Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
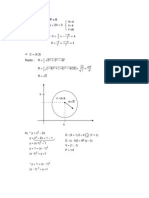
21 Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2x
Caricato da
SeanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
21 Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2x
Caricato da
SeanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
21
Linear Programming
1. (a)
0
y
x < 3
x = 3
x
(b)
0
2
4
y
y = 2x 4
y
2x 4
x
(c)
0
5
5
y
y = x + 5
y > x + 5
x
2. (a) y < 2x + 3
(b) y , x + 2
3. (a)
0
y
x = 3
y = 1
y = x
x
(b)
0
5
1
y
y = x + 5
y = x + 1
y = 2x
x
4. (a) y . 3, x , 2 and y < 2x
(b) y > 1, y , x and x + y < 6
(c) Equation of OA is y = 2x
Equation of OB is y =
1
2
x
Equation of CD is x + y = 6
Therefore, y < 2x, y >
1
2
x and x + y , 6.
(d) Equation of AB is y 3 =
3 1
2 4
(x 2)
y 3 = x + 2
y = x + 5
Equation of BC is y =
1
2 1
0 4
2
x + 2
y =
1
4
x + 2
Therefore, y x 1 < 0, y < x + 5 and
y >
1
4
x + 2.
5. (a) y . x
(b) y . 2x
(c) y x . 5
(d) y , x 2
(e) y < 2x
(f) y > 3x
(g) y < 2x
(h) x + 2y < 10
2
(i) 2x y > 8
(j)
x
y
<
3
4
4x < 3y
(k) y . 3x
(l) y < 4x 1
(m)
x
y
<
2
5
5x < 2y
(n) (2x + 3y) (x + y) , 4
x + 2y , 4
6. (a) (i) Maximum x = 4
(ii) Minimum y = 2
(iii) 2 < y < 4
(iv) The maximum value of x + 2y = 4 + 2(4)
= 12
The minimum value of x + 2y = 2 + 2(2)
= 6
(b) (i) Maximum x = 3
(ii) Minimum y = 0
(iii) 1 < y < 5
(iv) The maximum value of x + 2y = 2 + 2(5)
= 12
The minimum value of x + 2y = 0 + 2(0)
= 0
(c) (i) Maximum x = 4
(ii) Minimum y = 2
(iii) None
(iv) The maximum value of x + 2y = 3 + 2(4)
= 11
The minimum value of x + 2y = 4 + 2(2)
= 8
7. (a) x > 8, y < 2x, 0.5x + 0.4y < 20
5x + 4y < 200
0
20
30
40
50
10
x
x + y = 10
x = 8 y = 2x
5x + 4y = 200
y
10
(16, 30)
30 20 40
(b) Total number of fruits = x + y
(c) (i) Maximum number of fruits bought
= 16 + 30
= 46
(ii) The range of number of oranges
= {y : 0 < y < 26, y [ w}
(iii) The range of number of apples
= {x : 8 < x < 40, x [ w}
(iv) Cost = 0.5x + 0.4y
The total cost spent = 0.5(20) + 0.4(25)
= 10 + 10
= RM20.00
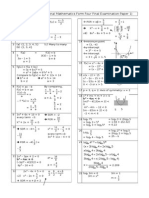
1. (a) I: 30x + 30y < 540
3x + 3y < 54
II: 40x + 30y > 480
4x + 3y > 48
III:
x
y
>
1
2
2x > y
(b)
0
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
2
x
2x + y = 2
y = 2x
4x + 3y = 48
3x + 3y = 54
y
R
2 6 4 8 10 12 14 16 18
(c) (i) Maximum number of cake A produced is
8
(ii) Prot = 2x + y
Minimum prot = 2(5) + 10
= RM20.00
3
2. (a) x + y > 100, y < 2x, y + 3x < 240
(b)
0
40
60
80
100
20
x
120x + 140y = 1680
y = 2x
x + y = 100
y + 3x = 240
y
R
20 60 40 80 100
(c) (i) When y = 45, the maximum value of x = 65
and the minimum value of x = 55
(ii) Charges = 120x + 140y
The maximum charges paid
= 120(48) + 140(96)
= RM19 200
3. (a) x + y < 80, x < 3y, x y < 10
(b)
0
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
10
x
40x + 20y = 400
x = 3y
x + y = 80 x y = 10
y
R
10
30 20 40 50 60 70 80
(c) (i) If the number of students for subject
P is 20, then the range for subject C is
10 < y < 60.
(ii) Fees = 40x + 20y
The maximum total fees per month
= 40(45) + 20(35)
= 1800 + 700
= RM2500
4. (a) x + y < 30, x > 2y, 40x + 50y < 1000
(b)
0
10
15
20
25
30
5
x
40x + 50y = 1000
x = 2y
x + y = 30
y
R
5
15 10 20 25 30
(c) When Mr Tan buys 5 basketballs, the maximum
amount for volleyballs is 18.
The minimum amount of money left
= 1000 [40 18 + 50 5]
= RM30
1. (a) x < 80, y < 60, x + y . 30
4
(b)
0
20
40
30
50
60
10
x
20x + 10y = 200
y = 60
x = 80
5x + 2y = 100
x + y = 30
y
R
30 20 10 50 40 60 70 80
(c) (i) Cost for a piece of alloy = 20x + 10y
The minimum cost of production
= 20(1) + 10(30)
= RM320
(ii) Prot = 5x + 2y
Maximum prot = 5(80) + 2(60)
= RM520
2. (a) x > 45, y . 40, x + y > 90
(b)
0
20
40
30
50
60
70
80
90
10
x
y = 40
x + y = 90
x = 45
y
30 20 10 50 40 60 70 80 90
(c) (i) 50 ways
(ii) 10 ways
3. (a) x + y < 200,
x
y
<
1
8
, that is, 8x < y
100x + 500y > 10 000, that is, x + 5y > 100
(b)
0
100
200
150
50
x
y = 8x
x + y = 200
100x + 50y = 2500
x + 5y = 100
y
R
150 100 50 200
(c) (i) 160 < y < 180
(ii) Prot = 100x + 50y
The maximum prot = 100(22) + 50(178)
= RM11 100
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Solving Quadratic and Cubic EquationsDocumento1.201 pagineSolving Quadratic and Cubic EquationsPANDRANKI VENKATESHNessuna valutazione finora
- Coll. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Documento546 pagineColl. - Success One HSC Physics 2017 (2017, Pascal Press)Sean100% (2)
- The Four Humor Mechanisms 42710Documento4 pagineThe Four Humor Mechanisms 42710Viorel100% (1)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDa EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNessuna valutazione finora
- USAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)Documento295 pagineUSAF Electronic Warfare (1945-5)CAP History LibraryNessuna valutazione finora
- ME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetDocumento2 pagineME2142E Feedback Control Systems-CheatsheetPhyo Wai Aung67% (9)
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Documento53 pagineSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 6Sean75% (4)
- Instructional Module Training PlanDocumento5 pagineInstructional Module Training Planapi-246767803100% (1)
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Documento22 pagineSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Sean71% (7)
- Varying ViewsDocumento5 pagineVarying Viewsforevertay2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 AflareatermenuluinecunoscutDocumento12 pagine1 Aflareatermenuluinecunoscutancaana8457Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDa EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2 AnswersDocumento4 paginePaper 2 AnswersSean100% (1)
- Cls.5 - Factor Comun - Fisa - 2Documento1 paginaCls.5 - Factor Comun - Fisa - 2gefinnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge C1 Advanced Exam Overview PDFDocumento1 paginaCambridge C1 Advanced Exam Overview PDFrita44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xDocumento5 pagineLinear Programming: y X 3 y y X + 1 y 2xShwe WenNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Programming OptimizationDocumento5 pagineLinear Programming OptimizationSyed NazmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Paper 1Documento9 pagineMathematics Paper 1James LusibaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jawapan Modul 21Documento10 pagineJawapan Modul 21Nur SabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 5: Chapter 21 (Linear Programming) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocumento4 pagineForm 5: Chapter 21 (Linear Programming) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsruvenvishaliNessuna valutazione finora
- B7c7e f4 Math Chapter 1 Solution - DoneDocumento4 pagineB7c7e f4 Math Chapter 1 Solution - Doneforyourhonour wongNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Gain - Maths f4Documento48 pagineTop Gain - Maths f4Menaka SundramNessuna valutazione finora
- Matematik Pengurusan - Bab 9Documento4 pagineMatematik Pengurusan - Bab 9Mardi UmarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 IQM Suggested AnswersDocumento10 pagine1.4 IQM Suggested AnswersCollen MahamboNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Group5Documento27 pagineCalculus Group5VictoriaReyes_Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 5.3 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsDocumento6 pagineExercise 5.3 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- CE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Documento5 pagineCE Maths 2009 Paper1 (ANS)Mok Sze Nga100% (1)
- Nabila Awalia - 1906403572 - Tugas Sesi 9Documento7 pagineNabila Awalia - 1906403572 - Tugas Sesi 9Nabila AwaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- G Cen Tre: SSC Mock Test - 102 (Solution)Documento8 pagineG Cen Tre: SSC Mock Test - 102 (Solution)Mayank GuptNessuna valutazione finora
- bbmp1103 Sem 2Documento13 paginebbmp1103 Sem 2irisardellaNessuna valutazione finora
- DERIVATIVESDocumento3 pagineDERIVATIVESheynuhh gNessuna valutazione finora
- DERIVATIVESDocumento3 pagineDERIVATIVESheynuhh gNessuna valutazione finora
- DerivativesDocumento3 pagineDerivativesheynuhh gNessuna valutazione finora
- Matematika TugasDocumento6 pagineMatematika TugasEnzo KeenamNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 2&3Documento3 pagineExercise 2&3Nabeel AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 AflareatermenuluinecunoscutDocumento5 pagine1 AflareatermenuluinecunoscutLIANA POPNessuna valutazione finora
- SOAL INTEGRAL BAB 2Documento29 pagineSOAL INTEGRAL BAB 2Muhammad BurhannzNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluacion Profesor GuillermoDocumento8 pagineEvaluacion Profesor GuillermolisisficeNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - Test Integral - Razonamiento Matemático SolucionarioDocumento16 pagine06 - Test Integral - Razonamiento Matemático SolucionarioRenzo_Flores_M_4665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Checkpoint 4.3 Conic SectionDocumento8 pagineCheckpoint 4.3 Conic SectionMUHAMMMAD LUQMAN IMRAN BIN AMIRNessuna valutazione finora
- DSC1520 2013 S1 Students Assignment 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineDSC1520 2013 S1 Students Assignment 2 PDFKhathutshelo KharivheNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving quadratic equations and maximizing profitDocumento10 pagineSolving quadratic equations and maximizing profitJessica Chumpitaz MozombiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Emcet Bits PDFDocumento7 pagineEmcet Bits PDFPaladugurevanth40% (5)
- 35 - ch5-COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS PDFDocumento15 pagine35 - ch5-COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS PDFLohith LoliNessuna valutazione finora
- Math QTR 2 - Module 2Documento3 pagineMath QTR 2 - Module 2REN OFFICIALNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Polynomial Equations and Finding Integer RootsDocumento64 pagineSolving Polynomial Equations and Finding Integer RootsMontse NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 S4 MYE IM1 Solutions Matrix EquationsDocumento2 pagine2014 S4 MYE IM1 Solutions Matrix EquationsmiaowNessuna valutazione finora
- Expanding Brackets and Solving 10pn3Documento12 pagineExpanding Brackets and Solving 10pn3Anna ElkinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cape Pure MathDocumento2 pagineCape Pure MathFabio LayneNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental MathsDocumento1 paginaMental Mathsamol.perkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mat Minat Padahal Ra MinatDocumento3 pagineMat Minat Padahal Ra MinatNeti Umi LatifahNessuna valutazione finora
- © Praadis Education Do Not Copy: Exercise 2.5Documento19 pagine© Praadis Education Do Not Copy: Exercise 2.5A MANIMARAN manimaran.shNessuna valutazione finora
- Syde114 Solutions 1Documento7 pagineSyde114 Solutions 1AzeemAnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic expressions simplifiedDocumento5 pagineAlgebraic expressions simplifiedMy fluffy MochiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 5Documento10 pagine2 5Shanthosh .sNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic Expressions and Solving EquationsDocumento5 pagineAlgebraic Expressions and Solving EquationsMy fluffy MochiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus Exercise Solutions with Step-by-Step WorkingsDocumento2 pagineCalculus Exercise Solutions with Step-by-Step WorkingsFakhar AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- 初二07e 温习Documento17 pagine初二07e 温习joshua chewNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCIONESDocumento27 pagineFNCIONESmam2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answers (2006 Additional Mathematics Form Four Final Examination Paper 1) 1Documento6 pagineAnswers (2006 Additional Mathematics Form Four Final Examination Paper 1) 1casbenxNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.2Documento5 pagineUnit# 5 Factorization Exercise # 5.2Asghar AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of FactoringDocumento3 pagineTypes of Factoringyin yinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 I Quadratic Expressions ENHANCEDocumento12 pagineChapter 10 I Quadratic Expressions ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Assignment 01Documento19 pagineMatlab Assignment 01Muhammad Irfan MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper KDocumento3 pagine© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper KPa GesNessuna valutazione finora
- For MuleDocumento7 pagineFor MuleGroze LarisaNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 SM - Ch07Documento26 pagine09 SM - Ch07Ashish BhallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Axis of An Unsymmetrical Beam and Moment of InertiaDocumento4 pagineAxis of An Unsymmetrical Beam and Moment of Inertiazrie premesNessuna valutazione finora
- 128 Type Math For SSCDocumento35 pagine128 Type Math For SSCetceterashahriar hqNessuna valutazione finora
- 6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2Documento18 pagine6093 - w18 - w21 - QP - 03 - Question 2SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1Documento5 pagine2021 Kedah Fizik MPAT Paper 1SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH - 4 - Part IIDocumento16 pagineCH - 4 - Part IIBAHARUDIN BURAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocumento6 pagineSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemDocumento8 pagineChallenge 2021 - Smart Car SystemSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocumento10 pagineSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- UCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020Documento21 pagineUCSI University 33RD CONVOCATION CEREMONY YEAR 2021 - Convocation Details - 31.12.2020SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- CAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5Documento1 paginaCAIE 9709 03 ComplexNumber M/J2008/Q5SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDocumento2 pagine964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH - 4 - Part IIIDocumento19 pagineCH - 4 - Part IIIBAHARUDIN BURAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocumento5 pagineSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH - 4 - Part IDocumento12 pagineCH - 4 - Part IBAHARUDIN BURAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverDocumento5 pagineHomeostasis: S14.1 Structure of The LiverSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsDocumento10 pagineSolution Manual: Static Magnetic FieldsSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 4551 w19 QP 03Documento16 pagine4551 w19 QP 03SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocumento18 pagineCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biologi K2 SPM 2019 PDFDocumento34 pagineBiologi K2 SPM 2019 PDFfd bdbbn fjfbNessuna valutazione finora
- Co Co: U-Trac U-TracDocumento25 pagineCo Co: U-Trac U-TracSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFDocumento5 pagineTutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFDocumento5 pagineTutorial - Lesson 7 Solution PDFSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Nov p11, 21Documento73 pagine2017 Nov p11, 21SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Documento25 paginePhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Documento24 paginePhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P3Documento25 paginePhysics H2 9749 Specimen P3SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeDocumento21 paginePhysics H2 9749 Specimen P1 MarkschemeSeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics H2 9749 Specimen P2Documento24 paginePhysics H2 9749 Specimen P2SeanNessuna valutazione finora
- Leader 2Documento13 pagineLeader 2Abid100% (1)
- What Is A Political SubjectDocumento7 pagineWhat Is A Political SubjectlukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and RecommendationsDocumento68 pagineSummary and Recommendationssivabharathamurthy100% (2)
- The STP Guide To Graduate Student Training in The Teaching of PsychologyDocumento101 pagineThe STP Guide To Graduate Student Training in The Teaching of PsychologyNeilermindNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilingual Language Development TypesDocumento29 pagineBilingual Language Development Typesirish delacruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Wave Hydro Dynamics Prof. V. Sundar Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocumento32 pagineWave Hydro Dynamics Prof. V. Sundar Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasMuralidhar YarakalaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Report On T&D by IbrahimDocumento17 pagineA Report On T&D by IbrahimMohammed IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia HistoryDocumento4 pagineStandard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia Historyjeffmiller1977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution To Information TheoryDocumento164 pagineSolution To Information Theorynbj_133% (3)
- COM295r3 Communication Process WorksheetDocumento2 pagineCOM295r3 Communication Process Worksheetfa1therrNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and ConditionDocumento10 pagineScheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and ConditionwicvalNessuna valutazione finora
- 7949 37085 3 PBDocumento11 pagine7949 37085 3 PBAman ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Background and Introduction of The ProblemDocumento48 pagineBackground and Introduction of The ProblemElizebethNessuna valutazione finora
- Biologicalisation - Biological Transformation in ManufacturingDocumento32 pagineBiologicalisation - Biological Transformation in ManufacturingGuillermo AvilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDocumento8 pagineSynthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDipteemaya BiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseDocumento2 pagineSPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseJessica NgNessuna valutazione finora
- INGLESDocumento20 pagineINGLESNikollay PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section I - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocumento2 pagineMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section I - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationMu ClasNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Pre Processing in WEKADocumento5 pagineData Pre Processing in WEKAPrashant SunejaNessuna valutazione finora
- (Genus - Gender in Modern Culture 12.) Segal, Naomi - Anzieu, Didier - Consensuality - Didier Anzieu, Gender and The Sense of Touch-Rodopi (2009)Documento301 pagine(Genus - Gender in Modern Culture 12.) Segal, Naomi - Anzieu, Didier - Consensuality - Didier Anzieu, Gender and The Sense of Touch-Rodopi (2009)Anonymous r3ZlrnnHcNessuna valutazione finora
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocumento22 pagineDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationPachyiappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lpi - 101-500Documento6 pagineLpi - 101-500Jon0% (1)
- SINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONDocumento5 pagineSINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNessuna valutazione finora
- Detection of Self-Mutating Computer VirusesDocumento17 pagineDetection of Self-Mutating Computer VirusesVMads3850Nessuna valutazione finora