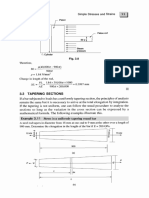
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Timber
Caricato da
John Presly IlardeDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Timber
Caricato da
John Presly IlardeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
I.
DESIGN OF ROOF TRUSS
Using 80 %stess grade molave (Vitex parviflora Juss)
Bending and tension parallel to grain =24.0 MPa
Modulus of elasticity in bending = 6.54 x
MPa
Compression parallel to grain = 15.4 MPa
Compression perpendicular to grain =6.34 MPa
Shear parallel to grain = 2.88 MPa
A. PURLINS
tan =
= 29.05
Weight of roofing = 80 Pa
Velocity of wind = 200 kPa
Relative density of molave = 0.64
Size of Purlins = 50 mm x 100 mm @ 0.80 m O.C
Trusses @ 2.47 m apart
1. Wind load normal to roof:
Pn =
P = 0.0000473
P = 0.0000473
P = 1.892 kPa of vertical surface
Pn =
Pn = 1.49 kPa (normal to roof surface)
2. Maximum bending stress of purlins:
X = 0.80 = 0.70 m
Wind load normal to the purlins:
= Pn (spacing of purlins )(spacing of truss )
= 1.49(0.80)(2.47)
=2.944 kN
Weight of roofing:
= 80(2.47)(0.70)
= 138.32 N
= 0.138 kN
Weight of purlins:
= (0.05)(0.1)(0.69)(9.81)(2.47)
= 0.084 kN
= 2.944 + (0.138 + 0.084)
= 3.052 kN
= 0.942 kN.m
= (0.138 + 0.084)
= 0.108 kN
= 0.033 kN.m
= 11.304 MPa
= 0.396 MPa
= 11.304 + 0.396
= 11.7 MPa < 24.0 MPa (SAFE)
Maximum shearing stress
= 1526 N
= 0.458 MPa
= 54 N
= 0.16 MPa
= 0.458 MPa < 2.88 MPa (SAFE)
3. TRUSSES
1. Total load carrying by the trusses excluding its weight
P =
P =
P = 1544.53 MPa
2. Analysis of the truss members
x =
= 1.37 m
y =
= 1.144 m
= 0.685 m
= y-
= 1.144 0.685 = 0.459 m
a. Forces acting normal to the top chord
= P(spacing of trusses)(
= 1544.53(2.47)(0.685)
= 2613.27 N
= P(spacing of trusses)(x)
= 1544.53(2.47)(1.37)
= 5226.535 N
= P(spacing of trusses)(
= 1544.53(2.47)(0.459)
= 1751.08 N.
b. Resultant and its location from 1.
R =
+ 3
R = 2613.27 + 2(5226.535) + 1751.08
R = 20043.955 N
R=
(y) +
(y + x) +
(y+2x) +
(y + 3x)
20043.955 = 5226.535(1.2 +1.2 +1.5 + 1.2 + 3) +2613.27(1.2 +.5)
= 2.855 m
x = 1.711
= 1.496
y =1.1711
= 0.831
c. Reactions:
= 0
(7.2) + 20043.955
(0.831) 20043.955
(7.2 1.496) = 0
= 12758.27 N
= 0
= 20043.955
= 9732.8 N
= 0
(7.2) + 20043.955
(0.831) 20043.955
(1.496) = 0
= 4764.08 N
CHECKING:
= 0
20043.955
= 12758.27 + 4764.08
17522.35 = 17522.35 OK!
d. Analysing truss by the method of sections:
For row truss, the maximum internal stress to be found at L/4 of the truss measured
horizontally from point of maximum reaction:
4 ) Interaction Value:
< 1.0
= 4.77 MPa
= 1.15 MPa
J =
J = 1.41
0 J 1.0
Therefore J = 1.0
= 0.319 1.0.
Therefore the section is safe
5.) Design for web members:
Section = 75 mm x 75 mm
1. Allowable bending stress
= 5.92 < 10
= 24.0 MPa
2. Allowable compression stress:
18.27 >11
5.88 MPa
3. Interaction value:
< 1.0
= 8.49 MPa
=0.77 MPa
J =
J = 2.57
0 J 1.0
= 0.496 1.0.
Therefore the section is safe.
II. Design for girts at second floor ceiling:
(use the same kind of timber)
Using 80% stress grade molave, allowable stress are as follows:
Bending and tension parallel to grain = 24.0 MPa
Modulus of elasticity in bending = 6.54x
MPa
Compression parallel to grain = 15.4 MPa
Compression perpendicular to grain = 6.3MPa
Shear parallel to grain = 2.88MPa
If shear controls: (assume b = 75 mm)
2.88 =
d = 82.61 mm say 100 mm
If bending controls: (assume b = 75 mm)
24 =
d = 99.57 mm say 100 mm
Try 75 mm x 100 mm
Weight of girts = (0.075)(.10)(0.69)(9.81)(1000)
= 50.77 N/m
Checking:
By shear
= 2.4 MPa < 2.88 MPa SAFE
By bending
= 23.97 MPa < 24.0 MPa SAFE
III. Design for columns
Using 80% stress grade molave, allowable stress are as follows:
Bending and tension parallel to grain = 24.0 MPa
Modulus of elasticity in bending = 6.54x
MPa
Compression parallel to grain = 15.4 MPa
Compression perpendicular to grain = 6.34 MPa
Shear parallel to grain = 7.88 MPa
Timber column size = 250 mm x 250 mm
(use tpe of the same type of timber)
category of column:
= 10.8
K = 0.671
= 0.671
= 13.83
k therefore the column is intermediate
For allowable stress of intermediate column
Fc = Fc[1-
]
= 15.4 [1-
= 13.49 MPa
Allowable axial load
P = FcA
= 13.49(
= 843,125 N > 13714.24 N SAFE
IV. Design of second floor:
Using 80% stress grade molave
Floor load = 70 kPa
Relative density of molave = 0.64
Spacing of floor joist = 0.40 m O.C
Source: NSCP 2001
A. Design for floor joist
1. Size of joist by bending
Live load
WL = 7000 Pa (0.40)
WL = 2800 N/m
Relative stiffness:
= 1
= 1
Fixed end moment =
= + 1.29kN.m
M
= - 1.29kN.m
M
= + 1.29kN.m
M
= - 1.29kN.m
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Example On Design of Timber Structure Part2Documento21 pagineExample On Design of Timber Structure Part2Nur Syazana88% (8)
- Design of Column FootingDocumento14 pagineDesign of Column Footingdash1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Timber Truss Design CourseDocumento15 pagineStructural Timber Truss Design CourseTony Lee Jones87% (15)
- Timber Beam Design Module Input DataDocumento5 pagineTimber Beam Design Module Input DataArnel V. EsllerNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Timber PurlinsDocumento1 paginaDesign of Timber Purlinssoleb100% (3)
- Example1 Timber DesignDocumento3 pagineExample1 Timber DesignCollin NguNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Structural DesignDocumento8 paginePreliminary Structural Designaikaless100% (1)
- Timber Beam Design PDFDocumento5 pagineTimber Beam Design PDFnurulselangor50% (2)
- Design Example of Timber Column To BS 5268Documento3 pagineDesign Example of Timber Column To BS 5268Niceman Natiqi71% (7)
- Timber Design Project - Design of A Two Storey House (Excel File)Documento79 pagineTimber Design Project - Design of A Two Storey House (Excel File)Emmanuel Lazo100% (1)
- Unit 8 Roof Trusses: StructureDocumento24 pagineUnit 8 Roof Trusses: StructureanbugobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Beam DesignDocumento5 pagineTimber Beam DesignnurulselangorNessuna valutazione finora
- Roof DesignDocumento19 pagineRoof DesignB-sheep ArtsNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Timber Roof Truss To British Code - Solved Example - StructvilleDocumento9 pagineDesign of Timber Roof Truss To British Code - Solved Example - StructvilleDeRudy100% (3)
- TIMBER BEAM DESIGNDocumento144 pagineTIMBER BEAM DESIGNweng paraleNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber DesignDocumento279 pagineTimber Designzannik67% (6)
- Howe truss design with 29 members supporting 15 kipsDocumento6 pagineHowe truss design with 29 members supporting 15 kipsmichellem329100% (1)
- Two Way Slab (First Slab Level Slabs)Documento15 pagineTwo Way Slab (First Slab Level Slabs)Anjali DudhyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Truss DesignDocumento14 pagineTruss DesignIsaac Mureithi Maina100% (2)
- Design Computation of TrussDocumento3 pagineDesign Computation of Trussdash19910% (1)
- Eddie Naldoza Engineering Design Beam AnalysisDocumento5 pagineEddie Naldoza Engineering Design Beam AnalysisBong-Bong Rodriguez Bianzon100% (1)
- Advance Design of Timber StructuresDocumento49 pagineAdvance Design of Timber StructuresUzair Maqbool Khan100% (2)
- Chapter 7 - Timber DesignDocumento97 pagineChapter 7 - Timber DesignIqbarMaliki100% (2)
- 13 - 8 Design of 2 Way Slab For PrintingDocumento7 pagine13 - 8 Design of 2 Way Slab For PrintingAlbert DimayugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Roof (Pratt) TrussDocumento17 pagineDesign of Roof (Pratt) TrussD.V.Srinivasa Rao100% (4)
- Timber DesignDocumento10 pagineTimber DesignAprille Lyn Silla100% (1)
- Timber Sizes and Section PropertiesDocumento2 pagineTimber Sizes and Section PropertiesRichard KansinallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber DesignDocumento3 pagineTimber DesignAJ17% (6)
- Timber Design Project - Design of A Two Storey House (Word File)Documento92 pagineTimber Design Project - Design of A Two Storey House (Word File)Emmanuel Lazo90% (20)
- Corbel DesignDocumento10 pagineCorbel DesignJoe A. CagasNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of PurlinsDocumento8 pagineDesign of PurlinsLa BeamNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber DesignDocumento26 pagineTimber DesignRichmon Pangilinan100% (6)
- Timber DesignDocumento25 pagineTimber DesignNicole RodilNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel Program For Timber StructuresDocumento36 pagineExcel Program For Timber StructuresCarmel Buniel Sabado100% (9)
- 15 Footing DesignDocumento10 pagine15 Footing DesignLaura HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Example Calculations For Purlins (Ver 1.1 1098)Documento5 pagineExample Calculations For Purlins (Ver 1.1 1098)Ear Choungchhay100% (1)
- Structural Design of TimberDocumento9 pagineStructural Design of Timberdharul khairNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Design Lecture Notes Prelim PDFDocumento4 pagineTimber Design Lecture Notes Prelim PDFSteve BariaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Documento32 pagineAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Danilo NeryNessuna valutazione finora
- Roof Truss Analysis Definitions and Load CombinationsDocumento2 pagineRoof Truss Analysis Definitions and Load CombinationsVane DG50% (2)
- Timber ExceDocumento28 pagineTimber ExceBryan MagparangalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Purlins for a Proposed Two-Storey Library BuildingDocumento14 pagineDesign of Purlins for a Proposed Two-Storey Library BuildingRai RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignDa EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions To Test 1Documento25 pagineSolutions To Test 1Princess Gupo TañasNessuna valutazione finora
- Eccentric Loaded Bolted ConnectionsDocumento17 pagineEccentric Loaded Bolted ConnectionsRandieleo AsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps in Designing Beam Reinforced For TensionDocumento12 pagineSteps in Designing Beam Reinforced For TensionRogen Graciano DelgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1. PurlinsDocumento29 pagine6.1. PurlinsCherry Amor AbalosNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Column&Wall FootingDocumento20 pagineDesign of Column&Wall FootingJo Eli MacadangdangNessuna valutazione finora
- Size of Footing ProblemsDocumento2 pagineSize of Footing ProblemsJake CuencaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Cantilever Retaining Wall 4m EarthDocumento8 pagineDesign Cantilever Retaining Wall 4m EarthRahul Sinha100% (1)
- Design of Counterfort Retaining WallDocumento14 pagineDesign of Counterfort Retaining WallMonjit Gogoi100% (5)
- R C C +Retaning+WallDocumento24 pagineR C C +Retaning+Walladeewijaya32100% (1)
- Geotechnical Design PilesDocumento4 pagineGeotechnical Design PilesdmeharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Retaining Wall (Counterfort)Documento11 pagineRetaining Wall (Counterfort)Er R Raman0% (1)
- Counterfort Retaing Wall-OriginalDocumento15 pagineCounterfort Retaing Wall-OriginalHarish Kumar MahavarNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Ii1Documento17 pagineCase Ii1123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2017-CE May PDFDocumento32 pagine2017-CE May PDFKristin Argosino100% (2)
- Wing WallDocumento10 pagineWing WallSchelner Simon SihombingNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Five Results and DiscussionDocumento17 pagineChapter Five Results and DiscussionKawan EngNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportDa EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendations For The Design of Bridges To BS EN 1993: Published DocumentDocumento94 pagineRecommendations For The Design of Bridges To BS EN 1993: Published DocumentMohammed RiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Control Volume AnalysisDocumento30 pagineFinite Control Volume Analysishari tubagusNessuna valutazione finora
- Applus 15-10899-2428 P2 Af SystemDocumento5 pagineApplus 15-10899-2428 P2 Af SystemChristian LunardiNessuna valutazione finora
- 150x100x10UA STANDARD LINTEL 3.6mDocumento9 pagine150x100x10UA STANDARD LINTEL 3.6mTerry CheukNessuna valutazione finora
- TrussDocumento1 paginaTrusstdimala tdimalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mill Housings Mangal SinghDocumento5 pagineMill Housings Mangal SinghGun SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Wellbore Clean UpDocumento77 pagineWellbore Clean Upmvuka100% (4)
- Sylabus Selection in AMIEDocumento12 pagineSylabus Selection in AMIEdraj.deNessuna valutazione finora
- Waffle Slab DesignDocumento23 pagineWaffle Slab DesignMwengei Muteti100% (1)
- Overlay Design of PavementDocumento36 pagineOverlay Design of PavementRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CSI Color Hardener: Technical Data Sheet 1.0509DSDocumento2 pagineCSI Color Hardener: Technical Data Sheet 1.0509DSAyman MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- HYDRO 2023 PamphletDocumento2 pagineHYDRO 2023 PamphletBhargava ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental - Kalkan 2009Documento9 pagineExperimental - Kalkan 2009Ivan VoriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- DurabondDocumento44 pagineDurabondAndre BourgeoisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1936 Casagrande A. Characteristics of Cohesionless Soils Affecting The Stability of Slopes and Earth FillsDocumento10 pagine1936 Casagrande A. Characteristics of Cohesionless Soils Affecting The Stability of Slopes and Earth FillsErickaNessuna valutazione finora
- RCD Beam Analysis and DesignDocumento33 pagineRCD Beam Analysis and DesignLynx101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notching On BeamsDocumento28 pagineNotching On BeamsElvie Rodado GubalaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Stresses and Strains: ThereforeDocumento4 pagineSimple Stresses and Strains: ThereforeSuraj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Column Analogy Method PDFDocumento2 pagineColumn Analogy Method PDFHeather0% (1)
- Effect of Compression On T H E Shear Modulus of Rubber: of of of of of of ofDocumento3 pagineEffect of Compression On T H E Shear Modulus of Rubber: of of of of of of ofstefan.vince536Nessuna valutazione finora
- F-7721 Discharge NozzleDocumento2 pagineF-7721 Discharge NozzleCv. muda karya jayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Well FoundationsDocumento3 pagineDesign of Well Foundationssharathr22100% (1)
- Static Equipment (Mechanical)Documento36 pagineStatic Equipment (Mechanical)AKHIL JOSEPH100% (1)
- W'?RH%'M: Design and Construction For Ground Improvement - GuidelinesDocumento22 pagineW'?RH%'M: Design and Construction For Ground Improvement - GuidelinesSanjoy BhowmikNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment I For WWEDocumento2 pagineAssignment I For WWEwengelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rain Loads 1611 From IBCDocumento9 pagineRain Loads 1611 From IBCJim GregsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Soil Moduli 2018-White BackgroundDocumento45 pagineIntroduction To Soil Moduli 2018-White BackgroundYassin Abd El AalNessuna valutazione finora
- References Design 201304Documento9 pagineReferences Design 201304BagasAdhiwangsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flood and Debris Loads On Bridges PHD Thesis Mark Jempson PDFDocumento457 pagineFlood and Debris Loads On Bridges PHD Thesis Mark Jempson PDFThong NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief Note On NH-361 Sect 1 P 2Documento2 pagineBrief Note On NH-361 Sect 1 P 2Sravanthi MeharNessuna valutazione finora