Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sciencestudyguide 3
Caricato da
api-251436295Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sciencestudyguide 3
Caricato da
api-251436295Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Science Study Guide
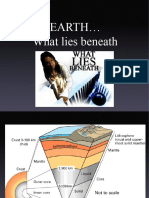
1. Describe characteristics of the various layers of the interior of the earth and be able to identify their relative position inside the Earth. The Crust Made of oceanic crust and continental crust. Solid Oceanic crust is made of basalt (igneous). Continental crust is made of granite(igneous). The oceanic crust is denser than the continental crust. Plates make up the crust. most outer layer of the earth The Mantle The mantle is made of the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. Convection currents because there are hot and cold spots It is a visco-solid (solid, but can move) like silly putty The lithosphere (tectonic plates) is more dense and cooler than the asthenosphere. Asthenosphere is the lower layer, convection currents. Underneath the crust The Outer Core Liquid and really hot Iron and nickel Beneath the mantle The Inner core Solid because of the pressure iron and nickel Inside the outer core 2.What makes up the lithosphere The uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. 3,What is the Asthenosphere? The lower and biggest layer of the earth's mantle, below the lithosphere, in which there is relatively low resistance to plastic flow and convection is thought to occur. 4. Describe the process scientists used to determine the shape and size of the Core? The shadow effect, earthquakes bounce off the liquid core and are not felt on ; like shining a light on something and getting a shadow. 5. Identify Pangaea. Describe Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift. List and describe 4 pieces of evidence he used to support his theory. In 1910, Alfred Wegener hypothesized that all of Earths continents were once joined together in a single supercontinent, Pangaea, and have since then drifted apart through the ocean floor. Over tens of millions of years, Pangaea began to break apart, as the new land masses slowly drifted to their modern day locations.
Wegner gathered evidence from:
Fit of the continents: such as South America and Africa. -land features: Mountains and other features provided evidence that when the continents were pieced together originally, mountain ranges on two different continents seemed compatible like jigsaw puzzle pieces. Examples of these borders are South America and Africa. - fossils: Glossopteris, a fern-like plant that lived 250 million years ago, was found in rocks in Africa, South America, Australia, India and Antarctica. The fact that these fossils were found so far apart, provided Wegner with more evidence that Pangaea existed. -evidence of climate change: Although when a continent moves closer to the equator it is warmer, and one further away is colder, the continent still carries fossils and rocks that formed at its previous location. The fossils of tropical plants found on the island Spitsbergen an island now in the Arctic Ocean. 6. What were his main issues scientists had with Wegners theory of Continental drift?. Wegner couldn't provide an explanation for the force that pushes or pulls the continents. 7. How is the false theory of continental drift different than todays widely accepted theory of plate tectonics. Floating masses on a sphere would collect at the equator, and stay there. some parts of the Earth's surface (crust) should have solidified while other parts were still fluid. 8. Explain what is meant by theory of plate tectonics. The plates are moving due to mantle convection. scientific theory that describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. 9. Be able to label the major Tectonic plates on Earth.
10. Explain how the convection in the mantle affects the plates motion. The slow motion of Earth's visco-solid mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior of the Earth to the surface.The lithosphere, which rides atop the asthenosphere is made up of tectonic plates that are being created and destroyed at their plate boundaries. The mantle is added to the growing edges of a plate by seafloor spreading. This hot added material cools down by conduction and convection of heat. At the consumption edges of the plate, the material has thermally contracted to
become dense, and it sinks under its own weight in the process of subduction usually at an ocean oh my lawd trench.
11. Describe the process of subduction. Subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate and sinks into the mantle as the plates converge. Regions where this process occurs are known as subduction zones. 12. Explain the concept of sea-floor spreading, who explained it, and how magnetism can be used to prove it occurred. Mid ocean rifts from where two plates are moving apart form new sea floor when magma rises up from the crack this is pushing all of the plate to one side. Hess explained the theory of sea floor spreading. 13. Given a set of data, be able to calculate the rate at which a Tectonic plate moves. Speed(cm/yr)= Distance (cm)/ Age Difference (yrs) 14. Identify three types of plate boundaries. describe what is happening at each. convergent-two plates come together divergent- where two plates move, most occur along mid-ocean ridges, some on land where two of the earths plates slide apart transform-two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions 15. Describe where on Earth each of the following are located: mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, trenches, mountains, island arc, volcanoes, hot spots, convergent, divergent and transform Convergent tectonic plates When two continental plates collide a mountain like Everest is formed. When a plate subducts a hot spot seeps up forming Coastal Volcanoes, Volcanoes like Mt. Helens and Island Arcs like Japan Divergent Tectonic plates mid-ocean ridges-Oceanic crust diverging and magma rises from the mantle rift valleys- Where continental crust spreads apart. trenches-Where there is are ocean and continental plate or two oceanic plates that is denser than another the trench is place where one goes down like the Mariana Trench. 16. Explain which plates are interacting to form the following land features: mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, trenches, mountains, island arc and coastal volcanoes. mid-ocean ridges,-2 oceanic plates diverging rift valleys, - 2 continental plates diverging trenches, - 1 oceanic plate and 1 continental plate converging. 2 oceanic plates converging mountains, - 2 continental plates converging island arc - hot spots coastal volcanoes.- 1 oceanic and 1 continental plate converging
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Dynamic Earth QuestionsDocumento2 pagineDynamic Earth QuestionsDrew ClaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksDa EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo Notes o LevelDocumento137 pagineGeo Notes o LevelAlbert MuswewemombeNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftDocumento31 paginePlate Tectonics: Earth's Plates and Continental DriftTeena SeiclamNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics Story Dynamic EarthDocumento2 paginePlate Tectonics Story Dynamic EartharmenianpricessNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Plate Movement 1Documento46 pagineCauses of Plate Movement 1AnnRubyAlcaideBlandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate TectonicsDocumento19 paginePlate Tectonicsapi-354859496Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plate TectonicsDocumento32 paginePlate TectonicsJericho Luiz Sipin RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- ANSWERS Clickview Video WorksheetDocumento3 pagineANSWERS Clickview Video Worksheet李之由Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sci Reporting Lesson InfaurrDocumento6 pagineSci Reporting Lesson InfaurrmelissakatevfloresNessuna valutazione finora
- TectonicsDocumento32 pagineTectonicsFlavyus06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics GR 10Documento2 paginePlate Tectonics GR 10musaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Plate Tectonics KDDocumento16 pagine4 Plate Tectonics KDStephen Richard Kirkley100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocumento35 paginePlate Tectonicslightningpj1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plate TectonicsDocumento41 paginePlate TectonicsJohn100% (1)
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDocumento16 pagineReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tectonics TitiwDocumento23 pagineTectonics Titiwmary joy v, chiquilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesDocumento2 pagineActivity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesaiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 Module 2.2-1Documento88 pagineScience 10 Module 2.2-1marisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 Continents Change Position Over TimeDocumento13 pagine1.2 Continents Change Position Over TimeseheehanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocumento47 pagineThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsShakerMahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocumento5 paginePlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNessuna valutazione finora
- Continental Drift Theory ExplainedDocumento15 pagineContinental Drift Theory ExplainedAndrea BaluyotNessuna valutazione finora
- Geology Module 2 ReviewerDocumento8 pagineGeology Module 2 ReviewerElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning OutcomesDocumento6 pagineLearning OutcomesAida EsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Semesterproject 2Documento62 pagineSemesterproject 2api-281484560Nessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento29 pagineUntitledIyana GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- Continental Drift To Plate Tectonics and Earth's StructureDocumento15 pagineContinental Drift To Plate Tectonics and Earth's StructureJomar IsonNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento28 pagineScienceCJ MacasioNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Quarter 1 Reviewer G10Documento12 pagineScience Quarter 1 Reviewer G10jahri ruzeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Screenshot 2022-12-06 at 11.32.07 PMDocumento1 paginaScreenshot 2022-12-06 at 11.32.07 PMCrypticNessuna valutazione finora
- PLATE TECTONICS AND RUPTURINGDocumento10 paginePLATE TECTONICS AND RUPTURINGBocam la LegendeNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 1st PeriodicalDocumento2 pagineScience 1st PeriodicalAgatha AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- From Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsDocumento6 pagineFrom Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsyabaeveNessuna valutazione finora
- What Can You Say About The Ages of The Oceanic Rocks Far From The MidDocumento2 pagineWhat Can You Say About The Ages of The Oceanic Rocks Far From The MidBreianah Jare SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics-WPS OfficeDocumento21 paginePlate Tectonics-WPS OfficeAila Jane Olano VestidasNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 1Documento9 pagineDocument 1NADIAHTUL MARYAM BINTI RUSYDI RUSNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocumento39 pagineThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- 3 Plate-TechtonicsDocumento33 pagine3 Plate-TechtonicsSakshi BhalewadikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science g10Documento4 pagineScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNessuna valutazione finora
- IEQ-05 Earthquake Geology and Geoinformatics CourseDocumento23 pagineIEQ-05 Earthquake Geology and Geoinformatics CourseShubham BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Continental Drift Theory HandoutsDocumento3 pagineThe Continental Drift Theory Handoutslorraine baysicNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Plate TectonicsDocumento5 pagineLecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Plate TectonicsQP0125 Vu Song HaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 Plate TectonicsDocumento40 pagineLesson 7 Plate TectonicsPsycho The GreatestNessuna valutazione finora
- Earths MechanismDocumento25 pagineEarths MechanismCyree ElishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Reviewer YesDocumento5 pagineScience Reviewer YesJeffNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics ReadingDocumento6 paginePlate Tectonics Readingapi-506851645Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022Documento54 pagineGrade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022shanesha blackhood100% (1)
- Key Concept Review (Answers To In-Text "Concept Checks")Documento3 pagineKey Concept Review (Answers To In-Text "Concept Checks")serkansancakNessuna valutazione finora
- Continental Drift HypothesisDocumento4 pagineContinental Drift HypothesisRaymart Dave MirandoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocumento57 pagineThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicshatdoghatdogNessuna valutazione finora
- SciencemidtermDocumento9 pagineSciencemidtermapi-281100019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 2 WordDocumento12 pagineGroup 2 WordJhyrelle A. MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate TectonicsDocumento46 paginePlate TectonicsBoni Almueda Valdez Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Tectonics: Presentation By: James Bernard R. Quiben 10 - ThomsonDocumento13 paginePlate Tectonics: Presentation By: James Bernard R. Quiben 10 - ThomsonDelta [GD]Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week-3 - Plate TectonicsDocumento81 pagineWeek-3 - Plate TectonicsRashid AhmedovNessuna valutazione finora
- ReviewerDocumento8 pagineReviewerMelody Bong ZitaNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 PPT - Continental Drift Seafloor Spreading Convection - Plate Tectonics - 1673063368 1Documento72 pagineL4 PPT - Continental Drift Seafloor Spreading Convection - Plate Tectonics - 1673063368 1Aron AronNessuna valutazione finora
- Geology of the Pacific Northwest: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsDa EverandGeology of the Pacific Northwest: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Chemical Kinetics and Charge Transfer Based On Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsDocumento17 pagineTheory of Chemical Kinetics and Charge Transfer Based On Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsYoana Yoa YoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser Beam Energy Distribution Affects Weld DimensionsDocumento8 pagineLaser Beam Energy Distribution Affects Weld Dimensionskppsiva87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingDocumento4 pagineJournal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingJohan Pranata BarusNessuna valutazione finora
- Bleeding of ConcreteDocumento3 pagineBleeding of ConcreteANessuna valutazione finora
- Radar PlottingDocumento23 pagineRadar Plottingthugsdei100% (2)
- Galloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IDocumento18 pagineGalloway 1989 Genetic Stratigraphic Sequence Basin Analysis IMitreNessuna valutazione finora
- L-3/T-2/CE Date: 07/08/2016Documento30 pagineL-3/T-2/CE Date: 07/08/2016নীল জোছনা0% (1)
- ATS - Design Manual CaterpillarDocumento84 pagineATS - Design Manual CaterpillarSharik Khan100% (1)
- Maxwell Stress Tensor ExplainedDocumento6 pagineMaxwell Stress Tensor ExplainedSyeda Tehreem IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Master1 AM CoursesDocumento3 pagineMaster1 AM CoursesParokotil MidhunNessuna valutazione finora
- Diketopiperazines RevDocumento27 pagineDiketopiperazines RevIsaí MillánNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 16 - CEL - BottleDocumento14 pagineTutorial 16 - CEL - BottleRezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Controls Exit OTDocumento13 pagineControls Exit OTJeffrey Wenzen AgbuyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interference PatternsDocumento8 pagineInterference PatternsAsa mathewNessuna valutazione finora
- PNA Chemistry Expedite 8900 User's GuideDocumento114 paginePNA Chemistry Expedite 8900 User's GuideJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjoint Rans With Filtered Shape Derivatives For Hydrodynamic OptimisationDocumento11 pagineAdjoint Rans With Filtered Shape Derivatives For Hydrodynamic Optimisationvolo87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFDocumento6 pagineMaximum Material Boundary (MMB) and Its Advantages in GD&T Analysis PDFSangeethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gay-Lussac's Law Problems and SolutionsDocumento1 paginaGay-Lussac's Law Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Notesch # 18Documento11 pagineNotesch # 18ZeeshanMahdiNessuna valutazione finora
- 85 Describing Motion OrganizerDocumento10 pagine85 Describing Motion OrganizerFernando Sorto50% (2)
- Harmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor ModelsDocumento14 pagineHarmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor ModelsJisu RyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Audio Processing Quiz 1Documento2 pagineAudio Processing Quiz 1Tony BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Slope ND DeflectionDocumento19 pagineSlope ND DeflectionprashantbaraskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearings ShaftsDocumento74 pagineBearings ShaftsCik MinnNessuna valutazione finora
- PFlow ScriptDocumento6 paginePFlow Scripttohu777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pages From Cinematography-Theory and PracticeDocumento74 paginePages From Cinematography-Theory and PracticeSalazar SliterinNessuna valutazione finora
- FLUIDME Quiz 02 AnswersDocumento5 pagineFLUIDME Quiz 02 AnswersSam Denielle TugaoenNessuna valutazione finora
- A+A Diagnostics: Chemray 420Documento2 pagineA+A Diagnostics: Chemray 420Saleh HamadanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Technology Internal Assessment QuestionsDocumento2 pagineConcrete Technology Internal Assessment QuestionsSubodh AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- Curtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochureDocumento38 pagineCurtain Wall System From Technal - Geode-BrochurebatteekhNessuna valutazione finora