Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Adjective and Adverbs
Caricato da
Santiago Francisco Zamora0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
71 visualizzazioni5 pagineAdjective An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun. Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important Adverb An adverb is usually a verb.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoAdjective An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun. Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important Adverb An adverb is usually a verb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
71 visualizzazioni5 pagineAdjective and Adverbs
Caricato da
Santiago Francisco ZamoraAdjective An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun. Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important Adverb An adverb is usually a verb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you
something about the noun.
Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important
Adverb
An adverb is a word which usually describes a verb. It tells you
how something is done. It may also tell you when or where
something happened.
Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here,
everywhere
Examples of Adjectives
Proper Adjectives
These are formed from proper nouns.
They always begin with a capital letter.
Proper Noun Proper Adjective
America American
Britain British
Canada Canadian
China Chinese
Christianity Christian
France French
Articles
There are only three of these special types of adjectives: a, an , and the.
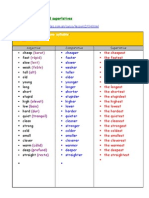
Regular Comparatives and Superlatives
Most adjectives can be described in degrees. This means that something can have
more or less of the adjective's quality.
Regular comparatives end in -er or start with more.
Regular superlatives end in -est or start with most.
Positive Comparative Superlative
ambitious more ambitious most ambitious
cold colder coldest
comfortable more comfortable most comfortable
dry drier driest
enchanting more enchanting most enchanting
funny funnier funniest
hot hotter hottest
organized more organized most organized
pretty prettier prettiest
radiant more radiant most radiant
sharp sharper sharpest
wavy wavier waviest
Irregular Comparatives and Superlatives
These can still be given in degrees, but they don't follow the patterns listed above.
Positive Comparative Superlative
bad worse worst
good better Best
little less Least
many more Most
Adjectives That Cannot Be Comparative or Superlative
Some adjectives don't have degrees. There is only one level of these adjectives.
(For example, something cannot be more half than something else. It either is
half, or it isn't.)
entire fatal Final
half main Pregnant
List of Adverbs
This list of adverbs should help you to understand adverbs a little better. For a
more in-depth look at adverbs
They tell us how, when, where, to what extent, and why.
Adverbs that tell us How?
A: absentmindedly, adoringly, awkwardly
B: beautifully, briskly, brutally
C: carefully, cheerfully, competitively
E: eagerly, effortlessly, extravagantly
G: girlishly, gracefully, grimly
L: lazily, lifelessly, loyally
Q: quietly, quickly, quizzically
R: really, recklessly, remorsefully, ruthlessly
S: savagely, sloppily, so, stylishly
U: unabashedly, unevenly, urgently
W: well, wishfully, worriedly
Adverbs that tell us When?
A: after, afterwards, annually
B: before
D: daily
N: never, now
S: soon, still
T: then, today, tomorrow
W: weekly, when
Y: yesterday
Adverbs that tell us Where?
A: abroad, anywhere, away
E: everywhere
H: here, home
I: in, inside
O: out, outside
S: somewhere
T: there
U: underground, upstairs
Adverbs that tell us To what extent?
E: extremely
N: not (this includes n't)
Q: quite
R: rather, really
T: terribly, too
V: very
Comparative and Superlative Adverbs
Don't know what this means? See the adverbs page to learn more about this.
Positive Comparative Superlative
badly worse Worst
carefully more carefully most carefully
little less Least
much more Most
soon sooner soonest
well better
Best
Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech:
interjection pron. conj. adj. noun verb prep. noun adverb
Well, she and young John walk To school slowly.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- HSPT Test Prep: Three Full-Length Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsDa EverandHSPT Test Prep: Three Full-Length Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On AdverbsDocumento8 pagineNotes On AdverbsIrene Tan100% (1)
- Simple Adverbs:: Time: Answers The QuestionsDocumento5 pagineSimple Adverbs:: Time: Answers The QuestionsLeslie Yamat-ArellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs 21Documento20 pagineAdverbs 21Carola TorrealbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Group 5Documento6 pagineAssignment Group 5maram JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- ADVERBDocumento20 pagineADVERBHan YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On AdverbsDocumento16 pagineNotes On AdverbsMinaChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison: Adverbs (Worse, More Easily) : Adverbs: Comparative and Superlative FormsDocumento9 pagineComparison: Adverbs (Worse, More Easily) : Adverbs: Comparative and Superlative FormsFABIAN FIENGONessuna valutazione finora
- English Grammar: Parts of Speec HDocumento14 pagineEnglish Grammar: Parts of Speec HAl Bee AlsNessuna valutazione finora
- Trabalho IngleshDocumento12 pagineTrabalho IngleshJúnior SilvérioNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs: Adverbs Usually Answer The Following QuestionsDocumento7 pagineAdverbs Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs: Adverbs Usually Answer The Following QuestionsAbhimanyu SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Form and Function of AdjectivesDocumento8 pagineForm and Function of AdjectivesHelmi AbdillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tone and Feelings and Emotion Adjectives - 1st Pre IntermediateDocumento20 pagineTone and Feelings and Emotion Adjectives - 1st Pre IntermediateTeofilo Alvarez100% (1)
- D360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 16 (Rodrigo A.) - GabaritoDocumento24 pagineD360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 16 (Rodrigo A.) - GabaritoPedro VillasNessuna valutazione finora
- D360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 16 (Rodrigo A.)Documento23 pagineD360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 16 (Rodrigo A.)Pedro VillasNessuna valutazione finora
- AdverbsDocumento22 pagineAdverbsMarko KasaysayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas B. InggrisDocumento11 pagineTugas B. InggrisTiffany BlackNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs of Degree Java LauditDocumento15 pagineAdverbs of Degree Java LauditPepitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocumento5 pagineAdverbs of FrequencyRobert SavNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: Nur Aulia Zachriani Bahasa Inggris NIM: C 201 18 088Documento6 pagineName: Nur Aulia Zachriani Bahasa Inggris NIM: C 201 18 088Nur Aulia ZachrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjectives: An, and The - Are AdjectivesDocumento7 pagineAdjectives: An, and The - Are AdjectivesARIANessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsDocumento22 pagineWeek 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsVivian MwangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Proper: Articles Like The, A, and An Are Also Limiting Adjectives Because They Denote Whether A Noun Is Definite orDocumento16 pagineProper: Articles Like The, A, and An Are Also Limiting Adjectives Because They Denote Whether A Noun Is Definite orhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjectives & AdverbsDocumento37 pagineAdjectives & AdverbslujantamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverb: Dirsya Febrina Fitria Humaira M. Ifaldi Phonna Syahrial Bahrain Tashya FarradillaDocumento13 pagineAdverb: Dirsya Febrina Fitria Humaira M. Ifaldi Phonna Syahrial Bahrain Tashya FarradillaFitriaHumairaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocumento4 pagineAdverbs of FrequencyUsagi Yuki AnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 - AdjectiveDocumento14 pagineGroup 4 - AdjectiveErssaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs BoxDocumento2 pagineAdverbs BoxAli GalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinds of AdverbsDocumento5 pagineKinds of AdverbsANA BORONDONessuna valutazione finora
- Adjective Types: The Adjective in English GrammarDocumento15 pagineAdjective Types: The Adjective in English GrammarPadhy ParthosarathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparatives SuperlativesDocumento10 pagineComparatives SuperlativesmsoldugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjective Grammar PDFDocumento6 pagineAdjective Grammar PDFAtitta ImarilalengNessuna valutazione finora
- ADVERB Structure of English1Documento43 pagineADVERB Structure of English1Donna Faith FajardoNessuna valutazione finora
- English GrammarDocumento17 pagineEnglish GrammarVansh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Flower in The Vase Is A PeonyDocumento8 pagineThe Flower in The Vase Is A PeonySheilah Mae PadallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 79 SheetDocumento30 pagineLesson 79 SheetAshutosh MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs FileDocumento7 pagineAdverbs FileCzarinah PalmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs - Big List of Adverbs and Its Types - Learn What Are AdverbsDocumento4 pagineAdverbs - Big List of Adverbs and Its Types - Learn What Are AdverbsSharksNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14 AdjectivesDocumento54 pagineChapter 14 Adjectives耿雨栋Nessuna valutazione finora
- Part of Speech 2Documento4 paginePart of Speech 2Cha Gao-ayNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjectives - Seminarski RadDocumento11 pagineAdjectives - Seminarski RadBlagica ZivicNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of SpeechDocumento44 pagineParts of SpeechdelvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverb - NotaDocumento3 pagineAdverb - NotaChristopher Larry LiminNessuna valutazione finora
- English Assignment: Modals & AdverbsDocumento6 pagineEnglish Assignment: Modals & AdverbsNi Chi GenaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjectives and Adverbs - CAEDocumento10 pagineAdjectives and Adverbs - CAEAna Maria Del Castillo-Olivares MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of ThumbDocumento62 pagineRules of Thumbhector zarateNessuna valutazione finora
- Los Adjetivos en InglésDocumento17 pagineLos Adjetivos en InglésRafael PirelaNessuna valutazione finora
- AdverbsDocumento13 pagineAdverbsDelia CatrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- The AdverbDocumento15 pagineThe AdverbAnca ParlogeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Www.allonlinefree.comDocumento23 pagineWww.allonlinefree.comarsalankhurshidNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Grammar For IELTSDocumento26 pagineComplete Grammar For IELTSjakiafnan07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adjectives AdverbsDocumento22 pagineAdjectives AdverbsbinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar PPDocumento4 pagineGrammar PPsammer30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synonym and AntonymDocumento24 pagineSynonym and AntonymAstrid Nadya RizqitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative and Superlative AdverbsDocumento2 pagineComparative and Superlative AdverbsJesica González100% (1)
- Unidade 1 - IbeuDocumento4 pagineUnidade 1 - IbeuNathália RaggiNessuna valutazione finora
- List of AdverbsDocumento29 pagineList of AdverbscochconniNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs - Lecture I PermbledhurDocumento17 pagineAdverbs - Lecture I PermbledhurFrida QordjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas COMPARISONDocumento15 pagineTugas COMPARISONMuhammad Irfan DzakyNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning of Unit 10 GradeDocumento13 paginePlanning of Unit 10 GradeSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento35 pagineUnit 1Santiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1.1Documento2 pagineLesson 1.1Santiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Material For Unit 6. 6-4Documento1 paginaExtra Material For Unit 6. 6-4Santiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson-Plan 9thDocumento38 pagineLesson-Plan 9thSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom PhrasesDocumento5 pagineClassroom PhrasesSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Planing To Unit 8 GradeDocumento2 paginePlaning To Unit 8 GradeSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Verb To DoDocumento15 pagineThe Verb To DoSantiago Francisco Zamora100% (1)
- 7Documento4 pagine7JunaidKhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom PhrasesDocumento5 pagineClassroom PhrasesSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Megatrends 1,2,3Documento37 pagineUnit 1 Megatrends 1,2,3Santiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom PhrasesDocumento0 pagineClassroom PhrasesSerban MihaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- LetterDocumento1 paginaLetterSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Verb To DoDocumento2 pagineThe Verb To DoSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Megatrends 6Documento8 pagineMegatrends 6Santiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- My RubricDocumento12 pagineMy RubricSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing TaskDocumento2 pagineWriting TaskSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- OEGTAG Answer BookDocumento59 pagineOEGTAG Answer Bookgonza100% (2)
- 2 Communicative Approach SurveyDocumento1 pagina2 Communicative Approach SurveySantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Interchange Fourth Edition Class AudioDocumento5 pagineInterchange Fourth Edition Class AudioSantiago Francisco Zamora71% (14)
- 99 Ways To Improve Your English PDFDocumento81 pagine99 Ways To Improve Your English PDFHakan Citlak100% (1)
- 50 Irregular Verbs Past Simple Part 1Documento2 pagine50 Irregular Verbs Past Simple Part 1zefkerNessuna valutazione finora
- 500 Real English PhrasesDocumento38 pagine500 Real English PhrasesIon Sava100% (2)
- Spanish Grammar LessonsDocumento8 pagineSpanish Grammar Lessonskinfolk321Nessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Hight Intermediate Grammar Object 3 PagesDocumento3 pagine17 Hight Intermediate Grammar Object 3 PagesSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide4BankExams English GrammarDocumento11 pagineGuide4BankExams English GrammarShiv Ram Krishna100% (3)
- SuperlativesDocumento2 pagineSuperlativesSantiago Francisco Zamora50% (2)
- Basic English:A General Introduction With Rules and GrammarDocumento8 pagineBasic English:A General Introduction With Rules and Grammarsk. salahuddin ahammad67% (3)
- 18 Grammatical Rules For Writing Personal Statements 3 PagesDocumento3 pagine18 Grammatical Rules For Writing Personal Statements 3 PagesSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- American Big Picture Exercises StudentDocumento3 pagineAmerican Big Picture Exercises StudentSantiago Francisco ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Past Tense: Dosen Pemgampu: Binar Ayu DewantiDocumento8 pagineSimple Past Tense: Dosen Pemgampu: Binar Ayu DewantiHesty EkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Overview - Mis VacacionesDocumento3 pagineUnit 3 Overview - Mis VacacionesSayidito MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pashto English DictionaryDocumento864 paginePashto English Dictionaryinamullah87% (31)
- Passive Voice 1Documento4 paginePassive Voice 1awanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan in Reflexive Pronoun Grade 10Documento89 pagineLesson Plan in Reflexive Pronoun Grade 10Elmer Pineda Guevarra0% (1)
- General Rules For Active Voice and Passive VoiceDocumento21 pagineGeneral Rules For Active Voice and Passive VoiceGulfam RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Parts of SpeechDocumento2 pagineBasic Parts of SpeechDonnia MayeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Grammatical Structure of Munster IrishDocumento136 pagineThe Grammatical Structure of Munster Irishalanward100% (4)
- Yes, I Can PDFDocumento38 pagineYes, I Can PDFATNessuna valutazione finora
- Word Building Anglosaxon EndingsDocumento3 pagineWord Building Anglosaxon EndingslanfubNessuna valutazione finora
- SpeakOut StudyBooster AdvancedDocumento6 pagineSpeakOut StudyBooster AdvancedAna Cardoso33% (3)
- Leaving Cert Higher Notes 1Documento4 pagineLeaving Cert Higher Notes 1api-384311544Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reading DiagnosticDocumento3 pagineReading DiagnosticLaure OlivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Verb ComplementationDocumento6 pagineVerb ComplementationAlexandra GrégerNessuna valutazione finora
- Modals PermissionDocumento2 pagineModals PermissionGuillermo Peruyero ArguetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Morphological Typology - Spring 2016 - Ling 100 Guest LectureDocumento34 pagineMorphological Typology - Spring 2016 - Ling 100 Guest LecturePradip MapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Arabic Grammar BookDocumento80 pagineAdvanced Arabic Grammar Bookhyalinmaganda75% (4)
- Gold B2 First, Unit 2 KeyDocumento7 pagineGold B2 First, Unit 2 KeyPigasus60% (5)
- Formal Vs Informal NewDocumento13 pagineFormal Vs Informal NewSamuel IsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Reported Speech HANDOUTDocumento3 pagineReported Speech HANDOUTmmarijanamavicNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-BASIC Vocabulary: Brilliant English CourseDocumento7 paginePre-BASIC Vocabulary: Brilliant English Courseryan kurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar For Grade 9 II SentenceDocumento17 pagineGrammar For Grade 9 II SentenceSaid HabibNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of The First 17 Lessons of Homeric GreekDocumento54 pagineSummary of The First 17 Lessons of Homeric Greekutuk3333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Expressions of Place and Time in SentencesDocumento4 pagineExpressions of Place and Time in SentencesDecembrie MiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammatica SvedeseDocumento40 pagineGrammatica SvedeseTiziano LicataNessuna valutazione finora
- Present-Simple-Continuous Rules PDFDocumento3 paginePresent-Simple-Continuous Rules PDFcajoca1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Order of AdjectivesDocumento5 pagineOrder of Adjectivestworivers100% (1)
- Verbe RegulateDocumento15 pagineVerbe RegulateElenaCibotariNessuna valutazione finora
- Navigate B2 Wordlist Unit 2 PDFDocumento4 pagineNavigate B2 Wordlist Unit 2 PDFBen Then100% (1)
- English 3 (2nd Periodical Test) Lesson 9-16Documento3 pagineEnglish 3 (2nd Periodical Test) Lesson 9-16Codythedogify100% (14)