Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MRCP 1 Basic Sciences
Caricato da
homework8589Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MRCP 1 Basic Sciences
Caricato da
homework8589Copyright:
Formati disponibili
MRCP 1
Basic Medical Sciences
Best of Five Questions and Answers
Second Edition
v
CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT page vii
INTRODUCTION ix
NORMAL VALUES xi
1. GENETICS 1
2. MOLECULAR MEDICINE 19
3. MICROBIOLOGY 41
4. IMMUNOLOGY 69
5. ANATOMY 95
6. PHYSIOLOGY 117
7. CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 159
8. STATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY 185
9. PHARMACOLOGY 201
INDEX 233
Correct answers and teaching notes follow the questions
in each chapter.
1
Chapter 1
GENETICS
Questions
1. Which one of the following conditions has autosomal dominant
inheritance?
A Friedreichs ataxia
B Haemochromatosis
C Agammaglobulinaemia
D Malignant hyperthermia
E Wilsons disease
2. Which one of the following statements regarding autosomal
recessive inheritance is true?
A If both parents are carriers, then 25% of their children will be
carriers
B The disease is not usually as severe as a dominantly inherited
disease
C If one parent is affected and one is not, then 50% of their
children will be carriers
D It occurs in colour blindness
E There is a tendency to skip a generation
3. Which one of the following disorders is transmitted on the X
chromosome?
A Homocystinuria
B Phenylketonuria
C Marfans syndrome
D Gilberts syndrome
E Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deciency
Answers on pages 911
QUESTI ONS MRCP 1 BASI C MEDI CAL SCI ENCES
2
4. A 25-year-old man suffers from haemophilia, and is troubled
with recurrent bleeds into his joints. As a result, he now requires
a shoulder replacement. Which one of his relatives may also
manifest the disease?
A Father
B Mother
C Sister
D Fathers brother
E Mothers brother
5. A 56-year-old woman is diagnosed with primary biliary cirrhosis.
She presents to her general practitioner concerned about her
condition and wants to know if she is at risk of any other disease
processes. Based on her possible I-HA typing, which one of the
following is she most at risk of developing?
A Myasthenia gravis
B Pernicious anaemia
C Sjgrens syndrome
D Behets disease
E Ankylosing spondylitis
6. A 16-year-old boy is known to have cystic brosis. This was
diagnosed in infancy by means of a sweat test which was
performed as part of investigations for failure to thrive. He is
quite severely disabled with breathlessness and is admitted to
hospital several times a year with severe chest infections. Which
one of the following statements about the pattern of inheritance
of this disease is true?
A It occurs mainly in males
B Affected individuals usually have an affected parent
C Both parents are homozygous carriers of the gene
D A quarter of the children of two heterozygous parents will be
affected
E A quarter of the children of two heterozygous parents will be
heterozygous carriers for the trait
3
Answers on pages 1213
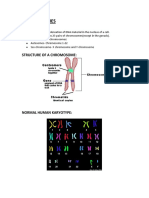
7. Which one of the following statements about DNA structure is
correct?
A There are two purine bases called adenine and thymidine
B Guanine always pairs with adenine and cytosine with
thymidine
C An amino acid codon consists of two base pairs
D Each strand of DNA has a sugar-phosphate backbone with
projecting bases
E There are 32 possible codons
8. Which one of the following chromosomal abnormalities is
usually the result of a deletion alone?
A Patau syndrome
B Turner syndrome
C Chronic myeloid leukaemia
D Testicular feminisation
E Cri-du-chat syndrome
9. Which one of the following conditions has an autosomal
recessive pattern of inheritance?
A Vitamin D-resistant rickets
B Cystinuria
C Manic depressive illness
D Acute intermittent porphyria
E Congenital pyloric stenosis
10. A 19-year-old woman is known to have a 45,XO karyotype. She
is short in stature, and inspection reveals a webbed neck and
widely spaced nipples. She is of normal intelligence. Which
one of the following features may also be associated with this
syndrome?
A Tumour of the ovary
B Adrenal hyperplasa
C Congenital absence of the uterus
D Ovarian agenesis
E Virilising tumour of the adrenal gland
GENETI CS QUESTI ONS
QUESTI ONS MRCP 1 BASI C MEDI CAL SCI ENCES
4
11. Which one of the following features is characteristically
associated with Klinefelter syndrome?
A Increased incidence of breast cancer
B Precocious puberty
C Coarctation of the aorta
D Short metacarpals
E Aggressive behaviour
12. Pre-natal testing in a 38-year-old pregnant woman has revealed
the presence of Down syndrome in the fetus. She asks whether
individuals with the syndrome are at risk of having other
problems with their health. Which one of the following is a
feature of Down syndrome?
A Coarctation of the aorta
B Primum atrial septal defects
C Early development of Alzheimers disease
D Increased prevalence of atherosclerosis
E Deletion of chromosome2l
13. Which one of the following is true of Turner syndrome?
A There is an increased risk of neoplasia in the streak ovary
B Treatment with growth factor may increase nal height
C The mllerian structures are absent
D There is ambiguity of the external genitalia
E Hypertension is rarely seen
14. Which one of the following is true of Charcot-Marie-Tooth
disease?
A The onset is usually in childhood
B There is often mental retardation
C It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner in most cases
D Nerve conduction studies may be normal
E It only affects the lower limbs
9
GENETICS
Answers
1. D: Malignant hyperthermia
Autosomal dominant conditions affect both sexes equally. There
is no carrier condition, with heterozygotes being phenotypically
affected. With one affected parent, 50% of children will be
affected.
Autosomal dominant inheritance is seen in:
Achondroplasia
Acute intermittent porphyria
Adult polycystic kidney disease
Ehiers-Danlos syndrome
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Gilbert syndrome
Hereditary sensory and motor neuropathy
Hereditary spherocytosis
Huntingtons disease
Hyperlipidaemia type II
Malignant hyperthermia
10
Marfan syndrome
Myotonia congenita
Myotonic dystrophy
Neurobromatosis
Osteogenesis imperfecta type I
Noonan syndrome
Polyposis coli
Rotor syndrome
Retinobiastoma
Tuberose sclerosis
Von Hippel-Lindau disease
von Willebrands disease
2. E: There is a tendency to skip a generation
If one parent is affected and one is normal, then all of their
children will be carriers. If both parents are carriers, then 50% of
their children will be carriers and 25% will be affected. Autosomal
recessive disease is usually more severe than autosomal dominant
disease. Colour blindness has X-iinked inheritance.
The following are autosomal recessive conditions:
Albinism
1
-Antitrypsin deciency
Ataxia telangectasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Cystinuria
Cystic brosis
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Familial Mediterranean fever
ANSWERS MRCP 1 BASI C MEDI CAL SCI ENCES
11
Fanconis anaemia
Friedreichs ataxia
Galactosaemia
Gauchers disease
Glycogen storage diseases
Haemochromatosis
Homocystinuria
Hurler syndrome
Niemann-Pick disease
Osteogenesis imperfecta types Ill and IV
Pendred syndrome
Phenylketonuria
Sickle cell disease
Tay-Sachs disease
Thalassaemias
Wilsons disease
3. E: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deciency
The following are all inherited in an X-linked fashion:
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Agammaglobulinaemia
Beckers muscular dystrophy
Chronic granulomatous disease
Colour blindness
Complete testicular feminisation
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Fabrys disease
Glucose-6-phosphatedehydrogenase deciency
GENETI CS ANSWERS
12
Haemophilia A (factor VIII deciency)
Haemophilia B (factor IX deciency)
Hunter syndrome
lchthyosis
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Ocular albinism
Retinitis pigmentosa
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
4. E: Mothers brother
Haemophilia is transmitted by female carriers, who produce
affected boys, normal boys, carrier girls and normal girls with
equal frequency. Affected boys and men have affected brothers
and maternal uncles, and can only have normal sons and carrier
daughters. (See answer to Question 3.)
5. C: Sjgrens syndrome
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is associated with HLA-DR3.
Sjgrens syndrome is also associated with HLA-DR3 and
approximately 80Yo of patients with PBC are thought to develop
a sicca syndrome. Myasthenia gravis is also associated with HLA-
DR3 butto a lesser degree. Pernicious anaemia is associated with
HLA-DR2 and HLA-DR5, Behets disease with HLA-B5, and
ankylosing spondylitis with HLA-B27.
6. D: A quarter of the children of two heterozygous parents will
be affected
Both sexes are equally affected in disorders with an autosomal
recessive inheritance. Asymptomatic carriers produce affected
children. Homozygous implies that the individual is affected.
When both parents carry the gene, one in four children are
affected, and two in four children are carriers. (See answer to
Question 2.)
ANSWERS MRCP 1 BASI C MEDI CAL SCI ENCES
13
7. D: Each strand of DNA has a sugar-phosphate backbone with
projecting bases
The purine bases are adenine (A) and guanine (G); the pyrimidines
are thymidine (T) and cytosine (C). G always pairs with C and A
with T. An amino acid codon consists of three bases. As each base
in the triplet may be any of the four types of nucleotide (A, G, C
or T), this results in 64 possible codons. Most amino acids have
more than one codon and some codons signal chain termination.
Each base in the codon may be one of the four, so there are 4
3
(ie
64) possible codons.
8. E: Cri-du-chat syndrome
Approximately 5.6 per 1000 live births are affected by
chromosome abnormalities. Of these, 2 per 1000 are caused by
a variation in the number of sex chromosomes (Turner syndrome,
45,XO; Klinefelter syndrome, 47,XXY); 1.7 per 1000 are due
to variation in the number of autosomal chromosomes (Down
syndrome, trisomy 21; Patau syndrome, trisomy 13; Edwards
syndrome, trisomy 18); and 1.9 per 1000 are due to chromosomal
rearrangement. Chronic myeloid leukaemia is associated with
the Philadelphia chromosome in 85% of cases: this is a deletion
of the long arm of chromosome 22 with translocation, usually
onto chromosome 9. Cri-du-chat syndrome is caused by a partial
deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5.
9. B: Cystinuria
Vitamin D-resistant rickets has X-linked dominant inheritance.
Acute intermittent porphyria is an autosomal dominant disorder.
Manic depressive illness and congenital pyloric stenosis have
polygenic inheritance.
10. D: Ovarian agenesis
The phenotypic features of Turner syndrome (45,XO) comprise
a female with short stature, a webbed neck, short metacarpals,
a wide carrying angle, sexual infantilism, primary amenorrhoea,
GENETI CS ANSWERS
14
high gonadotrophin levels, low oestrogen levels and slight
intellectual impairment. Renal abnormalities and coarctation of
the aorta are also associated.
11. A: Increased incidence of breast cancer
Klinefelter syndrome may have a karyotype of 47,XXY, 48,XXYY,
48,XXXY, or 49,XXXXY. The affected male is tall and thin with
bilateral gynaecomastia (there is an increased incidence of breast
cancer) and infertility (irreversible) due to hypogonadism, and a
slight predisposition to germ cell tumours compared with other
males. Mental retardation is often seen. Karyotype XYY is usually
associated with tall, aggressive men and is commoner in prison
communities.
12. C: Early development of Alzheimers disease
The most common heart defects in Down syndrome are
atrioventricular canal defects (40% compared with 2-3% in the
normal population), secundum atrial septal defect and patent
ductus arteriosus. Aortic stenosis and coarctation of the aorta
are rare. Nearly all people with Down syndrome have some
evidence of Alzheimers disease by the time they are 40 years
old. There is decreased prevalence of atherosclerosis in Down
syndrome, although the reasons for this are not clear. Deletion of
chromosome 15q11-q13 is typical of the Prader-Willi syndrome.
Trisomy 21 is the classic chromosomal abnormality in Down
syndrome.
13. B: Treatment with growth factor may increase nal height
If started sufciently early enough, large doses of growth hormone
may result in increased height. Immature mllerian structures are
present. An increased risk of gonadal dysplasia applies only to
gonadal dysgenetic syndromes where there is a Y chromosome
(eg pure gonadal agenesis, 46,XY). Ambiguity of the external
genitalia is not seen. Hypertension is common and is caused by
renal abnormalities and coarctation of the aorta.
ANSWERS MRCP 1 BASI C MEDI CAL SCI ENCES
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cardiac ArrestDocumento3 pagineCardiac Arresthomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1-15 Day CoursePLAB2Documento1 paginaForm 1-15 Day CoursePLAB2homework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Stones ManagementDocumento2 pagineRenal Stones Managementhomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chocolate Chip Cookies: Sugar Free Chocolate MeltsDocumento2 pagineChocolate Chip Cookies: Sugar Free Chocolate Meltshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormalities of the JVP: Identification and CausesDocumento1 paginaAbnormalities of the JVP: Identification and Causeshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Early Detection of Invasive Aspergillosis Using Galactomannan TestingDocumento5 pagineEarly Detection of Invasive Aspergillosis Using Galactomannan Testinghomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Rabia 1700 Plab Material McqsDocumento1.092 pagineDr. Rabia 1700 Plab Material McqsMuhammad Amin100% (9)
- Jurnal 3 PDFDocumento8 pagineJurnal 3 PDFAmalia Dwi AryantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal MedicineDocumento96 pagineRenal Medicinehomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Born Too Soon The Global Action Report On Preterm BirthDocumento126 pagineBorn Too Soon The Global Action Report On Preterm BirthΒασίλης ΒασιλείουNessuna valutazione finora
- Quoi"... : 1. Louvre-Tuileries and Faubourg Saint-HonoréDocumento5 pagineQuoi"... : 1. Louvre-Tuileries and Faubourg Saint-Honoréhomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetrics 12: Managing Breech and Occiput Posterior PresentationsDocumento5 pagineObstetrics 12: Managing Breech and Occiput Posterior Presentationshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Milk PurisDocumento1 paginaHow To Make Milk Purishomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Milk Butter RotiDocumento1 paginaHow To Make Milk Butter Rotihomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hindi LyricsDocumento1 paginaHindi Lyricshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ingredients: For The CakeDocumento1 paginaIngredients: For The Cakehomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocumento2 pagineHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make ChirotiDocumento1 paginaHow To Make Chirotihomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal Laboratory Results: C-Reactive ProteinDocumento3 pagineAbnormal Laboratory Results: C-Reactive ProteinRolando AgustianNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial LineDocumento2 pagineArterial LineRaghav Goyal100% (1)
- EpilepsyDocumento3 pagineEpilepsyhomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- NHS AnginaDocumento63 pagineNHS Anginahomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hindi LyricsDocumento1 paginaHindi Lyricshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- NHS AnginaDocumento63 pagineNHS Anginahomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Travel Agent Handbook 818g EngDocumento390 pagineTravel Agent Handbook 818g Enghomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hindi LyricsDocumento1 paginaHindi Lyricshomework8589Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Reproductive AssessmentDocumento17 pagineReproductive AssessmentKim DajaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperestrogenism, Klinefelter Syndrome & SupermalesDocumento39 pagineHyperestrogenism, Klinefelter Syndrome & SupermalesGerald John Paz100% (1)
- Karyotyping Activity Week 2 - Ian SibalDocumento6 pagineKaryotyping Activity Week 2 - Ian SibalIan SibalNessuna valutazione finora
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocumento2 pagineKlinefelter SyndromesyedzhaferNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical and intellectual symptoms of Klinefelter syndromeDocumento3 paginePhysical and intellectual symptoms of Klinefelter syndromeNeo RealyouNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Mutation SCDocumento54 pagine7 Mutation SCThivya SritharNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Disorders Guide: Causes, Types & DescriptionsDocumento18 pagineGenetic Disorders Guide: Causes, Types & Descriptionstango0385100% (1)
- Genetic Disorders ProjectDocumento15 pagineGenetic Disorders ProjectAshwin ShajithNessuna valutazione finora
- Human KaryotypingDocumento10 pagineHuman KaryotypinggabyNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineModule 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Genetics 1Documento10 pagineLab Genetics 1Nurul Iman Che AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeDocumento27 pagineChromosomes: Structure of A ChromosomeLaika LaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Sex Socially DeterminedDocumento3 pagineIs Sex Socially Determinedwaleed33% (3)
- Klinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Documento14 pagineKlinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Anonymous LAWfm7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sindroma KlinefelterDocumento27 pagineSindroma KlinefelterSamuelRexyNessuna valutazione finora
- Developmental Psychology Test BankDocumento25 pagineDevelopmental Psychology Test BankCharmaine CuarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Mutation and SuppressorDocumento102 pagineMutation and SuppressorJomalyn DaduyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic disorders from meiotic errorsDocumento1 paginaGenetic disorders from meiotic errorsJayrelle D. SafranNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Karyotyping: Sarwat MaroofDocumento49 pagineHuman Karyotyping: Sarwat MaroofZeeshan YousufNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Genetic Disorders and Pedigrees ExplainedDocumento51 pagineHuman Genetic Disorders and Pedigrees Explainedcm4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral Phenotypes 48XXYY 48XXXY 49, XXXXYDocumento6 pagineBehavioral Phenotypes 48XXYY 48XXXY 49, XXXXYsindrome49Nessuna valutazione finora
- Klinefelter SyndromeDocumento3 pagineKlinefelter SyndromeMuhammad FikrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender and Society LessonDocumento31 pagineGender and Society LessonItshaaa MeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 PDFDocumento49 pagine4 PDFArieles1984Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Genetics and Society 2nd Edition Yashon Test BankDocumento12 pagineHuman Genetics and Society 2nd Edition Yashon Test Banksandramillerobpmsjgtze100% (19)
- GeneticsDocumento27 pagineGeneticsvahedianna100% (1)
- Cell CycleDocumento69 pagineCell CycleJustine FariscalNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 4 MutationDocumento21 pagineScience Form 4 MutationAsyrafAlvezNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Science Q3 MutationDocumento39 pagineG10 Science Q3 MutationEvadine LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromosome Pathology: S. DahounDocumento9 pagineChromosome Pathology: S. DahounSkybreakerNessuna valutazione finora