Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Elecs Diagnostic Exam
Caricato da
mgoldiieeeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Elecs Diagnostic Exam
Caricato da
mgoldiieeeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
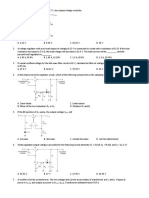
1. In an inverting op amp circuit, Ri = 100 and Rf = 1 k.
What
is the gain?
a. -1 c. 11
b. -10 d. 9
2. Calculate the over-all gain of a non-inverting op amp circuit
whose Ri = 100 and Rf = 1k.
a. -1 c. 11
b. -10 d. 9
3. Calculate the input voltage in a non-inverting op amp circuit
whose Ri = 100 and Rf = 1k if the output voltage is
550mV.
a. -50mV c. 550mV
b. -5mV d. 50mV
4. What is the slew rate of an op-amp if the output voltage
change from 2 V to 3 V in 0.2ms?
a. 5 V/ms c. 2 V/ms
b. 3 V/ms d. 1 V/ms
5. For an op-amp having a slew rate SR = 5 V/ms, what is the
maximum closed-loop voltage gain that can be used when
the input signal varies by 0.2 V in 10 ms?
a. 150 c. 250
b. 200 d. 300
6. Calculate the output impedance of an inverting op-amp
using the 741 op-amp (r
o
= 75, A
OL
= 200 V/mV) if R1 =
100 and Rf = 1k.
a. 0.011 c. 0.0375
b. 0.00375 d. 0.375
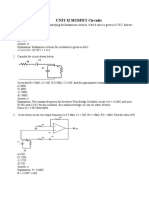
7. Determine the voltage gain with feedback for a voltage-
series feedback having A = -100, R1 = 15 k, Ro = 20 k and
feedback of = -0.25
a. 3.85 c. -9.09
b. -3.85 d. 9.09
8. Determine the voltage gain with feedback for a voltage-
series feedback having A = -100, R1 = 15 k, Ro = 20 k and
feedback of = -0.25
a. 110 k c. 390 k
b. 290 k d. 510 k
9. Determine the voltage gain with feedback for a voltage-
series feedback having A = -100, R1 = 15 k, Ro = 20 k and
feedback of = -0.25
a. 0.2 k c. 1.82 k
b. 392.16 k d. 769.23 k
10. Calculate the resonant frequency of Wien-bridge oscillator
whose resistors and capacitors in the tank circuit has values
of 50 k and 2 nF respectively
a. 1560.34 Hz c. 4661.07 Hz
b. 3120.70 Hz d. 6241.37 Hz
11. In a certain oscillator, Av = 50. The attenuation of the
feedback circuit must be
a. 1 c. 10
b. 0.01 d. 0.02
12. Which of the following is the roll-off rate of an op-amp
above the critical frequency?
a. 6 dB/decade
b. 20 dB/octave
c. 10 dB/decade
d. 20 dB/decade
13. What is responsible for the roll-off above the critical
frequency of an op-amp?
a. the external coupling and bypass capacitors
b. the internal coupling capacitors in an op amp
c. the stray and parasitic capacitance
d. the RC lag circuits internal to an op amp
14. What happens when the initial slope of the signal is less than
the slew rate?
a. slew rate distortion occurs
b. the signal is linearly amplified
c. harmonic distortion occurs
d. amplitude distortion occurs
15. In the common mode, if the input signals to an op amp have
the same frequency and polarity but different magnitude,
the output
a. is always zero
b. is the sum of the two inputs
c. can be zero or greater than zero
d. is never zero
16. If the gain of an op amp decreases
a. the bandwidth decreases as well
b. the bandwidth remains unaffected
c. the bandwidth will increase
d. the amplifier becomes nonlinear
17. A comparator uses
a. positive feedback
b. negative feedback
c. positive or negative feedback
d. positive or no feedback at all
18. A circuit whose output voltage is proportional to the rate of
change of the input voltage
a. summing amplifier
b. differentiator
c. subtractor
d. integrator
19. The first silicon IC was developed by
a. Kilby
b. Noyce
c. Moore
d. Shockley
20. The second generation of Intel i7 processors uses the ____
nm manufacturing technology
a. 65 c. 32
b. 45 d. 22
21. According to Moores Law, the number of transistors in a
chip doubles after every approximately _______ months
a. 12 c. 16
b. 16 d. 24
22. Which is not a linear IC?
a. Logic gate c. Comparator
b. Op amp d. Voltage regulator
23. The process used to transfer that circuit layout in the
photomask into the wafer substrate
a. diffusion c. ion implantation
b. photolithography d. etching
24. Cylindrical silicon crystal made of only one type of crystal
structure
a. wafer c. ingot
b. die d. seed crystal
25. The most commonly used wafer size is
a. 150 mm c. 300 mm
b. 200 mm d. 450 mm
26. The process of adding materials on the surface of the wafer
a. deposition c. diffusion
b. metallization d. doping
27. This is a very thin circular mask made of high level purity
silicon used as substrate in the manufacture of ICs
a. die c. ingot
b. wafer d. oxide
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Microelectronics QuestionsDocumento55 pagineMicroelectronics QuestionsAchilles AldaveNessuna valutazione finora
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDa Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- ELEX Evaluation 6Documento4 pagineELEX Evaluation 6Achilles AldaveNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesDa EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A. A. B. A. A. A.: Group Study - Op Amps and Ic'S Digital Electronics Answer KeyDocumento6 pagineA. A. B. A. A. A.: Group Study - Op Amps and Ic'S Digital Electronics Answer KeyLorenz ArdienteNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Sample Problems 09Documento6 pagineElectronics Sample Problems 09Genesis PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Linear IC Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineLinear IC Answer KeyVarshni KarthikeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Poweramps MCQ ReviewerDocumento20 paginePoweramps MCQ ReviewerJoecynnOycoNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Documento8 pagineQuestion Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Nithya SNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics 100 Important MCQDocumento23 pagineElectronics 100 Important MCQRaghu Veer KNessuna valutazione finora
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Da EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Zener diode voltage regulator circuit problems and solutionsDocumento5 pagineZener diode voltage regulator circuit problems and solutionsJonas ParreñoNessuna valutazione finora
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorDa Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Electronics Mastery 3 Problem SetDocumento4 pagineElectronics Mastery 3 Problem SetJonas ParreñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Engineering For Oct 2012Documento136 pagineElectronics Engineering For Oct 2012anna kulasaNessuna valutazione finora
- BEL Placement Paper 2Documento21 pagineBEL Placement Paper 2Saikiran RaghuNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits MCQs and SolutionsDocumento7 paginePractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits MCQs and SolutionsGrace ShykolNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal Teori Elektronika (Lks 2010)Documento17 pagineSoal Teori Elektronika (Lks 2010)Mardanus MelayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Test-I Linear Integrated Circuits 21-22 YPPDocumento9 pagineUnit Test-I Linear Integrated Circuits 21-22 YPPVedant SonawaneNessuna valutazione finora
- DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY EXAM REVIEWDocumento6 pagineDE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY EXAM REVIEWSahara MalabananNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE Licensure Examination Pre-board ReviewDocumento10 pagineECE Licensure Examination Pre-board ReviewAnndrea MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple ChoiceDocumento4 paginePractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple Choiceapi-127299018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Circuits - Unit - 2 - MCQDocumento4 pagineElectronic Circuits - Unit - 2 - MCQShivani AndhaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Past Board April 2005 With AnswersDocumento17 pagineElectronics Past Board April 2005 With AnswersJose Maria ManabatNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems in MalvinoDocumento3 pagineProblems in MalvinoKrit JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- AicDocumento6 pagineAicSatwik JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Documento10 pagineFinal Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2RaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECA Mid-1 ECE 2-2Documento5 pagineECA Mid-1 ECE 2-2Mohan DasNessuna valutazione finora
- AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS: TEEE/TETE 2103Documento3 pagineAMPLIFIER CIRCUITS: TEEE/TETE 2103Suubi brianNessuna valutazione finora
- Relec Refresher v.2Documento2 pagineRelec Refresher v.2Yancha PagdagdaganNessuna valutazione finora
- For More InformationDocumento22 pagineFor More InformationJothsna PraveenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Electronic Communication 7th Edition by Beasley & Miller MCQDocumento18 pagineModern Electronic Communication 7th Edition by Beasley & Miller MCQJulio Gabriel Aseron100% (1)
- For Nos. 1 - 6: BJT Ac and DC Analysis MmleDocumento4 pagineFor Nos. 1 - 6: BJT Ac and DC Analysis MmlemgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee Module 4 April 2012Documento3 pagineEe Module 4 April 2012Znevba QuintanoNessuna valutazione finora
- DM Lab Set 1Documento4 pagineDM Lab Set 1Jitesh ShiramshettyNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRE-BOARD EXAM REVIEWDocumento18 pagineELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PRE-BOARD EXAM REVIEWAshlien Valdez0% (2)
- Introductory Topics in Communication SystemsDocumento21 pagineIntroductory Topics in Communication SystemsMark Allan CalubNessuna valutazione finora
- Compilations of Problems by Thomas FloydDocumento4 pagineCompilations of Problems by Thomas FloydmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- ObjectiveDocumento20 pagineObjectiveAnonymous sBvtnZQNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFDocumento10 pagineAnalog Electronics MCQ Test 7 28th April 2020 PDFPalani CNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuits 2Documento3 pagineCircuits 2lesterPECE100% (5)
- ASUBAR - PART 14 - MicroelectronicsDocumento8 pagineASUBAR - PART 14 - MicroelectronicsEmmanuel RapadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dsaaasdg FgdsDocumento6 pagineDsaaasdg Fgdstetimo mekutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Opamp CircuitsDocumento5 pagineOpamp CircuitssayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Documento12 pagineFinal Exam Questions - Electrical Fundamentals 2Ahyad Arif Abdul Rahman100% (2)
- Computer Engineering Correlation 1 (Electronics 1 and 2) QuestionsDocumento45 pagineComputer Engineering Correlation 1 (Electronics 1 and 2) QuestionsNorman OcoNessuna valutazione finora
- ANALOGE AND DIGITAL ELECTRONICS MCQ NOTESDocumento7 pagineANALOGE AND DIGITAL ELECTRONICS MCQ NOTESAkshay KarmareNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics Objective QuestionDocumento77 pagineAnalog Electronics Objective QuestionYOGESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Radio-Frequency CircuitsDocumento6 pagineChapter 2 Radio-Frequency Circuitsmarkanthonycorpin100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Intro Topics Comm SystemsDocumento14 pagineChapter 1 Intro Topics Comm Systemsaoi_blue89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics RefresherDocumento2 pagineElectronics RefresherPaolo Steven PolintanNessuna valutazione finora
- Elecs Ref 2019Documento8 pagineElecs Ref 2019Hary KrizNessuna valutazione finora
- The relationship between information and bandwidthDocumento18 pagineThe relationship between information and bandwidthPhilip CuetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac DC Circuitsset ADocumento3 pagineAc DC Circuitsset ALiFamily OnebeeNessuna valutazione finora
- MathematicsDocumento13 pagineMathematicsmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Apolinario MabiniDocumento8 pagineApolinario MabinimgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- AsfdasdDocumento14 pagineAsfdasdmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rizal Is ADocumento1 paginaRizal Is AmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Order de (With Ans)Documento2 pagine2nd Order de (With Ans)mgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics IecepDocumento12 pagineMathematics Iecepmgoldiieeee100% (1)
- Laws of Indices PDFDocumento2 pagineLaws of Indices PDFaerofit100% (1)
- For Nos. 1 - 6: BJT Ac and DC Analysis MmleDocumento4 pagineFor Nos. 1 - 6: BJT Ac and DC Analysis MmlemgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGECODocumento3 pagineENGECOmgoldiieeee20% (5)
- Est Question For Iecep 2012Documento4 pagineEst Question For Iecep 2012mgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabi For Electronics Engineering Licensure ExaminationDocumento3 pagineSyllabi For Electronics Engineering Licensure ExaminationmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Feedback ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineFeedback ObjectivesmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Instability A. Instability A. Instability A. InstabilityDocumento1 paginaA. Instability A. Instability A. Instability A. InstabilitymgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Elect Obj IIDocumento24 pagineElect Obj IIGaurav Pratap RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary - Electronic Communication - Kennedy - Chap2Documento2 pagineSummary - Electronic Communication - Kennedy - Chap2mgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Basics - From WebsiteDocumento2 pagineElectrical Basics - From WebsitemgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer ExcelDocumento4 pagineReviewer ExcelJC Tolentino67% (3)
- AlgebraTrig ProblemsDocumento17 pagineAlgebraTrig Problemsrizwan900Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Powerful e-SuperbookDocumento46 pagineThe Powerful e-Superbookmgoldiieeee100% (1)
- Virgin Islands: EtymologyDocumento3 pagineVirgin Islands: EtymologymgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Beta Test Fopr Upload OnlyDocumento1 paginaBeta Test Fopr Upload OnlymgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- For Upload For Upload For Upload For UploadDocumento3 pagineFor Upload For Upload For Upload For UploadJ Kingsley GreenlandNessuna valutazione finora
- José Rizal: Now I Had To Use It, Thus Giving Me The Appearance of An Illegitimate Child!"Documento1 paginaJosé Rizal: Now I Had To Use It, Thus Giving Me The Appearance of An Illegitimate Child!"mgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- UST-Geas Mechanics1Documento10 pagineUST-Geas Mechanics1TayntaynNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Usnco Exam Part IIDocumento11 pagine2014 Usnco Exam Part IImgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- UST-Geas Mechanics1Documento10 pagineUST-Geas Mechanics1TayntaynNessuna valutazione finora
- Andrés BonifacioDocumento1 paginaAndrés BonifaciomgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- BulSU2 Est PartDocumento39 pagineBulSU2 Est PartmgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMS 6 - Trans LineDocumento4 pagineCOMMS 6 - Trans LinemgoldiieeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Compiled Elecs QaDocumento10 pagineCompiled Elecs Qamgoldiieeee100% (1)
- MAX8211-MAX8212 (Monitor de Voltaje)Documento7 pagineMAX8211-MAX8212 (Monitor de Voltaje)apola5mNessuna valutazione finora
- Use A Transistor and An Ammeter To Measure InductanceDocumento4 pagineUse A Transistor and An Ammeter To Measure InductancePaulina Perez Carreño EncisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dasar Elektronikaa BJT BiasingDocumento10 pagineDasar Elektronikaa BJT Biasingremember sundayNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabDocumento12 pagineLaboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabZain HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- SAA1054Documento14 pagineSAA1054partho mondolNessuna valutazione finora
- 051796F0.sch-1 - Thu Dec 15 11:09:57 2005Documento25 pagine051796F0.sch-1 - Thu Dec 15 11:09:57 2005Aconatic tvhomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Esp32-H2 Hardware Design Guidelines enDocumento33 pagineEsp32-H2 Hardware Design Guidelines enpetrusz1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Signal Voltage LevelsDocumento51 pagineLogic Signal Voltage LevelsDoDuyBacNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio Power Amplifier With Speaker AGC Load With AGC Circuit - DocxDocumento11 pagineAudio Power Amplifier With Speaker AGC Load With AGC Circuit - Docxapi-3704005100% (4)
- Build a differential input op amp circuit to measure AC mains voltageDocumento2 pagineBuild a differential input op amp circuit to measure AC mains voltagelibrian_30005821Nessuna valutazione finora
- LMC835 Digital Controlled Graphic Equalizer: General Description FeaturesDocumento17 pagineLMC835 Digital Controlled Graphic Equalizer: General Description FeaturesKhairul NurzamNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6411 CircuitsSimulation LABDocumento98 pagineEC6411 CircuitsSimulation LABJ.Gowri ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practices For The Quartus Ii Timequest Timing AnalyzerDocumento48 pagineBest Practices For The Quartus Ii Timequest Timing AnalyzergorskiaNessuna valutazione finora
- MME-Electrical-Session-2 Network Theorems PDFDocumento74 pagineMME-Electrical-Session-2 Network Theorems PDFgpuonlineNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC 2147 Electrical Energy Technology: AC Circuit IIDocumento25 pagineELEC 2147 Electrical Energy Technology: AC Circuit IIKa Hei Ernest HoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IDocumento25 pagineUnit IRamarao BNessuna valutazione finora
- CT Assignment IDocumento4 pagineCT Assignment ImosesalvinNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Characteristics of Op-AmpDocumento6 pagineDC Characteristics of Op-Ampmahesh babuNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 1Documento5 pagineDifferential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 1lokeshwarrvrjcNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity: Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR) - ADALM1000 (Analog Devices Wiki)Documento1 paginaActivity: Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR) - ADALM1000 (Analog Devices Wiki)Justin OkumuNessuna valutazione finora
- IV ConverterDocumento16 pagineIV ConverterNeha SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Session # 8 Latches, Gated Latches and Flip-Flops: CircuitsDocumento10 pagineLab Session # 8 Latches, Gated Latches and Flip-Flops: Circuitsmaraim4eveNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 29 (No Sirve)Documento5 pagineDocument 29 (No Sirve)Alejandro Antonio Nuñez BonillaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 303 Syllabus Term 231Documento1 paginaEE 303 Syllabus Term 231Ahmed -j-aNessuna valutazione finora
- PWM Signal GenerationDocumento4 paginePWM Signal GenerationPravat SatpathyNessuna valutazione finora
- EC-101 Electrical Sciences Electrical Sciences 3-1-0-8: Course InstructorsDocumento13 pagineEC-101 Electrical Sciences Electrical Sciences 3-1-0-8: Course InstructorsMd ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- Pramod 2019Documento12 paginePramod 2019venkat301485Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data-Processing Circuits 3.2Documento83 pagineData-Processing Circuits 3.2DEEPAK UPADHYAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 Chp2-Microwave Filters - Withexamples - PPT 22Documento129 pagineLecture 3 Chp2-Microwave Filters - Withexamples - PPT 22Bitew AyalewNessuna valutazione finora
- 74HC590Documento18 pagine74HC590Juan José Lopez NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDa EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyDa EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (82)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Da EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionDa Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersDa EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Da EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Model-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodDa EverandModel-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodNessuna valutazione finora
- From Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionDa EverandFrom Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionNessuna valutazione finora
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XDa EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxDa EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsDa EverandCreative Selection: Inside Apple's Design Process During the Golden Age of Steve JobsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- Dancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldDa EverandDancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersDa Everand2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersNessuna valutazione finora
- Tor Darknet Bundle: Master the Art of InvisibilityDa EverandTor Darknet Bundle: Master the Art of InvisibilityNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionDa EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- iPhone 15 Pro User Guide for Beginners and SeniorsDa EverandiPhone 15 Pro User Guide for Beginners and SeniorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Systems: ARM Programming and OptimizationDa EverandEmbedded Systems: ARM Programming and OptimizationNessuna valutazione finora