Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lesson Plan 1 Introuduction To Linux
Caricato da
api-249493790Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lesson Plan 1 Introuduction To Linux
Caricato da
api-249493790Copyright:
Formati disponibili
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
1
1. Curriculum Analysis
1.1. Course Information
The department of this course is Communication Techniques. The major is
communication. In this course, we will learn about operating system which is the
course title. The code of this course is CMP 210. The previous or the Prerequisites
course code is CMP101. This course has three hours of lecture, two hours of
workshop and it does not have an hour of tutorial.
1.2. Course Description
This course covers an introduction to LINUX operating system, commands or
important commands, the file system in LINUX and creating files and directions.
1.3. Course Prerequisite
CMP 101 ( Introduction to computer application)
1.4. General Goal:
The goal of this course is to help students and give them an introduction to LINUX
operating System and give them the most important commands that used to operate
the system
1.5. Specific Objective
1. Understand the basics of the LINUX.
2. Work on the Command Line.
3. Display the files system in LINUX.
1.6. Unit
Introduction to LINUX operating system
What is LINUX?
Compering between LINUX and Windows
After this unit the students are able to understand the general idea about LINUX and
they will able to compare between LINUX and other operating systems.
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
2
2. Content Analysis
2.1. Introduction
After finish and understand the previous course which is introduction to computer
application the trainees are able to understand LINUX operating system but first what
is operating system?
An operating system is the chef program that manages all hardware and software. It
has control of every process, file, section of memory and device. The operating
system is an important thing that make sure both software and hardware are working
fine and interact quickly.
In the operating system there are four central manager and they all work like the team
to get job or process complete it. The operating system is like the boss of central
manager and it make sure that all of them work harmony.
Operating
System
Memory Manager
Process Manager
File Manger
Device Manger
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
3
2.2. What is Linux?
LINUX is a UNIX-based operating system. Its original creator was a Finnish student
name Linus Torvalds, although being open source it has change a great deal since its
original conception. Any changes to it are open for all to adopt. it is the powerful from
others operating system because it's difficult for beginning for any person. Than
comparing.
2.3. Different Between Linux and Windows Operating System
Security is for Linux because is for professional.
Free to download is for Linux because a few people to download it for
working for example big a company.
Windows is easier to use it than Linux.
When you want to learn Linux OS it takes long time because it opposed of
Windows.
You can improve and development Linux because it's open source.
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
4
2.4. Advantages and disadvantages of Linux operating system:
Advantages:
1. open source:
Means you can develop it by yours because it does not belong anybody.
2. cost (free to download ):
It is not like windows to buy it to install it in your computer. Linux, you can
download it in internet to your computer.
Disadvantages:
1. High cost (learning):
It's not easy to learn it so in this situation you have to bring someone
professional to learn you.
2. Time :
It will take from you long time to learn it.
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
5
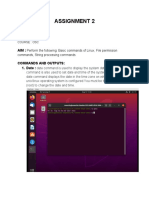
2.4. Example of Linux
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
6
3. Didactic Analysis
Didactic principle of motivation and reduction
First, we would like to start by showing a video about introduction to operating
system (Inductive Approach), this way of teaching is Didactic Principle of motivation
because we want to make or lesson interesting. Then, we will ask trainees about what
they saw. After that, we will link one of specific objective ( understand the basic of
the Linux operating system) due to this introduction to Operating System. We use the
vertical way of didactic reduction because our subject needs 6 hours to cover it so we
reduce it to 50 min of teaching.
Didactic principle of vividness, securing information and motivation
Next, we will distribute a worksheet to the trainees about our lesson, so they can
follow us during our teaching. After that we will use classroom conversation method
by asking the trainees to define Linux Operating System. The trainees will find the
definition of Linux Operating System on the power point and they should write it
down on their worksheet this way keep our information in their mind.
Didactic principle of vividness and securing information
After that, we will show them the different between Linux Operating System and
Window Operating System and we will use classroom conversation method and
power point to discuss it and also show the reason on the power point.
Didactic principle of motivation, self-activity and vividness.
We will bring big sheets and marker with us to distribute it to trainees to make group
work about Advantages and Disadvantages of Linux Operating System. After that, we
will make a challenge between them which the best group make a good reason about
what they did and. Each group will present their work in the white board and we will
give the best group a good gift.
Didactic principle of vividness
We will show the trainees video about example of Linux Operating System.
Didactic principle of securing information
At the end of the lesson, we will ask the trainees some specific question that covers
each part in the lesson. We will give the feedback by answering these question. We
did this way because we want to see how the trainees understood our lesson.
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
7
DEPARTEMENT: Communication Techniques
SUBJECT: Linux Operating System
AVP-2
I General Information
o Topic: Linux Operating System
o Name: Mohammed Ibrahim Mujalli 202332116
o Name: Osama Saeed Bafaqeeh 202332107
o Name: Zeyad Mohammed Binaqeel 202332120
o Date: 29/10/2013
II Objectives
General Objectives:
The Trainees
1. Interact with the trainer (Affective)
2. Listen to each other (Affective)
3. Interesting in the lesson with trainees (Affective)
4. Discusses together and presenting own opinion (Affective)
Specific Learning Objectives:
The Trainees
1. Describe what is Linux? (Cognitive, Reorganization)
2. Distinguish between Linux and other operating system
(Cognitive, Transfer)
3. List 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of a Linux
(Cognitive, Reproduction)
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
8
III Overview of the Intended Process
Opening /Entrance/Motivation Methodology Media Time
Expected Trainer-action Expected Trainee-action Minut
es
-The trainer starts the lesson by greeting.
-The trainer will take attends list for the
trainees (107)
-The trainer shows the trainees short
video about introduction to operating
system and after they seeing the video he
will discuss about what they saw
(107) (120)
-The trainer will give the trainees work
sheets to write the important information
for them and also to follow us. (107) (116)
-The trainer will ask the trainees what is
Linux OS? (107) (120)
-The trainer explains what Linux OS is.
(107)
-The trainees will respond the trainer.
-The trainees will see the video and they
will write some notes and discuss with
the trainer about what they saw
-The trainees will write the important
information and also to write what they
saw.
-The trainees will take attention with
trainer and some of them maybe they
will answer the question also they will
find all what the need from what is
Linux? And they will take some notes
-Inductive
approach.
-Discovery
-Classroom
Conversation
-Classroom
Conversation.
-Lecture
-Video
-Projector
PPT
Slides
3-4
5
5
5
Body(Information/Elaboration) Methodology Media Time
Expected Trainer-action Expected Trainee-action Minutes
-The trainer will show the trainees the
different between Linux and Windows
Operating System (116) (120)
-The trainer will give the trainees a
group work of three trainees for each.
Then the trainer will give them a few
minutes to search in the internet about
advantages and disadvantages about
Linux OS. Before that trainers will
give trainees big sheets to write on it
-The trainer will take notes
during the trainer
explanation.
-The trainees will make a
group of two and they will
search and discuss about
it.
-Lecture.
-Classroom
conversation
-Group work
-Classroom-
-Projector
-whiteboard
PPT
Slide
5
5
10
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
9
to write their result on the whiteboard
(107) (116)
-The trainer will let the trainees
explain about what their found.
(107) (116)
-The trainer will explain the main
advantages and disadvantages on the
whiteboard. (116)
-The trainees will discuss
it
with trainer on the white
board and show their
result
-The trainees will take
notes during the
explanation of the trainer
conversation
-Classroom
Conversation
.
-Whiteboard.
Projector.
PPT
Slide
6
5
5
-The trainer will show the trainees a
short video about an example of
Linux System.
(116) (120)
-The trainees will see the
video and discuss
-Classroom-
conversation
-Discovery
-Projector.
PPT
Slide
7
-Video
6
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
11
Close (Reflection, Exercises, Homework, Feedback) Methodology Media time
Expected Trainer-action Expected Trainee-action Minutes
-The trainer asks the trainees about what
we did in the whole lesson, the video and
so on.
-Describe what is Linux? (107)
-Distinguish between Linux and other
operating system. (116) (120)
- List 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of
a Linux (107)
-The trainees will interact with the
trainer and answer the questions
-Classroom
conversation
Projector
PPT
Slide
8
4
IV Applied Didactic Principles:
o Didactic principle of reduction by using vertical reduction to reduce our
lesson.
o Didactic principle of motivation by showing a video.
o Didactic principle of vividness, securing information and motivation by
distributing worksheets.
o Didactic principle of vividness and securing information by seeing a clear
table of comparing between Linux and Widows operating system.
o Didactic principle of motivation, self-activity and vividness by doing a group
work.
o Didactic principle of vividness by seeing a video.
o Didactic principle of securing information by asking a question.
29/10/2013 TRTS-1 AVP-2
11
V Reverences:
o http://www.techlila.com/introduction-linux-operating-system/
o Beginning Ubuntu Linux from Novice to Professional book
o Linux for Dummies book
o CompTIA Linux+ book
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Unit 15 AssignmentDocumento13 pagineUnit 15 Assignmentapi-339083063100% (4)
- Microsegmentation Architectures A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandMicrosegmentation Architectures A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Linux Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineLinux Lesson PlanmaitcptNessuna valutazione finora
- Boano Thesis 2009Documento172 pagineBoano Thesis 2009cjwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Certified Network Professional CyberOps A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandCisco Certified Network Professional CyberOps A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Hands On Contiki OS and Cooja Simulator: Exercises (Part II)Documento15 pagineHands On Contiki OS and Cooja Simulator: Exercises (Part II)Vassilios KotsiouNessuna valutazione finora
- Linux CommandsDocumento7 pagineLinux CommandsBharath ThambiNessuna valutazione finora
- SDNRG Nemo API For Intent Driven Nets Ietf 91Documento20 pagineSDNRG Nemo API For Intent Driven Nets Ietf 91sinansarmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Congestion ManagementDocumento15 pagineNetwork Congestion Managementcarlos_lopez_gordoNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 CSA Assignment QuestionsDocumento3 pagine01 CSA Assignment QuestionsSurendran RmcNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Linux: Core & Advanced Drafted By: Abhishek RoshanDocumento46 pagineIntroduction To Linux: Core & Advanced Drafted By: Abhishek RoshanKarthika TatiparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Windows Deployment Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandWindows Deployment Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Spiral Model Mthandy AssignmentDocumento6 pagineWhat Is The Spiral Model Mthandy AssignmentPeace Runyararo MutenderiNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Time Operating System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandReal Time Operating System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Hat Certified Architect A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandRed Hat Certified Architect A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Simulation Using OPNETDocumento16 pagineNetwork Simulation Using OPNETTema HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Packet Tracer TipsDocumento17 pagineCisco Packet Tracer TipsAyan ChakravortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Internet: A Glimpse into the Building Blocks, Applications, Security and Hidden Secrets of the WebDa EverandUnderstanding the Internet: A Glimpse into the Building Blocks, Applications, Security and Hidden Secrets of the WebNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Top Linux Interview Q&A PDFDocumento10 pagine1.1 Top Linux Interview Q&A PDFmaheshsekar25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thin ClientDocumento23 pagineThin ClientDevender Rohilla0% (1)
- LAN RedundancyDocumento33 pagineLAN RedundancyJoseph Al BayonasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Packet Tracer ProjectsDocumento4 pagineCisco Packet Tracer ProjectsAlmysariNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento31 pagineAssignment 2SALIM TADVINessuna valutazione finora
- Infrastructure As A Code A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDa EverandInfrastructure As A Code A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 OS - PPT Compatibility ModeDocumento33 pagine6 OS - PPT Compatibility ModeBagus FatkhurroziNessuna valutazione finora
- The Comprehensive Guide To SNMPDocumento22 pagineThe Comprehensive Guide To SNMPreajNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Remote Desktop ConnectionDocumento5 pagineWhat Is A Remote Desktop ConnectioncolleebNessuna valutazione finora
- High Availability Guide PDFDocumento63 pagineHigh Availability Guide PDFhaffez23100% (1)
- CCNA Security Chapter 1 AssessmentDocumento5 pagineCCNA Security Chapter 1 Assessmentp6aes2008100% (2)
- Cisco Aicte Internship: How To Create and Submit Project On Packet Tracer Project Submission Last Date: 3-JUL-2022Documento43 pagineCisco Aicte Internship: How To Create and Submit Project On Packet Tracer Project Submission Last Date: 3-JUL-2022AyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 TestingDocumento11 pagineChapter 7 TestingHarsh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento5 pagineAssignment 1Parker Bollinger IIINessuna valutazione finora
- HSN SolutionDocumento65 pagineHSN SolutionmuthuramrrNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Systems Characterization and DesignDocumento35 pagineDistributed Systems Characterization and DesignkhoadplaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento7 pagineCase StudyÀüsåf MûghãlNessuna valutazione finora
- Datacomm Lab1 Osi Layer ModelDocumento2 pagineDatacomm Lab1 Osi Layer ModelJojo CansinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Multimedia in Embedded Linux GuideDocumento75 pagineMultimedia in Embedded Linux Guidedenkins2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCS-034 Solved AssignmentsDocumento30 pagineMCS-034 Solved AssignmentsAbhinand Rajeev SNessuna valutazione finora
- Professionalpracticesi N Information Technology: HandbookDocumento8 pagineProfessionalpracticesi N Information Technology: HandbookHaseeb ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- CentOS 8 Essentials: Learn to Install, Administer and Deploy CentOS 8 SystemsDa EverandCentOS 8 Essentials: Learn to Install, Administer and Deploy CentOS 8 SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- 32524L&R - Case Study - 2011ADocumento9 pagine32524L&R - Case Study - 2011AamazingmengNessuna valutazione finora
- Client/Server Software Testing: Hongmei YangDocumento21 pagineClient/Server Software Testing: Hongmei YangIrfan67% (3)
- Designing ProLogDocumento17 pagineDesigning ProLogSatenaw Gojame Satenaw GojameNessuna valutazione finora
- COMP 2141 Windows Server Network Infrastructure-4Documento5 pagineCOMP 2141 Windows Server Network Infrastructure-4dc0% (1)
- Aelf Blockchain Development Process: 1) Development Environment Preparation & Contract WritingDocumento5 pagineAelf Blockchain Development Process: 1) Development Environment Preparation & Contract WritingEdwin OngNessuna valutazione finora
- CSC 205 Past Question PDFDocumento2 pagineCSC 205 Past Question PDFDavid Gbadamosi100% (1)
- Network Standards: (The Osi Reference Model & Ieee 802.X Standard)Documento12 pagineNetwork Standards: (The Osi Reference Model & Ieee 802.X Standard)tesfuNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine-to-Machine M2M Communications Third EditionDa EverandMachine-to-Machine M2M Communications Third EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Multithreading Introduction Creating Threads Process and Threads Thread Life Cycle Thread Priorities Synchronizing ThreadsDocumento19 pagineMultithreading Introduction Creating Threads Process and Threads Thread Life Cycle Thread Priorities Synchronizing ThreadsG.l. Saini100% (1)
- Bidirectional Data Import To Hive Using SQOOPDocumento6 pagineBidirectional Data Import To Hive Using SQOOPInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Operating Systems and Linux: Presented by Aaruni Giriraj Viiith Sem I.TDocumento24 pagineEmbedded Operating Systems and Linux: Presented by Aaruni Giriraj Viiith Sem I.TAaruni GirirajNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllbosDocumento7 pagineSyllbosapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Routers CommandsDocumento14 pagineRouters Commandsapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade SheetDocumento6 pagineGrade Sheetapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5/5/2014 Worksheet Vp9: Amplitude Modulation Osamasaeedbafaqeeh Mohammed Ibrahim Mujalli Zeyad Mohammed BinqeelDocumento1 pagina5/5/2014 Worksheet Vp9: Amplitude Modulation Osamasaeedbafaqeeh Mohammed Ibrahim Mujalli Zeyad Mohammed Binqeelapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cross Word AnswersDocumento1 paginaCross Word Answersapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cross WordsDocumento1 paginaCross Wordsapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching MaterialDocumento16 pagineTeaching Materialapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 2 ConnectorsDocumento11 pagineLesson Plan 2 Connectorsapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yourtrts 2Documento16 pagineYourtrts 2api-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- GlossaryDocumento3 pagineGlossaryapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- E LearningDocumento6 pagineE Learningapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Didactic ReflectionpmDocumento11 pagineDidactic Reflectionpmapi-249493790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic LeadershipDocumento8 pagineStrategic LeadershipMazlina MazlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan - TPT 4Documento9 pagineLesson Plan - TPT 4Lindete MaranhaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Forensic Science Paper 1Documento4 pagineForensic Science Paper 1api-341256494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kuesioner EnglishDocumento2 pagineKuesioner Englishels elisaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesi 4 Systems ThinkingDocumento35 pagineSesi 4 Systems ThinkingNur Fadly IkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Sir Garnel Lesson Plan 1Documento3 pagineSir Garnel Lesson Plan 1api-339350946Nessuna valutazione finora
- Feminist Theory 2011 Meagher 297 316Documento21 pagineFeminist Theory 2011 Meagher 297 316Georgiana GrigorasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Vijnaptimatratasiddhi TrimsikaiDocumento9 pagineThe Vijnaptimatratasiddhi TrimsikaiKartala SumanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2, Quarter 1, Date - : 1. Realize The Value of Doing Philosophy in Obtaining A Broad Perspective On LifeDocumento2 pagineWeek 2, Quarter 1, Date - : 1. Realize The Value of Doing Philosophy in Obtaining A Broad Perspective On LifeMark Anthony GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Here Is The Complete List of Contract Removal Documents I Came Up With I Will Add More Here As I Come Up With The RestDocumento15 pagineHere Is The Complete List of Contract Removal Documents I Came Up With I Will Add More Here As I Come Up With The Restsnaps7850% (2)
- Research-G2-12-Gas-C-Chapter 1-3Documento24 pagineResearch-G2-12-Gas-C-Chapter 1-3Nicole Ann BaroniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jerrold Levinson-Contemplating Art-Oxford University Press Inc (2006)Documento432 pagineJerrold Levinson-Contemplating Art-Oxford University Press Inc (2006)Guillermo Jaimes BenítezNessuna valutazione finora
- Titel Der Dissertation /title of The Doctoral ThesisDocumento461 pagineTitel Der Dissertation /title of The Doctoral ThesisJothi AnandamNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Barriers QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineCommunication Barriers Questionnairepranav sarawagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 3Documento43 pagineMod 3John marvin caisip100% (1)
- Media Relations StrategyDocumento18 pagineMedia Relations StrategyBolaji Okusaga100% (1)
- Group Discussion GuidelinesDocumento2 pagineGroup Discussion GuidelinesRonil JainNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP-in-science (AutoRecovered)Documento11 pagineDLP-in-science (AutoRecovered)Richard EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineBrand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty QuestionnaireAnonymous GhyLaqEcUUNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductive Vs DeductiveDocumento2 pagineInductive Vs Deductivemnizamuddin1975Nessuna valutazione finora
- God's For-BEAR-ance With Bullies-Condensed VersionDocumento205 pagineGod's For-BEAR-ance With Bullies-Condensed VersionPatricia BackoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Eaton V LDR711A Week 7 Reflective Leadership PlanDocumento7 pagineEaton V LDR711A Week 7 Reflective Leadership PlanvjeatonNessuna valutazione finora
- Oliver Twist Chapter 9-12 - UpdatedDocumento21 pagineOliver Twist Chapter 9-12 - UpdatedBee FeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Webster School District Directory 2010-11Documento32 pagineWebster School District Directory 2010-11timesnewspapersNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbc-Evaluation-Instrument Acp NC IiDocumento6 pagineCbc-Evaluation-Instrument Acp NC IiDanny R. SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Choice: A Theoretical Analysis: Abstract'Documento20 pagineStrategic Choice: A Theoretical Analysis: Abstract'Nuzulul Khaq100% (1)
- BSBLED401 - Learner GuideDocumento58 pagineBSBLED401 - Learner GuideLuiz100% (5)
- THIS MOMENT - Jeff FosterDocumento2 pagineTHIS MOMENT - Jeff FosterjammessNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Two Statements Are True About Organization GoalsDocumento24 pagineWhich Two Statements Are True About Organization GoalsRavindraNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Rockefeller Habits - BriefDocumento4 pagine10 Rockefeller Habits - BriefMeetu SharmaNessuna valutazione finora