Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Prepositions: Space Geography Means of Transportation Time "To" W Ith Indirect Objects Related Topics
Caricato da
James Danilo InácioDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Prepositions: Space Geography Means of Transportation Time "To" W Ith Indirect Objects Related Topics
Caricato da
James Danilo InácioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
08/10/13 ak.englishtown.com/EtownResources/Grammar/23.
html
ak.englishtown.com/EtownResources/Grammar/23.html 1/2
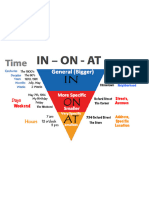
Prepositions
Space
Geography
Means of transportation
Time
"To" with indirect objects
Related topics
Space
In their simplest f orm, prepositions are used to indicate position (in time or space) of one thing with respect to another:
I put the book on the table.
She arrived bef ore the others.
He came toward me.
There are many prepositions. Here is a partial list, with examples:
to -- He gave the book to his f riend.
at -- They arrived at his house at 5 o'clock.
of -- It was the third day of the month.
f rom -- That young women comes f rom Thailand.
on -- She put the plate on the table.
under -- The cat crawled under the bed.
over -- The boy threw the rock over the tree.
underneath -- The rabbit escaped underneath the f ence.
bef ore -- (time) She arrived bef ore the movie started.
af ter -- He called his mother af ter he f inished shopping.
in f ront of -- His mother parked her car in f ront of his apartment.
behind -- The dog ran behind the house.
f or -- He went to the store f or more milk.
toward -- The criminal walked toward him with a gun.
against -- Everyone was against that idea.
around -- The athletes ran around the track six times.
close to -- He placed the f ood close to the squirrel.
f ar f rom -- He placed the f ood f ar f rom the lion.
next to -- He was hot, so he sat down next to the air conditioning.
f acing -- She sat down on the other side of the table, f acing him.
in the midst of -- I don't know where to f ind any f ree time in the midst of these emergencies.
Usage of prepositions
The use of prepositions is one of the most complex aspects of English, and it is impossible to cover all cases. Some general guidelines,
however, may be helpf ul.
Geography
Movement toward a town, country, state, or continent is generally expressed by the preposition "to"; presence in a city, state, etc. is
expressed by "in"; movement away f rom a city, state, etc., is expressed by "from" (if the verb requires a pronoun):
When are you going to Canada.
He went to Asia last year.
I spent three years in London.
She was born in Normandy.
He comes f rom Mexico.
Transportation
As a general rule, the preposition "by" is used to describe how one has traveled. The prepositions "in" and "on" describe one's
presence inside a vehicle. In the case of small vehicles (a car, a helicopter...), the preposition "in" is required:
I came by bike.
Traveling by plane is my f avorite.
I was already on (in) the train when he arrived.
She is waiting f or me in the car.
Time
08/10/13 ak.englishtown.com/EtownResources/Grammar/23.html
ak.englishtown.com/EtownResources/Grammar/23.html 2/2
To designate an hour the preposition "at" is used:
Let's meet at six o'clock.
They arrived at 4:45.
For dates and days of the week, one uses "on":
His birthday is on Monday.
It happened on March 3, 1997.
For months one uses "in":
My birthday is in September.
We will begin work in August.
To express duration, the preposition "for" is used; "in" can be used to express the time it will take to complete a task:
I am going away f or a f ew days.
He worked with them f or three years.
I can read that book in a day.
Indirect objects
The preposition "to", which generally precedes an indirect object, will disappear bef ore a noun (or pronoun) when the indirect object
precedes a direct object. ("To" will be retained when the indirect object f ollows a direct object.)
Examples :
She gave John the ticket.
Mais : She gave the ticket to John.
or:
He sent her a letter.
Mais : He sent a letter to her.
Ou : He sent it to her.
This can also be seen in certain phrases in which the direct object is implicit.
I already told it to him.
Mais : I already told him (the news).
Related topics
Verbs with prepositions
Prepositional verbs
Back to Index
Copyri ght Ul tral i ngua 2002
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Thinking in English A Content Based ApprDocumento10 pagineThinking in English A Content Based ApprDolores Tapia VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Blooms TaxonomyDocumento4 pagineRevised Blooms TaxonomyJonel Pagalilauan100% (1)
- What Is A Preposition?: Nouns Pronouns Phrases Sentence ObjectDocumento5 pagineWhat Is A Preposition?: Nouns Pronouns Phrases Sentence ObjectalfansfcNessuna valutazione finora
- Verb Tense ExerciseDocumento9 pagineVerb Tense Exercisenickfreed100% (1)
- Philo. Periodical 2nd Quarter PedofileDocumento6 paginePhilo. Periodical 2nd Quarter PedofileArwin NikkosNessuna valutazione finora
- Level 1, Module 3 Hot Spot Extra Reading PDFDocumento3 pagineLevel 1, Module 3 Hot Spot Extra Reading PDFNgan HoangNessuna valutazione finora
- The Use of PrepositionDocumento26 pagineThe Use of PrepositionGeraldine VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMON ERRORS AVOIDEDDocumento10 pagineCOMMON ERRORS AVOIDEDvineetNessuna valutazione finora
- PREPOSITIONSDocumento2 paginePREPOSITIONSMilena RíosNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar RulesDocumento9 pagineGrammar RulesgsathyascewNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Unit 2 Professional SkillsDocumento47 pagineNotes Unit 2 Professional SkillsshagunkukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ficha Prepositions 1º AnoDocumento7 pagineFicha Prepositions 1º AnoGianna MeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions of TimeDocumento20 paginePrepositions of TimeSergio Adrián TadeoNessuna valutazione finora
- A prepositionDocumento9 pagineA prepositionmattookrishna599Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Uses of PrepositionsDocumento9 pagineBasic Uses of PrepositionsjaimeeliganNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions of Time and PlaceDocumento11 paginePrepositions of Time and PlaceJose ReynosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions - Time: English Usage ExampleDocumento5 paginePrepositions - Time: English Usage ExampleSaurabh Dutt PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Talking About The Future: Level: IntermediateDocumento9 pagineTalking About The Future: Level: IntermediateUyen BUiNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions 1 (Time)Documento2 paginePrepositions 1 (Time)Jordi Fosch MonteverdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions Explained: Uses of At, On, In and Other Common PrepositionsDocumento12 paginePrepositions Explained: Uses of At, On, In and Other Common PrepositionsOmar H. AlmahdawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions-WPS OfficeDocumento19 paginePrepositions-WPS OfficeRekha Rajyan100% (1)
- Communication and Soft Skills CourseDocumento6 pagineCommunication and Soft Skills CourseMuhammad FarazNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Verb TensesDocumento5 pagineUsing Verb TensesklipordNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of PrepositionsDocumento3 pagineTypes of PrepositionsFahmi FahrruziNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of PrepositionsDocumento10 pagineTypes of PrepositionsMohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Note PrepositionDocumento22 pagineNote Prepositionsyazwani_azmal591Nessuna valutazione finora
- Imp Link For CtsDocumento11 pagineImp Link For CtsSiddharth SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammer - Preposition, Adjective, InterjectionDocumento17 pagineGrammer - Preposition, Adjective, InterjectionNor Zuraidah JaafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Purdue OWL PrepositionDocumento25 paginePurdue OWL Prepositiondsn_sarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF ArticlesDocumento16 paginePDF ArticlesManish AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions Explaination LatestDocumento9 paginePrepositions Explaination LatestMehran RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Preposition by Ms. Fatima BatoolDocumento18 paginePreposition by Ms. Fatima BatoolFayaz JumaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Present TenseDocumento8 pagineSimple Present Tenseapostuadrian01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Past TensesDocumento7 paginePast TensesPetronelaNessuna valutazione finora
- The PronounDocumento17 pagineThe PronounmagNessuna valutazione finora
- Preposition: For ExampleDocumento12 paginePreposition: For Exampleebabitha.reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions of Time and PlaceDocumento6 paginePrepositions of Time and Placehem777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - Ii 1. PrepositionsDocumento9 pagineUnit - Ii 1. PrepositionsBALAKRISHNANNessuna valutazione finora
- Locomotor Skills Basic Motor Skills Involving A Change of Position of The Feet andDocumento3 pagineLocomotor Skills Basic Motor Skills Involving A Change of Position of The Feet andRoseAnnPletadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverb Time ClausesDocumento2 pagineAdverb Time ClausesFran English GrammarNessuna valutazione finora
- CC C C C C C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocumento11 pagineCC C C C C C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCudayNessuna valutazione finora
- Verb Tenses Complete LessonDocumento5 pagineVerb Tenses Complete LessonRoselyn B. AnimoNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepositionsDocumento7 paginePrepositionsashril awwabNessuna valutazione finora
- Correct Use of Prepositions of PlaceDocumento4 pagineCorrect Use of Prepositions of PlaceBapuNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepostionDocumento5 paginePrepostionSilvio DominguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Preposition Guideline Uploaded by Hafiz BilalDocumento6 paginePreposition Guideline Uploaded by Hafiz BilalfaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Preposition Word Doc 1636912903421Documento20 paginePreposition Word Doc 1636912903421md.muzzammil shaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepositionsDocumento6 paginePrepositionsnoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit TwoDocumento7 pagineUnit TwofekfekiraNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepositionsDocumento11 paginePrepositionsMonika LangngagNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepositionsDocumento4 paginePrepositionsJelai M. BarreraNessuna valutazione finora
- All About PrepositionDocumento63 pagineAll About PrepositionAdam NadirNessuna valutazione finora
- HS6151 - Technical English I - Notes & Question BankDocumento205 pagineHS6151 - Technical English I - Notes & Question BankRahil TasawarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Use of ArticlesDocumento19 pagineThe Use of Articlesavril55Nessuna valutazione finora
- PrepositionDocumento14 paginePrepositionPrabha KaruppuchamyNessuna valutazione finora
- My Report: Data CollectionDocumento12 pagineMy Report: Data CollectionmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- B. Select Two (2) Sets of Exercises For Each Parts of Speech From TheDocumento19 pagineB. Select Two (2) Sets of Exercises For Each Parts of Speech From TheKaliammah AyerNessuna valutazione finora
- Verbs Followed by PrepositionDocumento32 pagineVerbs Followed by PrepositionJorge Alberto CardozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Behind, From, Near, Of, On, Since, To, Until, and WithDocumento39 pagineBehind, From, Near, Of, On, Since, To, Until, and WithBondfriendsNessuna valutazione finora
- AdjectiveDocumento15 pagineAdjective7026 G. Lakshmi AishwaryaNessuna valutazione finora
- COURS ANGLAIS M1TOXICOLOGIE - Lesson 04. PrepositionsDocumento4 pagineCOURS ANGLAIS M1TOXICOLOGIE - Lesson 04. Prepositionsmasankagentil88Nessuna valutazione finora
- D360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 02 (Rodrigo A.) PDFDocumento11 pagineD360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 02 (Rodrigo A.) PDFrobson ferreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinds of Prepositions - Simple PrepositionsDocumento40 pagineKinds of Prepositions - Simple Prepositionsnoreen diorNessuna valutazione finora
- The Wiradyuri and Other Languages of New South WalesDa EverandThe Wiradyuri and Other Languages of New South WalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Programming Paradigms and Prolog IntroductionDocumento31 pagineProgramming Paradigms and Prolog IntroductionSalman IjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership Qualities & StylesDocumento43 pagineLeadership Qualities & StylesAmaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Prime Time 3 Work Book 78-138pgDocumento60 paginePrime Time 3 Work Book 78-138pgSalome SamushiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuzzy Logic Controller and Applications: Presented byDocumento32 pagineFuzzy Logic Controller and Applications: Presented byAyush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Mind Lesson Plan 1Documento2 pagineOpen Mind Lesson Plan 1api-240251617Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nidia Bustamante PBJ MemoDocumento1 paginaNidia Bustamante PBJ Memoapi-283776804Nessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Simple Present 1Documento3 pagine04 Simple Present 1Natália DiottoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Preparing Hacks by KHTuhinDocumento22 pagineQuiz Preparing Hacks by KHTuhinShaugat AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- ملزمة اللغة الكتاب الازرق من 1-10Documento19 pagineملزمة اللغة الكتاب الازرق من 1-10A. BASHEERNessuna valutazione finora
- Building A Fear-Free Organization A Psychologist Uses Brain Science To Reflect On The Nature of Fear in OrganizationsDocumento6 pagineBuilding A Fear-Free Organization A Psychologist Uses Brain Science To Reflect On The Nature of Fear in OrganizationsMukul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Abrams - The Effect of Synchronous and A SynchronousDocumento26 pagineAbrams - The Effect of Synchronous and A SynchronouswaxpoeticgNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Attainment Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineConcept Attainment Lesson Planapi-189534742100% (1)
- Herbert Spencer's Evolutionary Educational TheoryDocumento9 pagineHerbert Spencer's Evolutionary Educational Theoryalvin mandapatNessuna valutazione finora
- EVT For Visual Recognition Review PDFDocumento108 pagineEVT For Visual Recognition Review PDFPOOJANKUMAR OZANessuna valutazione finora
- Dapus GabunganDocumento4 pagineDapus GabunganNurkhalifah FebriantyNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Diverse Students: Culturally Responsive PracticesDocumento5 pagineTeaching Diverse Students: Culturally Responsive PracticesJerah MeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Feminist Philosopher Persona in Deleuze's WorkDocumento153 pagineFeminist Philosopher Persona in Deleuze's WorkAragorn EloffNessuna valutazione finora
- The Executive As CoachDocumento10 pagineThe Executive As CoachDNessuna valutazione finora
- STENIUS, Erik - Wittgenstein's Tractatus. A Critical Exposition of Its Main Lines of ThoughtsDocumento250 pagineSTENIUS, Erik - Wittgenstein's Tractatus. A Critical Exposition of Its Main Lines of ThoughtsJuan ErlleNessuna valutazione finora
- School Development Plan Data StoryDocumento4 pagineSchool Development Plan Data StoryigorNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Is A Process That Allows People To Exchange Information by One of Several Method1Documento5 pagineCommunication Is A Process That Allows People To Exchange Information by One of Several Method1haq nawaz100% (1)
- Gumaca National High School's Daily Math Lesson on Quadratic EquationsDocumento4 pagineGumaca National High School's Daily Math Lesson on Quadratic EquationsArgel Panganiban DalwampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mica ResumeDocumento1 paginaMica ResumeHannah TumasisNessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing (IJAISC)Documento2 pagineInternational Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing (IJAISC)CS & ITNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 80, No. 6, 2022Documento129 pagineProblems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 80, No. 6, 2022Scientia Socialis, Ltd.Nessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN Sensory-Perception DisturbanceDocumento2 pagineNURSING CARE PLAN Sensory-Perception DisturbanceBernadette100% (1)