Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bariatric Surgery Copia para Pacientes
Caricato da
Carlita SantosDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bariatric Surgery Copia para Pacientes
Caricato da
Carlita SantosCopyright:
Formati disponibili
O
B
E
S
I
T
Y
The Journal of the American Medical Association JAMA PATIENT PAGE
Bariatric Surgery
M
illions of individuals in the United States and around the world
are overweight or obese (severely overweight). When weight
increases to an extreme level, it is called morbid obesity. Obesity
is associated with diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, some types of
cancer, and other medical problems. Bariatrics is the field of medicine that
specializes in treating obesity. Bariatric surgery is the term for operations to
help promote weight loss. Bariatric surgical procedures are only considered
for people with severe obesity (about 100 pounds overweight or a body
mass index greater than 40) and not for individuals with a mild weight
problem. The February 10, 2010, issue of JAMA includes an article about
laparoscopic (surgery performed through tubes) adjustable gastric banding
for severely obese adolescents. This Patient Page is based on one previously
published in the October 19, 2005, issue of JAMA.
OBESITY
FOR MORE INFORMATION
American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery
www.asmbs.org
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, BMI Calculator
www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/bmi/calc-bmi.htm
INFORM YOURSELF
To find this and previous JAMA Patient Pages, go to the Patient Page link on
JAMAs Web site at www.jama.com. Many are available in English and Spanish.
Janet M. Torpy, MD, Writer
Cassio Lynm, MA, Illustrator
Richard M. Glass, MD, Editor
576 JAMA, February 10, 2010Vol 303, No. 6
The JAMA Patient Page is a public service of JAMA. The information and recommendations
appearing on this page are appropriate in most instances, but they are not a substitute for
medical diagnosis. For specifc information concerning your personal medical condition, JAMA
suggests that you consult your physician. This page may be photocopied noncommercially
by physicians and other health care professionals to share with patients. To purchase bulk
reprints, call 312/464-0776.
The body mass index (BMI) is a standard way to define overweight, obesity,
and morbid obesity. The BMI is calculated based on a persons height and
weightweight in kilograms (2.2 pounds per kilogram) divided by the
square of height in meters (39.37 inches per meter). A BMI of 25 or more is
considered overweight; 30 or more, obese; and 40 or more, morbidly obese.
Bariatric surgery may be offered to patients with severe obesity when medical
treatments, including lifestyle changes of healthful eating and regular exercise,
have not been effective.
CONSIDERATIONS FOR BARIATRIC SURGERY
Individuals considering bariatric surgery must discuss risks and possible
benefits with their doctor. Bariatric surgery has associated risks and long-
term consequences and should be considered only one part of an approach
to treating obesity. Most bariatric surgeons think that the operations work
best when they help promote lifelong behavioral and dietary changes. Long-
term follow-up with doctors experienced in the care of patients having these
procedures, as well as lifelong vitamin supplementation, is essential to avoid
life-threatening complications.
Sources: American Society of Bariatric Physicians, American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery,
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, American Obesity Organization,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)
The size of the
stomach is
permanently reduced
to an egg-sized pouch.
The pouch is
reattached to a
2-foot-long tube of
intestine that bypasses
the stomach.
The amount of food
taken in is restricted by
the size of the pouch
and the size of the
connection of the
pouch to the intestine.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
The size of the opening
from the esophagus to
the stomach is reduced
by the gastric band,
decreasing the amount
of food that can be
comfortably eaten.
The surgeon can adjust
the size of the opening by
inflating or deflating the
band via an adjustment
port placed in the wall of
the abdomen just
underneath the skin. The
band can be removed
when desired.
Types of Bariatric Operations
Bariatric surgery can be performed using an open (an 8- to
10-inch incision in the middle of the abdomen) approach or
using a laparoscopic (several 12-to 2-inch incisions allowing
cameras and instruments to enter the abdomen) approach.
Esophagus
Pouch
Intestine
Path of
food
Adjustment
port
Intestine
Staples
Stomach
Stomach
Path of
food
Removal of most of
the stomach, turning
it into a narrow tube.
Outcomes from this
procedure have not
been well studied.
Portion of
stomach removed
Intestine
Path of food
Adjustable band
Remaining
stomach
Esophagus
Gastric Sleeve Resection
Staples
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bariatric Cookbook: Learn How To Manage Your Weight With Recipes That Are Easy To Prepare, High In Nutrients And Tasty At The Same TimeDa EverandBariatric Cookbook: Learn How To Manage Your Weight With Recipes That Are Easy To Prepare, High In Nutrients And Tasty At The Same TimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastric Sleeve Cookbook: Fluid and Puree: Effortless Bariatric Cooking, #1Da EverandGastric Sleeve Cookbook: Fluid and Puree: Effortless Bariatric Cooking, #1Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Bariatric SurgeryDocumento5 pagineBariatric SurgeryMiguelito JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- BariatricebookDocumento10 pagineBariatricebookapi-245566944Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bariatric Surgery in Relation To FertilityDocumento13 pagineBariatric Surgery in Relation To Fertilityapi-535065302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bariatric Operations For Management of Obesity: Indications and Preoperative Preparation - UpToDateDocumento14 pagineBariatric Operations For Management of Obesity: Indications and Preoperative Preparation - UpToDatemariescs23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity and Overweight PresentationDocumento20 pagineObesity and Overweight PresentationAmbreen AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Bariatric Surgery - Mayo ClinicDocumento1 paginaBariatric Surgery - Mayo Clinicpby5rw82ztNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastric Sleeve Diet: Step By Step Guide For Planning What to Do and Eat Before and After Your SurgeryDa EverandGastric Sleeve Diet: Step By Step Guide For Planning What to Do and Eat Before and After Your SurgeryNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Weight Loss Surgery: All You Need To Know Before And AfterDa EverandWhat Is Weight Loss Surgery: All You Need To Know Before And AfterNessuna valutazione finora
- Cirugia BariatricaDocumento9 pagineCirugia BariatricaedwardmenesesNessuna valutazione finora
- Morbid Obesity Is A Serious Health ConditionDocumento14 pagineMorbid Obesity Is A Serious Health ConditionCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNessuna valutazione finora
- Bariatric Surgery AlokDocumento75 pagineBariatric Surgery AlokAlok BhallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualwinifredmilcah4oo1100% (15)
- Dwnload Full Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual PDFjaydenpowellqt2100% (10)
- BariatricSurgery Dec 4Documento1 paginaBariatricSurgery Dec 4Manipal HospitalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Intervention For Bariatric Surgery Patients PDFDocumento98 pagineNutrition Intervention For Bariatric Surgery Patients PDFMayadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recipes for Life After Weight-Loss Surgery: Delicious Dishes for Nourishing the New YouDa EverandRecipes for Life After Weight-Loss Surgery: Delicious Dishes for Nourishing the New YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity: Differencial DiagnosisDocumento6 pagineObesity: Differencial DiagnosisclubsanatateNessuna valutazione finora
- Research EssayDocumento4 pagineResearch Essayapi-609557680Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case 2 Bariac SurgeryDocumento8 pagineCase 2 Bariac Surgeryapi-437425014100% (1)
- CURS NOU An 4 Chirurgie Bariatrica Timofte DanielDocumento51 pagineCURS NOU An 4 Chirurgie Bariatrica Timofte DanielLuca RoxanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Obesity: Ournal of Linical NcologyDocumento13 pagineManagement of Obesity: Ournal of Linical NcologyDjustiela KarrangNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal DindaDocumento6 pagineJurnal Dindachiendo ymNessuna valutazione finora
- BriatricDocumento5 pagineBriatricmago1961Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines Metabolic IndiaDocumento3 pagineGuidelines Metabolic Indiadrjohn232323Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperatwe Care of The Mtient With Morbid ObesityDocumento17 paginePerioperatwe Care of The Mtient With Morbid Obesityaza_docNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper On Weight Loss SurgeryDocumento4 pagineResearch Paper On Weight Loss Surgeryaflbsjnbb100% (1)
- Update On Office-Based Strategies For The Management of ObesityDocumento8 pagineUpdate On Office-Based Strategies For The Management of ObesityRalph Huebner BogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition in the Chemo Chair: From an Oncology Dietitian’s PerspectiveDa EverandNutrition in the Chemo Chair: From an Oncology Dietitian’s PerspectiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity ProjectDocumento10 pagineObesity Projectapi-385383966Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity Vs Diet ExerciseDocumento19 pagineObesity Vs Diet Exerciseapi-661465000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gastric Bypass Surgery by DR Nagi SafaDocumento6 pagineGastric Bypass Surgery by DR Nagi SafaDr Nagi SafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateDocumento17 pagineObesity in Adults - Overview of Management - UpToDateGabrielle AndersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver and Liver Transplant Program Nutrition GuidelinesDocumento15 pagineLiver and Liver Transplant Program Nutrition GuidelinesRobert G. Gish, MDNessuna valutazione finora
- Lit ReviewDocumento19 pagineLit Reviewapi-240895351Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 4th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 4th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual PDFdallosgemej100% (8)
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 4th Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 4th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualwinifredmilcah4oo1100% (18)
- Research Paper Final Draft 2Documento12 pagineResearch Paper Final Draft 2api-662079177Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity Presentation 4 Nov 17Documento79 pagineObesity Presentation 4 Nov 17AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Latest Surgical Procedures Required For The Treatment of ObesityDocumento3 pagineLatest Surgical Procedures Required For The Treatment of Obesityainamajid598Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ObesityDocumento9 pagineWhat Is ObesityAzean MohamadNessuna valutazione finora
- ObesityDocumento18 pagineObesityRawabi rawabi1997Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Updated Obesity StatisticsDocumento1 pagina2011 Updated Obesity StatisticsRocio OsunaNessuna valutazione finora
- 36 ObesityDocumento59 pagine36 ObesitySheikNessuna valutazione finora
- Counseling Patients On Bariatric Surgery For ObesityDocumento6 pagineCounseling Patients On Bariatric Surgery For ObesityMohamed EssallaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Management of ObesityDocumento13 pagineSurgical Management of Obesityمحمد حميدانNessuna valutazione finora
- The Surgical Management of ObesityDocumento110 pagineThe Surgical Management of ObesityArYa OPNessuna valutazione finora
- Klasifikasi ObesitasDocumento10 pagineKlasifikasi ObesitasJoyaa ShaloomNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity PPT (Mahla)Documento97 pagineObesity PPT (Mahla)kamlesh pariharNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity Screening Recommendations and Emerging Policies: Wanda NicholsonDocumento8 pagineObesity Screening Recommendations and Emerging Policies: Wanda NicholsonSalsabilla KimikoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical News Issue24 Managing Obesity Jul Sep 2017Documento40 pagineMedical News Issue24 Managing Obesity Jul Sep 2017Min Kaung KhantNessuna valutazione finora
- Patient Handbook Gastric Sleeve FinalDocumento62 paginePatient Handbook Gastric Sleeve Finalapi-36297638575% (4)
- Obesity Prevention and ManagementDocumento2 pagineObesity Prevention and ManagementElcana OtekiNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity Prevalence AmericaDocumento7 pagineObesity Prevalence AmericaKevin MulyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract Book IFSO 2014Documento373 pagineAbstract Book IFSO 2014Sarah LawrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- VIII 2018 OPTReport OPT4A 2.21.2019Documento3 pagineVIII 2018 OPTReport OPT4A 2.21.2019Debbie Ann MartirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento9 pagineDaftar PustakaDhian ZhahirahNessuna valutazione finora
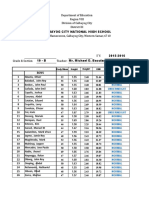
- After The Last Sheet.: Ronnie D. Caringal Canubing National High SchoolDocumento15 pagineAfter The Last Sheet.: Ronnie D. Caringal Canubing National High SchoolThea Margareth MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- BMI End ReportDocumento1 paginaBMI End ReportTrishia Mae PacleNessuna valutazione finora
- Popular Diets and Commercial Weight Loss Programs: Kimberly Gudzune, MD MPHDocumento48 paginePopular Diets and Commercial Weight Loss Programs: Kimberly Gudzune, MD MPHM woodhallNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ObesityDocumento2 pagineWhat Is ObesityAidil AlidanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition Debruyne Test BankDocumento31 pagineNutrition and Diet Therapy 9th Edition Debruyne Test Banktiffanynelsonqejopgnixy100% (33)
- Equations Jackson PollockDocumento3 pagineEquations Jackson PollockgaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Weight Loss Is HardDocumento8 pagineWeight Loss Is HardLUMINITA GIUCANessuna valutazione finora
- Let's Change Our Lifestyle: Activity 2: Healthy Food Habits Lead inDocumento5 pagineLet's Change Our Lifestyle: Activity 2: Healthy Food Habits Lead inInti FXNessuna valutazione finora
- Tackling Obesity in The Western WorldDocumento7 pagineTackling Obesity in The Western WorldAnh DucNessuna valutazione finora
- Weightloss Questionnaire 1Documento3 pagineWeightloss Questionnaire 1j.j0% (2)
- 22 M6 Check in Activity 2 1Documento2 pagine22 M6 Check in Activity 2 1Banana QNessuna valutazione finora
- Obesity FDocumento25 pagineObesity FRashmi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- KDSFC 1Documento1 paginaKDSFC 1OtisNessuna valutazione finora
- A.P.A FormatDocumento5 pagineA.P.A FormatGobinath SubramaniamNessuna valutazione finora
- BMIDocumento20 pagineBMIMichael Dulza BaculantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutritional Status ReportDocumento23 pagineNutritional Status ReportJada Kate SarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Documento1 paginaNutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Laarni Kiamco Ortiz EpanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sbfp-Forms-1,2,3 & Attendance QesDocumento14 pagineSbfp-Forms-1,2,3 & Attendance QesSarah Mae Sario MelegritoNessuna valutazione finora
- Weight ManagementDocumento36 pagineWeight ManagementAbdur RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- BMI-for-age GIRLS: Obesity OverweightDocumento2 pagineBMI-for-age GIRLS: Obesity OverweightRaemon Alexandro MauNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Child Growth StandardsDocumento10 pagineWHO Child Growth StandardsThiên Minh100% (1)
- Sindrom Metabolik Dr. IndahDocumento60 pagineSindrom Metabolik Dr. IndahdiahpermataNessuna valutazione finora
- Pengiraan Bmi Pelajar 2 Permai 1 Dan Penentuan Klasifikasi BmiDocumento2 paginePengiraan Bmi Pelajar 2 Permai 1 Dan Penentuan Klasifikasi BmisyaddadsarraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 205 LabDocumento4 pagineNCM 205 LabAlthea Meg MasicampoNessuna valutazione finora
- BMI ProcedureDocumento8 pagineBMI ProcedureFatma MegahedNessuna valutazione finora