Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unified Quiz practice questions and answers explained
Caricato da
Mohit ModyDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unified Quiz practice questions and answers explained
Caricato da
Mohit ModyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Please be aware that these questions do not represent all topics that can be asked in the
Unified Quiz and that they are just meant for practice!
It is suggested to take all 4 questions in a row with a time limit of ! min"
#he answer key at the end will point out the correct answers and e$plain why the others
are incorrect" Please feel free to contact me when you do not agree with the best correct
answer and I will be glad to discuss the question with you" %y e&mail is mtrotz'sgu"edu
Q() *ependent on the polarity+ we separate polar lipids and neutral lipids" ,eutral lipids+ like
triacylglycerols -#./s0+ are clea1ed by lipases" 2ne of the lipases that digest dietary #./s is lingual
lipase which
a" needs colipase for its acti1ity
b" is acid&stable at the stomach proton concentration
c" needs conjugated bile salts for its acti1ity
d" is deficient in patients with cystic fibrosis
e" clea1es both+ #./s and phospholipids
Q(3 . 4!&year old man was seriously injured in an accident" 5e needs parenteral nutrition+ which should
include dietary essential fatty acids" 6hich of the following fatty acids is a dietary essential fatty acid
of the &! family7
a" Palmitoleic acid
b" 2leic acid
c" 8inoleic acid
d" &linolenic acid
e" .rachidonic acid
Q ( 9 6hat is a characteristic indication that a child with common long bone fractures could ha1e defecti1e
collagen as found in osteogenesis imperfecta tarda -2I #ype I07
a" hypermobility of joints
b" bleeding of gums
c" stretchy skin
d" blue sclerae
e" long limbs
Q(4 2ur knowledge about enzymes has increased immensely since the first description of a protein acting
as a catalyst" :nzymatic catalysis
a" changes the thermodynamics of the reaction
b" works without a transition state
c" is independent of the p5
d" can in1ol1e a prosthetic group like ;.*
e" in1ol1es binding of the substrate to its huge acti1e site
Q(4 . 43&year&old man is brought to the emergency room by his wife" 5e had suffered a mild heart attack
two years ago and e$perienced similar pain during the last night" 5is :</ does not indicate an acute
%I and blood samples are taken" 5is blood plasma is used to test for both+ total serum creatine kinase
-<=0 and serum <=&%>" 6hat is the reasoning behind this7
a" #otal serum <= alone is an injury marker for the li1er
b" Increase of serum <=&%> but not of total <= indicates rhabdomyolosis
c" ?erum <=&%> larger than about 4@ of total serum <= can indicate an acute %I
d" ?erum c#n# is also a marker for %I+ but accumulates only after 3 days in blood
e" ?erum le1els of <=&%> but not total serum <= are increased after an acute %I
Q(!
Pharmaceutical companies in1estigate the possible inhibition of enzymes by drugs" 6hich graph is
obtained when the data are e$pressed in the 8inewea1er&>urk plot7 It results in data presentation that
a" shows a sigmoidal cur1e that reaches Ama$ at high B?C
b" is plotted as initial 1elocity -Ao0 1ersus )DB?C
c" results in a reciprocal 1alue of Ama$ to be found at the intercept with the $&a$is
d" shows a hyperbolic cur1e that reaches Ama$ at high B?C
e" results in a straight line due to plotting )DAo to )DB?C
Q(E
In many graphs that in1estigate the action of enzymes+ the data are shown as 1elocity in response to
increased substrate concentrations" #he 1elocity
a" reaches Ama$ at the substrate concentration at =m
b" represents product formation -mol0 o1er time -min0
c" is independent of the amount of enzyme
d" increases for human enzymes at temperatures abo1e 4
<
e" is proportional to substrate concentrations at 1ery high B?C
Q(F
8ipids are a major component of our normal diet and we ha1e se1eral digesti1e lipases" 6hat is
special of pancreatic lipase+ often just named lipase7 Pancreatic lipase
a" clea1es dietary triacylglycerols to mainly free glycerol and fatty acids
b" in serum can be an injury marker for pancreatitis
c" clea1es mainly triacylglycerols with medium&chain fatty acids
d" is proteolytically acti1ated by trypsin
e" is released as zymogen from the pancreas
Q(G #he fibrous proteins collagen and elastin ha1e a specific amino acid composition" 6hich amino acid
represents about one third of amino acids in collagen and also in elastin7
a" ?erine
b" .lanine
c" /lycine
d" 5ydro$yproline
e" 5ydro$ylysine
Q()
#he digestion of dietary carbohydrates is 1ery much watched in programs that promote weight loss"
2ne could target the enzymes that degrade comple$ sugars or one could target the uptake of glucose
and galactose into intestinal mucosal cells" #his uptake is performed by
a" facilitated transport
b" /8U#&4
c" /8U#&3
d" primary acti1e transport
e" co& transport with sodium ions
Q())
*uring your clinical rotations+ you come to learn about a family with a child who suffers from <ystic
;ibrosis" ,ot only is the child treated with physical clearing of the lungs from the accumulating
mucus+ but also a special nutrition is of importance and part of the treatment" 6hat is special about
the digestion in cystic fibrosis patients7 Patients with cystic fibrosis
a" lack the glucose transporter ?/8#
b" are deficient in the digestion performed by pepsin
c" should eat a diet low in lactose
d" can digest #./s with medium&chain fatty acids
e" should eat a diet low in purine nucleotides
Q()3
*igestion of food starts in the mouth and after swallowing it continues in the stomach" #he stomach
performs the digestion of
a" sucrose and lactose
b" #./s with long&chain fatty acids
c" proteins to mainly peptides
d" nucleic acids to bases and sugars
e" phospholipids to fatty acids and lysophospholipids
Q()9
#here are se1eral hormones in1ol1ed with the digestion of our normal food intake" .mongst them are
gastrin+ secretin and cholecystokinin -<<=0" 6hat is special about <<=7 <holecystokinin
a" is a hormone formed in the pancreas
b" acti1ates trypsinogen to trypsin
c" leads to release of bicarbonate from the pancreas
d" leads to release of protons into the stomach lumen
e" leads to release of bile from the gallbladder
Q()4
. 44&year&old woman complains to her physician of feeling night&blind while dri1ing home late at
night" It happened to her only recently+ and she is worried about her health" Upon questioning+ she
tells her physician that she is since last month 1ery strict with her diet+ which is mostly fat&free" #here
is no change in her feces" 6hat could most likely be the reason for her problems7
a" 8ess uptake of the lipid&soluble 1itamin .
b" 8ack of conjugated bile salts
c" #he deficiency of dietary cholesterol
d" . diet that is too high in proteins
e" . diet too high in purine nucleotides
Q()4 <holesterol is released by the li1er into the bile" #he solubility of cholesterol in bile is achie1ed by
conjugated bile salts and phosphatidylcholine" #aurocholic acid is formed from cholic acid and
taurine" #his conjugated bile salt is
a" synthesized in the gallbladder
b" the main component of gallstones
c" able to pre1ent gallstone formation
d" grouped as secondary conjugated bile salt
e" mainly released and e$creted in feces
Q()! *igesti1e enzymes are 1ery powerful enzymes that cannot only digest dietary proteins or
phospholipids+ but also cell components which are not meant to be digested" Proteolytic acti1ation of
digesti1e zymogens is often used" . key player in that respect is trypsin which proteolytically
acti1ates in the duodenum
a" pepsinogen
b" enteropeptidase
c" chymotrypsinogen
d" &amylase
e" pancreatic lipase
Q()E *igesti1e proteases ha1e specific clea1age sites and work all together in the intestinal lumen in order
to efficiently digest proteins to amino acids" 6hich amino acid side chain contains a positi1e charge
and is -besides lysyl residues0 the clea1age site for trypsin7
a" .sparagine
b" .rginine
c" /lutamine
d" #ryptophan
e" 5istidine
Q()F #he plasma membrane separates the cell from its neighbor cells and the e$tracellular or interstitional
fluid" #he correct fluidity of the plasma membrane is regulated by
a" free cholesterol which buffers the fluidity changes of fatty acids during temperature changes
b" by the amounts of glucose transporters and other proteins
c" arachidonic acid in phospholipids which will reduce the fluidity
d" palmitic acid which is more fluid than oleic acid
e" free cholesterol which increases the fluidity at the area of the polar head groups
Q()G
. )G&year&old *anish female de1eloped se1ere diarrhea on a hiking trip" .fter her return+ she
consults a physician as she still suffers from continued abdominal pain with bloating and painful
cramping" #his takes place especially after eating sweets and drinking milk"
6hat could be most likely the reason for her problems7
a" *eficiency of disaccharidases due to her se1ere diarrhea
b" . strong genetic predisposition for primary lactose intolerance
c" <ongenital lactase deficiency
d" *eficiency of secretin and cholecystokinin
e" Inability to clea1e lactose in the stomach
Q(3 Hou might ha1e seen on cans of diet soft drinks the warning that phenylketonurics should not
consume drinks containing aspartame" .spartame is an artificial dipeptide sweetener that contains
phenylalanine" 6hat can you say about the structure and grouping of this amino acid7 Phenylalanine
a" contains a hydro$yl group
b" is an aromatic amino acid
c" contains a sulfhydryl group
d" is a dietary nonessential amino acid
e" is grouped as a branched&chain amino acid
Q(3) #he neurotransmitter /.>. can be formed by the decarbo$ylation of the &carbo$yl group of a
specific amino acid" 6hich amino acid is decarbo$ylated to /.>.7
a" /lycine
b" #ryptophan
c" /lutamate
d" .spartate
e" /lutamine
Q(33 Proteins consist of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds" #he sequence is represented in the
primary structure" ?ome proteins form the secondary structure of an &heli$" #he &heli$
a" can bend inside of the peptide bonds in1ol1ed in the protein structure
b" cannot be changed into a &pleated sheet once it is formed as &heli$
c" contains amino acids with their side chains to the outside of the heli$
d" is a structure fa1ored by a high amount of proline residues
e" is a structure found in myoglobin but not in hemoglobin
Q( 39 <reatine kinase is an enzyme that is named after the fact that it phosphorylates creatine" 6hat is
special about this enzyme7 <reatine kinase
a" catalyses an irre1ersible reaction
b" is a serum injury marker for bone damage
c" can be used to form .#P
d" has two different subunits and consists of a tetramer
e" is a serum injury marker of %I which peaks after 3 days
Q (34 <o1alent bonds and nonco1alent bonds are found in the tertiary structure of proteins" 6hich of the
following bonds is a co1alent bond formed by side chains of amino acids7
a" ionic bonds between aspartate and lysine
b" hydrogen bonds between serine and glutamate
c" 1an der 6aals forces found in the &heli$
d" disulfide bonds between two cysteine residues
e" hydrophobic forces between 1aline and isoleucine
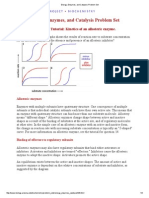
Q(34
?hown are the 8inewea1er&>urk plots for the uninhibited reaction -no inhibitor added0 and also two
data plots for a high and a low concentration of the same specific inhibitor added to the assays"
6hich statement best describes the data shown in line 37
a" no inhibitor added
b" high concentration of a competiti1e inhibitor
c" high concentration of a non&competiti1e inhibitor
d" low concentration of a competiti1e inhibitor
e" low concentration of a non&competiti1e inhibitor
)DA
)
3
9
& )DB?C )DB?C
Q(3! *efecti1e fibrous proteins can lead to serious illness due to defects related to the synthesis of
collagen or elastin" ?ome enzymes are needed for intracellular post&translational modifications
or e$tracellular for preparation of co1alent cross&linking" #he enzyme lysyl o$idase
a" is needed for both+ collagen and elastin synthesis
b" needs zinc as cofactor
c" is mainly found inside fibroblasts
d" is defecti1e in osteogenesis imperfecta
e" acts on pro&&chains of procollagen
Q(3E #he fibril forming collagens show a staggered arrangement of collagen molecules" #hese
collagen fibrils need co1alent bonds to link them together" #he cross&linking of collagen
molecules
a" is performed inside fibroblasts
b" in1ol1es disulfide bonds
c" uses desmosine
d" is performed by collagenase
e" in1ol1es lysine and allysine&residues
Q(3F 6hich of the following enzymes are in the serum injury marker for li1er damage7
a" <reatine kinase %>
b" <reatine kinase %%
c" .mylase
d" .lanine aminotransferase
e" 8actate dehydrogenase &)
Q(3G <ollagen and elastin contain an amino acid which is needed for e1entual co1alent cross&
linking" #his amino acid is
a" /lycine
b" 8ysine
c" Proline
d" .lanine
e" <ysteine
Q(9 . low&dose of aspirin -F) mg0 is used to
a" Inhibit acetylcholine esterase
b" Ie1ersibly inhibit cycloo$ygenase
c" Ieduce the acti1ity of prostacyclin
d" <hemically modify thrombo$ane
e" Ieduce the amount of thrombo$ane
Q(9)
Phospholipids are components of polar lipids that often can be used to form biomembranes due
to their amphipathic character" #he group includes cardiolipin which contains totally four
esterified fatty acids" 6hat else is special about cardiolipin7 <ardiolipin is
a" e$clusi1ely found in the heart
b" found in high concentration in mitochondria
c" a major component of all biomembranes
d" part of the glycocaly$
e" a sphingophospholipid
Q(93 5uman enzymes allow the regulation of their catalysis dependent on the changing needs of the
cells or the total human body" 6hich of the following regulations is used in humans when
insulin is ruling7
a" Increased synthesis of key enzymes for gluconeogenesis
b" Induction of key enzymes for fatty acid de&no1o synthesis
c" Increased degradation of the key enzyme for cholesterol synthesis
d" Phosphorylation of key enzymes of pathways by protein kinase .
e" Inhibition of protein phosphatases
Q(99 .llosteric enzymes do not follow %ichaelis&%enten kinetics" 6hat is special about the graph
plotted with the 1elocity at the y&a$is and the substrate concentration at the $&a$is7 #he cur1e
for allosteric enzymes
a" 6ould not lead to a Ama$
b" Is sigmoidal due to a cooperati1e effect of the substrate
c" Is shifted to the right when a feed&forward acti1ator is added
d" <annot be used to determine = "4
e" ?hows only first order kinetics
Q(94 #he enzyme lactate dehydrogenase
a" contains ;.* as prosthetic group
b" is a protein dimer with the compostition 5%
c" in serum is an early %I marker
d" needs 1itamin < for its reaction
e" cannot form pyru1ate at high ,.*5 le1els
Q(94 %ost phospholipases are found inside of cells and are membrane&bound and tightly regulated"
2ne of the e$ceptions is a soluble phospholipase .
3
that clea1es dietary phospholipids" #his
enzyme
a" is the result of proteolytic acti1ation by enteropeptidase
b" has a p5 optimum of 3
c" is synthesized as prophospholipase in the stomach
d" is e1entually degraded by digesti1e proteases
e" is released in its acti1e form by the pancreas
Q(9! %embranes contain different transporters" 6hich of the following is an e$ample of an .><&
transporter7
a" ?/8#
b" /8U#&)
c" <;#I
d" /8U#&4
e" ,a
J
D=
J
&.#Pase
Q(9E 5epatocytes contain a specific glucose transporter" #his transporter is
a" insulin&dependent
b" a low&affinity transporter
c" only found in hepatocytes
d" also found in I><
e" only used for uptake of glucose but not for release of glucose
Q(9F Premature babies are often treated with lung surfactant which
a" is a glycosphingolipid
b" is a plasmalogen
c" lines the al1eoli of the lungs and pre1ents collapse
d" contains mainly protein and some phospholipids
e" contains two arachidonic acids in its structure
Q(9G /lucagon is released by the &cells of the pancreas and signals low blood glucose le1els" #he
glucagon receptor
a" is found in the li1er and kidney
b" allows the c.%P second messenger system
c" acti1ates phospholipase <
d" is found in the nucleus of hepatocytes
e" binds both+ glucagon and epinephrine
Q(4 <reatine phosphate
a" is formed in the heart by cytochrome < o$idase
b" contains two phosphoanhydride bonds
c" is grouped as a high&energy compound
d" is formed by creatine kinase in cytosol at low .#P le1els
e" is formed using creatine and inorganic phosphate as substrates
?hort answer keyK
)>+ 3<+ 9*+ 4*+ 4<+ !:+ E>+ F>+ G<+ ):+ ))*+ )3<+ )9:+ )4.+ )4<+ )!<+
)E>+ )F.+ )G.+ 3>+ 3)<+ 33<+ 39<+ 34*+ 34:+ 3!.+ 3E:+ 3F*+ 3G>+ 9:+
9)>+ 93>+ 99>+ 94:+ 94*+ 9!<+ 9E>+ 9F<+ 9G>+ 4<
Answers and explanations for the practice exam: Unified Quiz
Q()
B is correct: Lipid digestion can be performed by lingual lipase in the stomach. The
enzyme is acidstable at the stomach proton concentration
a" incorrectK not lingual lipase+ but pancreatic lipase needs colipase for its acti1ity
b" correctK+ lingual lipase clea1es preferably #./s with medium&chain fatty acids
c" incorrectK lingual lipase does not need conjugated bile salts for its acti1ity
d incorrectK it is pancreatic lipase that is deficient in <; patients
e incorrectK lingual lipase does not clea1e phospholipids+ it clea1es only neutral lipids
Q(3 ! is correct: Linoleic acid is dietary essential and is of the " family #$%:&'"(.
a" incorrectK palmitoleic acid -)!K)0 can be formed in humans from palmitic acid -)!K0
b incorrectK oleic acid -)FK)0 can be formed in humans from stearic acid -)FK0
c correct+ it can then be used to form arachidonic acid of the same family
d" incorrectK &linolenic acid -)FK9,90 is a dietary essential fatty acid of the &9 family"
e incorrectK arachidonic acid -3K4+!0 is normally not dietary essential
Q(9 ) is correct: blue sclerae are an indication that a child with common long bone fractures
could ha*e osteogenesis imperfecta tarda #+, Type ,(.
a" incorrectK hypermobility of joints is mostly an indication of :*?
b" incorrectK bleeding of gums is mostly an indication of 1itamin < deficiency
c" incorrectK stretchy skin is mostly an indication of :*?
d" correct+ it is also found in other diseases+ but used mostly as indicator for 2I
e" incorrectK long limbs can be a sign of %arfanLs disease
Q(4
) is correct: enzymatic catalysis can in*ol*e a prosthetic group li-e .A)
a" incorrectK enzymes do not change the thermodynamics of the reaction
b" incorrectK enzymatic catalysis does not work without a transition state
c" incorrectK enzymatic catalysis shows a respecti1e p5 optimum
d correct+ ;.* is a bound coenzyme for some o$idoreductases
e incorrectK the acti1e site is small+ not large
Q(4 ! is correct: serum !/0B1total !/ larger than about 23 can indicate a 0,
a" incorrectK total <= is not an injury marker for the li1er+ <= is not found in the li1er
b" incorrectK rhabdomyolosis leads to increase of mainly total <= and little <=&%>
c" correct+ <=&%> alone can be used+ but the @ related to total <= is better
d" incorrectK serum c#n# and c#nI accumulate already se1eral hours after %I
e" incorrectK both+ total <= and <=&%> increase in plasma as indication for a %I
Q(!
4 is correct: the Linewea*erBur- plot leads to a graph with a straight line due to
plotting $15
6
to $1789 #double reciprocal(
a" incorrectK a sigmoidal cur1e+ 1elocity 1ersus B?C is found for allosteric enzymes
b" incorrectK it does not show A
data 1ersus )DB?C but instead )DA
1ersus )DB?C
c" incorrectK )DAma$ is at the intercept with the y&a$is and not the $&a$is
d" incorrectK a hyperbolic cur1e is found when plotted in the %ichaelis&%enten plot
e correct+ less e$perimental data are needed in comparison to %ichaelis&%enten plot
Q(E B is correct: the *elocity of a reaction represents product formation #mol( o*er time
a" incorrectK =m is the substrate concentration at half Ama$
b" correct+ 1elocity describes formation of product in concentrationDmin+ not total amount
c" incorrectK the 1elocity is dependent on the amount of the enzyme"
d" incorrectK human enzymes start to denature abo1e 4 < -high fe1er0
e" incorrectK the 1elocity is proportional to the substrate at low B?C+ not large B?C
Q(F
B. is correct: pancreatic lipase in serum can be a used as in:ury mar-er for pancreatitis
a" incorrectK pancreatic lipase clea1es #./ to %./ and two fatty acids
b correct+ often just named lipase as injury marker in serum
c" incorrectK it clea1es #./s with long&chain fatty acids -majority of food0
d incorrectK pancreatic lipase is not acti1ated by trypsin
e" incorrectK pancreatic lipase does not need to be synthesized as zymogen
Q(G !. is correct: glycine represents about one third of amino acids in collagen and also in
elastin.
.ll other choices are incorrectK no other amino acid represents one third of amino acids in both
collagen and also in elastin"
.lanine and serine are found in elastin and are besides glycine clea1age sites of elastase"
5ydro$yproline and hydro$ylysine are found in collagen and mostly absent in elastin"
Q()
4 is correct: dietary glucose or galactose are ta-en up into the intestinal mucosal cells by
cotransport with sodium ions
a" incorrectK dietary glucose and galactose are taken up by secondary acti1e transport
b" incorrectK /8U#&4 is found in fat and muscle cells
c" incorrectK /8U#&3 is used for release into the portal circulation
d incorrectK it is not primary but secondary acti1e transport
e correct+ either glucose or galactose is transported by ?/8# into mucosal cells
Q())
). is correct: cystic fibrosis patients can digest triacylglycerols with mediumchain fatty
acids #using lingual and gastric lipase(
a" incorrectK <; patients ha1e a defect related to <;#I - specific chloride ion channel0
b" incorrectK <; patients are not deficient in the digestion performed by pepsin"
c" incorrectK <; patients are not lactose intolerant and can eat a diet containing lactose
d" correct+ some milk #./s can be digested in the stomach -medium&chain fatty acids0
e" incorrectK <; does not lead to gout"
Q()3 !. is correct: the stomach performs digestion of proteins to mainly peptides
a" incorrectK sucrose and lactose are not digested in the stomach
b" incorrectK #./s with long&chain fatty acids are mainly digested in the duodenum
c"correct+ pepsin is an endopeptidase and leads mainly to peptides
d" incorrectK nucleic acids are denatured in the stomach but not degraded
e" incorrectK phospholipids are digested by pancreatic phospholipase .3 in the duodenum
Q()9 4. is correct: cholecysto-inin #!!/( leads to release of bile from the gallbladder
a" incorrectK <<= is a hormone formed in endocrine cells of the duodenum
b" incorrectK <<= does not acti1ate trypsinogen+ enteropeptidase acti1ates trypsinogen
c" incorrectK it is mainly secretin+ that leads to release of bicarbonate from the pancreas
d incorrectK it is gastrin that leads to release of protons into the stomach lumen
e" correct+ <<= has its name from the fact that it contracts the gallbladder
Q()4 A is correct: the most li-ely reason for her night blindness is less upta-e of the lipid
soluble *itamin A. ;etinol leads to cisretinal for the *ision cycle.
b incorrectK lack of conjugated bile salts would lead to change in her feces -steatorrhea0
c incorrectK night blindness is not related to deficiency of dietary cholesterol
d incorrectK a diet that is too high in proteins does not lead to night&blindness
e incorrectK the diet too high in purine nucleotides can lead to a gout attack
Q( )4 !. is correct: Taurocholic acid is able to pre*ent gallstone formation
a" incorrectK conjugated bile salts are only synthesized in the li1er
b" incorrectK cholesterol is the main component of gallstones"
c" correct+ conjugated bile salts are negati1ely charged and fa1or cholesterol solubility
d" incorrectK cholic acid is a primary bile acid synthesized in the li1er
e incorrectK conjugated bile salts are clea1ed to bile acids which are G4@ taken up again
Q()! !. is correct: trypsin acti*ates in the small intestine chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin.
a" incorrectK pepsinogen is not acti1ated by trypsin
b" incorrectK enteropeptidase is acti1ated by <<="
c" correct+ trypsin is an endopeptidase that proteolytical clea1es chymotrypsinogen
d" incorrectK &amylase is not synthesized as zymogen
e incorrectK pancreatic lipase is not synthesized as zymogen
Q()E B. is correct: the amino acid arginine contains a positi*e charge in its side chain and is
#besides lysine( the clea*age site in proteins for trypsin
a" incorrectK asparagine side chain is not charged
b" correct+ clea1age at the carbo$yl site of the long+ positi1ely charged side chain
c" incorrectK glutamine side chain is not charged
d" incorrectK tryptophan has a bulky+ aromatic side chain
e incorrectK histidine side chains can be positi1ely charged but do not fit into trypsin pocket
Q()F a. A is correct: the fluidity of the plasma membrane is controlled by free cholesterol'
which buffers fluidity changes of fatty acids during temperature changes
b" incorrectK glucose transporters do not regulate the fluidity of the plasma membrane
c" incorrectK arachidonic acid in phospholipids will increase the fluidity"
d" incorrectK palmitic acid is less fluid than oleic acid
e" incorrectK cholesterol stiffens the plasma membrane at the polar head groups
Q()G a. A is the correct answer: the deficiency of sucrase and lactase due to se*ere
diarrhea are most li-ely the reason for her problems
b" incorrectK ,orthern :uropeans do not ha1e a strong genetic pre&disposition
c" incorrectK congenital lactase deficiency e$ists at birth and can lead to early death
d" incorrectK this is not a defect related to secretin or <<= deficiency
e" incorrectK lactose is clea1ed by lactase bound to the outside of intestinal mucosal cells
Q(3 B is correct: phenylalanine is an aromatic amino acid
a incorrectK a hydro$yl group is found in serine+ threonine or tyrosine
b" correct+ phenylalanine is used to form tyrosine in humans -hydro$ylation0
c" incorrectK a sulfhydryl group is found in cysteine
d" incorrectK phenylalanine is a dietary essential fatty acid
e" incorrectK branched&chain amino acids are 1aline+ leucine and isoleucine
Q(3) ! is correct: glutamate is decarboxylated to <ABA #aminobutyric acid(
a" incorrectK glycine is not decarbo$ylated
b" incorrectK tryptophan is first hydro$ylated+ and then serotonin is formed
c" correctK renaming as the former carbo$yl group is now carbon ()
d" incorrectK aspartate is not used to form /.>.+ does not ha1e carbo$yl group
e" incorrectK glutamine needs first to be deaminated to form glutamate
Q(33 ! is correct: the amino acid side chains are outside of the structure of an helix
a incorrectK the peptide bond cannot bend+ it has partial double&bond character
b incorrectK an &heli$ can change into a &pleated sheet+ as shown in the prion disease
c" correct+ side&chains can be used for tertiary structure
d incorrectK proline residues disrupt the formation of an &heli$ and force a bend
e incorrectK the &heli$ is found in both myoglobin and hemoglobin
Q(39 ! is correct: creatine -inase can be used to form AT= when it uses !r= and A)=
a incorrectK creatine kinase catalyzes a re1ersible reaction -unususal for a kinase0
b incorrectK it is not a serum injury marker for bone disease+ .8P is
c" correct+ at low .#P le1els+ <rP and .*P are used to form .#P by creatine kinase
d incorrectK <= has two different subunits -% and >0 and it consists of a dimer"
e incorrectK it is an early injury marker and back to baseline after 3 days
Q(34 ) is correct: disulfide bonds between two cysteine side chains are co*alent bonds. ,n
proteins they stabilize the tertiary structure.
a incorrectK the bonds between aspartate and lysine are nonco1alent ionic bonds
b incorrectK hydrogen bonds between serine and glutamate are nonco1alent bonds
c incorrectK 1an der 6aals forces found in the &heli$ are 1ery weak nonco1alent bonds
d. correct' disulfide bonds are not meant to be bro-en during conformational change
e incorrect+ hydrophobic forces between 1aline and isoleucine side chains are nonco1alent
Q(34 4. is correct: Line & is the line for a low concentration of a noncompetiti*e inhibitor.
Type of inhibition> A noncompetiti*e inhibition shows the same /m but
apparent 5max is smaller. Line & shows the same $1/m for all lines' and it shows a
changed $15max. The next ?uestion is' whether Line & represents a low or high
concentration of the inhibitor.
The uninhibited reaction shows the largest 5max which means a small number
for $15max on the yaxis and is represented by Line @. Line $ represents the highest
concentration of the inhibitor as the apparent 5max is the smallest' shown by a large
number of $15max on the yaxis.
a" incorrectK if no inhibitor is added+ then )DAma$ should be the smallest
b" incorrectK 8ine 3 is not the line for a competiti1e inhibitor"
c" incorrectK 8ine 3 is not the line of a high concentration of a noncompetiti1e inhibitor
d" incorrectK line 3 does not represent a competiti1e inhibition
Q(3! a. A is correct: the enzyme lysyl oxidase is needed for both' collagen and elastin
synthesis. ,t forms allysine residues and prepares co*alent crosslin-ing
b" incorrectK lysyl o$idase+ contains copper as cofactor+ not zinc
c" incorrectK it is an e$tracellular enzyme not found in fibroblasts
d" incorrectK lysyl o$idase can be defecti1e in :hlers&*anlos syndromes
e" incorrectK it does not act on pro&&chains of procollagen
Q(3E 4. is correct: crosslin-ing of collagen molecules uses lysine and allysine residues
a" incorrectK cross&linking takes place outside of fibroblasts
b" incorrectK disulfide bonds link propeptides of procollagen
c" incorrectK desmosine is used to cross&link elastin
d" incorrectK collagenase clea1es collagen molecules+ and does not cross&link collagen
e" <orrect+ cross&linking leads to tensile strength in fibril forming collagens
Q(3F ). is correct: alanine aminotransferase in the serum is a mar-er for li*er damage
a" incorrectK <reatine kinase %> is characteristic for heart infarction
b" incorrectK <reatine kinase %% is characteristic for skeletal muscle damage
c" incorrectK .mylase is characteristic for pancreatic disease
d" correct+ high concentration in li1er cytosol+ used with other markers
e" incorrectK 8*5&) is found in heart and I><+ li1er contains 8*5&4
Q(3G B. is correct: !ollagen and elastin contain lysine which is needed for e*entual co*alent
crosslin-ing.
a" incorrectK both contain glycine but it is not used for co1alent cross&links
b" correct+ both need lysyl o$idase to form allysine residues
c" incorrectK both contain proline but it forms hydrogen bonds in collagen&triple&heli$
d" incorrectK alanine is mainly found in elastin and is not used for cross&links
e" incorrectK cysteine is only used for cross&links in procollagen propeptides
Q(9 4. is correct: A lowdose of aspirin is used to reduce the amount of thromboxane
a" incorrectK acetylcholine esterase is inhibited by *;P
b" incorrectK the inhibition of <2M is irre1ersible+ e1en at low dose
c" incorrectK the acti1ity of prostacyclin is not reduced
d" incorrectK thrombo$ane is not chemically modified
e" correctK mature platelets cannot synthesize new <2M
Q(9)
B. is correct: cardiolipin is found in high concentration in mitochondria
a" incorrectK cardiolipin is found in all mitochondrial membranes
b" correct+ it is necessary in the inner mitochondrial membrane
c" incorrectK cardiolipin is not a major component of all biomembranes
d" incorrectK cardiolipin is a phospholipid that is not found in the plasma membrane
e" incorrectK it is a glycerophospholipid+ sphingomyelin is a sphingophospholipid
Q(93 B is correct: insulin induces -ey enzymes for fatty acid deno*o synthesis
a incorrectK glucagon+ not insulin+ induces key enzymes of gluconeogenesis
b" correct+ insulin signals high blood glucose le1els that need to be buffered
c" incorrectK the key enzyme of cholesterol synthesis is not degraded but induced instead
d" incorrectK insulin leads to dephosphorylated key enzymes of pathways
e" incorrectK protein phosphatases are acti1e after insulin action
Q(99 B is correct: the cur*e is sigmoidal due to the cooperati*e effect of the substrate
a" incorrectK Ama$ is also found for allosteric enzymes
b" correct+ the substrate is a homotropic effector for the allosteric enzyme
c" incorrectK it is shifted to the left
d" incorrectK ="4 B?C can be determined from the graph at half Ama$
e" incorrectK it shows first order and zero order kinetics
Q(94 4 is correct: The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase cannot form pyru*ate at high AA)B
le*els' as it needs for this direction AA)C as coenzyme
a" incorrectK it does not contain ;.* as prosthetic group
b" incorrectK it is a tetramer with 5 and % subunits
c" incorrectK it is in serum not an early %I marker+ it accumulates later
d" incorrectK prolyl hydro$ylase and lysyl hydro$ylase need 1itamin <
e" correct+ at high ,.*5 le1els lactate cannot be used for gluconeogenesis
Q(94 ) is correct: pancreatic phospholipase A& is e*entually degraded by digesti*e proteases
a" incorrectK trypsin performs the proteolytic acti1ation of prophospholipase .3
b" incorrectK pepsin has a p5 optimum of 3+ phospholipase acts at duodenal p5
c" incorrectN it is synthesized as zymogen in the pancreas+ not in the stomach
d" correctK digesti1e proteases will e1entual degrade all digesti1e enzymes
e" incorrectK it is released in its zymogen form by the pancreas
Q(9! ! is correct: !.T; is an example of an AB!transporter #chloride ion channel(
a" incorrectK ?/8# is in1ol1ed with secondary acti1e transport
b" incorrectK /8U#&) performs facilitati1e diffusion
c" correctK <;#I is an epithelial chloride ion channel in the plasma membrane
d" incorrectK /8U#&4 performs facilitated diffusion of fructose
e" incorrectK ,aJD=J&.#Pase performs primary acti1e transport
Q(9E B is correct: Bepatocytes contain a specific glucose transporter. This transporter is a
lowaffinity transporter
a" incorrectK /8U#&4 is insulin&dependent and found in fat cells and muscle
b" correct+ it is /8U#&3+ a low&affinity transporter with a large =t
c" incorrectK it is /8U#&3 which is also found e"g" in kidney+ &cells of pancreas
d" incorrectK /8U#&3 is not found in I><
e" incorrectK it is used in li1er for uptake of glucose and also for release of glucose
Q(9F ! is correct: =remature babies are often treated with lung surfactant which lines the
al*eoli of the lungs and pre*ents collapse
a" incorrectK it is a glycerophospholipid
b" incorrectK it is a specific phosphatidylcholine+ not a plasmalogen
c" correct+ it is mainly *PP< released by #ype II al1eolar cells
d" incorrectK it is the other way round+ mainly phospholipids and some proteins
e" incorrectK it does not contain arachidonic acid in its structure
Q(9G B is correct: The glucagon receptor allows the cA0= messenger system
a" incorrectK the receptor is found in the li1er but not in the kidney
b" correct+ it stimulates adenylate cyclase
c" incorrectK it does not acti1ate phospholipase <
d" incorrect+ it is found in the cell membrane of hepatocytes
e" incorrectK it binds only glucagon and not epinephrine
Q(4 ! is correct: !reatine phosphate is grouped as a highenergy compound
a" incorrectK it is not formed in the electron transport chain by cyt < o$idase
b" incorrectK creatine phosphate contains one energy&rich phosphoamide bond
c" <orrect+ it can be used to form .#P from .*P
d" incorrectK at high .#P le1els+ it can be formed by creatine kinase in cytosol
e" incorrectK it is formed from creatine and .#P+ inorganic phosphate is not used
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Scrumptious Paleo Desserts: Low Fat Low Cholesterol Dessert Recipes For A Healthy, Happy, Lean & Clean Eating LifestyleDa EverandScrumptious Paleo Desserts: Low Fat Low Cholesterol Dessert Recipes For A Healthy, Happy, Lean & Clean Eating LifestyleNessuna valutazione finora
- GI Practice Exam With AnswersDocumento3 pagineGI Practice Exam With AnswerskcpuffsNessuna valutazione finora
- 17case Questions Mnt4eDocumento5 pagine17case Questions Mnt4eapi-250448678Nessuna valutazione finora
- Max Gerson - The Gerson Therapy Has Proved EffectiveDocumento8 pagineMax Gerson - The Gerson Therapy Has Proved EffectiveFernando CordeiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Klenner Protocol For 2013Documento10 pagineKlenner Protocol For 2013jcoppala4476Nessuna valutazione finora
- (273453294) Fat BurnersDocumento27 pagine(273453294) Fat BurnersPablo SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide to a balanced diet and human digestive systemDocumento4 pagineGuide to a balanced diet and human digestive systemSaya MenangNessuna valutazione finora
- ASMPH YL5 Renal Module Small Group Discussion On Acid Base Balance Student's GuideDocumento2 pagineASMPH YL5 Renal Module Small Group Discussion On Acid Base Balance Student's GuideLiza MelendrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippe Ducrotté and Pierre Déchelotte Moïse Coëffier, Sophie Claeyssens, Bernadette Hecketsweiler, Alain LavoinneDocumento9 paginePhilippe Ducrotté and Pierre Déchelotte Moïse Coëffier, Sophie Claeyssens, Bernadette Hecketsweiler, Alain LavoinneMoonsferatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Newborn Jaundice Causes, Signs, TreatmentDocumento7 pagineNewborn Jaundice Causes, Signs, Treatmentr_ramos0759Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry CVSDocumento13 pagineBiochemistry CVSKalichandren ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento9 pagineUntitledaisha atikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Remarkable Recoveries From Severe Health ProblemsDocumento16 pagineRemarkable Recoveries From Severe Health ProblemsTrismegisteNessuna valutazione finora
- Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Diabetic Subjects: and Insulin Resistance in Lean, ObeseDocumento34 pagineRetinol-Binding Protein 4 and Diabetic Subjects: and Insulin Resistance in Lean, ObeseFernando Daniel Jinez MontesdeocaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocumento27 pagineGastrointestinal DisordersRI NA100% (5)
- GIT Lect A2Documento43 pagineGIT Lect A2Ayurveda PgNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetric Nursing: D. Side-Lying PositionDocumento11 pagineObstetric Nursing: D. Side-Lying PositionVOn Calda VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Digestion Absorption NASPGHANDocumento4 pagineProtein Digestion Absorption NASPGHANDahiru MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysphagia GIT GraceDocumento63 pagineDysphagia GIT GraceGrace KahonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Small Fasting GuideDocumento29 pagineRevised Small Fasting Guidemysticmaster49Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin A: Essential for Vision, Growth and ImmunityDocumento14 pagineVitamin A: Essential for Vision, Growth and ImmunityRamadhan OdiestaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 3Documento2 pagineCase Study 3api-305352286Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary ModuleDocumento10 paginePulmonary Moduleapi-242547654Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ma1910o Elijah Afresika Aduna - Practical Lesson 8 Part IIDocumento8 pagineMa1910o Elijah Afresika Aduna - Practical Lesson 8 Part IIMA1910o nii odoi pattersonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Form sp14 RepairedDocumento6 pagineNCP Form sp14 Repairedapi-251349687Nessuna valutazione finora
- MLS309 TutorialsDocumento16 pagineMLS309 TutorialsTAMBI TANYINessuna valutazione finora
- Management Nutrisi ICUDocumento8 pagineManagement Nutrisi ICUAgustinus BethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento41 pagineDiabetes Mellitusria_inairtifNessuna valutazione finora
- GIT Lect A2Documento45 pagineGIT Lect A2Aira Jill PadernillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion ReviewDocumento71 pagineDigestion ReviewParasakthi MNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions Class 11th Biology: Chapter 16 Digestion and AbsorptionDocumento12 pagineNCERT Solutions Class 11th Biology: Chapter 16 Digestion and AbsorptionsuryababaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestion & Absorption ProteinsDocumento44 pagineDigestion & Absorption ProteinsPutri Indah NirmalasariNessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento23 pagineTestParth sarthi Sen guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Drug Study KetoanalogueDocumento2 pagineComprehensive Drug Study KetoanalogueDolly Benitez100% (9)
- Case 13 Case StudyDocumento8 pagineCase 13 Case Studyklee100% (2)
- Importance of The Liver For HealingDocumento146 pagineImportance of The Liver For Healing3adrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 13 Medical Nutrition TherapyDocumento8 pagineCase 13 Medical Nutrition TherapykleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogenesis of acute pancreatitisDocumento7 paginePathogenesis of acute pancreatitisAnailil MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bile Acid Malabsorption May 2020Documento9 pagineBile Acid Malabsorption May 2020MUTHMAINNAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Karaganda Medical University Pathphysiology Submitted By: Uppal Prachi GROUP: 3001 Task 1Documento4 pagineKaraganda Medical University Pathphysiology Submitted By: Uppal Prachi GROUP: 3001 Task 1Prachi UppalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gastrointestinal Tract: صقن اهيب ةرضاحملا Cron disease Ulcerative colitis Lipase enzyme Calprotectin ليصافتDocumento31 pagineThe Gastrointestinal Tract: صقن اهيب ةرضاحملا Cron disease Ulcerative colitis Lipase enzyme Calprotectin ليصافتامجد حسين جواد كاظمNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice QuizDocumento82 pagineGastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice QuizZhailyn Joy DumlaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids in FoodsDocumento36 pagineAmino Acids in FoodsRueth AnnafeyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem Genetics USMLE Practice Questions (2 of 4)Documento13 pagineBiochem Genetics USMLE Practice Questions (2 of 4)MedSchoolStuff100% (2)
- DnlodDocumento43 pagineDnlod312887Nessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Diabetes and ComplicationsDocumento35 pagineManaging Diabetes and ComplicationsOmie TumanguilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan Section IDocumento17 pagineLesson Plan Section IAshly NygilNessuna valutazione finora
- Bile Metabolism and LithogenesisDocumento15 pagineBile Metabolism and LithogenesisJEFFERSON ANDRES MUÑOZ LONDOÑONessuna valutazione finora
- Vandenbraak2013 - CoagulaciónDocumento7 pagineVandenbraak2013 - CoagulaciónLeti PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Curriculum MCQ Pre-TestDocumento14 pagineNutrition Curriculum MCQ Pre-Testraanja2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lomer 2008 (Intolerancia A La Lactosa)Documento11 pagineLomer 2008 (Intolerancia A La Lactosa)michellevcfNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketoacidosis in A Non-Diabetic Patient: Clinical VignetteDocumento2 pagineKetoacidosis in A Non-Diabetic Patient: Clinical VignetteDr ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento20 pagineUntitledAbegail BerberNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care The Patient With Chronic Renal FailureDocumento8 pagineNursing Care The Patient With Chronic Renal FailuresetyawatikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erik Kata PengantarDocumento4 pagineErik Kata PengantarbayykumNessuna valutazione finora
- DM Practice QuestionsDocumento6 pagineDM Practice QuestionsSavanna ChambersNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancreatic Function TestsDocumento12 paginePancreatic Function TestsDhera CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Healthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasDa EverandHealthy Pancreas, Healthy You. Part 1: Structure, Function, and Disorders of the PancreasValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Paleo Diet, Shred Diet and Mediterranean Diet Made Easy: Paleo Diet Cookbook Edition with Recipes, Diet Plans and More: Paleo Diet Cookbook Edition with Recipes, Diet Plans and MoreDa EverandPaleo Diet, Shred Diet and Mediterranean Diet Made Easy: Paleo Diet Cookbook Edition with Recipes, Diet Plans and More: Paleo Diet Cookbook Edition with Recipes, Diet Plans and MoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5: Complement, EtcDocumento7 pagineLecture 5: Complement, EtcMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9: T-Lymphocyte ActivationDocumento5 pagineLecture 9: T-Lymphocyte ActivationMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6: B-Lymphocytes, EtcDocumento2 pagineLecture 6: B-Lymphocytes, EtcMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8: Adaptive ImmunityDocumento3 pagineLecture 8: Adaptive ImmunityMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 11/12: Inflammation and Wrap UpDocumento3 pagineLecture 11/12: Inflammation and Wrap UpMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3: MHC and HLADocumento2 pagineLecture 3: MHC and HLAMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1: Introduction To ImmunologyDocumento3 pagineLecture 1: Introduction To ImmunologyMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- B Cell Activation StagesDocumento2 pagineB Cell Activation StagesMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4: Specific Immunology: Antigen Binding Capacity of The Antibody Will DifferDocumento5 pagineLecture 4: Specific Immunology: Antigen Binding Capacity of The Antibody Will DifferMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityDocumento3 pagineLecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityMohit ModyNessuna valutazione finora
- HND Sector 2 Vol3-1Documento530 pagineHND Sector 2 Vol3-1mbabit leslieNessuna valutazione finora
- Flavonoides PDFDocumento18 pagineFlavonoides PDFmekaekNessuna valutazione finora
- Gpat - 2018 Question PaperDocumento14 pagineGpat - 2018 Question PaperKamalendu PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Enzymology: Enzyme Classification and NomenclatureDocumento27 pagineClinical Enzymology: Enzyme Classification and NomenclaturePatrick DazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy, Enzymes, and Catalysis Problem SetDocumento3 pagineEnergy, Enzymes, and Catalysis Problem SetRicha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Documento6 pagineBiochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Juren LasagaNessuna valutazione finora
- ThesisDocumento34 pagineThesisyugimotooNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs in Step 1Documento13 pagineDrugs in Step 1Zaraith Sanchez-Oviol PeareNessuna valutazione finora
- Revisiting The Enzymatic Kinetics of Pepsin Using Isothermal TitrationcalorimetryDocumento7 pagineRevisiting The Enzymatic Kinetics of Pepsin Using Isothermal TitrationcalorimetryIoana MoldovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFDocumento172 pagineComplete MCAT PracticePsgs FINAL3 PDFWollo NeftegnawNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Exam QuestionsDocumento7 paginePharmacology Exam QuestionsKenny TuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dehydrogenase Activity in The Soil EnvironmentDocumento28 pagineDehydrogenase Activity in The Soil EnvironmentluisiunesNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of An Extracellular Protease of Bacillus Megaterium DSM 319 As Depilating Aid of HidesDocumento6 pagineProperties of An Extracellular Protease of Bacillus Megaterium DSM 319 As Depilating Aid of HidesSarah Fitriani MuzwarNessuna valutazione finora
- MelanoidinDocumento5 pagineMelanoidinrayos100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology of Antiviral DrugsDocumento1 paginaPharmacology of Antiviral Drugssarah90222100% (1)
- ANS AND NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION REVIEWDocumento34 pagineANS AND NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION REVIEWWilliam StaffNessuna valutazione finora
- Rattan 2010Documento8 pagineRattan 2010Bere GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plants With Traditional Uses and Activities, Relevant To The Management of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Cognitive DisordersDocumento18 paginePlants With Traditional Uses and Activities, Relevant To The Management of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Cognitive DisordersRaquelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rocafort Et Al., 2020 Apoplastic Effector Proteins of Plant-Associated Fungi and Oomycetes PDFDocumento11 pagineRocafort Et Al., 2020 Apoplastic Effector Proteins of Plant-Associated Fungi and Oomycetes PDFJuan Muñoz CuellarNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectal Drug Delivery: A Promising Route For Enhancing Drug AbsorptionDocumento7 pagineRectal Drug Delivery: A Promising Route For Enhancing Drug AbsorptionDwi Puspita AyuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotransmitters in Brain and The DiseasesDocumento13 pagineNeurotransmitters in Brain and The DiseasesSharmila JeromeNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Biochemistry PracticeDocumento6 pagineEnzyme Biochemistry PracticealirezamdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry 7Th Edition Berg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento29 pagineBiochemistry 7Th Edition Berg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (11)
- Plant - Physiology - 5th Edition, Tazi, Zeiger-48-68Documento21 paginePlant - Physiology - 5th Edition, Tazi, Zeiger-48-68hairin yumeNessuna valutazione finora
- GANZON and OCCEÑA - Garcinia Binucao As AntidiabeticDocumento12 pagineGANZON and OCCEÑA - Garcinia Binucao As Antidiabeticleann ganzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Respiration Post-Lab ReportDocumento3 pagineCell Respiration Post-Lab ReportDaniel Seth AndalNessuna valutazione finora
- 9700 s09 Ms 4Documento11 pagine9700 s09 Ms 4ridafNessuna valutazione finora
- PatrickDocumento16 paginePatrickكسلان اكتب اسمي100% (2)
- Pipeline Cleaning and Batch Inhibition Treatment Using Pigs: Filming/Batching InformationDocumento2 paginePipeline Cleaning and Batch Inhibition Treatment Using Pigs: Filming/Batching Informationamin32Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atkins EnzimasDocumento5 pagineAtkins EnzimasConstanza Espinoza LaraNessuna valutazione finora