Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
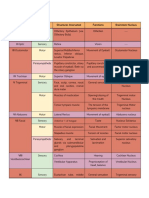
CN Name Site of Exit From Skull FXN Lesions How To Test
Caricato da
D0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
50 visualizzazioni2 pagineneuro, cranial nerves, school
Titolo originale
Cranial Nerves
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoneuro, cranial nerves, school
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
50 visualizzazioni2 pagineCN Name Site of Exit From Skull FXN Lesions How To Test
Caricato da
Dneuro, cranial nerves, school
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
CN Name Site of Exit from Skull Fxn Lesions How to test
I Olfactory Cribiform plate Smell
Cribiform fx
Kallmans syndrome
Smell something
II Optic
Optic canal
Vision
(1) Snellen eye chart
(2) Test peripheral vision too
III Oculomotor Superior orbital fissure
Parasympathetic to ciliary &
sphincter m.
Innervates:
superior rectus m.
inferior rectus m.
medial rectus m.
inferior oblique m.
Uncal (transtentorial)
herniation
Diabetes
Webers syndrome: form of
stroke characterized by
presene of CN III palsy &
contralateral hemiparesis
(1) H in space test
(2) Convergence
(3) Pupillary light reflex test
IV Trochlear Superior orbital fissure Superior oblique m. Head trauma H in space test
V
1
st
branch:
Ophthalmic n.
Superior orbital fissure
Provides sensory from medial
nose & forehead
Trigeminal neuralgias Facial sensation test
2
nd
branch:
Maxillary n.
Foramen rotundum
Provides sensory from lateral
nose, upper lip, buccal area
Facial sensation test
3
rd
branch:
Mandibular n
Foramen ovale
(1) Motor fxn to muscles of
mastication
(2) Provides sensory from
lateral lip to lower border of
mandible
Jaw deviates to side of lesion
(1) Opening & closing jaw (2)
Facial sensation test
VI Abducens n Superior orbital fissure Innervates lateral rectus m.
Medial inferior pontine
syndrome: contralateral
hemiparesis, contralateral loss
of tacile & vibration
H in space test
VII Temporal n Parasympathetics to: Bells palsy: paralysis of (1) Wrinkle forehead
Zygomatic n Sublingual gland and
Submandibular gland
Muscles of facial expression
(stapedius, stylohyoid,
posterior belly of digastric m)
Sensory & taste for anterior
2/3 of tongue
muscles on one side of face
(2) Puff out cheeks
(3) Close eyes tighly
(4) Say Mimimimi to test lip
fxn
Buccal n
Marginal
mandibular n
Cervical n
VIII Vestibulocochlear Internal Acoustic meatus Equilibrium & hearing
(1) Acoustic schwannoma
(2) vertigo (n/v)
(1) Hearing test
(2) Nystagmus test
IX Glossopharyngeal Jugular foramen
Parasympathetic to paroid
gland
Innervates:
Stylopharyngeus m
Sensory from pharynx, middle
ear, auditory tube, carotid
body & sinus, external ear
Sensory & taste for posterior
1/3 of tongue
Posterior inferior cerebellar
artery (PICA) infarct:
Test by gag reflex
Listen for hoarseness
X Vagus Jugular foramen
Parasympathetic to body
viscera
Laryngeal & pharyngeal m
Sensory from trachea,
esophagus, viscera, external
ear, epiglottis
Thyroidectomy injury
PICA infarct
Uvula deviates AWAY from
side of lesion (weak side
collapses)
Gag reflex
Elevate palate w/ Ah
XI Spinal accessory Jugular foramen
Innervates
Sternocleidomastoid m
Trapezius m
PICA infarct
Turning head
Shrugging shoulders
XII Hypoglossal Hypoglossal canal Intrinsic tongue muscles
Anterior spinal artery infarct
Deviates TOWARD lesion
Anterior tongue protrusion
Muscles that close jaw = masseter m, temporalis m, medial pterygoid m
Muscles that open jaw = lateral pterygoid m
To distinguish b/w Bells palsy & a stroke:
usu Bells palsy will involve forehead, stroke does not.
Facial nerve runs thru parotid gland but does NOT innervate it.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Behavioral FinalsDocumento28 pagineBehavioral FinalsKofiBNessuna valutazione finora
- Osmolarity&tonicitypracticeproblemsfrominternetDocumento14 pagineOsmolarity&tonicitypracticeproblemsfrominternetbsktblbabe88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skitchy MicroDocumento190 pagineSkitchy MicrohaneenNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 NotesDocumento54 pagineExam 1 NotesAnonymous If9p21kwZKNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Documento377 pagineMedical Boards Step 2 Made Ridiculously Simple (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Benyamin KhalevNessuna valutazione finora
- MuscleDocumento4 pagineMusclesho700oqNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodynamic DisordersDocumento34 pagineHemodynamic DisordersLiesel Illyry100% (1)
- 2 Renal Buzzword ChartDocumento6 pagine2 Renal Buzzword ChartTyler KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Chapter 1 DiagramsDocumento18 pagineRobbins Chapter 1 DiagramsYoja GarzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Stem 1Documento25 pagineBrain Stem 1api-19641337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Genitourinary 1Documento9 pagineGenitourinary 1Leshan PrattNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Mnemonic BookletDocumento14 pagineMedical Mnemonic Bookletahmed abd elazizNessuna valutazione finora
- (8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineDocumento9 pagine(8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineBhumiShahNessuna valutazione finora
- 149 First Aid CH 06 General Pathology FlashcardsDocumento23 pagine149 First Aid CH 06 General Pathology FlashcardsSomiZafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial NervesDocumento2 pagineCranial NervesakexisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDocumento16 pagineChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologyDocumento3 pagineEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologySamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Brachial Plexus Most ImportantDocumento2 pagineBrachial Plexus Most ImportantFlowerNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Chapter 3 DiagramsDocumento16 pagineRobbins Chapter 3 DiagramsjeffaguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Nerves Moore NotesDocumento7 pagineCranial Nerves Moore NotesCristina A RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Block 13 Patho SlidesDocumento62 pagineBlock 13 Patho SlidesLennon Ponta-oyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Genetic VariationDocumento21 pagineChapter 3 Genetic VariationAbdulkarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathoma 2087m (34h47) : 1) Growth Adaptations, Cell Injury 154 MinsDocumento5 paginePathoma 2087m (34h47) : 1) Growth Adaptations, Cell Injury 154 MinsKing John PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Bates Outline of Chapter 8Documento15 pagineBates Outline of Chapter 8KatherynSotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsDocumento29 pagineAnatomy 2 MnemonicsOmenaalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento40 pagineCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Bones & Joints Pathology 4thDocumento8 pagineBones & Joints Pathology 4thlovelyc95Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Documento3 paginePain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Ryan TurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Physio-DES-6 (Cardiac)Documento56 paginePhysio-DES-6 (Cardiac)Joseph Kim100% (1)
- Superficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus DorsiDocumento23 pagineSuperficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus Dorsimeyouhere100% (1)
- เฉลยข้อสอบ MCQ R2ครั้งที่2Documento362 pagineเฉลยข้อสอบ MCQ R2ครั้งที่2Kareem Sukwihan100% (2)
- ASTHMA - WatermarkedDocumento7 pagineASTHMA - WatermarkedShubhangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anat - Respi Gross CompiledDocumento8 pagineAnat - Respi Gross CompiledLeslie Kimberly Lisay100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology CNS Brain and Spinal Cord Chart Completed AP BiologyDocumento12 pagineAnatomy and Physiology CNS Brain and Spinal Cord Chart Completed AP BiologyTiffany GallinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Physiology IDocumento16 pagineRenal Physiology IJubilee Christiene AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Inguinal CanalDocumento4 pagineInguinal CanalspiraldaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain MnemonicsDocumento1 paginaBrain Mnemonicsphileo182Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology Pneumonics For BegginersDocumento38 paginePathology Pneumonics For BegginersAnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inDocumento13 pagineGenetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inQworld100% (1)
- Table of 12 Cranials and TractusDocumento5 pagineTable of 12 Cranials and TractusjuwitavalenNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA Viruses: P P P A H H PDocumento2 pagineDNA Viruses: P P P A H H PKimberly KanemitsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Robbins Chapter 2 DiagramsDocumento20 pagineRobbins Chapter 2 Diagramsjeffaguilar100% (2)
- Medical Physiology Learning Objectives: Robert G. Carroll L. Gabriel Navar Mordecai P. BlausteinDocumento75 pagineMedical Physiology Learning Objectives: Robert G. Carroll L. Gabriel Navar Mordecai P. BlausteinirajosephsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pons MedullaDocumento32 paginePons MedullaEnaWahahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Mnemonics 4 PrintDocumento65 pagineMedical Mnemonics 4 Printanne0521100% (1)
- Renal PathologyDocumento5 pagineRenal PathologyEmmanuel De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 StudyGuide CellAdaptandNec Latham 0820-22Documento8 pagine01 StudyGuide CellAdaptandNec Latham 0820-22ivankcurryNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1Documento130 pagineEndocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1api-19824701Nessuna valutazione finora
- Histology - Git Table 1Documento1 paginaHistology - Git Table 1lcrujidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fcps Past Papers ExamplesDocumento93 pagineFcps Past Papers ExamplesBilal Muhammad100% (1)
- Anatomy Exam Notes CNSPDFDocumento60 pagineAnatomy Exam Notes CNSPDFBerk SonmezNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology: Lung DevelopmentDocumento91 pagineEmbryology: Lung DevelopmentPrarthanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical MneumonicsDocumento139 pagineMedical MneumonicsdrtpkNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneDa EverandAdvances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneSakamuri V. ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Draw Anatomy for Anaesthetists, second editionDa EverandQuick Draw Anatomy for Anaesthetists, second editionNessuna valutazione finora
- PID Topic OverviewDocumento2 paginePID Topic OverviewDNessuna valutazione finora
- Handp TemplateDocumento3 pagineHandp TemplateLauren GrandpreNessuna valutazione finora
- Megs History PhysicalDocumento1 paginaMegs History Physicalrmelendez001Nessuna valutazione finora
- WUSM Class of 2019 Advice For Class of 2020Documento10 pagineWUSM Class of 2019 Advice For Class of 2020DNessuna valutazione finora
- The Normal Kidney: Kidney Size by AgeDocumento7 pagineThe Normal Kidney: Kidney Size by AgenadiautaminoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Obgyn HXDocumento1 paginaObgyn HXDNessuna valutazione finora
- OBGYN QuestionsDocumento1 paginaOBGYN QuestionsDNessuna valutazione finora
- EU - WEST - 1 Prod s3 Ucmdata Evise C - O6618179 - 3789308Documento58 pagineEU - WEST - 1 Prod s3 Ucmdata Evise C - O6618179 - 3789308DNessuna valutazione finora
- Earplugs? 2 Foamy Watches? Clocks Bags? Size of Locker? No Lock, BackpackDocumento1 paginaEarplugs? 2 Foamy Watches? Clocks Bags? Size of Locker? No Lock, BackpackDNessuna valutazione finora
- TestingDocumento1 paginaTestingDNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Text FileDocumento1 paginaGeneric Text FileDNessuna valutazione finora
- KEY Resources TableDocumento6 pagineKEY Resources TableDNessuna valutazione finora
- Earplugs? 2 Foamy Watches? Clocks Bags? Size of Locker? No Lock, BackpackDocumento1 paginaEarplugs? 2 Foamy Watches? Clocks Bags? Size of Locker? No Lock, BackpackDNessuna valutazione finora
- Standardized Test FAQDocumento4 pagineStandardized Test FAQDNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide CardioDocumento29 pagineStudy Guide CardioDNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci MethDocumento1 paginaSci MethDNessuna valutazione finora
- CDP3Documento3 pagineCDP3DNessuna valutazione finora
- Prendergast's Guide To Housestaff Etiquette: Long Bad Presentations Is TortureDocumento1 paginaPrendergast's Guide To Housestaff Etiquette: Long Bad Presentations Is TortureDNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Name Site of Exit From Skull FXN Lesions How To TestDocumento2 pagineCN Name Site of Exit From Skull FXN Lesions How To TestDNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Diagnosis of Chest Pain CardiovascularDocumento2 pagineDifferential Diagnosis of Chest Pain CardiovascularDNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ 1 MCQ 2 MCQ 3 MCQ 4 MCQ Average MCQ Points Role Play Paper Nutrition Paper Ethics Paper Paper Average #DIV/0! #DIV/0! 0 28 24 30 0 0 0Documento3 pagineMCQ 1 MCQ 2 MCQ 3 MCQ 4 MCQ Average MCQ Points Role Play Paper Nutrition Paper Ethics Paper Paper Average #DIV/0! #DIV/0! 0 28 24 30 0 0 0DNessuna valutazione finora
- OBGYN - Lecture Clicker QuestionsDocumento8 pagineOBGYN - Lecture Clicker QuestionsDNessuna valutazione finora
- OB/Gyn Clinical PearlsDocumento4 pagineOB/Gyn Clinical PearlsD50% (4)
- Microbes, BacteriaDocumento68 pagineMicrobes, BacteriaDNessuna valutazione finora
- Study TipsDocumento6 pagineStudy TipsDNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro, NotesDocumento136 pagineNeuro, NotesDNessuna valutazione finora
- Psych D/o PrevalenceDocumento2 paginePsych D/o PrevalenceDNessuna valutazione finora
- OutlineDocumento1 paginaOutlineDNessuna valutazione finora
- SLEDocumento14 pagineSLEDNessuna valutazione finora