Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
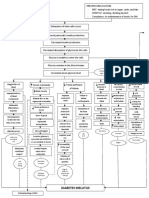
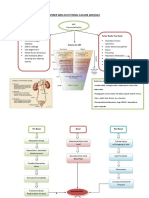
Chronic Nephropathy Diabetic Glomerulonephritis Chronic Pyelonephritis
Caricato da
ssiton886Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chronic Nephropathy Diabetic Glomerulonephritis Chronic Pyelonephritis
Caricato da
ssiton886Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Diabetic
Chronic
ChronicGlomerulonephritis
Nephropathy
Pyelonephritis Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Polycystic Kidney Dse. HPN Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Failure
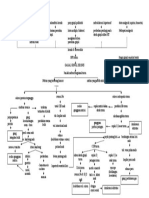
Intracellular Glucose Multiple Bilateral Cysts Long Standing HPN Production of large variety of
Non-modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk Factors: leads to further auto antibodies against normal
Age Diet arteriosclerosis body components such as nucleic
Repeated Inflammation Gender Sedentary Lifestyle acids, RBC, platelet, and WBC
Supports the formation of Heredity Nephrotoxins As cysts fill, enlarge
abnormal glycoprotein in the & multiply, kidneys
basement membrane of also enlarge SLE antibodies react with
Ischaemia, Nephron loss,
glomerulus Renal Blood their corresponding antigen
Shrinkage of Kidney
Renal blood vessels &
Renal Reserve nephrons are compressed &
Stage Forms Immune Complexes
obstructed & functional tse.
Glomerulosclerosis impairs are destroyed
the filtering fxn. of the Damage to Nephrons
glomerulus thus protein
lost in urine GFR 50% Renal Parenchyma Deposited in the
50% damage Normal BUN, atrophies & become connective tse. such as
Creatinine fibrotic & scarred blood volume & kidneys
More than 75% damage
GFR 20-50% Trigger an inflammatory
Stage Renal Insufficiency BUN, response and damage
Creatinine the kidney
As nephrons are destroyed, the
remaining nephrons undergo
changes to compensate for those
Remaining nephrons must filter
more solute particles from the
Hypertrophy of remaining nephrons
Nephrons cannot tolerate the work
Further damage of nephrons
80-90% damage
GFR 10-20%
Renal Failure Sharp
Stage BUN,
Impaired kidney function & Uremia
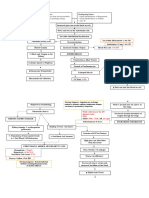
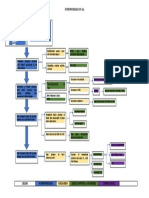
Nitrogenous
Na
HHCO3
+
&KH2O
+
Erythropoietin Mg +
Vit. D Phosphate Toxins Toxins impair Salivary Deposit of Toxins affect the Toxins causes Retentio
retention
retention
retention
waste
production
production retention activation retention Continuous decline in renal fxn. irritate WBCs, humoral & urea urea on nerve fibers CNS affectation n of
impairs
in kidney pericardial cell mediated breakdown skin
platelets sac immunity;
Hyperkalemia Hyper- Hyperphosphatemi > 90% kidney Fever is Atrophy & Uremic Cells become
Urine magnesemia suppressed; Uremic Uremic Frost Demyalination Encephalopathy resistant to
Metabolic
Bleeding
GI
Blood
Output Pericarditi Fetor Yellowish hue insulin
Phagocyte becomes
stress
AcidosisAnemia
tendencies Ca+ Reduction in renal
defective
absorption capillaries Peripheral Reduction in
Oliguria Scarring of Glomeruli Cardiac Irritation of Neuropath alertness & Erratic blood
Malfunction
Lungs Atrophy & Fibrosis of Tamponade Phrenic glucose level
awareness
of GI
Compensates
RAAS Blood loss Hypo- Immune Changes in
bleeding during calcemia System Decline Restless Leg
End Stage Renal Dse. mentation
hemodialysis Hiccups Syndrome Because of
Kussmaul’s Stage (ESRD) Difficulty of
concentrating glucose
Respiration Parathyroid GFR less Risk for Superinfection
Fatigue intracellularly,
overworks than 10%
Heart
Edema
Loss of Continuous Multisystem Insomnia liver produces
(Hyperpara-
Anorexia
Failure appetite Affectation Psychiatric tryglycerides
thyroidism)
Nausea symptoms & HDL
Vomiting
Fatigue
Gastroenteritis PTH secretion Death
Weakness
Peptic Ulcer
Pallor Atherosclerosis
Pulmonary Edema Ca+ resorption
Peripheral Edema from bone +
Ca absorption
from GI tract Thrombus
& Embolus
Renal Osteodysthrophy Formation
Osteomalacia By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi
Osteoporosis
Bone BSN 4-B
tenderness
Bone pain
Muscle
Weakness
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Psychiatric Clinical SkillsDocumento376 paginePsychiatric Clinical SkillsSamuel Agunbiade100% (5)
- 20100829035427388Documento374 pagine20100829035427388Reeza Amir Hamzah100% (1)
- Secret Chernobyl Documents Expose The CoverUpDocumento6 pagineSecret Chernobyl Documents Expose The CoverUpTroy LivingstonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of PIHDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiology of PIHCarren_Louise__8090Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsJu Lie AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeDocumento2 paginePathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal and Urinary Concept MapsDocumento8 pagineRenal and Urinary Concept Mapsnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Psychiatric Disability AssessmentDocumento19 paginePsychiatric Disability AssessmentDivya ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Documento4 paginePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jo_annamae4413100% (3)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramRnspeakcom50% (2)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocumento3 pagineAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Documento3 paginePathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Francis Kevin Sagudo100% (10)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocumento7 paginePathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocumento7 paginePathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Allopurinol (Drug Study)Documento2 pagineAllopurinol (Drug Study)Daisy PalisocNessuna valutazione finora
- PharmacyDocumento27 paginePharmacyJenilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Renal FailureDocumento1 paginaChronic Renal Failurejj_cuttingedges100% (2)
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Module 11 Rational Cloze Drilling ExercisesDocumento9 pagineModule 11 Rational Cloze Drilling Exercisesperagas0% (1)
- BiotechnologyDocumento39 pagineBiotechnologyChrystal Kyla SalengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureAina HaravataNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology AML DiagramDocumento4 paginePathophysiology AML DiagramKlerra Hope60% (5)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Documento3 pagineDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHOPHYDocumento3 paginePATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadNessuna valutazione finora
- Light and Electron Microscopy of Cells and TissuesDa EverandLight and Electron Microscopy of Cells and TissuesNessuna valutazione finora
- Urogenital Imaging: A Problem-Oriented ApproachDa EverandUrogenital Imaging: A Problem-Oriented ApproachS. MorcosValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Acute Renal Failureminangsung minangnengNessuna valutazione finora
- Modifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento5 pagineModifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSteffi MurielNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocumento3 paginePre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- Aki EditedDocumento8 pagineAki EditedLarabelle Avila CoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysDocumento1 paginaPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: KidneysChe CacatianNessuna valutazione finora
- Ricin T?xicity T?xic Minds Maps For T?xic Detective ?????of ISTDocumento1 paginaRicin T?xicity T?xic Minds Maps For T?xic Detective ?????of ISTGiovanni ValerNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento3 pagineAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Ugib PathoDocumento2 pagineAnemia Ugib PathoAj GoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisDocumento1 paginaPa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisJhaziel BermejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho Sickle CellDocumento1 paginaPatho Sickle CellDan MandigNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERirish_estrellaNessuna valutazione finora
- RLEhospLUMC PATHOPHYSIOLOGYcasepresDocumento3 pagineRLEhospLUMC PATHOPHYSIOLOGYcasepresSandy DuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology, Bone CancerDocumento7 paginePathophysiology, Bone CancerMaria Grace Raquel Ormeneta100% (1)
- O High Fat, High Carbohydrate o Caffeinated and Carbonated o 73 Years Old o MaleDocumento4 pagineO High Fat, High Carbohydrate o Caffeinated and Carbonated o 73 Years Old o MaleJoherNessuna valutazione finora
- Preeclampsia Eclampsia PathophyDocumento2 paginePreeclampsia Eclampsia PathophyLesther Alba Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Ix. Pathophysiology: Age Gender Heredity Diet Sedentary Lifestyle NephrotoxinsDocumento1 paginaIx. Pathophysiology: Age Gender Heredity Diet Sedentary Lifestyle NephrotoxinsXy-Za Roy MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 106 Module 2 Lesson 1.1Documento3 pagineNCM 106 Module 2 Lesson 1.1Joselyn M. LachicaNessuna valutazione finora
- GUADIZ - Concept Map Med CoroDocumento1 paginaGUADIZ - Concept Map Med CoroYESSAMIN GUADIZNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology of Sepsis Secondary To Typhoid IleusDocumento6 paginePa Tho Physiology of Sepsis Secondary To Typhoid IleusPhatsee PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocumento2 paginePa Tho Physiologydavica0413Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study DoneDocumento12 pagineDrug Study DoneSheila Mae PanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Spider Web Acute Renal FailureDocumento3 pagineSpider Web Acute Renal FailureTien KartiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisSandra PagoboNessuna valutazione finora
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocumento2 paginePredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningDocumento15 pagineQuality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningAnya IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology: Nursing Diagnosis and Plan of CareDocumento2 paginePathophysiology: Nursing Diagnosis and Plan of CareCarmella CaritosNessuna valutazione finora
- Patofisiologi Tumor KolonDocumento2 paginePatofisiologi Tumor Kolonnur hijriahNessuna valutazione finora
- CEFUDocumento9 pagineCEFUAira AlaroNessuna valutazione finora
- 1035 Pathway CKDDocumento1 pagina1035 Pathway CKDeka pandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Modifiable: Modifiable:: (BP 158/87 MMHG)Documento1 paginaNon Modifiable: Modifiable:: (BP 158/87 MMHG)Quintin MangaoangNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa ThoDocumento4 paginePa ThoErnest Genesis Mercado GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Streptococcus Infection, On TheDocumento3 pagineStreptococcus Infection, On TheMonica DomingoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho On Upper GI BleedingDocumento1 paginaPatho On Upper GI BleedingJustin CubillasNessuna valutazione finora
- EA Cocept Map2Documento2 pagineEA Cocept Map2Katie LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Renal Disease StudentDocumento34 pagine7 Renal Disease Studentrbm121415chyNessuna valutazione finora
- Urolithiasis NP: Deficit of KnowledgeDocumento2 pagineUrolithiasis NP: Deficit of Knowledgevictor zhefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Concussion - PathophyDocumento6 pagineCerebral Concussion - PathophyFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AllDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of AllBGHMC PEDIAHONessuna valutazione finora
- Dunkin DonutsDocumento2 pagineDunkin DonutszerpthederpNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteoarthritis of The Hip and Knee Flowchart PDFDocumento2 pagineOsteoarthritis of The Hip and Knee Flowchart PDFsilkofosNessuna valutazione finora
- Autism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptDocumento26 pagineAutism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptWanessa FernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Acetylsalicylic AcidDocumento6 pagineAcetylsalicylic AcidAdmin DownloadNessuna valutazione finora
- Free End SaddleDocumento5 pagineFree End SaddleAdry AnnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes:: Accident and Incident InvestigationDocumento10 pagineLecture Notes:: Accident and Incident InvestigationajayikayodeNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 - The Generics Act of 1988Documento22 pagine10 - The Generics Act of 1988rhydelNessuna valutazione finora
- Avocado Production in The PhilippinesDocumento20 pagineAvocado Production in The Philippinescutieaiko100% (1)
- PHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Documento12 paginePHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Harry WeiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ISO 22000 S. 2005?: An OverviewDocumento23 pagineWhat Is ISO 22000 S. 2005?: An OverviewMario Norman B. CelerianNessuna valutazione finora
- Promoting Smart Farming, Eco-Friendly and Innovative Technologies For Sustainable Coconut DevelopmentDocumento4 paginePromoting Smart Farming, Eco-Friendly and Innovative Technologies For Sustainable Coconut DevelopmentMuhammad Maulana Sidik0% (1)
- Pre-Emplopyment RequirementsDocumento2 paginePre-Emplopyment RequirementsPatricia TorrianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment NoDocumento3 pagineExperiment NoMaxene Kaye PeñaflorNessuna valutazione finora
- Feeding Norms Poultry76Documento14 pagineFeeding Norms Poultry76Ramesh BeniwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps To Reduce Drug Abuse 1800 11 0031 National Toll Free Drug de Addiction Helpline NumberDocumento4 pagineSteps To Reduce Drug Abuse 1800 11 0031 National Toll Free Drug de Addiction Helpline NumberimranNessuna valutazione finora
- Starlight ProgramsDocumento12 pagineStarlight Programsllacara@nncogannett.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Trasturel 440mg Anti CancerDocumento3 pagineTrasturel 440mg Anti CancerRadhika ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiDocumento3 pagineA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Prehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionDocumento3 paginePrehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionAnjelica Louise MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeDocumento20 pagineCommon Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeEng Stephen ArendeNessuna valutazione finora
- CCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroDocumento5 pagineCCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroKrishnan KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7. Presented - The Phil Health Program On Degenerative Diseases 93Documento105 pagineModule 7. Presented - The Phil Health Program On Degenerative Diseases 93Roma ClaireNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 Overview Digestive System HandoutDocumento11 pagine2018 Overview Digestive System HandoutdraganNessuna valutazione finora