENDATIONS
. BIBLIOGRAPHY
F D I IN RETAIL
0
INTRODUCTION:
When a firm invests directly in facilities
to produce and market a product in a
foreign country.
FDI is very much concerned with the
operation and ownership of the host
country firm.
As per US Department of Commerce and
IMF, It occurs when investor invests 10
percent or more in foreign business entity.
In this case investor holds majority votes
and have control on management and
equity.
Once a firm under takes FDI, it becomes
(Multinational enterprise) MNC.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
ANALYSIS:
FDI CONCEPT
. Long term investment by a foreign direct investor in
an enterprise resident in an economy other than that in
which the foreign direct investors is based.
. The FDI relationship consists of a parent and enterprise
and a foreign affiliate which together form a
transnational corporation (TNC).
. Parents enterprise investment must afford the parent
enterprise control over its foreign affiliate (owning 10%
or more of the ordinary shares or voting power of an
incorporated firm or its equivalent for an
unincorporated firm (UN definition)
F D I IN RETAIL
0
FDI:
. Direct investment by a controlling Parent enterprise in the assets of an
affiliate enterprise located in an economy other than Parent enterprise is based.
. Investment by any corporation that proposes to carry out business in the
country other than its own.
. Long term & direct investment in plant & machinery aimed to carry out/
expand business in the affiliates country.
. Regulated by RBI and FIPB (Foreign Investment Promotion Board) of the
dept. of Commerce under Ministry Of Finance.
. Sector specific limits prescribed for FDI under automatic/ approval route.
FII:
. Investment in the capital/ debt stock of a company/ govt. securities by an
investor that is from or registered in a country outside of the one in which it is
investing.
. Includes hedge funds, insurance companies, pension funds and mutual funds
. Short term investment (generally) made under portfolio management to earn
profits from value appreciation.
.SEBI registration is required to operate as an FII in India.
. Aggregate investment ceiling for FII investment is 10%(5% for single) of the
paid up capital of a company 24% in case of listed Indian companies under a
General Body Resolution.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
FDI ADVANTAGES Vs disadvantages
ADVANTAGES:
. Inflow of equipment & technology.
. competitive advantage and inn ovation.
. Financial resources for expansion.
.Employment of generation.
. Access to global marketplace for domestic players.
. Access to new market/ distribution channel for products.
. Improved consumer welfare through reduced costs, wider choice and improved
quality.
DISADVANTAGES:
. Crowding of local industry.
. Loss of control in business and its activities.
. Repatriation of profits/ dividend by investor.
. Conflicts of codes/ laws.
. Possible exploitation of resources-materials/ wages.
. Effect on local culture/ sentiments-socio cultural effect.
. Effect on natural environment.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
FDI PROCEDURE IN INDIA:
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is permitted as under the following forms of
investments:
. Through financial collaborations.
. Through joint ventures and technical collaborations.
.Through capital markets via Euro issues.
. Through private placements or preferential allotments.
Forbidden Territories: FDI is not permitted in the following industrial sectors.
a. Arms and ammunition.
b. Atomic Energy, Railway Transport, Coal and lignite.
c. Mining of iron, manganese, chrome, gypsum, gold , diamonds, copper, zinc.
. Indian companies are allowed to raise equity capital in the international
market through the issue of Global Depository Receipt(GDRs).
.GDRs are designated in dollars and are not subject to any ceilings on
investment.
. Applicant company seeking approval should have consistent track record for
good performance(financial otherwise)for a minimum period of 3 years(this
condition is relaxed for infrastructure projects such as power generation,
telecommunication, petroleum exploration and refining, ports, airports and
roads)
.GDR proceeds can be used for financing capital goods imports, capital
expenditure including domestic purchase/installation of plant, equipment and
building and investment in software development, prepayment or scheduled
repayment of earlier external borrowings , and equity investment in JV/WOSs.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
CURRENT INDIAN FDI LIMITS:
Sector Specific Foreign Direct Investment in India
. Hotel and Tourism: FDI in Hotel & tourism sector in India-100% FDI
is permissible in the sector on the automatic route. The term hotel includes
restaurants, beach resorts, and other tourist complexes providing
accommodation and/or catering ad food facilities to tourists.
. Private Sector Banking: Non-Banking Financial Companies
(NBFC)-49% FDI is allowed from all sources on the automatic route subject to
guidelines issued from RBI from time to time in 19 NBFC activities
.MERCHANT BANKING,UNDERWRITING,PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
SERVICES,INVESTMENT ADVISORY SERVICES,FINANCIAL
CONSULTANCY,SOCK BROKING,ASSET MANAGEMENT,VENTURE
CAPITAL,CUSTODIAL SERVICES,FACTORING,CREDIT REFERNCE
AGENCIES,CREDIT RATING AGENCIES,LEASING & FINANCE,HOUSING
FINANCE,FOREIGN EXCHANGE BROKERING,CREDIT CARD
BUSINESS,MONEY CHANGING BUSINESS,MIRO CREDIT AND RURAL
CREDIT.
There are separate prescribed minimum capitalization norms for fund/non
fund based NBFCs.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
. Insurance Sector: Up to 26% FDI is allowed on the automatic route
subject to obtaining license from Insurance Regulatory & Development
Authority (IRDA)
. Telecommunication Sector: Limited to 49% in basic, cellular,
value added services and global mobile personal communications by satellite,
subject to licensing and security requirements and adherence by the companies
(by both investor and investee companies) to the license conditions, up to 74%
in ISPs with gateways radio-paging and end-to-end band width, up to 100% is
allowed subject to the condition that such companies would divest 26% of their
equity in favor of Indian public in 5 years, if these companies are listed in other
parts of the world
.Trading Companies: Up to 51% under automatic route provided it is
primarily export activities, and the undertaking is an export house/trading
house/super trading house/star trading house. However, under the FIPB route,
100% FDI is permitted in case of trading companies for activities like exports,
bulk imports with export/ ex-bonded warehouse sales, cash and carry wholesale
trading etc.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
.Power Sector: Up to 100% FDI allowed in respect of projects relating to
electricity generation, transmission and distribution, other than atomic reactor
power plants. There is no limit on the project cost and quantum of foreign direct
investment.
. Drugs and Pharmaceuticals: Up to 100% under automatic route
for manufacture of drugs and pharmaceutical, provided the activity does not
attract compulsory licensing or involve use of recombinant DNA technology,
and specific cell/tissue targeted formulation, otherwise prior Government
approval is required.
. Pollution Control and Management: Up to 100% under
automatic route in both manufacture of pollution control equipment and
consultancy for integration of pollution control systems.
. Call Centre/ BPO in India: Up to 100% is allowed subject to certain
conditions.
. Roads, Highways, Ports and Harbors: Up to 100% under
automatic route in projects for construction and maintenance of roads,
vehicular bridges, toll roads, vehicular tunnels, ports and harbors.
. Retail Sector: The proposal for FDI in Retail sector has loomed into a
controversy with the proposal being put on the backburner.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
F D I IN RETAIL
0
SUGGESTIONS & RECOMMENDATIONS:
F D I IN RETAIL
0
. FDI should be leveraged to create back end
structure.
. FDI will be a powerful driver to curb inflation.
. Restrict the number of stores that can be operated
in a city.
. Allow access to the small retailers to the stores
through special windows.
F D I IN RETAIL
0
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
1. http://businesstoday.intoday.in/story/f
di-in-retail/1/20408.html
2. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/top
ic/FDI-in-retail
3. http://www.livemint.com/Search/Link/
Keyword/FDI%20IN%20RETAIL%20IN%
20INDIA#title=From the Newsroom:
Pavers moves to comply with FDI norms
4. http://www.banknetindia.com/books/fdi
guide.htm
F D I IN RETAIL
0
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Santrock Section 1 Chapter 1Documento19 pagineSantrock Section 1 Chapter 1Assumpta Minette Burgos75% (8)
- Managerial Accounting 14th Edition Warren Solutions Manual DownloadDocumento28 pagineManagerial Accounting 14th Edition Warren Solutions Manual DownloadRose Speers100% (22)
- Exotic - March 2014Documento64 pagineExotic - March 2014Almir Momenth35% (23)
- 02 FdiDocumento23 pagine02 FdiAmit Mishra100% (1)
- FDI PresentationDocumento15 pagineFDI PresentationSunil KoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdi in India: Submitted byDocumento56 pagineFdi in India: Submitted byKuntal DasNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 4 Fdi Final 1Documento23 pagineCH 4 Fdi Final 1arushiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nisha PresentaionDocumento21 pagineNisha PresentaionSeHrawat Nishu NiShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 1Documento8 paginePart 1Namrata BachhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- FDI and Its FrameworkDocumento23 pagineFDI and Its FrameworkPragya KasanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sardar Patel College of Administration and Management Bba-Vi Global Business Environment Ch:2 International InvestmentDocumento7 pagineSardar Patel College of Administration and Management Bba-Vi Global Business Environment Ch:2 International InvestmentJigisha MugdalNessuna valutazione finora
- K.E.S. Shroff College of Arts & CommerceDocumento19 pagineK.E.S. Shroff College of Arts & CommerceNirali AntaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento6 pagineForeign Direct InvestmentPinkal KaramavatNessuna valutazione finora
- Mithra Mini Project 2019Documento10 pagineMithra Mini Project 2019abhishekNessuna valutazione finora
- 20bbah005 A1dwdvDocumento18 pagine20bbah005 A1dwdvUtkarsh AryanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Investment Climate Statement - IndiaDocumento23 pagine2009 Investment Climate Statement - IndiaRukshana PraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento11 pagineForeign Direct Investmentdivyesh_variaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sector Specific Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaDocumento15 pagineSector Specific Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaPrasad VanarseNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento32 pagineForeign Direct InvestmentVikas GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 BEDocumento11 pagineUnit 5 BESharwan SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- H.P National Law University, Shimla: AssignmentDocumento10 pagineH.P National Law University, Shimla: AssignmentadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By:: Fdi Policies in IndiaDocumento15 paginePresented By:: Fdi Policies in IndiabhjbhjkNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On FDI in RetailDocumento52 pagineProject Report On FDI in Retailprasenjitbiswas4515Nessuna valutazione finora
- Full Report On Reasons For FDIDocumento19 pagineFull Report On Reasons For FDIKrishnapalsinh Indrajitsinh VirparaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento13 pagineForeign Direct InvestmentGaurav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- FDIDocumento30 pagineFDIKARISHMAATNessuna valutazione finora
- SM Assignment 1Documento25 pagineSM Assignment 1Utkarsh AryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin of Investment in IndiaDocumento8 pagineOrigin of Investment in IndiaD Attitude KidNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between FDI & Portfolio Investment: PurposesDocumento6 pagineDifference Between FDI & Portfolio Investment: PurposesNupur MathurNessuna valutazione finora
- Give Ten Reasons Why FDI Is Beneficial To Developing Economy? AnsDocumento19 pagineGive Ten Reasons Why FDI Is Beneficial To Developing Economy? AnsFaisal MohdNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTPSWWW Icsi edumediaportals2pptForeign20Investment-Shri20Bubul20Bordoloi PDFDocumento72 pagineHTTPSWWW Icsi edumediaportals2pptForeign20Investment-Shri20Bubul20Bordoloi PDFJain GhritikshNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business ManagementDocumento13 pagineInternational Business Managementtarun sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- SM Project .FinalDocumento40 pagineSM Project .Finalaniketbhosale_012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ugc Net: CommerceDocumento20 pagineUgc Net: CommerceAyan AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdi in IndiaDocumento21 pagineFdi in Indiabestowedart8905Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - International Marketing: TopicDocumento12 pagineAssignment - International Marketing: Topicdhirendra_fmsNessuna valutazione finora
- FDIDocumento9 pagineFDIPankaj ChetryNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaDocumento4 pagineForeign Direct Investment in IndiaRanu SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business ManagementDocumento13 pagineInternational Business Managementtarun sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdi in IndiaDocumento36 pagineFdi in IndiaRohal SoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct Investment: ProductionDocumento21 pagineForeign Direct Investment: ProductionAniket BardeNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report Master of Management Studies-MMS Degree in Partial Requirement During 3 Semester, 2010-11Documento14 pagineProject Report Master of Management Studies-MMS Degree in Partial Requirement During 3 Semester, 2010-11mandy_t06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct Investments Malay DamaniaDocumento16 pagineForeign Direct Investments Malay DamaniaDivya RanawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Fdi in Agriculture.Documento62 pagineFdi in Agriculture.lalsinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y yDocumento32 pagineY y y y y y y y y y y y y y y ychandra4145Nessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestnmentDocumento23 pagineForeign Direct InvestnmentAryan BhageriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Executive Summary On Global Capital Flows (Overview of FDI in and From India)Documento6 pagineExecutive Summary On Global Capital Flows (Overview of FDI in and From India)Basant SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- IJRMEC Volume2, Issue 12 (December-2012) ISSN: 2250-057X Impact of Fdi On Indian Banking SectorDocumento15 pagineIJRMEC Volume2, Issue 12 (December-2012) ISSN: 2250-057X Impact of Fdi On Indian Banking SectorVeeraVictoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Business EnvironmentDocumento7 pagineBusiness EnvironmentAnkur RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento9 pagineForeign Direct InvestmentMir AqibNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct Investment in India: Hitender Mehta Sr. Associate & Head Vaish Associates Advocates Gurgaon, IndiaDocumento61 pagineForeign Direct Investment in India: Hitender Mehta Sr. Associate & Head Vaish Associates Advocates Gurgaon, IndiaParag DadheechNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business: Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento23 pagineInternational Business: Foreign Direct InvestmentKapil PrabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Financing Operations in IndiaDocumento38 pagineFinancing Operations in IndiaAvnish SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- I.B. Unit 5Documento16 pagineI.B. Unit 5Nandini SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento23 pagineChapter 8 Foreign Direct InvestmentMd. Mehedi HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento2 pagineForeign Direct InvestmentSrivatsav BhoopathyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaDocumento16 pagineA Guide To Foreign Direct Investment in IndiaShoe MantraNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Onforeign Direct InvestmentDocumento20 pagineProject Onforeign Direct InvestmentNimesh MokaniNessuna valutazione finora
- FDIDocumento15 pagineFDIakriti bawaNessuna valutazione finora
- FII Vs FDIDocumento10 pagineFII Vs FDIChetan HardikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented TO: Prof. Vidya Sekri Presented byDocumento13 paginePresented TO: Prof. Vidya Sekri Presented bysaurabhagrawal_1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Success in India: A Complete Guide to Build a Successful Business Knot with Indian FirmsDa EverandBusiness Success in India: A Complete Guide to Build a Successful Business Knot with Indian FirmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Name - Rohit Singh: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineName - Rohit Singh: ObjectivejhapushkarjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Fdi in Retail PPT - Presentation TranscriptDocumento4 pagineFinal Fdi in Retail PPT - Presentation TranscriptjhapushkarjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Go Air Vs Indi GoDocumento17 pagineGo Air Vs Indi GojhapushkarjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indigo vs. Go AirDocumento7 pagineIndigo vs. Go AirjhapushkarjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hard Rock Miner - S Handbook - Jack de La Vergne - Edition 3 - 2003Documento330 pagineHard Rock Miner - S Handbook - Jack de La Vergne - Edition 3 - 2003Adriel senciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade Three U3l2Documento84 pagineGrade Three U3l2Mohamed ElsisyNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoke Rehabilitation NICE GuidelinesDocumento591 pagineStoke Rehabilitation NICE GuidelinesHardeep Singh BaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Review "The TKT Course Clil Module"Documento8 pagineBook Review "The TKT Course Clil Module"Alexander DeckerNessuna valutazione finora
- Warcraft III ManualDocumento47 pagineWarcraft III Manualtrevorbourget78486100% (6)
- Vishnu Dental College: Secured Loans Gross BlockDocumento1 paginaVishnu Dental College: Secured Loans Gross BlockSai Malavika TuluguNessuna valutazione finora
- The Study of Zooplankton Community Diversity in Zaghen Restored WetlandDocumento6 pagineThe Study of Zooplankton Community Diversity in Zaghen Restored WetlandAlexandra GeorgianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Related Theoretical Design Inputs 2.1 Sihwa Lake Tidal Power StationDocumento9 pagineChapter 2: Related Theoretical Design Inputs 2.1 Sihwa Lake Tidal Power Stationaldrin leeNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Poea Rules and Regulations Governing RecruitmentDocumento8 pagineRevised Poea Rules and Regulations Governing RecruitmenthansNessuna valutazione finora
- Hibike Euphonium - Crescent Moon DanceDocumento22 pagineHibike Euphonium - Crescent Moon Dancelezhi zhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Engineering Research PapersDocumento8 pagineMechanical Engineering Research Papersfvfzfa5d100% (1)
- Schedule 1 Allison Manufacturing Sales Budget For The Quarter I Ended March 31 First QuarterDocumento16 pagineSchedule 1 Allison Manufacturing Sales Budget For The Quarter I Ended March 31 First QuarterSultanz Farkhan SukmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Practicing Statistics Guided Investigations For The Second Course 1st Edition Kuiper Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Practicing Statistics Guided Investigations For The Second Course 1st Edition Kuiper Solutions Manual PDFdavidkrhmdavis100% (11)
- The 296 Proposed New (Baseline & Monitoring) Methodologies Sent To The Executive BoardDocumento264 pagineThe 296 Proposed New (Baseline & Monitoring) Methodologies Sent To The Executive Boarddjuneja86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Banana Oil LabDocumento5 pagineBanana Oil LabjbernayNessuna valutazione finora
- Em Swedenborg THE WORD EXPLAINED Volume IX INDICES Academy of The New Church Bryn Athyn PA 1951Documento236 pagineEm Swedenborg THE WORD EXPLAINED Volume IX INDICES Academy of The New Church Bryn Athyn PA 1951francis batt100% (2)
- Micro Analysis Report - Int1Documento3 pagineMicro Analysis Report - Int1kousikkumaarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading SkillsDocumento8 pagineReading SkillsBob BolNessuna valutazione finora
- Preface: How To Use This BookDocumento1 paginaPreface: How To Use This BookCarlos SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- Part DDocumento6 paginePart DKaranja KinyanjuiNessuna valutazione finora
- @PAKET A - TPM BAHASA INGGRIS KuDocumento37 pagine@PAKET A - TPM BAHASA INGGRIS KuRamona DessiatriNessuna valutazione finora
- Crimiology MCQ 2Documento15 pagineCrimiology MCQ 2varunendra pandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Neurologist in BangaloreDocumento3 pagineBest Neurologist in BangaloreAlgoTrends AlgoTrendsNessuna valutazione finora
- Constantin Floros, Kenneth Chalmers - New Ears For New Music-Peter Lang GMBH, Internationaler Verlag Der Wissenschaften (2014)Documento242 pagineConstantin Floros, Kenneth Chalmers - New Ears For New Music-Peter Lang GMBH, Internationaler Verlag Der Wissenschaften (2014)paperocamillo100% (3)
- DRTA-directed Reading Thinking Activity: M. Truscott Staff Development 9-24-10Documento13 pagineDRTA-directed Reading Thinking Activity: M. Truscott Staff Development 9-24-10ehaines24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tesla, Inc.: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Tesla Induction Motor AC MotorDocumento90 pagineTesla, Inc.: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Tesla Induction Motor AC MotorEdi RaduNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Personal FinanceDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Personal FinanceMa'am Katrina Marie MirandaNessuna valutazione finora