Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Learning Pyramid
Caricato da
Anna SusieCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Learning Pyramid
Caricato da
Anna SusieCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Guide for Instruction by Preceptors
This document contains three RLS tools that provide preceptors with an overall strategy
for practice-based teaching and an accompanying set of practice-based teaching
techniques.
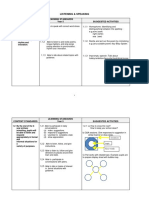
The Learning Pyramid
The Learning Pyramid summarizes preceptor roles as residents progress through
the three stages of learning to solve patient-care problems a carefully scheduled
transition from the role of direct instruction to modeling to coaching to
facilitation.
Guide to Selecting Techniques for Instruction for Cognitive Learning
The guide to help preceptors select an appropriate instructional method that
matches with both the Learning Pyramid's framework and the level of learning
specified in the objective to be taught. The table associates the preceptor's role as
specified in the Learning Pyramid with specific practice-based teaching
techniques for clinical problem solving.
Practice-based Teaching Techniques Associated with Preceptor Roles and
Theories of Cognitive Problem Solving
This table gives more detailed guidance for practice-based teaching, listing
specific techniques for use in each of the four preceptor roles identified in the
Learning Pyramid.
The Learning Pyramid (Source: Nimmo CM. Developing training materials and
programs: facilitating learning in staff development. In: Nimmo CM, Guerrero R,
Greene SA, Taylor JT, eds. Staff development for pharmacy practice. Bethesda, MD:
ASHP; 2000.)
Preceptors Role
Foundation Skills and Knowledge
Practical Application
Culminating
Integration
Direct
Instruction
Modeling
Coaching
Facilitating
Stage of Learning
Guide to Selecting Techniques for Instruction for Cognitive Learning (Source: Nimmo
CM. Developing training materials and programs: facilitating learning in staff
development. In: Nimmo CM, Guerrero R, Greene SA, Taylor JT, eds. Staff development
for pharmacy practice. Bethesda, MD: ASHP; 2000.)
STAGES OF LEARNING IN
THE
FRAMEWORK OF
INSTRUCTIONAL
STRATEGIES
BLOOM'S LEVELS OF
COGNITIVE LEARNING
APPROPRIATE
INSTRUCTIONAL
METHODS
Knowledge
Reading
Lecture
Foundation Knowledge and
Skills
Comprehension
Guided discussion
Interactive lecture
Application
Analysis
Practical Application
Synthesis
Culminating Integration
Evaluation
Case presentation
Case-based teaching
Simulation/Role play
Practice-based teaching
Practice-Based Teaching Techniques Associated with Preceptor Roles and Theories of
Cognitive Problem Solving (Source: Nimmo CM. Developing training and programs:
facilitating learning in staff development. In: Nimmo CM, Guerrero R, Greene SA,
Taylor JT, eds. Staff development for pharmacy practice. Bethesda, MD: ASHP; 2000.
Text modified with permission of the author. )
PRECEPTOR
ROLE
TECHNIQUE
ASSOCIATED COGNITIVE
APPROACH
Direct learners to content specific to their
practice problems.
Organize content in the mind for
quick recall.
Teach how a new piece of content relates to
other pieces.
Organize content in the mind for
quick recall.
Direct Instruction
Introduce new content in the context of
solving a direct patient care practice
problem.
Organize content in the mind for
quick recall.
Teach strategies to help clarify problems.
Define and classify problems.
Teach the patterns that characterize
different categories of direct patient care
practice problems.
Define and classify problems.
Modeling
Explain out loud what you are thinking as
you solve a problem.
Master problem-solving
strategies.
Give learners opportunities to practice
solving direct patient care practice problems
coupled with feedback on their use of
strategies.
Master problem-solving
strategies.
Provide sufficient problem-solving practice
to build speed.
Master problem-solving
strategies.
Coaching
Ask learners to explain out loud what they
are thinking as they solve a problem.
Self-monitor quality of problem
solving.
Facilitating Teach learners to evaluate their own work. Self-monitor quality of problem
solving.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- T&D.CH 6Documento37 pagineT&D.CH 6Arju LubnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Toney Id4t Final ReflectiveDocumento9 pagineToney Id4t Final Reflectiveapi-404825677Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q. 1 Why Is A Model of Teaching Needed? What Approaches Are Used in Building Model of Teaching?Documento25 pagineQ. 1 Why Is A Model of Teaching Needed? What Approaches Are Used in Building Model of Teaching?rameezaranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Peer Coaching ModelsDocumento9 paginePeer Coaching ModelsCesar MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Telaah JurnalDocumento7 pagineTelaah JurnalAremia VaneshaNessuna valutazione finora
- ED 710 - Activities For Lesson 10aDocumento5 pagineED 710 - Activities For Lesson 10aAlex Brian AlmarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- FS2 Eo3Documento5 pagineFS2 Eo3Tinker JelNessuna valutazione finora
- Drill Method Teaching TechniqueDocumento24 pagineDrill Method Teaching TechniqueJibran idreesNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Evaluation Action ResearchDocumento17 pagineProgram Evaluation Action Researchapi-664208920Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blooms Revised-Wps OfficeDocumento4 pagineBlooms Revised-Wps Officeapi-514282949Nessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Strategies for Social Studies TeachingDocumento41 pagineEffective Strategies for Social Studies Teachingjade tagabNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan CompilationDocumento8 pagineLesson Plan CompilationEljemay C. Abellanosa100% (1)
- 006 Training Methods and TechniquesDocumento27 pagine006 Training Methods and TechniquesPulkit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Peer Coaching ModelsDocumento9 paginePeer Coaching Modelsapi-295279477Nessuna valutazione finora
- January MTL Meeting: 2010 - 2011 MTL Meetings Research-Based Literacy StrategiesDocumento2 pagineJanuary MTL Meeting: 2010 - 2011 MTL Meetings Research-Based Literacy StrategiesAbdul Kadir BagisNessuna valutazione finora
- Sytematic Approach To TeachingDocumento3 pagineSytematic Approach To TeachingAlan HabalNessuna valutazione finora
- RTI, MTSS, Data Collection, Interventions, and Special Education EligibilityDocumento2 pagineRTI, MTSS, Data Collection, Interventions, and Special Education EligibilityMUSYOKA KITUKUNessuna valutazione finora
- InstructionalDocumento4 pagineInstructionalBrianne MarshallNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Teaching in Times of PandemicDocumento4 pagineHome Teaching in Times of PandemicDan PradesNessuna valutazione finora
- Explain The Importance o Evaluating Teachers' PerformanceDocumento6 pagineExplain The Importance o Evaluating Teachers' PerformanceShitty headNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategies On Health EducationDocumento81 pagineStrategies On Health Educationjamie100% (3)
- PROBLEM-SOLVING AND QUESTIONING STRATEGIESDocumento6 paginePROBLEM-SOLVING AND QUESTIONING STRATEGIESClinTon MaZoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Simulation TechniquesDocumento38 pagineNursing Simulation Techniquessankareswari.RNessuna valutazione finora
- SOCIAL STUDIES Activity No. 7Documento6 pagineSOCIAL STUDIES Activity No. 7Jen AMBNessuna valutazione finora
- HR Training MethodsDocumento18 pagineHR Training MethodsmanalishetyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Title About Classroom ManagementDocumento8 pagineThesis Title About Classroom Managementotmxmjhld100% (1)
- Action ResearchDocumento61 pagineAction ResearchLance Aldrin Adion67% (3)
- Effectiveness of Teaching StrategiesDocumento13 pagineEffectiveness of Teaching StrategiesMarilyn Tamboon100% (2)
- Comment On The Value of The Two Weeks' Topics To Your Understanding of Instructional DesignDocumento3 pagineComment On The Value of The Two Weeks' Topics To Your Understanding of Instructional DesignMattie WaltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento7 pagineCase StudyAyman Dwedar100% (1)
- Final Reflection and ConclusionDocumento6 pagineFinal Reflection and Conclusionapi-245618331Nessuna valutazione finora
- FS 2 EPISODE 1 - Effective Teaching QualitiesDocumento2 pagineFS 2 EPISODE 1 - Effective Teaching Qualitieskaren marie dela pasionNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Principles of MotorDocumento25 pagineModule 5 Principles of Motorzedy gullesNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Teaching Strategies for Student LearningDocumento4 pagineEffective Teaching Strategies for Student LearningEver Shekhaina-XavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories and Models of Learning for Educational Research and PracticeDocumento14 pagineTheories and Models of Learning for Educational Research and PracticeDiane ChuNessuna valutazione finora
- Motivation theories in tutoringDocumento8 pagineMotivation theories in tutoringjens_stahmannNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching as Decision Making FrameworkDocumento20 pagineTeaching as Decision Making FrameworkENRICONessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 27Documento8 pagineLecture 27junaid khanNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 IsDocumento16 pagine20 Isapi-323269525Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reflective Coaching Model for TeachersDocumento24 pagineReflective Coaching Model for Teacherskojo tikoNessuna valutazione finora
- Satisfying The Need For Empowerment-Routines Routines: Consider These Two ClassroomsDocumento5 pagineSatisfying The Need For Empowerment-Routines Routines: Consider These Two ClassroomsAngela A. AbinionNessuna valutazione finora
- Edid 6503 Assignment 3 DDocumento11 pagineEdid 6503 Assignment 3 Dapi-248721683Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Performance Using Behavior: UniversityDocumento9 pagineTeaching Performance Using Behavior: UniversityRégis VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Review RequirementDocumento3 pagineJournal Review RequirementAuvrei MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature ReviewDocumento7 pagineLiterature ReviewArsalan NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- First Principle Print-1 PDFDocumento4 pagineFirst Principle Print-1 PDFRox FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- FS2 EP3 (Gregori, BEED 4-A)Documento14 pagineFS2 EP3 (Gregori, BEED 4-A)Sheina Gregori100% (1)
- Curriculum Alignment ExampleDocumento8 pagineCurriculum Alignment Exampleapi-315988114Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis of Classroom Action ResearchDocumento8 pagineThesis of Classroom Action Researchbsdy4ahp100% (1)
- Pelagio - Fs Module Lesson 4Documento6 paginePelagio - Fs Module Lesson 4api-613019400Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch 2 Guidelines Review and discussion questions and MCQ CoetzeeDocumento5 pagineCh 2 Guidelines Review and discussion questions and MCQ CoetzeeCameron BezuidenhoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Past and Current Reflection PracticesDocumento6 paginePast and Current Reflection Practicesapi-377149492Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocumento28 pagineThe Problem and Its BackgroundChristian Paul ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognitive Strategies for Learning ProblemsDocumento7 pagineCognitive Strategies for Learning ProblemsLizra DanielleNessuna valutazione finora
- ENDTERM - READINGS 3 (CHN) - AmitDocumento2 pagineENDTERM - READINGS 3 (CHN) - AmitVincent AmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Teaching StrategiesDocumento6 pagineEffective Teaching StrategiesJohn Paul M. MoradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Analysis & Probability - Drill Sheets Gr. 3-5Da EverandData Analysis & Probability - Drill Sheets Gr. 3-5Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4a) How To Teach Descriptive WritingDocumento1 pagina4a) How To Teach Descriptive WritingAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 BijakDocumento1 pagina1 BijakAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Steel and Translation MachineDocumento4 pagineReal Steel and Translation MachineAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1Documento3 pagineGroup 1Anna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 - Reading ComprehensionDocumento2 pagineGroup 5 - Reading ComprehensionAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Template Year 3 Edited by FizaDocumento1 paginaTemplate Year 3 Edited by FizaAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Bibiography: Tsl3103 English Language Teaching MethodologyDocumento2 pagineBibiography: Tsl3103 English Language Teaching MethodologyAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Body PartsDocumento3 pagineBody PartsvgcenNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Suggested ActivitiesDocumento12 pagine3 Suggested ActivitiesNurhayati SalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Oliver Twist SummaryDocumento2 pagineOliver Twist SummaryAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Example 8Documento3 pagineExample 8Anna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fisherman (Teacher's Version)Documento2 pagineThe Fisherman (Teacher's Version)Anna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 2 ConectoresDocumento4 pagineTema 2 ConectoresmaheriNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazing Race 2015 English Society IPGKTBDocumento176 pagineAmazing Race 2015 English Society IPGKTBAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5Documento1 paginaGroup 5Anna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- English - Lesson Plan HotseatDocumento4 pagineEnglish - Lesson Plan HotseatAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 - Reading ComprehensionDocumento2 pagineGroup 5 - Reading ComprehensionAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisys Report Linus Bi Saringan 1 (2013)Documento2 pagineAnalisys Report Linus Bi Saringan 1 (2013)Anna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Brush Blood Blade Broom Brother BlackDocumento2 pagineBrush Blood Blade Broom Brother BlackAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tentatif Eng WeekDocumento1 paginaTentatif Eng WeekAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- The Three Billy Goats Gruff Play ScriptDocumento3 pagineThe Three Billy Goats Gruff Play ScriptAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Butterfly Cartoon Edisi Jimat InkDocumento1 paginaButterfly Cartoon Edisi Jimat InkSyada RiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory AssignmentDocumento9 pagineTheory AssignmentAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- ResponsibleDocumento1 paginaResponsibleAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Butterfly Cartoon Edisi Jimat InkDocumento1 paginaButterfly Cartoon Edisi Jimat InkSyada RiaNessuna valutazione finora
- TSL3107 My NotesDocumento7 pagineTSL3107 My NotesSuhaimi ShaaraniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - JanDocumento35 pagine1 - JanAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Lesson Plans PDFDocumento26 pagineSample Lesson Plans PDFAnna SusieNessuna valutazione finora
- Little Red Ridinghood SupplementDocumento11 pagineLittle Red Ridinghood SupplementNorlizza Ismail0% (1)
- Analyzing Malaysian English ClassroomsDocumento59 pagineAnalyzing Malaysian English ClassroomsMu'iz BeatforteenNessuna valutazione finora
- Apostila de AseDocumento20 pagineApostila de AseOdair Pereira Dos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make Partitions in Windows 10 - Windows 8 PDFDocumento6 pagineHow To Make Partitions in Windows 10 - Windows 8 PDFAbhrajyoti DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Java Programming EbookDocumento110 pagineJava Programming EbookShaina Mae M. UngsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Explicit Vocabulary Instruction in MathDocumento10 pagineExplicit Vocabulary Instruction in Mathapi-249323843Nessuna valutazione finora
- Delete Entries On TRBAT and TRJOB Tables ..Documento3 pagineDelete Entries On TRBAT and TRJOB Tables ..ssssssssssNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Purposive CommunicationDocumento70 pagineChapter 1 - Purposive CommunicationEnola HolmesNessuna valutazione finora
- THEORY Transformation Question BankDocumento7 pagineTHEORY Transformation Question Bankpankaj12345katreNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP Inventory Module ProcessDocumento37 pagineSAP Inventory Module ProcessRajesh ChalkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Thesis Natural Oil AbsorbentDocumento178 pagineMaster Thesis Natural Oil AbsorbentFaris Mat100% (1)
- Labsheet 1 (Int)Documento3 pagineLabsheet 1 (Int)mail meNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Q3 PPT3Documento20 pagineG10 Q3 PPT3Ma. Shiela Mira NarceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Loaders and Linkers: - Machine-Independent Loader FeatureDocumento7 pagineChapter 3 Loaders and Linkers: - Machine-Independent Loader FeatureNimisha JithNessuna valutazione finora
- ManualDocumento572 pagineManualjoejunkisNessuna valutazione finora
- Los Valores en InglesDocumento4 pagineLos Valores en InglesYeinyNessuna valutazione finora
- ICAO Annex 19 PresentationDocumento46 pagineICAO Annex 19 PresentationBenoit Paré100% (1)
- Wsa CiscoDocumento6 pagineWsa Ciscoanhtuan29Nessuna valutazione finora
- February 26 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid MechanicsDocumento6 pagineFebruary 26 Homework Solutions: Mechanical Engineering 390 Fluid Mechanicsshun84Nessuna valutazione finora
- NACA Four-Digit Airfoil Profile 8% 4 12%Documento1 paginaNACA Four-Digit Airfoil Profile 8% 4 12%Raymond Yonathan HutapeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bb101 Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocumento14 pagineBb101 Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and MeasurementAidi AmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Uni SolutionsDocumento8 pagineSoft Uni Solutionsnrobastos1451Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDICONChina2019 - (87) - Vye, David - Designing A Narrowband 28-GHz Bandpass Filter For 5G Applications PDFDocumento41 pagineEDICONChina2019 - (87) - Vye, David - Designing A Narrowband 28-GHz Bandpass Filter For 5G Applications PDFkhyatichavdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment I Topics: LevellingDocumento2 pagineAssignment I Topics: LevellingsagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Battlestars VsDocumento56 pagineBattlestars VsSkiman94100% (2)
- ETHICS AND VALUES EDUCATION: What is PHILOSOPHYDocumento26 pagineETHICS AND VALUES EDUCATION: What is PHILOSOPHYdominic nicart0% (1)
- DLL Mtb-Mle3 Q2 W2Documento6 pagineDLL Mtb-Mle3 Q2 W2MAUREEN GARCIANessuna valutazione finora
- Sem-1 Drama: Do You Consider It As A Tragic Play? Submit Your Review. (Documento20 pagineSem-1 Drama: Do You Consider It As A Tragic Play? Submit Your Review. (Debasis ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Sentence Patterns - Ielts WritingDocumento5 pagineKey Sentence Patterns - Ielts Writingranga priyasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Sanitary Conditions of FoodDocumento83 pagineAssessment of The Sanitary Conditions of FoodtebebeNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Integrative TherapyDocumento91 pagineIntroduction To Integrative Therapynikos kasiktsis100% (1)
- Bus Bar White PaperDocumento16 pagineBus Bar White PaperShweta KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora