Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Argentina Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Venezuela
Caricato da
iulias040 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
22 visualizzazioni6 pagineThis document provides information on leadership styles and cultural dimensions in various countries and regions according to Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory. It discusses leadership styles and cultural characteristics in South Africa, Anglo countries, Eastern Europe, Latin America, Confucian Asia, Nordic Europe, South Asia, Germanic Europe, the Middle East, the United States, Russia, China, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
Descrizione originale:
Hofsteder theory for different countries
Titolo originale
Hofsteder
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document provides information on leadership styles and cultural dimensions in various countries and regions according to Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory. It discusses leadership styles and cultural characteristics in South Africa, Anglo countries, Eastern Europe, Latin America, Confucian Asia, Nordic Europe, South Asia, Germanic Europe, the Middle East, the United States, Russia, China, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
22 visualizzazioni6 pagineArgentina Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Venezuela
Caricato da
iulias04This document provides information on leadership styles and cultural dimensions in various countries and regions according to Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory. It discusses leadership styles and cultural characteristics in South Africa, Anglo countries, Eastern Europe, Latin America, Confucian Asia, Nordic Europe, South Asia, Germanic Europe, the Middle East, the United States, Russia, China, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 6
South Africa
Arrange a meeting before discussing business over the phone.
Appointments should be made as far in advance as possible.
When introduced, maintain eye contact, shake hands, and provide business cards to everyone.
Women are highly respected.
Make business plans clear.
Patience between proposition and answer
Keep presentation short and concise
Anglo
The British value laughter above all else. The typical broad, self-depreciating British commercial amuses
by mocking both the advertiser and consumer.
Participative leadership
Charismatic Leadership
Eastern Europe
Autonomous Leadership
Protective Leadership
Latin America - Argentina Brazil Chile Colombia Ecuador Venezuela
Charismatic Leadership
Team-oriented leadership
Self-protective leadership
Confucian Asia
Self-protective leadership
Team-oriented leadership
Nordic Europe
Charismatic Leadership
Participative Leadership
South Asia
Self-protective leadership
Germanic Europe
Autonomous Leadership
Middle East - Egypt India Saudi Arabia Turkey United Arab Emirates
Self-protective leadership
UNITED STATES
Individualism ranks highest and is a significant factor in the life of U.S. Americans. The low
ranking of Long-term Orientation reflects a freedom in the culture from long-term traditional
commitments, which allows greater flexibility and the freedom to react quickly to new opportunities.
The high Individualism (IDV) ranking for the United States indicates a society with a more
individualistic attitude and relatively loose bonds with others. The populace is more self-reliant and
looks out for themselves and their close family members.
This indicates the country experiences a higher degree of gender differentiation of roles. The
male dominates a significant portion of the society and power structure. This situation generates a
female population that becomes more assertive and competitive, with women shifting toward the male
role model and away from their female role.
Has greater equality between societal levels, including government, organizations, and even
within families. This orientation reinforces a cooperative interaction across power levels and creates a
more stable cultural environment.
A low ranking in the Uncertainty Avoidance Dimension is indicative of a society that has fewer
rules and does not attempt to control all outcomes and results. It also has a greater level of tolerance for
a variety of ideas, thoughts, and beliefs.
RUSSIA
Russia is a nation where power is very distant in society. This is underlined by the fact that the
largest country in the world is extremely centralized: 2/3 of all foreign investments go into Moscow
where also 80% of all financial potential is concentrated. The huge discrepancy between the less and the
more powerful people leads to a great importance of status symbols.
Family, friends and not seldom the neighborhood are extremely important to get along with
everyday lifes challenges. Relationships are crucial in obtaining information, getting introduced or
successful negotiations. They need to be personal, authentic and trustful before one can focus on tasks
and build on a careful to the recipient, rather implicit communication style.
At second glance one can see, that Russians at workplace as well as when meeting a stranger
rather understate their personal achievements, contributions or capacities. They talk modestly about
themselves and scientists, researchers or doctors are most often expected to live on a very modest
standard of living. Dominant behaviour might be accepted when it comes from the boss, but is not
appreciated among peers.
Russians feel very much threatened by ambiguous situations, as well as they have established
one of the most complex bureaucracies in the world. Presentations are either not prepared, e.g. when
negotiations are being started and the focus is on the relationship building, or extremely detailed and
well prepared. Also detailed planning and briefing is very common. Russians prefer to have context and
background information. As long as Russians interact with people considered to be strangers they
appear very formal and distant. At the same time formality is used as a sign of respect.
Russia is definitely a country with a pragmatic mindset. In societies with a pragmatic orientation,
people believe that truth depends very much on situation, context and time. They show an ability to
adapt traditions easily to changed conditions, a strong propensity to save and invest. thriftiness and
perseverance in achieving results.
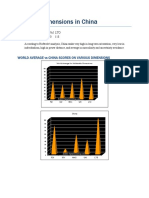
CHINA
Long-term Orientation (LTO) the highest-ranking factor (118), which is true for all Asian cultures.
This Dimension indicates a society's time perspective and an attitude of persevering; that is, overcoming
obstacles with time, if not with will and strength.
The low Individualism ranking is manifest in a close and committed member 'group', be that a
family, extended family, or extended relationships. Loyalty in a collectivist culture is paramount. The
society fosters strong relationships where everyone takes responsibility for fellow members of their
group.
Of note is China's significantly higher Power Distance ranking of 80 compared to the other Far
East Asian countries' average of 60, and the world average of 55. This is indicative of a high level of
inequality of power and wealth within the society. This condition is not necessarily forced upon the
population, but rather accepted by the society as their cultural heritage.
JAPAN
The Geert Hofstede analysis for Japan is dramatically different from other Asian Countries such
as Hong Kong, Korea or China. In Japan Masculinity is the highest characteristic. The lowest ranking
factor is Individualism, which coincides with their high ranking in Uncertainty Avoidance. Japan is a more
collectivist culture that avoids risks and shows little value for personal freedom.
In a business situation, business cannot begin until the meishi (business card exchange) exchange
process is complete.
If you are greeted with a bow, return with a bow as low as the one you received. How low you
bow determines the status of the relationship between you and the other individual. When you bow
keep your eyes low and your palms flat next to your thighs. The business card should be given after the
bow. This is very important to remember.
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
The Geert Hofstede analysis for the United Arab Emirates is almost identical to other Arab
countries their Muslim faith plays a large role in the peoples lives. Large power distance and uncertainty
avoidance are the predominant characteristics for this region. This indicates that it is expected and
accepted that leaders separate themselves from the group and issue complete and specific directives.
The Geert Hofstede analysis for the Arab World, that includes the countries of Egypt, Iraq,
Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates, demonstrates the Muslim faith
plays a significant role in the peoples lives.
They are also highly rule-oriented with laws, rules, regulations, and controls in order to reduce the
amount of uncertainty, while inequalities of power and wealth have been allowed to grow within the
society.
Large Power Distance (PDI) (80) and Uncertainty Avoidance (UAI)
When these two Dimensions are combined, it creates a situation where leaders have virtually ultimate
power and authority, and the rules, laws and regulations developed by those in power reinforce their
own leadership and control.
The high Power Distance (PDI) ranking is indicative of a high level of inequality of power and
wealth within the society.
The high Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) ranking of 68, indicates the societys low level of
tolerance for uncertainty. In an effort to minimize or reduce this level of uncertainty, strict rules, laws,
policies, and regulations are adopted and implemented. The ultimate goal of these populations is to
control everything in order to eliminate or avoid the unexpected.
Women in the Arab World are limited in their rights, it may be due more to Muslim religion rather than
a cultural paradigm.
Loyalty in a collectivist culture is paramount, and over-rides most other societal rules.
The predominant religion for these countries is Islam, the practice of the Muslim faith.
GERMANY
The Geert Hofstede analysis for Germany shows their emphasis on individualism, masculinity,
and uncertainty avoidance. Power distance and long-term orientation are both ranked considerably
lower than the others. This illustrates Germanys belief in equality and opportunity for each citizen, as
well as its ability to change and adapt rapidly.
Business dress in Germany is very conservative.
Germans are strongly individualistic.
The German thought process is extremely thorough, with each aspect of a project being
examined in great detail. This process is often times very time-intensive. However, once the planning is
over, a project will move very quickly and deadlines are expected to be honored.
Germans do not like surprises. Sudden changes in business transactions, even if they may
improve the outcome, are unwelcome.
Punctuality is necessity in Germany. Arrive on time for every appointment, whether for business
or social. Being late, even if it is only by a few minutes, is very insulting to a German executive.
UNITED KINGDOM
The Geert Hofstede analysis for England illustrates their strong feelings towards individualism
and masculinity. The power distance and uncertainty avoidance are ranked considerably lower than the
first two. Long-term orientation ranks the lowest, indicating that change in England can be achieved
more rapidly than in many other countries .
In analyzing Predominantly Christian countries, the primary correlation between religion and the
Geert Hofstede Dimensions is a high Individualism (IDV) ranking. This indicates that predominantly
Christian countries have a strong belief in individuality, with individual rights being paramount within
the society. Individuals in these countries may tend to form a larger number of looser relationships.
Always be punctual in England. Arriving a few minutes early for safety is acceptable.
Decision-making is slower in England than in the United States; therefore it is unwise to rush the English
into making a decision.
SAUDI ARABIA
The Geert Hofstede analysis for Saudi Arabia is almost identical to other Arab countries their
Muslim faith plays a large role in the peoples lives. Large power distance and uncertainty avoidance are
the predominant characteristics for this region. This indicates that it is expected and accepted that
leaders separate themselves from the group and issue complete and specific directives.
These populations have an expectation and acceptance that leaders will separate themselves
from the group and this condition is not necessarily subverted upon the population, but rather accepted
by the society as their cultural heritage.
The society has low level of tolerance for uncertainty. In an effort to minimize or reduce this
level of uncertainty, strict rules, laws, policies, and regulations are adopted and implemented. The
ultimate goal of these populations is to control everything in order to eliminate or avoid the
unexpected. As a result of this high Uncertainty Avoidance characteristic, the society does not readily
accept change and is very risk adverse.
Women in the Arab World are limited in their rights; it may be due more to Muslim religion
rather than a cultural paradigm.
This translates into a Collectivist society as compared to Individualist culture and is manifested in a close
long-term commitment to the member 'group', that being a family, extended family, or extended
relationships. Loyalty in a collectivist culture is paramount, and over-rides most other societal rules.
Hofstede Analysis
Power Distance Index (PDI) focuses on the degree of equality, or inequality, between people in the
country's society. AHigh Power Distance ranking indicates that inequalities of power and wealth have
been allowed to grow within the society. These societies are more likely to follow a caste system that
does not allow significant upward mobility of its citizens. A Low Power Distance ranking indicates the
society de-emphasizes the differences between citizen's power and wealth. In these societies equality
and opportunity for everyone is stressed.
Individualism (IDV) focuses on the degree the society reinforces individual or collective, achievement
and interpersonal relationships. A High Individualism ranking indicates that individuality and individual
rights are paramount within the society. Individuals in these societies may tend to form a larger number
of looser relationships. A Low Individualism ranking typifies societies of a more collectivist nature with
close ties between individuals. These cultures reinforce extended families and collectives where
everyone takes responsibility for fellow members of their group.
Masculinity (MAS) focuses on the degree the society reinforces, or does not reinforce, the traditional
masculine work role model of male achievement, control, and power. A High Masculinity ranking
indicates the country experiences a high degree of gender differentiation. In these cultures, males
dominate a significant portion of the society and power structure, with females being controlled by male
domination. A Low Masculinity ranking indicates the country has a low level of differentiation and
discrimination between genders. In these cultures, females are treated equally to males in all aspects of
the society.
Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) focuses on the level of tolerance for uncertainty and ambiguity
within the society - i.e. unstructured situations. A High Uncertainty Avoidance ranking indicates the
country has a low tolerance for uncertainty and ambiguity. This creates a rule-oriented society that
institutes laws, rules, regulations, and controls in order to reduce the amount of uncertainty. A Low
Uncertainty Avoidance ranking indicates the country has less concern about ambiguity and uncertainty
and has more tolerance for a variety of opinions. This is reflected in a society that is less rule-oriented,
more readily accepts change, and takes more and greater risks.
Long-Term Orientation (LTO) focuses on the degree the society embraces, or does not embrace, long-
term devotion to traditional, forward thinking values. High Long-Term Orientation ranking indicates the
country prescribes to the values of long-term commitments and respect for tradition. This is thought to
support a strong work ethic where long-term rewards are expected as a result of today's hard work.
However, business may take longer to develop in this society, particularly for an "outsider". A Low Long-
Term Orientation ranking indicates the country does not reinforce the concept of long-term, traditional
orientation. In this culture, change can occur more rapidly as long-term traditions and commitments do
not become impediments to change.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Summary of Joseph Henrich's The WEIRDest People in the WorldDa EverandSummary of Joseph Henrich's The WEIRDest People in the WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Hostede ModelDocumento6 pagineHostede Modelgowhar2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Culture WorkDocumento30 pagineCulture WorkoshashNessuna valutazione finora
- Geet Hofstead ModelDocumento11 pagineGeet Hofstead ModelHasibul HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Russian Culture Through The Lens of HofstedeDocumento3 pagineRussian Culture Through The Lens of HofstedeAlisa PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- PaperDocumento9 paginePaperAhmad RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intercultural CommunicationDocumento20 pagineIntercultural CommunicationJ R GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hftede's Analysis ChinaDocumento5 pagineHftede's Analysis ChinaReema SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 64252RMRDocumento3 pagine6 64252RMRAgung SupriyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocumento3 pagineHofstede's Cultural DimensionsChandrani ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocumento8 pagineHofstede's Cultural DimensionsKhoirul AnamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstedes Cultural DimensionsDocumento8 pagineHofstedes Cultural DimensionsthrierNessuna valutazione finora
- HOFSTEDE'S Cultural Dimentions of ChinaDocumento3 pagineHOFSTEDE'S Cultural Dimentions of Chinavijayendar421Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Two Major Perceptions of Time, and How Does Each Affect International Business? AnswerDocumento2 pagineWhat Are The Two Major Perceptions of Time, and How Does Each Affect International Business? AnswerVikram KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocumento34 pagineHofstede's Cultural Dimensionsdan_obd726Nessuna valutazione finora
- HTBMS (F) - 002 - International BusinessDocumento10 pagineHTBMS (F) - 002 - International BusinessEshitwa AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- IB-American CultureDocumento9 pagineIB-American CultureTrang CarnesNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimenson of Geert HofstedeDocumento4 pagineDimenson of Geert HofstedemyraNessuna valutazione finora
- Geert Hofstede Analysis Is Discussed On Each Country's Page in This Website With The Following FormatDocumento2 pagineGeert Hofstede Analysis Is Discussed On Each Country's Page in This Website With The Following FormatFaith AmenkhienanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede OutputDocumento7 pagineHofstede OutputPavan Reddy MareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- HofstedeDocumento2 pagineHofstedesavita kNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultu Re and Accounting: 1.abstractDocumento12 pagineCultu Re and Accounting: 1.abstractSanaRajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede Comparison of Germany and ChinaDocumento11 pagineHofstede Comparison of Germany and ChinaTrang Pham67% (3)
- Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Understanding Workplace Values Around The WorldDocumento5 pagineHofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Understanding Workplace Values Around The WorldJannie LinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Power DistanceDocumento30 pagineHofstede's Cultural Dimensions: Power Distanceaim panipatNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Dimensions, Measuring Cultural Differences Between Australia and IndiaDocumento4 pagineHofstede's Dimensions, Measuring Cultural Differences Between Australia and IndiaSumit BhagatNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstedeapproch To CultureDocumento6 pagineHofstedeapproch To Culturene002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour Rugs & Carpet in LithuaniaDocumento7 pagineConsumer Behaviour Rugs & Carpet in LithuaniaMolu WaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Analysis of Four Countries Through Hofstede DimensionsDocumento10 pagineComparative Analysis of Four Countries Through Hofstede DimensionsNISHTHA OraNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business and CultureDocumento43 pagineInternational Business and CultureTabeer Yaseen70Nessuna valutazione finora
- China in Comparison With Russia..: Golubeva ValeriaDocumento8 pagineChina in Comparison With Russia..: Golubeva ValeriaВалерия ГолубеваNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 3: Who Gets The Assignment?Documento5 pagineCase 3: Who Gets The Assignment?api-325274809Nessuna valutazione finora
- What About Thailand?: Power DistanceDocumento3 pagineWhat About Thailand?: Power DistanceHồng NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Cultural Management in Globalized ContextDocumento4 pagineCross Cultural Management in Globalized ContextMialy RabemanantsoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Cultural Barriers in CommunicationDocumento47 pagineCross Cultural Barriers in Communicationpriyanka100% (3)
- Notes Low High ContextDocumento4 pagineNotes Low High ContextLenny ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahan PIODocumento4 pagineBahan PIOdidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Compare The Cultures of US and Qatar Using Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocumento6 pagineCompare The Cultures of US and Qatar Using Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsPhượng Nguyễn Thị KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Organization ManagementDocumento15 pagineLesson 2 Organization ManagementCian Paul GadinganNessuna valutazione finora
- CrosswordDocumento34 pagineCrosswordShanu JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Australian Business CultureDocumento20 pagineAustralian Business CultureNirav BrahmbhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Across CulturesDocumento8 pagineManaging Across Culturescrazzychaps1987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daryl Kayle SantosDocumento12 pagineDaryl Kayle Santosdarylkaylesantos21Nessuna valutazione finora
- IntoManagement - 5 LectureDocumento19 pagineIntoManagement - 5 LectureNurt TurdNessuna valutazione finora
- CultureDocumento1 paginaCulturemihirNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business Chapter 2Documento7 pagineInternational Business Chapter 2DhavalNessuna valutazione finora
- Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions Theory: Risty D. Despillo HBO Jan 31, 2018Documento8 pagineHofstede's Cultural Dimensions Theory: Risty D. Despillo HBO Jan 31, 2018lucasNessuna valutazione finora
- International CultureDocumento6 pagineInternational Culturemanali_thakar100% (1)
- Apa Sample PaperDocumento8 pagineApa Sample PaperFazeen FaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 (OB)Documento4 pagineLecture 4 (OB)Mahvesh ZahraNessuna valutazione finora
- Geert Hofstede™ Cultural DimensionsDocumento4 pagineGeert Hofstede™ Cultural Dimensionsangela328Nessuna valutazione finora
- HofsedDocumento16 pagineHofsedPragati JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing Chapter 5Documento3 pagineInternational Marketing Chapter 5Abviel YumulNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 2 CultureiiDocumento14 pagineMod 2 CultureiimuneerppNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Research Paper International BusinessDocumento19 pagineGroup Research Paper International Businessapi-251762470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Distance: and Organisations Within A Country Expect and Accept That Power Is Distributed UnequallyDocumento3 paginePower Distance: and Organisations Within A Country Expect and Accept That Power Is Distributed UnequallyLinh Bảo BảoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 10 Diversity Management in Organisation PDFDocumento12 pagineTopic 10 Diversity Management in Organisation PDFAlister AshleyNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business - CultureDocumento12 pagineInternational Business - Cultureisnush100% (1)
- Reporting GRP 2Documento20 pagineReporting GRP 2Rose Ann Mae PescasioNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Across Cultures Chapter6Documento4 pagineManagement Across Cultures Chapter6AYMaNe boutbatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Cultural Study of Workplace TalkDocumento27 pagineCross Cultural Study of Workplace TalkJumani Fauzi100% (1)
- Unit 3: Differences in Cultural EnvironmentDocumento11 pagineUnit 3: Differences in Cultural Environment088jay IsamaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- FTC 4 ModuleDocumento17 pagineFTC 4 ModuleAngel Rose Sampilo - MercadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2练习 Personality and ValuesDocumento34 pagineChapter 2练习 Personality and ValuesFengChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Organisational Structure and MotivationDocumento7 pagineOrganisational Structure and MotivationGobin SookramNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Cultural Management - Birame Gueye 2021Documento92 pagineCross Cultural Management - Birame Gueye 2021AYYOUB ESSAKKAKINessuna valutazione finora
- Doing Business in Mexico Understanding CDocumento18 pagineDoing Business in Mexico Understanding CmarcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Think Communication 3rd Edition Engleberg Wynn Test BankDocumento36 pagineThink Communication 3rd Edition Engleberg Wynn Test Bankorbate.bendlet.fdszz100% (32)
- For Review Only: Assimilating and Differentiating: The Curvilinear Effect of Social Class On Green ConsumptionDocumento71 pagineFor Review Only: Assimilating and Differentiating: The Curvilinear Effect of Social Class On Green ConsumptionRemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural Dimensions of Global Is at IonDocumento26 pagineCultural Dimensions of Global Is at IonbemusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Redbull Marketing StrategyDocumento34 pagineRedbull Marketing StrategyOmer Bari75% (4)
- Ib - Reading MaterialDocumento10 pagineIb - Reading MaterialShahenaNessuna valutazione finora
- UB2783298 BUMGT6958 Vishal Shukla Comparative Issues in International ManagementDocumento7 pagineUB2783298 BUMGT6958 Vishal Shukla Comparative Issues in International Management王亚琪Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural Differences Between Australia and LibyaDocumento11 pagineCultural Differences Between Australia and LibyaDorji DelmaNessuna valutazione finora
- National Culture and Its Impact On Organizational BehaviorDocumento49 pagineNational Culture and Its Impact On Organizational Behaviorpooja8288Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1108 - Arla 01 2018 0013Documento30 pagine10 1108 - Arla 01 2018 0013Arafat SaleheenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex and Gender: Module 1, Lesson 1Documento11 pagineSex and Gender: Module 1, Lesson 1Roma Rose HoneraNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Communication Skills-Cox 1105Documento113 pagineBusiness Communication Skills-Cox 1105otaka jamesNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM Unit 5Documento8 pagineHRM Unit 5kumar sahityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Communication PR PlanDocumento45 pagineCross Communication PR PlanJuliaNguyen100% (1)
- International Human Resource Management: HRM 2020 Set by Habtamu Dadi (PHD)Documento49 pagineInternational Human Resource Management: HRM 2020 Set by Habtamu Dadi (PHD)Mikiyas MelakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of Sony EricssonDocumento50 pagineCase Study of Sony EricssonDeno Ay100% (3)
- A.1 Explain The Dimensions of The Term Globalization and Discuss What The Outcome Might Be in The FutureDocumento4 pagineA.1 Explain The Dimensions of The Term Globalization and Discuss What The Outcome Might Be in The FutureFelicia TrecarlyNessuna valutazione finora
- INTERNATIONAL HRM - Dimensions of Culture - 1Documento35 pagineINTERNATIONAL HRM - Dimensions of Culture - 19986212378100% (1)
- Global Management Managing Across Borders: ©olivier Renck/ Getty ImagesDocumento40 pagineGlobal Management Managing Across Borders: ©olivier Renck/ Getty ImagesAshikin AzlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ihrm - Understanding Culture and Multiculturalism: Rohini M BudhirajaDocumento26 pagineIhrm - Understanding Culture and Multiculturalism: Rohini M Budhirajanav sainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Culture of Turkey ...Documento14 pagineBusiness Culture of Turkey ...Muneeb AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Khaoulae Notes: Geert Hofstede's Five Dimensions of National CultureDocumento3 pagineKhaoulae Notes: Geert Hofstede's Five Dimensions of National CultureHassan 21Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Negotiate With The Chinese SupplierDocumento7 pagineHow To Negotiate With The Chinese SupplierWaseem SajjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Cultural Differences and Their Implications ForDocumento20 pagineCross Cultural Differences and Their Implications Formojahid123Nessuna valutazione finora