Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Term Definition or Description
Caricato da
900913n008Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Term Definition or Description
Caricato da
900913n008Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Term Definition or Description
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute is the principal standards-setting body in the
United States. ANSI is a nonprofit, nongovernmental organization supported by more than
1,000 trade organizations, professional societies, and companies. It belongs to the ITU-T
CCITT and the ISO.
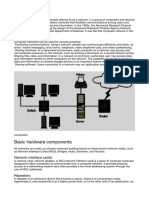
Backbone Network
A large network to which many networks within an organization are connected. It usually is a
network that interconnects all networks on a single site, but it can be larger if it connects all
the organizations terminals, computers, mainframes, LANs, and other communication
equipment.
Broadband
Originally, the term referred to analog communications, but it has become corrupted in
common usage so that it now usually means high-speed communications networks, typically
Internet access technologies with access speeds of 1 Mbps or higher.
Cat-5
Cat-5 or Category 5 cable consists of four twisted pairs of copper wire that terminate in the
RJ-45 connector. Cat-5 cables support frequencies up to 100 MHz and speeds up to 1000
Mbps
Cat-6
Cat-6 or Category 6 cable uses the same copper wire connectors as Cat-5; however they
provide performance of up to 250 MHz and speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Circuit
The path over which the voice, data, or image transmission travels. Circuits can be twisted-
wire pairs, coaxial cables, fiber-optic cables, microwave transmissions, and so forth.
Client
The inputoutput hardware device at the users end of a communication circuit. There are
three major categories of clients: computers, terminals, and special purpose terminals.
Data link Layer
The data link layer manages the physical transmission circuit in layer 1 and transforms it into
a circuit that is free of transmission errors as far as layers above are concerned.
Extranet
Using the Internet to provide access to information intended for a selected set of users, not
the public at large. Usually done by requiring a password to access a selected set of Web
sites.
FCC
The Federal Communications Commission is a board of seven commissioners appointed by
the U.S. president under the Communication Act of 1934, having the power to regulate all
interstate and foreign electrical communication systems originating in the United States.
Firewall
A router, gateway, or special-purpose computer that filters packets flowing into and out of a
network. No access to the organizations networks is permitted except through the firewall.
Two commonly used types of firewalls are packet level and application level.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: A professional organization for engineers in
the United States. Issues standards and belongs to the ANSI and the ISO. IEEE has defined
numerous standards for networks.
IETF
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a large, open international community of network
designers, operators, vendors, and researchers concerned with the evolution of the Internet
architecture and the smooth operation of the Internet. IETF operates through a series of
working groups, which are organized by topic (e.g., routing, transport, security). The requests
for comment (RFCs) that form the basis for Internet standards are developed by the IETF and
its working groups.
ITU
International Telecommunications UnionTelecommunications: An international
organization that sets worldwide communication standards. Its old name was Consultative
Committee on International Telegraph and Telephone
(CCITT).
Internet
The information superhighway. The network of networks that spans the world, linking more
than 20 million users.
Term Definition or Description
Intranet
Using Internet protocols on a network internal to an organization so that information is
accessible using a browser, for example, but only by employees, not the public at large.
Usually done by requiring a password to access a selected set of Web sites and protecting
the site by a firewall so no outsiders can access it.
ISP
Internet Service Providers offer connections to the Internet. Some access providers charge a
flat monthly fee for unlimited access (much like the telephone company), whereas others
charge per hour of use (much like a long-distance telephone call).
kB
1 kB = 1000bytes = 10 bytes is the definition recommended by the International Electro-
technical Commission (IEC).This definition is used in networking contexts and most storage
media, particularly hard drives, Flash-based storage, and DVDs, and is also consistent with
the other uses of the SI prefix in computing, such as CPU clock speeds or measures of
performance.
kb
The kilobit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix
kilo (symbol k) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 10 and
therefore, 1 kilobit = 10bits = 1000bits
LAN
Local Area Network: A network that is located in a small geographic area, such as an office, a
building, a complex of buildings, or a campus, and whose communication technology
provides a high-bandwidth, low-cost medium to which many nodes can be connected. These
networks typically do not use common carrier circuits, and their circuits do not cross public
thoroughfares or property owned by others. LANs are not regulated by the FCC or state
public utilities commissions.
Logical
Logical refers to how data flows within a network, regardless of its physical design. In other
words, the transmission characteristics of the connection.
Modem
A contraction of the words modulator-demodulator. A modem is a device for performing
necessary signal transformation between terminal devices and communication circuits.
Modems are used in pairs, one at either end of the communication circuit.
Open System
one of a class of computers and associated software that provides some combination of
interoperability, portability and open software standards, particularly Unix and Unix-like
systems.
Physical
Physical refers to the placement of the network's various components, including device
location and cable installation, as well as the physical media that carry the message we
transmit i.e. twisted pair, fiber, etc.
Plenum
The plenum is the space that is used for air circulation in heating and air conditioning
systems.
RFC
Request For Comment: A proposed standard for the Internet on which anyone in the world is
invited to comment.
Router
A device that connects two similar networks having the same network protocol. It also
chooses the best route between two networks when there are multiple paths between
them.
Term Definition or Description
Switch
Switches connect more than two LAN segments that use the same data link and network
protocol. They may connect the same or different types of cable. Switches typically provide
ports for 4, 8, 16, or 32 separate LAN segments, and most enable all ports to be in use
simultaneously, so they are faster than bridges.
VPN
Virtual Private Network: A hybrid network that includes both public and private facilities. The
user leases a bundle of circuits and configures the VPN on an as-needed basis so that some
traffic travels on the private leased network and some travels on the common carriers public
network.
WAN
Wide Area Network: A network spanning a large geographical area. Its nodes can span city,
state, or national boundaries. WANs typically use circuits provided by common carriers.
Wireless Access Point
In computer networking, a wireless access point is a device that allows wireless devices to
connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, or related standards. The AP usually connects to a
router as a standalone device, but it can also be an integral component of the router itself.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 4.0 Dialing PlanDocumento12 pagine4.0 Dialing Plandragelec100% (1)
- Osi ModelDocumento4 pagineOsi Modelapi-302418971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary: Types of NetworksDocumento9 pagineGlossary: Types of Networksstar gyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet: To YouDocumento14 pagineInternet: To YouMurali VasuNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Computer NetworksDocumento42 pagine02 Computer Networksanushka aroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosc 0160 Types of Computer NetworksDocumento6 pagineCosc 0160 Types of Computer NetworksIANNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Media Device and TopologyDocumento38 pagineNetworking Media Device and TopologySolan Solomon BerkessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Media Device and TopologyDocumento38 pagineNetworking Media Device and TopologySolan Solomon BerkessaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks: Network, Is A Collection ofDocumento8 pagineComputer Networks: Network, Is A Collection oftilak101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 25 Network FundamentalsDocumento5 pagineLesson 25 Network FundamentalsAssumpta Minette BurgosNessuna valutazione finora
- CN 1 - MergedDocumento32 pagineCN 1 - MergedLo VeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Computer NetworkingDocumento46 pagineWhat Is Computer NetworkingramprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report 1Documento19 pagineSeminar Report 1Narender Gupta100% (2)
- Computer Networks (2-3)Documento17 pagineComputer Networks (2-3)younas125Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 It ch1Documento6 pagine10 It ch1PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8 Computer NetworksDocumento4 pagineUnit 8 Computer NetworksNikolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethernet TutorialDocumento21 pagineEthernet TutorialKcirex GarinNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI and TCP ModelDocumento92 pagineOSI and TCP ModelAbhishek RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, See - "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento21 pagineComputer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, See - "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, Seesasi_17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1-Chap 1-Modern NetworkingDocumento64 pagineUnit 1-Chap 1-Modern NetworkingTim CookNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Computer Networks: Evolution of Data Networks, Networks ArchitectureDocumento20 pagineUnit 1: Computer Networks: Evolution of Data Networks, Networks ArchitectureVibhav MahaleNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2Documento49 pagineUNIT 3 Notes For Students - 2deepesh_gaonkarNessuna valutazione finora
- C.S Unit 3 Networks O levels-IBDPDocumento4 pagineC.S Unit 3 Networks O levels-IBDPgoper57118Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Computer NetworksDocumento23 pagineClassification of Computer NetworksPace InfotechNessuna valutazione finora
- PREL Dc1 LessonQDocumento18 paginePREL Dc1 LessonQshillamaelacorteNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1-Introduction To Computer - Networks RCCS209Documento88 pagineLesson 1-Introduction To Computer - Networks RCCS209ShamiMalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network - Access NetworksDocumento4 pagineComputer Network - Access NetworksMujahid HusainNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Networks The Internet and Beyond Types of LAN TechnologyDocumento12 pagineTypes of Networks The Internet and Beyond Types of LAN TechnologysiddhueceNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Administration and Management: Prepared By: Inocencio, Rose MDocumento92 pagineNetwork Administration and Management: Prepared By: Inocencio, Rose MJermyn G EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Networks 1Documento4 pagineNetworks 1sterrrrNessuna valutazione finora
- ClassX CA NotesDocumento75 pagineClassX CA NotesAshutosh TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Commerce-Final 111Documento25 pagineE-Commerce-Final 111Stephanie AndalNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet TCP Ip AntivirusDocumento12 pagineInternet TCP Ip AntivirusNirinjan MuddadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocumento14 pagineHardware and Network Servicing Level III: Determine Best Fit TopologyDagneWalleNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkDocumento4 pagineComputer Networkbalaji bysaniNessuna valutazione finora
- DCN PrefaceDocumento5 pagineDCN PrefaceAnonymous OQjmTwnVkNessuna valutazione finora
- IT AssignmentDocumento2 pagineIT AssignmentJohn YallNessuna valutazione finora
- InternetNotes PDFDocumento11 pagineInternetNotes PDFSungram SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 1 IntroductionDocumento36 pagineLec 1 IntroductionShima NafieNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Network SH11-12Documento26 pagineData Network SH11-12Edwin VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4: Types of NetworksDocumento17 pagineUnit 4: Types of NetworksSJ ShahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Network 20210426203825Documento51 pagineNetwork 20210426203825Rude AnimationNessuna valutazione finora
- Network 20210426203825Documento51 pagineNetwork 20210426203825M VAMSINessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Studies IiDocumento51 pagineComputer Studies Iiakaah.randyNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Name: Basics of Information Technology UNIT: 6 (Basics of Networking)Documento5 pagineSubject Name: Basics of Information Technology UNIT: 6 (Basics of Networking)Nitisha GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Priyanka CNDocumento6 paginePriyanka CNShubham KhotkarNessuna valutazione finora
- DDC Lec1 PreDocumento31 pagineDDC Lec1 PreGeorge Miguel Valenzuela Obusán (Youngblood)Nessuna valutazione finora
- CSC 218 NoteDocumento27 pagineCSC 218 NoteAyodeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communications: ECE 583 LectureDocumento6 pagineData Communications: ECE 583 Lecturechloe005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network NoteDocumento81 pagineComputer Network Noteupendrapaudel0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Data Commun and Compt Network Ch.1Documento40 pagineData Commun and Compt Network Ch.1Nuradiin AmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkDocumento16 pagineComputer NetworkMeenatchi VaradarasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lan WanDocumento7 pagineLan WanMuhammed YousafNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - PPT - 1Documento54 pagineModule 1 - PPT - 1Anubhab SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nts AndrewDocumento51 pagineNts Andrew21CSEH17 Mabal AndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Defining A Computer Network:: Chapter One Introduction To Computer NetworksDocumento8 pagineDefining A Computer Network:: Chapter One Introduction To Computer Networksmo3awia2099Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks Unit 1Documento30 pagineComputer Networks Unit 1Sowmiya SowmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Notes For TodayDocumento51 pagineNetworking Notes For Todaybrima kamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 6Documento14 pagineExperiment 6JJJKK yddyNessuna valutazione finora
- UoK - Computer NetWorksDocumento18 pagineUoK - Computer NetWorksaqsaanazir12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Who Rules the Net?: Internet Governance and JurisdictionDa EverandWho Rules the Net?: Internet Governance and JurisdictionNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - IP - Subnetting (UOK 2017)Documento117 pagineChapter 4 - IP - Subnetting (UOK 2017)Anonymous 6nN0wydgu100% (1)
- Suport Asea RomaniaDocumento1 paginaSuport Asea Romaniaalien asterixNessuna valutazione finora
- Service AssuranceDocumento143 pagineService AssuranceAlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Comm and Radio Planning CourseDocumento75 pagineMobile Comm and Radio Planning CourseMaya Homs100% (1)
- S1720, S2700, S5700, and S6720 Series Ethernet Switches Configuration Guide - SecurityDocumento13 pagineS1720, S2700, S5700, and S6720 Series Ethernet Switches Configuration Guide - Securitynodih20749Nessuna valutazione finora
- Implementation of Shortest Path in Packet Switching Network Using Genetic AlgorithmDocumento6 pagineImplementation of Shortest Path in Packet Switching Network Using Genetic Algorithmeditor_ijarcsseNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi-WAN Version 1.2.xDocumento11 pagineMulti-WAN Version 1.2.xrssebagalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Linksys Spa9000 Solution GuideDocumento9 pagineLinksys Spa9000 Solution GuideJuan Carlos LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- IMS For LTEDocumento149 pagineIMS For LTEChetan BhatNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDocumento11 pagine8.1.5.5 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 FeaturesDaniel OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- GigaBrick 2600 Quick ReferenceDocumento14 pagineGigaBrick 2600 Quick Referenceronsjr75Nessuna valutazione finora
- IPCAM User Guide FOSCAM FI8904WDocumento38 pagineIPCAM User Guide FOSCAM FI8904WDADICOMNessuna valutazione finora
- ECS4100-Series CLI-R06 0730Documento978 pagineECS4100-Series CLI-R06 0730David „Saijitsu“ N.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Skill Development (Final Term)Documento19 pagineSkill Development (Final Term)Zafar Ullah GharshinNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer: DslamDocumento14 pagineDigital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer: DslamwasiullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Mikrotik Sample - Exam 1Documento5 pagineMikrotik Sample - Exam 1Florlyn Mae Sudio RemegioNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Call FlowDocumento3 pagineGSM Call FlowBijaya RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- User's Manual KONIG RouterDocumento33 pagineUser's Manual KONIG RouterAlexa ElenaNessuna valutazione finora
- UMTS900 Co-Existence With GSM900 - Conference PaperDocumento5 pagineUMTS900 Co-Existence With GSM900 - Conference PaperTree SkinNessuna valutazione finora
- Fwa Handbook 30092020 PDFDocumento52 pagineFwa Handbook 30092020 PDFOc DienNessuna valutazione finora
- 3GPP TS 22.011Documento26 pagine3GPP TS 22.011santanameroNessuna valutazione finora
- UMTS Multi-Carrier Strategy Training-20120329Documento24 pagineUMTS Multi-Carrier Strategy Training-20120329Dee OyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Avanti - ADAPT - Specific Terms - ADAPT-VNO - H4 - Draft One 10.01.2020 - v1 - Eafrica DREAM1Documento29 pagineAvanti - ADAPT - Specific Terms - ADAPT-VNO - H4 - Draft One 10.01.2020 - v1 - Eafrica DREAM1Pierre FezeuNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI ModelDocumento16 pagineOSI ModelFaran Ul GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Barring (RAN15.0 02)Documento51 pagineCell Barring (RAN15.0 02)hekriNessuna valutazione finora
- Ran DimensioningDocumento77 pagineRan DimensioningrubenpatNessuna valutazione finora
- CCN Syllabus BAMU ETCDocumento2 pagineCCN Syllabus BAMU ETCanilbNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 ZTE's Future Oriented Microwave SolutionDocumento35 pagine04 ZTE's Future Oriented Microwave SolutionZeljko VrankovicNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento4 pagine2SaiSaiNessuna valutazione finora