Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Distribution Protection Question and Answer
Caricato da
Ritesh Jaiswal0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
12 visualizzazioni3 paginegood
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentogood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
12 visualizzazioni3 pagineDistribution Protection Question and Answer
Caricato da
Ritesh Jaiswalgood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
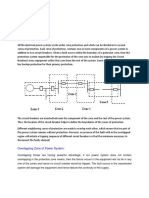
DISTRIBUTION PROTECTION
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1. Most of the fuses operate due to
(A) heating effect of current
(B) magnetic effect of current
(C) electrostatic effect of current
(D) none of the above.
Answer: A
2. The over-voltage surges in power systems may be caused by
(A) lightning
(B) switching
(C) resonance
(D) any of the above.
Answer: D
3. Which of the following statement about SF
6
gas is incorrect ?
(A) It is non-toxic gas
(B) It is non-inflammable
(C) It has density 5 times that of air at 20
0
C
(D) It has dark yellow color.
Answer: D
4. Dielectric strength of SF
6
is
(A) less than that of air at atmospheric pressure
(B) less than that of oil used in OCB
(C) more than that of oil used in OCB
(D) more at lower pressure and low at higher pressures.
Answer: B
5. A sudden short-circuit in an ac system causes a rise in __________ in the short-circuited phase.
Answer: CURRENT
6. A circuit breaker is
(A) power factor correcting device
(B) a device to neutralize the effect of transients
(C) a waveform correcting device
(D) a current interrupting device.
Answer: D
7. The function of protective relay in a circuit breaker is
(A) to each any stray voltages
(B) to close the contacts when the actuating quantity reaches a certain predetermined value
(C) to limit arcing current during the operation of circuit breaker
(D) to provide additional safety in the operation of circuit breaker.
Answer: B
8. The fault clearing time of a circuit breaker is usually
(A) few minutes
(B) few seconds
(C) one second
(D) few cycles of supply voltage.
Answer: D
9. The medium employed for extinction of arc in air circuit breaker is
(A) SF
6
(B) Oil
(C) Air
(D) Water.
Answer: C
10. For high voltage, ac circuit breakers, the rated short circuit current is passed for
(A) 0.01 sec
(B) 0.1 sec
(C) 3 seconds
(D) 30 seconds.
Answer: C
11. Differential relays are used for the protection of equipments against:
a) Internal faults
b) Over-current
c) Reverse current
d) Reverse power
Answer: A
SHORT ANSWER QUESTION
1. What are the functions of protective relays?
To detect the fault and initiate the operation of the circuit breaker to isolate the defective element from the rest of
the system, thereby protecting the system from damages consequent to the fault.
2. What is back up protection?
Is the second line of defence, which operates if the primary protection fails to activate within a definite time delay.
3. What is the need of relay coordination?
The operation of a relay should be fast and selective, ie, it should isolate the fault in the shortest possible time
causing minimum disturbance to the system. Also, if a relay fails to operate, there should be sufficiently quick
backup protection so that the rest of the system is protected. By coordinating relays, faults can always be isolated
quickly without serious disturbance to the rest of the system.
4. State the different types of faults.
Symmetrical faults and unsymmetrical faults and open conductor faults.
5. What is primary protection?
Primary protection is the protection in which the fault occurring in a line will be cleared by its own relay and circuit
breaker. It serves as the first line of defense.
6. Differentiate between a fuse and a circuit breaker.
Fuse is a low current interrupting device. It is a copper or an aluminum wire. Circuit breaker is a high current
interrupting device and it act as a switch under normal operating conditions.
7. What is the need of relay coordination?
The operation of a relay should be fast and selective, i.e., it should isolate the fault in the shortest possible time
causing minimum disturbance to the system. Also, if a relay fails to operate, there should be sufficiently quick
backup protection so that the rest of the system is protected. By coordinating relays, faults can always be isolated
quickly without serious disturbance to the rest of the system.
________________________________________________X______________________________________
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- QB 105722Documento7 pagineQB 105722Nuha Al awaisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- PSG Two Marks Q and A PDFDocumento21 paginePSG Two Marks Q and A PDFKRCT EEE HODNessuna valutazione finora
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesDa EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNessuna valutazione finora
- PSG Two Marks With AnswersDocumento21 paginePSG Two Marks With AnswersKRCT EEE HODNessuna valutazione finora
- On-Chip Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Protection for Radio-Frequency Integrated CircuitsDa EverandOn-Chip Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Protection for Radio-Frequency Integrated CircuitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Zone of ProtectionDocumento17 pagineZone of ProtectionAkimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDocumento12 pagineEe2402 Protection and SwitchgearVasudha SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Transient Protection Systems: Including Supercapacitor Based Design Approaches for Surge ProtectorsDa EverandDesign of Transient Protection Systems: Including Supercapacitor Based Design Approaches for Surge ProtectorsNessuna valutazione finora
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDocumento60 pagineUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection and Switchgear Important QuestionsDocumento38 pagineProtection and Switchgear Important QuestionsAkhil Surya0% (1)
- Chapter 1 RQDocumento3 pagineChapter 1 RQAb C100% (2)
- Relays: The Function of Protective RelaysDocumento14 pagineRelays: The Function of Protective RelayswazedbiplobNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Modern Electrical Substations - Part 2 - R2Documento22 pagineFundamentals of Modern Electrical Substations - Part 2 - R2Harish De SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE-455 Electrical PowerSystem Protection - F2013Documento48 pagineEE-455 Electrical PowerSystem Protection - F2013Vinícius Mota SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Questions of SWITCHGEAR & PROTECTIONDocumento2 pagineModel Questions of SWITCHGEAR & PROTECTIONSaroj kumar BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: Abhimanyu Jena Regd - No:0801214183 Branch: Electrical Date: 6 Sept, 2011Documento14 pagineSubmitted By: Abhimanyu Jena Regd - No:0801214183 Branch: Electrical Date: 6 Sept, 2011Dev KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection PhilosophyDocumento50 pagineProtection Philosophyrohan sainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Det50083 PTSBDocumento12 pagineChapter 4 Det50083 PTSBNUR RABBIATUL ADAWIYAH MOHAMMADNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Questions & AnswersDocumento47 pagineInterview Questions & AnswerssampathNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocumento14 pagineThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingDev SwainNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Interview QuestionsDocumento14 paginePower System Interview QuestionsMd.Imran Gazi JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocumento13 pagineThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingrajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDocumento16 pagineDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearSweqZNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment of System Protection Eeg 806Documento24 pagineAssignment of System Protection Eeg 806emechetasamuel27Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Purpose of An Electric Power System Is To Generate and Supply Electrical Energy To ConsumersDocumento12 pagineThe Purpose of An Electric Power System Is To Generate and Supply Electrical Energy To Consumerseuge sylNessuna valutazione finora
- EE6702 2marksDocumento21 pagineEE6702 2marksVISWA VikNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Marks PSGDocumento12 pagine2 Marks PSGSyed Z100% (1)
- PSWGDocumento53 paginePSWGDEPT MECHNessuna valutazione finora
- PSP ImpDocumento36 paginePSP ImpHarsh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocumento20 paginePhilosophy of Protective RelayingSasquatchCornNessuna valutazione finora
- ET601 - Chapter 1Documento25 pagineET601 - Chapter 1Thanaletchumy RamesamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Principle of Power SystemDocumento10 pagineChapter 1 Principle of Power SystemSurendra PanditNessuna valutazione finora
- Switchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggDocumento8 pagineSwitchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggKetan KishoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes21 ProtectionDocumento22 pagineNotes21 ProtectionJerome SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmi FinalsDocumento2 pagineTransmi FinalsHarold De ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesDocumento130 pagineBasic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesHafiziAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- All Topics Power SystemDocumento126 pagineAll Topics Power Systemtony kimaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Radial Feeder ProtectionDocumento6 pagineRadial Feeder ProtectionSrivalli ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Reclosing ConceptsDocumento7 pagineAuto Reclosing ConceptssrinivasaphanikiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Switch Gear and Protection Unit 1 by Ramu. SrikakulapuDocumento75 pagineSwitch Gear and Protection Unit 1 by Ramu. SrikakulapuAnkit RohatgiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit IDocumento38 pagineEe2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit INavneethNessuna valutazione finora
- Zones & QualitiesDocumento3 pagineZones & QualitiesgavinilaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transposition of The Communication LineDocumento157 pagineTransposition of The Communication LineHota bNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To System Protection - Protection BasicsDocumento94 pagineIntroduction To System Protection - Protection Basicsdaniel_2MNessuna valutazione finora
- Zone of Protection SystemDocumento4 pagineZone of Protection Systemtefe yabatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionDocumento41 pagineLect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters 5b ExercisesDocumento13 pagineChapters 5b ExercisesbibinbibinNessuna valutazione finora
- NGSDP P1 Final PDFDocumento407 pagineNGSDP P1 Final PDFchdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Transformer Protection Using Microcontroller-Based RelayDocumento66 paginePower Transformer Protection Using Microcontroller-Based Relaybisanikumarbabu100% (5)
- Ee1302 Protection and SwitchgearDocumento12 pagineEe1302 Protection and SwitchgearMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- Elec 5204 Review Quizzes AnsDocumento9 pagineElec 5204 Review Quizzes Ansveljal6317Nessuna valutazione finora
- 01d - Protection Principles 1Documento19 pagine01d - Protection Principles 1Abdul MoizNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Transformer ProtectionDocumento70 paginePower Transformer ProtectionKavuri Sai PradeepNessuna valutazione finora
- System ProtectionDocumento60 pagineSystem Protectionarshadanjum12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDa EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Benchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementDa EverandBenchmarking Best Practices in Maintenance ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignDa EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDa EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDa EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingDa EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDa EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDa EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- A Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingDa EverandA Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsDa EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EDa EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (6)
- Advanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationDa EverandAdvanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyDa EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsDa EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideDa EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresDa EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesDa EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)