Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
OB Exam 1 Study Guide
Caricato da
Alvin Maniago0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
130 visualizzazioni23 pagineExam study guide from like 2012
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoExam study guide from like 2012
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
130 visualizzazioni23 pagineOB Exam 1 Study Guide
Caricato da
Alvin ManiagoExam study guide from like 2012
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 23
OB Exam 1 Study Guide 7/2/2013 3:40:00 PM
Ch 5: Reproductive Anatomy & Physiology
Sexual differentiation in the embryo
Gender determined at the moment of conception but 8 weeks before reproductive system becomes differentiated as male
or female
Female fetus has a developed ovary by 10 weeks
Mesoderm (middle layer): develops at 5 weeks conception
o 1st structure formed is gonad medulla & cortex
Mesophrenic ducts-dominant in males, evolving into efferent ductile, vas deferens, epididymis, seminal vesicle and
ejaculatory duct
Paramesophrenic ducts-dominant in females, evolving into fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina
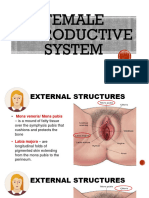
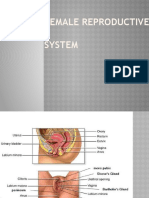
Female reproductive system
Vulva: Posterior to the mons pubis (lowest portion of the abdomen) that is usually covered with pubic hair. Provides
protection for the pelvis
Labia majora: 2 folds that protect tissues (highly vascular during pregnancy)
Labia minora: 2 folds w/in majora that converge near anus to form fourchette (posterior opening on vagina)
Clitoris: Upper junction of the labia minora consisting of thePrepuce (fold of skin that covers the gland)&secrete
Smegma. Rich in blood & nerves, serves as 1 organ of sexual pleasure
Vestibule: Oval shaped space that contains the openings to the urethra & vagina
o Teach about discomfort associated with chemicals (dyes, soaps)
Bartholins (vulvovaginal) gland: visible, secretes clear mucus during sexual arousal
Urehtral (Urinary) Meatus: inverted V shape below the clitoris
o Hymen: forms border of connective tissue that encircles vaginal introitus
Skenes gland: on each side of urethra producing mucus to help lubricate
Perineum: skin between vagina and anus
o Stretches and becomes thin during labor, often tears
o Episiotomy: surgical incision to allow perineal opening
Pelvic floor
Provides support and stability for surrounding structures
o Consists of: pelvic fascia, pubococcygeal, puborectal, illiococcygeal muscles
Relaxes and contracts during labor
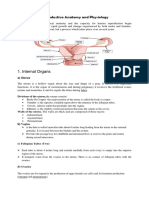
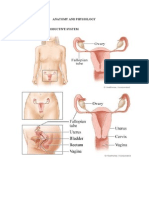
Organs
Ovaries: held in pelvis by ligaments: medovarian, ovarian, infundibular
o Essential b/c of production of ova for reproduction
o Does not become activity until puberty to release ova and hormones
o SECRETES ESTROGEN & PROGESTERONE that regulate menstrual cycle
Fallopian Tubes
o 4 layers peritoneal (serous), subserous (adventitial), muscular & mucous
Blood & nerve supply stored in subserous
o 3 sections of fallopian tubes
Infundibulum: distal opening where ovum enters
Ampulla: most common cite of conception
Isthmus: proximal end usual site of tubal ligation (tubes tied)
o If fertilization does not occur in 24-48 hours, OVUM DIES
Uterus: Centrally located between bladder & rectum (pear shaped) w/ 2 major functions
o 1. Permit sperm to ascend to fallopian tubes
o 2. Provide nourishing environment for zygote ( it protects & nurtures growing embryo)
o If no conception: uterus sheds outermost layers of endometrium (menstruation)
o Consists of:
Corpus: layers are perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
Perimetrium: outer most layer
Myometrium: middle layer consisting of smooth muscle in 3 directions
Endometrium: twiinner most layer shed during menses
Isthmus: midway b/w uterine body (site of low C-section)
Cervix: lower end of the uterus and opens into the vagina
Secretes mucus for lubrication, barrier against sperm penetration into uterus during non-fertile
periods, provides pathway for sperm during fertile periods, creates alkaline environment for
sperm& forms a solid plug called operculum to protect pregnancy from outside pathogens
o Fundus: Need to know position & height prenatal and post-partum
o Uterine pain nerve fibers reach the spinal cord at level T11 & T12
Vagina: Acidic at pH 4.5-5.5 & has 5 functions
o Lubrication during intercourse
o Stimulate penis during sex
o Act as receptacle for semen (apex is known as the vault)
o Transportation of tissue/blood during menses
o Lowest portion of the birth canal during birth
Ureters, Bladder, Urethra
o Mucous membrane-lined tube from bladder used for micturition
Pelvis
Bony Pelvis: bony ring that transmits body weight to lower extremities
4 bones: sacrum, coccycx, 2 hip bones
During labor, ischial spines serve as a landmark for assessing the level of the fetal presenting part into the pelvis
True/False Pelvis
o True: outlet lower portion located below lineaterminalis
3 parts: pelvic inlet, midpelvis, pelvic outlet
o False: inlet & upper portion of hip bones, support pregnant uterus
Diameters
o Pelvimetry: measurements to predict feasibility of birth (inlet, midpelvis, outlet)
TYPES
o Gynecoid: traditional (50%) best suited for birth
Inlet, midpelvis and outlet are largest
Inlet is round-oval shaped, ischial spine less prominent, short and deep sacrum, wide pubic arch
o Android: like male pelvis (23%)
Inlet: or heart-shaped with more bony prominences which can cause difficulty during fetal descent
o Anthropoid: ape-like (24%)
Pubic arch is narrow & inlet is OVAL shaped (ant to post)
o Platypelloid: CANT GIVE BIRTH due to transverse presentation of fetus
Inlet is laterally wide, sacral/ischial bony prominences w/ wide suprapubic arch
Breast: Nipples, areola & Montgomery tubules
1 function is lactation to provide nutrition to offspring
decrease of estrogen post-partum triggers increase of prolactin stimulating milk production
oxytocin (from posterior pituitary/hypothalamus) is responsible for ejection of breast milk
Montgomery tubules: secretes fatty substance for lubrication/protection of nipple & areola during breastfeeding
Hypothalamus Hormones
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
o Stimulates release of FSH & LH when Estrogen and Progesterone decrease
o Females: affects follicular growth, ovulation and corpus luteum
o Males: affects spermatogenesis (production of sperm)
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
o Regulates ACTH to activate sympathetic nervous system
o Reduces chances the mothers immune system will reject embryo
Growth-hormone releasing hormone (GH-RH)
o Stimulates the production of growth hormone (GH)
Growth-hormone inhibiting hormone (GH-IH) or somastatin
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
o Regulates T3 & T4; also stimulate prolactin
Prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF) or prolactostatin
o Inhibits synthesis and production of prolactin
Pituitary Gland Hormones
TSH or thyrotropin: regulation of endocrine function of thyroid
ACTH or corticotropin: controls development/function of adrenal cortex
Prolactin: stimulates maturity of mammary glands during pregnancy
o Initiates milk production & inhibits stimulation of FSH and LH (reason why breastfeeding women usually dont
conceive)
GH or somatotropin: stimulates cell and growth production
o Also resp for: muscle mass, Ca+ retention, bone mineralization, organ growth, protein synthesis & stimulation
of immune system
Gonadotropins (gonad-stimulating hormones)
o FSH & LH both stimulate & inhibit ovaries by producing +& feedback of estrogen and progesterone by the
ovaries
Oxytocin (released by posterior pituitary)
o Stimulates uterine contractions & release of milk
o Synthetic form available that can be given during labor to enhance contractions, promote expulsion of placenta
& minimize bleeding
Gonad Hormones
Estrogen: HIGH in women of childbearing age
o Responsible for 2 sex characteristics (breasts, hips, butt, mons pubis)
o Helps regulate menstrual cycle by stimulating proliferation of endometrial lining to prepare for pregnancy
Progesterone: helps regulate menstrual cycle
o Decreases uterine motility and contractility (relaxes smooth muscles)
o prepares uterus for embryo implantation& breasts for lactation
o HIGH during pregnancy
Other hormones
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCg) **important in early pregnancy**
o Increased levels in blood means pregnant
o Produces trophoblasts, outer layer of blastocyst which become the baby
o Maintains corpus luteum by keeping levels of estrogen & progesterone elevates until placenta is developed
Prostaglandins: during pregnancy, helps initiate labor
o Cause vasoconstriction & muscle contractions leads to tissue ischemia and pain associated with PMS
Relaxin: produced by corpus luteum& detected by the 1
st
missed menses
o Aids in softening & lengthening of cervix, also works on myometrial smooth muscle to promote uterine
contraction
Sexual maturation
Puberty: biological time frame between childhood and adulthood characterized by physical changes that lead to sexual
maturity
o Menarche: 1
st
menstrual period (9-15 y/o, avg 12.4 y/o)
FSH stimulates ovaries, LH promotes ovulation, corpus luteum left behind producing progesterone
Menstrual cycle and Reproduction: periodic d/c of bloody fluid from the vagina
o THE CYCLE: changes that occur in uterus, cervix, &vagina associated w/ menstruation
Avg. time: 28-32 days
The Uterine (endometrial) cycle
o Menstrual Phase: time of vaginal bleeding(DAYS 1-6)
Triggered by declining levels of estrogen and progesterone
s)
Prostaglandins released by uterus to cause contractions of smooth muscle to decrease risk of
hemorrhage (may cause dysmenorrhea)
Can also cause H/A & nausea
Menstrual fluid consists of endometrial tissue, blood, cervical/vaginal secretions, bacteria, mucus,
leukocytes, prostaglandins
o Proliferative phase: end of menses through ovulation (DAYS 7-14)
Estrogen is low but increases as uterine lining begins to thicken
o Secretory phase: prior to menses (DAYS 15-26)
Increasing amounts of progesterone, making uterus suitable for implantation
o Ischemic phase: onset of menses (DAYS 27-28)
Estrogen and progesterone levels are low
to endometrium
Endometrium becomes pale, vessels rupture. BEGIN DAY 1
o Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian cycle
Hypothalamus and ant. pituitary communicate through portal system
Important hormones: GnRH, LH, FSH, estrogen and progesterone
o Follicular Phase: DAY 1 of menstrual cycle beginning w/ bleeding, ends w/ ovulation
About 14 days in length
GnRH stimulates release of LH & FSH
LH stimulates theca cells of ovaries to produce androgens (ie estrogen)
FSH stimulates ovary to produce androgens to prep a mature ovum
Ovum is capable of fertilization 12-24 hours after ovulation
The follicle that contained mature ovum stays in ovary, becomes corpus luteum
o Luteal phase: Begins at ovulation and ends with onset of menses (14 days)
If not pregnant corpus luteum dominates over 2
nd
half of menstrual cycle and regresses after 14 days
Body changes related to menstrual cycle and ovulation
o Spinnbarkheit: elasticity of cervical mucus (to see if woman is ready to conceive)
o Ferning: test to see if woman is ready to conceive by through crustallization of mucus
o Body Temperature increases 0.3-0.6 C 24-48 hours after ovulation
Cessation menses: Menopause (last period)
o Climacteric phase: Due to decrease in ovary function
o Perimenopausal phase: # and production of follicles decrease
Experience hot flashes, vaginal atrophy, mood alterations, skeletal bone loss
Ch 6: Human Sexuality and Fertility
Sexuality and Reproductive Health Care
Must understand the womans views of her situation and asses her needs, values, beliefs and support system
Nurses Role: educator, counselor, care provider
4 Stages of Human Sexual Response
o Excitement, Plateau, Orgasmic, Resolution
Sexuality: Hetero, Homo, Bi (lesbian have increased risk of breast cxr due to not breastfeeding)
Promotion of .
Sexual dysfunction: manifested in the form of pain, arousal d/o, orgasmic d/o, lack of desire
Dyspareunia: painful intercourse
Establish trusting relationship
o Obtain sexual Hx: STI, dyspareunia, post-coital bleeding, and frequency of sex
o Dont judge adolescents for their sexual behavior
o Discuss chronic conditions affecting fertility: endometriosis or polycystic ovarian disease
Contraception: find what works best for that patient
o Medication free: identify fertile periods and avoid sex during that time
o Coitus interuptus: withdrawal or pull-out method
o Lactational amenorrhea: mother breast feeds since birth and does not menstruate
o Abstinence: No sex, No baby
o Barriers: inserted or applied prior to coitus KEY is consistent and correct use
Latex barriers work best IF NOT ALLERGIC
Diaphragm: fitted by nurse/physician filled with spermicide inserted 6 hrs before remains in place 6hrs
after sex. There is increased risk for UTI. Not used during menses bc risk of toxic shock syndrome
(rare but fatal)
Refitted q2years, teach pt how to insert it
Cervical cap: 74% like diaphragm but more difficult
Condoms 85% effective
Spermicide: chemical barrier that cause death of sperm before entering cervix
Do not douche after sex to increase effectiveness of spermicide (6 hrs)
Contraceptive sponge: (84-87%) fits over cervix allowing 24 hour protection, do not leave on >30 hrs
o Hormonal methods: medication, patches, injectibles, subdermal plants, other devices
KNOW ACHES: Abd pain, Chest pain, H/A, Eye problems, Severe leg pain
S/E can include irregular bleeding, depression, cyclic weight gain
Contraindicated in smokers, older than 35, HTN, uterine bleeding, DM for 20+ yrs, & those at risk for
DVT or pulm embolus
Oral: contain estrogen as ethinyl estradiol
Prevents release of FSH: follicle is unable to form and prevents ovulation
More effective when used w/ progestins: creates thick cervical mucus, produces hostile sperm
environment, caused endometrial atrophy
Meds the decrease effectiveness: rifampin, isoniazid, barbiturates, griseofulvin,
acetaminophen, and anticoagulants
Low-dose progestin pills: NO ESTROGEN and cant miss a dose
Transdermal patch: applied to large muscle weekly for 3 weeks, then 1 week off
Vaginal ring: Contains estrogen and progestin
Inserted in vagina on 5
th
day of cycle for 3weeks, removed on 4
th
week
Do not remove before, during after sex. Dont douche
Emergency contraception (NOT ABORTION): BC fails or unplanned due to rape
The morning after pill (Preven (4pills) or Plan B(2pills)): has E & P.
IUD: inserted w/in 5 days of unprotected sex for 10 years (EXPENSIVE)
Taken w/in 72 hrs, ineffective is implantation has already occurred
Injectible: Depo-Provera, Depo-SubQ Provera
Lasts for 3 months giving ~150mg progestin injected IM or ~104mg SubQ and site not
massaged
Given w/in 5 days of menstruation, ensuring no pregnancy
Prevents ovulation but can restart after 10 months off of injectibles
Teach about amenorrhea
Subdermal Implant (Implanon): in inner arm for 3 yrs containing progestin
Prevents pregnancy by suppressing ovulation and creating thick cervical mucus hindering
sperm penetration
Intrauterine device: T shaped device inserted through cervix in uterus
Know PAINS: Period late, Abd pain, Infection, Not well, String missing
Sterilization: Bilateral tubal ligation and Vasectomy
Clinical Termination of Pregnancy: deliberate ending of a pregnancy BEFORE viable age of 20-24
weeks (Thanks to ROE vs WADE)
Elective (pt request) or Therapeutic (known fetal disease or d/o)
1
st
tri (up to 12 weeks): vacuum, aspiration
2
nd
tri: cervical dilation, removal of fetus and placenta called dilation and evacuation
laminaria seaweed used to dilates cervix prior to termination
Medical Termination of pregnancy (up to 63 days): resembles miscarriage
Ashermans syndrome: presence of endometrial adhesions or scar tissue
Postabortal syndrome: severe abd cramping & pain from intrauterine blood clots
Role in Infertility Care
Nurse must be responsible for knowing that sperm at ovum meet
Sterility: absolutely prevent reproduction
Infertility: no conception after 12mo. of trying
o Must begin teaching about ovulation timing and best ways to enhance sperm retention
o Meds available to stimulate follicle development; many ova may be released
o Sx: endoscopic biopsy (assess endometrial response to progesterone), laparoscopy (visualization of pelvis),
microsurgical to correct obstructions to get pregnant
o Artifical insemination: placement of partner or donor sperm
o In Vitro: conceived in dish, placed in uterus after
o Other options: Surrogacy, Adoption, or remain childless
o Know ethical considerations w/ donors
Be sensitive to couple who can not conceive while providing them with info during the process
Ch 7: Conceptions and Development of the Embryo and Fetus
Basic concepts
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs from maternal & paternal gamete) (22 autosomal, 1 set of sex)
Fertilization occurs about 2 wks after beginning of last period
Gestation is length of time from conception to birth
Cellular division: Meiosis and Mitosis (2 identical daughter cells)
Some abnormalities: Turners and Klinefelters
Inheritance of disease
Multifactorial: combination of genetic and environment (Cleft lip, neural tube defects)
Unifactorial: traits or d/o caused by a single gene
o Autosomal dominant: i.e. a family w/ generations of a d/o due to gene mutations
Huntingtons: progressive disease of CNS by involuntary writhing, ballistic mvmnt
Achondroplasia: dwarfism
Neurofibromatosis: progressive d/o of nervous system forming tumors on body
o Autosomal Recessive: each parent has (25% chance of passing to offspring)
PKU
Cystic fibrosis
Tay-Sachs
Galactosemia
o X-linked dominant: Fathers 100% chance giving to daughter (XX)
o X-linked recessive: more common than dominant and common in male
Hemophillia A
Duchennes
Implantation
Oocyte/sperm meet in fallopian tube
Zygote propelled by cilia/peristalsis; reaches uterine cavity 3-4 days after fertilization, zygote becomes morula then
blastocyst
~10 days after fertilization, nidation occurs (implantation of fertilized ovum into endometrium)
Blastocyst is buried beneath the endometrial surface
Placenta: develops from trophoblast (essential organ for transfer of nutrients , O2, waste)
o Lacunae developed by trophoblasts invading endometrium space
Fills with fluid and nourishes the embryoblast (the fetus)
o Hormones: hCg maintains corpus luteum until placenta can do that
Human placental lactogen: regulates fetal glucose/promotion of fetal growth through macronutrients
Progesterone: maintains pregnancy, prevents maternal rejection of fetus
Estrogen: for growth; increases during pregnancy
o Placenta is for oxygenation and waste elimination
Progesterone vs Estrogen; Estrogen vs Prolactin; know the differences
Development of Embryo and Fetus
Yolk Sac: Develops 8 to 9 days after conception
o Essential for transfer of nutrients during second and third weeks of gestation
o Hematopoiesis (formation of RBC)
o Atrophies and is incorporated into umbilical cord
Umbilical Cord: located at center of placenta, 55 cm long (21 in); 1 to 2 cm diameter
o Vessels: one vein, two arteries (carries de-oxygenated blood)
o Whartons Jelly: protects umbilical cord from compression (the thicker the healthier)
Fetal Circulation
o Heart begins to beat and circulate blood by end of third week (22 days)
o Umbilical vein: blood from placenta to fetus
o Low Po
2
important to maintain fetal circulation
o Three unique shunts on the umbilical cord
Ductusvenosus: bypasses liver and enters inferior vena cava
Foramen ovale: right & left atria to supply blood to head, upper and lower extremities
Ductusarteriosus: returning blood bypasses lungs
Fetal membranes and amniotic fluid
o Chorion: forms 1
st
; is the outer membrane that forms the fetal portion of the placenta
Encloses amnion, embryo, and yolk sack
Contains villi used in genetic testing
o Amnion: thin, inner membrane that contains amniotic fluid
o Amniotic fluid is VITAL for growth an development
Protects and cushions, temp regulation, symmetrical growth, freedom of movement, fetal lung
development
Fluid present at 3 weeks, fetus swallows 600ml q4hrs
At 24 weeks, 800ml present, composed primarily of urine and lung secretions
Slightly alkaline containing antibacterial
o Amniotic fluid index: test by measuring 4 quadrants
Significance???
At full term, AFI should be 800
Human growth and development
Pre-Embryonic Period: First 2 weeks after conception
o Rapid cellular multiplication and differentiation
o Establishment of embryonic membranes and primary germ layers
Embryonic Period: 3rd week through end of 8th week
o Organogenetic period: formation, differentiation of all organs
o Germ layers (pg 176): ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm
o Fetus is most vulnerable from 2-8 weeks (teach mother care)
Fetal Period: 9th week until birth or termination of pregnancy
o Rapid body growth and differentiation of tissues, organs, and systems
o Weeks 9 to 12: external genitalia present at 12 wks
Body growth increases- weight triples & length doubles
Ossification centers appear
Intestines leave umbilical cord, enter abdomen
Urine production begins
o Weeks 13 to 16
Very rapid growth
Coordinated movements of limbs
Ossification of skeleton
o Weeks 17 to 20: Growth slows down By 20 weeksfetus 300 g and 19 cm (7.3 in)
Vernixcaseosa&Lanugo
o Weeks 21 to 25: Gains weight, Skin pink, Rapid eye movements, Surfactant by 24 wks
o Weeks 26 to 29: If born, fetus may survive
o Weeks 30 to 40: Strong hand grasp reflex&Orientation to light
38 to 40 weeks: 30003800 g and 4550 cm (17.319.2 in)
Threats to Embryonic and Fetal Development
Chromosomes, teratogens, medications and other substances, vitamins, alcohol, tobacco, caffeine, drugs, radiation, and
lead
TORCH infections
o Toxoplasmosis consumption of raw/uncooked meat; cat litter
o Other infections-chicken pox or HIV
o Rubella German measles
o Cytomegalovirus (herpes family): results in spontaneous abortion
o Herpes Simplex Virus: causes spontaneous abortion
Nurses Role in Prenatal Evaluation
o Assessment: cultural, emotional, physical, and physiological factors
o Teaching and education,
o Gathering of health history; genetic disorders andprenatal tests
Maternal Age and Chromosomes: age 35 and above
o Increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome - trisomy 21)
o Deletion- loss of portion of DNA from chromosome or translocation
o Trisomy 18- Edwards syndrome&Trisomy 13- Patau syndrome
These infants usually die within the first 3 months
Multifetal Pregnancy
o Monozygotic (identical) - Develop from one zygote (occurs at end of first week)
o Dizygotic - Develop from two zygotes with separate amnions and chorions
Nurses role in minimizing Threats to Embryo/Fetus
o Assessment: Environmental & lifestyle risks, physical & psychosocial well-being
o Counseling: assess knowledge bc may just be improperly educated and misinformed
Ch. 8: Physiological Preparation for Pregnancy
Physiological Preparation
Pituitary gland: Secretes hormones that influence follicular development, prompt ovulation, and stimulate the uterine
lining preparing for pregnancy
o Progesterone: primarily responsible for maintenance of pregnancy, relaxes smooth muscle, & slows GI to
ensure absorption for fetus
Causes vasodilation to increase blood flow to all body tissues
Ensures adequate nutrition and removal of wastes
o Estrogen: primarily for growth (breasts and uterus) and increases uterine contractility to prep muscles for labor
Causes uterine muscles to contract
o hCg: secreted by trophoblast to prompt corpus luteum to continue progesterone production until placenta can
take over
Ovarian Hormones: maintain endometrium, provide nutrition to zygote, aids in implantation, reduction in chance of
spontaneous abortion
Placenta Hormones: Essential to the survival of pregnancy and fetus
o protects fetus from maternal immune response, creates loosening of pelvis and other joints
Reproductive system
Uterus: from pear-shaped to a soft, enlarged globular structure
o E&P cause myometrial cells and muscle fibers to undergo hyperplasia and hypertrophy, allowing the uterus to
stretch and grow as the fetus does
o Braxton-Hicks: irregular/painless contractions that may occur around 16 wks which prepare the muscles for
activity of labor (no dilation of cervix)
o After implantation, the endometrium lining is termed the decidua containing 3 layers
Decidua vera: external layer and has no contact with fetus
Decidua basalis: beneath the site of implantation
Decidua capsularis: covers the embryo
o By term, uterine wall thins 0-6 inches
Cervix:
o Chadwicks sign: earliest sign of pregnancy; present with discolored bluish purple hue (due to increased blood
flow and engorgement) on cervix, vagina and vulva
o Goodells sign: cervical softening related to decrease in collagen fibers of connective tissue, increase in
vascularity, and tissue hyperplasia and hypertrophy
o Operculum: mucus plug
o Leukorrhea: white vaginal d/c resulting from hyperplasia of the vaginal mucosa and increased mucus
production from endocervical glands
Teach pt to call HCP if d/c smells, becomes bloody, thicker, yellow, green, etc
Vulva/Vagina: gets thicker, developing rugae which allow for stretching during delivery
o Teach pt not to douche bc area has become more acidic (pH3.5) to inhibit growth of bacteria into canal.
o Increased risk of yeast infx due to increased in glycogen
Ovaries: Ovulation ceases during pregnancy due to increased E & P, inhibiting FSH & LH
o Only responsibility is progesterone production corpus luteum until placenta takes over
Breasts: hormone Melanotropin causes tenderness and darkening of areolla
o Montgomery tubules: enlargement for production of nipple tissue lubrication
o Striaegravidarum: stretch marks develop as breast stretch
o Colustrum may leak around 2
nd
trimester
o TEACH: bra sizes, breast feeding, cotton bra liners for secretions
Integumentary: assess womens self-concept and body image caused by changes from E & P
o Linea negra, increase in sweat activity and oiliness of skin acne
o Cholasma (melisma gravidrum): presents as raccoon eyes
o Stretch marks, moles, freckles are a problem
o Photosensitivity/sunburn, angiomas, palmar erythema caused by estrogen
o Alterations in hair and nail growth: reassure mother this is all normal
Neurological: c/o decreased attention span, poor concentration and memory lapses
o Sleep disturbances: use daytime naps to help
o Carpal tunnel: develops in 3
rd
tri due to edema in wrist and pressure on median nerve
Elevate hand at night to help decrease edema
o Episodes of syncope: due to orthostatic hypotension or IVC compression by uterus
Vena Cava Syndrome
can occur from coughing, constipation
Teach to get up slowly and lie on left side to decrease pressure on IVC
Cardiac: Maternal heart is pushed upward and laterally left
o Hypertrophy results from increased blood volume and cardiac output
o 1
st
and 3
rd
heart sounds and systolic murmurs are exaggerated upon ausculatation
call MD if symptomatic of cardiac issues
o Blood Volume: increases during 1
st
tri & peaks at term, decreases by 2 wks post partum
Plasma and erythrocyts volume increase due to increased need of O2 for placenta
80% of extra blood goes to placenta
Renal blood flow increases 30-50%
o Iron: fetal need is greatest last 4 weeks of pregnancy
o Pseudoanemia: CBC, H&H may appear low due to increased volume
Teach to drink plenty of fluids and diet high in protein and iron
o Leukocytes, Proteins, Platelets and Immunoglobulins
WBC increase to 5000-15000mm3 & can increase to 25000 during labor/post partum
increased risk for infx during pregnancy due to decrease leukocyte funtion
Sedimentation rate increases (pT, PTT, INR) due to increase fibrinogen, which causes
hypercoagulability
Is pt at risk for DVT or embolism?
Only maternal IgG can be transported across placenta, not IgM
IgA is found in breast milk: for respiratory, GI & GU protection from infx
o Cardiac Output: increases and peaks at 20-24 wks
Respiratory: Tx mother to relax and take deep, slow breaths with head elevates
o Tidal volume increase 30-40% due to E & P; may experience dyspnea due to rise of diaphragm
Estrogen prompts hypertrophy and hyperplasia of lung tissue
Progesterone decreases airway resistance by causing relaxation of the smooth muscles of the bronchi,
bronchioles and alveoli
These changes increase O2 consumption
GI: N/V in 1
st
tri r/t to increase in hCg and altered carb metabolism
o Alteration in taste and smell, nonspecific gingivitis, epulisgravidarum
o Pyrosis: heart burn caused by progesterone, which relaxes esophagus, causing reflux
o Pytalism: increased saliva production
o Gall bladder issues: cholecystitis, cholestasia caused by progesterone, which relaxes gall
If mother has high cholesterol, gallstones may form
Avoid food high in fat
GU: during 1
st
tri, bladder in pelvic organ compressed by the uterus
o Progesterone induces relaxation of the urethra and spinchter causing urinary urgency, frequency and nocturia
o In 2
nd
tri, pressure is relieved but returns in 3
rd
tri as a result of fetal descent
o GFR increases up to 50% = increased reabsorption and high levels of glucose
Eyes, ears, nose, throat
o Blurred vision caused by corneal thickening associated with fluid retention and IOP
o Ears normally dont change
o Progesterone causes increase in mucus production stuffy nose and congestion
o Epistaxis common, rhinitis common
o Throat: dysphagia caused by increased relaxation of smooth muscle in esophagus
Endocrine:
o Thyroid: Increase in size (bc of E&P) & activity during pregnancy (T3 & T4 increase)
BMR increases
Heat tolerance and elevation of HR and CO develop
o Parathyroid: estrogen causes increases in size
Regulation of Ca+ and Phosphate metabolism and increase in 2
nd
/3
rd
tri for fetus
o Ca+ important and should be taking 1200-1500mg/day
Pituitary and placenta: anterior pituitary stimulated by hypothalamus
o Prolactin: needed for initial lactation, inhibited by the increase of E & P until post partum
o Oxytocin: from posterior lobe causes uterine contractions and stimulates milk ejection
o Vasopressin: Vasoconstrictor from posterior lobe causing fluid retention leading to increase of maternal BP and
exerts
o Human placental lactogen acts as GH to fetus
By increasing # of fatty acids to maternal metabolic needs and decreasing maternal glucose utilization,
the result is an increased glucose availability for the fetus
o Anterior secretes thryoptropin (increases BMR), adrenotropin (increases fluid retention)
Adrenals: Cortisol allows the body to respond to stressors
o Levels increase due to increased renal secretion
o May take up to 6 weeks post partum for cortisol level to normalize
o Aids in regulation of protein and carb metabolism
o Aldosterone increased in 2
nd
tri (increases Na+ reabsorption leading to increased BV)
Pancreas: secretes insulin due to increase of carb metabolism
o Beta cells increase during pregnancy
o Prostaglandins: lipid substance found in the female reproductive tract & uterine decidua
Decreased levels contribute to HTN and preeclampsia
At term, increased release from the cervix may contribute to onset of labor
Musculoskeletal:
o Abd wall weakens and rectus abdominus muscles separate (diastasis recti)
Caution for abd hernia
o Lumbar lordosis develops: anterior convex of spine to compensate for center of gravity
o Relaxin: produced by placenta which causes laxity of ligaments
o Pubis symphisis separates at week 28-30 producing a waddle gait
Stretching and hypertrophy of round ligaments surrounding uterus cause sharp groin pain
Must support lumbar and encourage good posture
Pain may be present; apply heat to reduce pain
o Teach to increase calcium in diet, fortified OJ and dark green leafy veggies
Due to increased calcitonin which decreased bone resportion
o Calf cramps may also be present due to Calcium and phosphate imbalance
Physiological Changes of pregnancy by trimester
1
st
: pain/tingling in breasts, N/V, fatigue, mood swings
o REPORT: vaginal bleeding, ABD cramping/pain
2
nd
: Abd enlargement, skin pigmentation, striaegravidarum, vascular spiders, constipation, heartburn, leg cramps,
leucorrhea, groin pain
o REPORT: vaginal bleeding, fever, increased pulse, decreased/absent fetal movement, unrelenting N/V, swelling
of face or fingers, headaches or visual disturbances
3
rd
: dyspnea, lower extremity cramps, constipation, indigestion, heartburn, reflux, pedal edema, fatigue, vaginal d/c,
urinary frequency, Braxton-Hicks contractions
o REPORT: visual disturbances, headache, hand and facial edema, fever, vaginal bleeding, ABD pain, uterine
contraction, premature rupture of the membrane
Psychosocial Adaptations during pregnancy
Developmental and Family Changes
o Duvalls stages of family development
Home must be reorganized to accommodate the infant
Duties and responsibilities must be realigned
Money management needs to be altered
Couples sexual relationship must adapt
Emotional changes
Expand their knowledge
Maternal Tasks and Role Transition: RUBIN to develop self concept of mother
Acceptance of the Pregnancy: known as binding in
Acceptance of the Child: Critical for successful adjustment to pregnancy, must develop unconditional acceptance
Reordering Relationships: must reorder relationships to allow for the child to fit into existing family structure
o If she is having her first child she may grieve the loss of her carefree life
o Work through doubts of her ability to be a good mother
Seeking Safe Passage Through Pregnancy, Labor and Birth: nesting
o Increased worry during and after 7
th
month
o Childbirth preparation classes can help with fear and anxiety
Developmental Tasks and the Pregnant Adolescent
o Tasks are associated with growth and maturity
o May not be able to accept the reality of the unborn child
o Paternal Adaptation to Pregnancy
o Men may view pregnancy as positive proof of their masculinity and play a dominant, supporting role
o When they find no value, the fail to develop any sense of responsibility
Observer: Father is passive and detached
Expressive:Father attempts to experience the pregnancy as much as possible
Instrumental:Father is the caretaker
Couvade is the observance of certain rituals and taboos; pregnancy related sx like weight gain and N/V
Adaptation of Siblings and Grandparents
o Children may express excitement/anger, regression of behavior, want to nurse or drink from a bottle
o Engage child with the developing fetus
o Grandparents are often very excited
o May express concern for the mothers health and fetal health
Cultural Influences
o Nurse needs to explore cultures and document specific beliefs and needs
o Native Americans and Latinos view pregnancy as normal and not an illness
o African nations impose rigid taboos concerning what they eat, drink, wear and do
o Middle Eastern cultures view pregnancy as womans work
o Asian cultures need a harmonious balance (yin and yang)
Anticipatory Guidance: for nurses to help guide mother through troubles of pregnancy
Ch 9: The Prenatal Assessment
Concerns over self-preservation
As the nurse: listen, educate, respect mother and choices
Goals include:
o Recognize deviations from the norm
o Provide individualized, evidence based care
o Provide culturally appropriate prenatal education
o To empower women to become actively involved in their pregnancy by being informed recipients and informed
decision makers
Prenatal care starts in 1
st
tri, then every 4 weeks until 28-32 weeks gestation
o Will change to q2wks, then q1wk after 36 weeks
CARE: remain non-judgmental, verbalize pt wishes, use understandable words
o Communicate: exchange info spoken or written
o Advocate: defend and support
o Respect: to feel/show admiration, pay attention
o Enable: provide resources/authority/opportunity to do something
Diminishing Stress
o Incorporate continuity of care (ie same nursing staff, HCP)
o Eustress (normal/healthy level) & Eustress (exceeding level w/ inability to deal)
First prenatal visit
BUILD RAPPORT to gain new mothers confidence, use of therapeutic communication
Should take place as early in the pregnancy as possible
Collect: pregnancy hx, med hx, exercise and nutrition patterns, financial income, psychosocial hx, and lifestyle choices
Genetic Tests??
Provide a user-friendly service that is efficient, caring and patient centered
DEEPER CARE
o Diet: whole grains, green/yellow/orange veggies, dry means, low fat, high Calcium, low mercury content,
o Exercise: aerobic
o Education: child classes, anticipatory guidance
o Play: recharge & reconnect
o Expectations: abnormal vs normal expectation
o Relaxation: promotes immunity and energy, decrease in BP and stress (YOGA)
o Communication:
o Attitude: keep positive for overall well-being
o Respect: honest, trust, compromise, negotiation
o Emergencies: know dangers (vaginal bleeding, decrease in fetal movement, fever over 100.5)
10% of fetal malformations r/t to exposure to hazards
o smoking, alcohol, drugs, malnutrition, viruses, pollution
Complementary/Altenative therapies
o Red raspberry tea is good, blue cohosh is bad
Hx of intimate partner violence
Domestic: most common (1 out of 6)
Femicide: refers to death of a woman resulting from acts of violence against her
o Does pt feel safe going home?
RADAR:
o Routinely screen every pt
o Ask directly, kindly, non-judgmental
o Document your findings
o Assess safety
o Review options referrals
Woman may turn to drugs to deal emotionally with abuse (methamphetamines, cocaine, MJ)
Psychological Assessment
Loss of a previous pregnancy may affect a womans ability to bond with her present pregnancy
May be reluctant to invest in a pregnancy that she fears may not come to fruition
The Obstetric History: Current & Previous Pregnancies
GP (gravida parity)
Preterm labor is before the 37
th
week (20-40% chance of pre-mie)
Assess hx of preeclampsia old/new partner?(increases likelihood of it re-occurrence)
o Classic symptoms: increased BP and proteinuria
Gestational DM: carb intolerance during pregnancy
Tx about SIDS: breastfeed, avoid smoking and position baby on the back to sleep
Current Pregnancy: Unexpected does not mean unwanted
Know the 1
st
day of last menstrual cycle know EDB
Testing: hCg in blood as early as 1 day after implantation, 26 days in urine
Chemical pregnancy = home test confirms pregnancy but is followed by menses
PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS of pregnancy:
o Amenorrhea, Morning sickness (N/V), Urinary frequency, Breast tenderness, Perception of fetal movement,
striaegravidarum, Fatigue
PROBABLE SIGNS
o Piskacek sign- uterine asymmetry with soft prominence on the implantation side
o Hegars sign- softening of the lower uterine segment
o Goodells sign- softening of the tip of the cervix
o Chadwicks sign- violet-bluish color of the vaginal mucosa and cervix
o Braxton-Hicks sign- intermittent irregular uterine contractions w/o dilation
o Ballottement- passive movement of the unengaged fetus
POSITIVE INDICATIONS:
o Fetal heartbeat
o Visualization of the fetus
o Fetal movements palpated by the examiner
Estimated Date of Birth (EDB)
Based on date of last normal menstrual period assuming that the woman has a 28-day cycle
NAEGELES RULE: add 7 days, then subtract 3 months from date of the patients LMP
Pill failure results from forgotten pills, poor absorption that may result from various causes such as vomiting, diarrhea, or
antibiotic use
Pregnancy Classification System
Gravid: state of being pregnant
Gravida: a pregnant woman
Gravidity: number of times a woman has been pregnant regardless of outcome
Nulligravida: never experiencing a pregnancy
Primigravida: woman pregnant for the first time
Secundigravida: woman pregnant for the second time
Multigravida: pregnant 3 or more times
Parity: number of pregnancies lasting longer than 24 weeks regardless of outcome
GTPAL classification system
G- Gravida
T- number of Term pregnancies
P- number of Preterm deliveries
Abortions both spontaneous and induced
L- number of Living children
Medical History
Lack of a family physician r/t: financial difficulties, lack of medical insurance, or cultural/value differences
o Refer patient to WIC
Dental Health: Promote to reduce the incidence of periodontal disease (gingivitis)
o Pregnancy hormones increase plaque and development of periodontal disease
o Oral bacteria can enter blood stream into placental membranes (trigger preterm labor)
Eye Health: Important for women with HTN, Graves , DM, and for women who wear contacts
Immunizations
o Rubella is contracted during first 12 weeks of pregnancy, fetus has 90% chance of being adversely affected
Typical symptoms: intrauterine growth restriction, cardiac defects, sensorineural defects, cataracts and
microcephaly
o Hepatitis B
focuses on effects on pregnancy, long-term maternal risks(chronic liver disease)
Household members and intimate partners should undergo screening
Seroconversion: process whereby an individual develops antibodies in response to an infection and subsequently tests positive when
screened, due to the presence of the antibodies
Environmental Hazards
Air pollution (most common): linked with preterm
Tobacco: premature rupture of the membranes, preterm labor, placential abruption, placenta previa, upper respiratory
infections, childhood asthma, and wheezing
Gynecological History
Diethylstilbestrol (DES): nonsteroidal, synthetic estrogen &several times more potent than natural estrogens
Hazardous!!!!!
o Used as a preventative treatment to reduce spontaneous abortion or preterm delivery
o Linked with infertility, ectopic pregnancies, preterm labor
Screening tests: IDs at risk pts&Diagnostic tests: confirms presence of a d/o or disease
o Blood type, Rh factor, Antibody (kell, duffy, rubella, varicella, toxoplasmosis, anti-rh), rapid plasma reagent,
venereal disease screen for syphllis, HepB
o CBC with differential H&H
o Testing for antibody to HIV
o STDs: presence can cause ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion, preterm labor
HIV: transmission occurs transplacentally
Mother taking AZT, retrovir& C-section reduces risk of transmission
Syphillis: can cause deafness, impaired cognitions, osteochondritis, fetal death
Treat with penicillin or erythromycin before 18 week
Chlamydia/Gonorrhea
Herpes simplex
Preparing Patient for Exam
Encourage patient to void (take urine sample tests for ASB)
Keep room warm, leave a cover for the patient, ensure privacy
Explain what the exam will involve, obtain consent
Actively engage the patient during the exam to calm her nerves, explain the process
BASE VITALS: know how the woman is progressing with each visit
Obtaining Information and Promoting Good Nutrition
Increase caloric needs by 300 per day
Folic acid increased by 400mcg/day before conception and continued at least through the first 3 months of pregnancy
(reduces neural tube defects)
Extreme weight loss could indicate hyperemesis
Low levels of Vit C predispose women to premature rupture of membrane
Assessment
Head/Neck/Lungs: hair loss is common indicative of vit/min deficiency
o Enlarged thyroid is common
Skin: cholasma, hyperpigmentation, lesions
Breasts: changes in nodularity, striae, enlargement and hyperpigmentation of nipples
o Colostrum and palpable lymph nodes
Abdomen: lineanigra, striaegravidum, bruising
Measure fundal height by using a tape measure (around umbilicus @ 20 weeks)
Initiate Leopolds maneuvers (determine position of the fetus)
o First maneuver determine fetal body part that occupies uterine fundus. Determine the head or the butt
occupies the uterine fundus- But feels soft & head feels firm- use the palmar surface of hands to palpate
o Second maneuver locate the spine
o Third maneuver (Pawlik) - compare fundus w/ lower uterine segment confirm fetus is cephalic
o Fourth maneuver- use finger tips of both hands to determine ballottement; engagement
Fetal heart auscultation: use least intrusive method - Pinard orfetoscope (120 to 160 bpm)
o Most clearly hear directly over fetal upper back (Maternal R or L lower quadrants)
Teen Pregnancy-Nurses role
Be an advocate for responsible sexual behavior (be sensitive)
Counsel the patient and educate for future responsible sexual decision making
Teens more likely to experiment at very early age and get involved in high-risk behaviors like substance abuse, gang
involvement, and violence
By law, a pregnant minor is an emancipated minor
Promote optimal nourishment: increase calcium, magnesium and phosphorous
Meeting Developmental Tasks of Adolescence
for teen mother to adapt & fulfill role of being a mother, must achieve 4 developmental tasks:
o Gain acceptance of pregnancy, Set goals, View self as mother, Grow up
Pregnant older than 35
Make sure: healthy, continue care, remain active, have the ability to make appointments
Down syndrome triple test: alpha fetoprotein, hCg, estriol
7/2/2013 3:40:00 PM
7/2/2013 3:40:00 PM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeDa EverandThe Illustrated Book of Medicine: The Making of MeNessuna valutazione finora
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocumento105 pagineMale and Female Reproductive Systemjanmic100% (3)
- Structure and Function of the Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocumento83 pagineStructure and Function of the Male and Female Reproductive SystemsMagy Tabisaura GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Menstrual Cycle:: MenarcheDocumento21 pagineMenstrual Cycle:: MenarcheAlpesh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingDocumento3 pagineI. Anatomy & Physiology: Readiness For Child BearingRalph Tama Mangacop BenitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Competency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemDocumento4 pagineCompetency 1-The Family Before Birth: 1. Explain The Structure and Function of The Female Reproductive SystemEnorl FerdinandNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN Nursing 1Documento107 pagineMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child (Family Concepts)Documento22 pagineMaternal and Child (Family Concepts)Lenny SucalditoNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive System - Jan. 22, 24, 2013 - Dr. C. AyochokDocumento10 pagineFemale Reproductive System - Jan. 22, 24, 2013 - Dr. C. AyochokmbdelenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Women's Health: An Overview of the Female Reproductive System and Menstrual CycleDocumento47 pagineIntroduction to Women's Health: An Overview of the Female Reproductive System and Menstrual CycleDarren LimNessuna valutazione finora
- 10FRSDocumento27 pagine10FRSWakanda ForeverNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob Review To The MaxDocumento40 pagineOb Review To The MaxMox SwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal Lectures EditedDocumento77 pagineMaternal Lectures EditedSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNessuna valutazione finora
- GE9 Module Lesson 3Documento6 pagineGE9 Module Lesson 3agnesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 4-Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocumento38 pagineLesson 4-Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDiana Hernandez100% (1)
- Review of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocumento104 pagineReview of The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemAj MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inbound 4525214668487640543Documento12 pagineInbound 4525214668487640543Neña Bautista PagalNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive System2Documento41 pagineFemale Reproductive System2joel1414Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal NursingDocumento37 pagineMaternal NursingCai Velasco DecenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Female Repro Mens. Cycle 1Documento60 pagine5 - Female Repro Mens. Cycle 1swbhxzm5qqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento7 pagineChapter 3Abhishek Yadav RNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetrical NursingDocumento36 pagineObstetrical NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (7)
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocumento13 pagine8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction-1Documento21 pagineHuman Reproduction-1Coni Espinoza YupanquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0020Documento52 pagineWa0020michaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mother and Child HealthDocumento33 pagineMother and Child HealthJennifer Solano CruelNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ReproductionDocumento6 pagineHuman Reproductionlakshshah5116Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOgyDocumento17 pagineANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOgyadriancalprNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento5 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologytwicetrashNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans PDF NotesDocumento61 pagineSexual Reproduction in Humans PDF NotesANWESHA BALNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of the Cervix and its PhysiologyDocumento8 pagineAnatomy of the Cervix and its PhysiologyNicaMariannePañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocumento22 pagineMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNessuna valutazione finora
- External StructuresDocumento7 pagineExternal StructuressittizhainabNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child Health IDocumento772 pagineMaternal and Child Health Ikarendelarosa06100% (6)
- Female ReproductiveDocumento55 pagineFemale ReproductiveDenise RegalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocumento39 pagineGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Gender and Society CompileDocumento32 pagineGender and Society Compileクイーンクイーン ロペスNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocumento10 pagineChapter Ii: Biochemical Perspective in Gender and Sexuality Lesson 1: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDevin Jake Maylas FeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemDocumento7 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemSherry Ann FayeNessuna valutazione finora
- GENSOC M2 Lesson 4Documento7 pagineGENSOC M2 Lesson 4cassy margaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocumento34 pagineWeek 3 Reproductive and Sexual Healthraise concern100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocumento33 pagineReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 3rd QuarterDocumento22 pagineScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EDocumento51 pagineFemale Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EGwyneth100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento38 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemnasyitahnorzlanNessuna valutazione finora
- 009 - Reproductive HistologyDocumento10 pagine009 - Reproductive HistologycharlieholdenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsDocumento40 pagineFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorDocumento25 pagineThe Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorShanon LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurDocumento15 pagineTerminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurInactiveAccountNessuna valutazione finora
- The Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideDocumento10 pagineThe Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideBurni GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 38 Human ReproductionDocumento38 pagineCh. 38 Human ReproductionERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1physiology of PregnancyDocumento58 pagineLecture 1physiology of PregnancyОлександра ЗагородняNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit XDocumento18 pagineUnit XPreeti ChouhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction: Important NotesDocumento6 pagineHuman Reproduction: Important NotesHema KamatNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesDocumento6 pagineBiology (Human Reproductive Anatomy) Lecture Notes or Book NotesCharline Lucille BanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiolog MyomaDocumento3 pagineAnatomy and Physiolog MyomaJisel-Apple BulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento42 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal DevelopmentDocumento60 pagineFetal DevelopmentElaine Malzan De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution From Novice To Beginning Professional NurseDocumento12 pagineEvolution From Novice To Beginning Professional NurseAlvin ManiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinatown Pluralism PaperDocumento8 pagineChinatown Pluralism PaperAlvin ManiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurse Brain Sheet New Shift ReportDocumento1 paginaNurse Brain Sheet New Shift ReportJenny Anne100% (1)
- HCA434 Current Event PaperDocumento5 pagineHCA434 Current Event PaperAlvin ManiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bad PaperDocumento1 paginaBad PaperAlvin ManiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bad PaperDocumento1 paginaBad PaperAlvin ManiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of PregnancyDocumento33 pagineComplications of PregnancyMilagros Maglasang100% (1)
- 61 Irregular Verbs Pink and PurpleDocumento18 pagine61 Irregular Verbs Pink and PurpleRebeca HR SKNessuna valutazione finora
- Science10 Q4 L1Documento17 pagineScience10 Q4 L1Sabine AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Shukra DhatuDocumento29 pagineShukra Dhatushilpa yermeNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Science 10-1-2 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocumento9 pagineIntegrated Science 10-1-2 Sexual Reproduction in Plantsfalesa matthewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Elvira Cuesta Gee7-Activity-1.2-1.5Documento5 pagineElvira Cuesta Gee7-Activity-1.2-1.5Elvira CuestaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Endocrine Control of The Pituitary-Ovarian Axis: Androgenic Influence and Chaotic DynamicsDocumento22 pagineModeling Endocrine Control of The Pituitary-Ovarian Axis: Androgenic Influence and Chaotic DynamicsKerin ArdyNessuna valutazione finora
- J5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis StudentDocumento3 pagineJ5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis Studentkristhel ann caringal reyes0% (1)
- DLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1Documento11 pagineDLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1Emmanuel Ramirez0% (1)
- LSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsDocumento64 pagineLSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsAbraham KangNessuna valutazione finora
- Algae 2022 37 5 11Documento17 pagineAlgae 2022 37 5 11Kathya Gómez AmigoNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1Documento9 pagineDLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W1MarichanLooc100% (4)
- Endometriosis: Aetiology, Pathogenesis and TreatmentDocumento16 pagineEndometriosis: Aetiology, Pathogenesis and Treatmentyuyu tuptupNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento3 pagineMitosis and Meiosisfghvfhf50% (2)
- Al-Khair Higher Secondary School.: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineAl-Khair Higher Secondary School.: ObjectiveTariq MuneerNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Stallion Management PowerpointDocumento25 pagineLesson 1 Stallion Management PowerpointelblazerNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocumento2 pagineRevision Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 10 - Reaching The Age of AdolescenceArpit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ContraceptionDocumento35 pagineContraceptionRhomizal MazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 26Documento23 pagineChapter 26Konishko DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Map Male Reproductive SystemDocumento1 paginaMind Map Male Reproductive SystemFuzna DahliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rekapitulasi ERT PONEKDocumento48 pagineRekapitulasi ERT PONEKKaleb Rudy HartawanNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN LectureDocumento8 pagineMCN LectureEmily BernatNessuna valutazione finora
- BioethicsDocumento7 pagineBioethicsClarissa Anne TabaosaresNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 m16 QP 42 PDFDocumento28 pagine9700 m16 QP 42 PDFAtef Ibrahim KhalifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsDocumento12 pagineUnderstanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsAnonymous klhru5ENessuna valutazione finora
- Ohana Circle (F4) / Fresh N Dash (F5) Sultanah Bahiyah National Secondary School Form 4Documento7 pagineOhana Circle (F4) / Fresh N Dash (F5) Sultanah Bahiyah National Secondary School Form 4Hafizuddin KamarudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Vog QDocumento62 pagineVog QDeep PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento12 pagineChapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice Questionsquiet19Nessuna valutazione finora
- PterisDocumento4 paginePterisSreeja RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Sea Urchin EmbryologyDocumento6 pagineSea Urchin EmbryologyAmy HollingsworthNessuna valutazione finora