Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Guide To Bdasoct03-05
Caricato da
gtslty99Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Guide To Bdasoct03-05
Caricato da
gtslty99Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07)
Guideline
BCA
Technology Development Division
Guide to the
Buildable Design Appraisal System
The Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System is electronically published by the Technology Development Division
of the Building and Construction Authority.
Building and Construction Authority, September 2005
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, without
permission in writing from the publisher.
This Guide is subjected to revision from time to time. Nothing herein shall be construed to exempt the person submitting
an application or any plans from otherwise complying with the provisions of the Building Control Act (Cap 29) or any
rules and/or guidelines made thereunder or any Act or rules and/or guidelines for the time being in force.
While every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the information presented in this publication, neither the Authority
nor its employees or agents can accept responsibility for any loss or damage incurred in connection with the use of the
contents.
*XLGH WR WKH
%XLOGDEOH 'HVLJQ
$SSUDLVDO 6\VWHP
for Code of Practice on
Buildable Design Sep 2005
(incorporating changes affecting
projects with planning applications
made on or after 1
st
Jan 2007)
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07)
Content Page
Introduction 1
General Guidelines
1. Gross Floor Area 2
2. Constructed Floor Area 4
3. Minimum Buildability Score 4
4. Decimal Points 6
5. Module 6
6. Structures to be Included in Computation 6
7. Basics of Buildable Design Appraisal System (BDAS) 7
8. Worked Examples 8
Part 1 Structural Systems
1. Labour Saving Indices for Different Structural Systems 13
2. Structural Areas Consideration 15
3. Prefabricated Reinforcement Consideration 15
4. Structural Systems 16
5. Measurement 24
6. Worked Examples 26
Part 2 Wall Systems
1. Labour Saving Indices for Different Wall Systems 35
2. Wall Length Consideration 37
3. Prefabricated Reinforcement Consideration 37
4. Measurement 37
5. Worked Examples 41
Part 3 Other Buildable Design Features
Points Awarded for Other Buildable Design Features 44
1. Standardisation 46
1.1 Columns 46
1.2 Beams 49
1.3 Door Leaf Openings 54
1.4 Windows 55
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07)
Content Page
2. Grids 56
2.1 Repetition of Floor-to-Floor Height 56
2.2 Vertical Repetition of Structural Floor Layout 61
3. Others 64
3.1 Multi-tier Precast Columns 64
3.2 Precast or Pre-assembled/Metal Staircases 65
3.3 Precast Meter Chambers 66
3.4 Precast Refuse Chutes 67
3.5 Precast Service Risers 68
3.6 Non-screed Floor 68
3.7 Columns Sit Directly on Top of Piles 69
3.8 Ground Beams on Top of Pilecaps and/or Integrated into Pilecaps 70
3.7 No column stumps 71
(for projects with planning applications made on or after 1 Jan 2007)
3.8 Precast bay windows 72
(for projects with planning applications made on or after 1 Jan 2007)
3.9 Precast planter boxes 73
(for projects with planning applications made on or after 1 Jan 2007)
A. Single Integrated Components (Bonus Points) 74
A.1 Prefabricated Bathroom/Toilet Units complete with piping/wiring 74
A.2 Precast Household Shelters 75
B. Demerit Points 76
B.1 Non-functional void on slab 76
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) 1
Introduction
This Guide serves to advise the industry on the computation of buildability score using the Buildable
Design Appraisal System. The guide is revised to the requirement specified in Code of Practice on
Buildable Design September 2005, and has incorporated changes affecting projects with planning
applications made on or after 1
st
January 2007. Interpretation on the terms and method of
measurement/computation are included to ensure that the buildability scores are computed by the
industry in a consistent manner. More examples of buildable design scoring are given to illustrate the
computation sequence and methodology.
The buildability score of a design consists of 3 main parts:
Part 1: Structural Systems (maximum 50 points);
Part 2: Wall Systems (maximum 40 points);
Part 3: Other Buildable Design Features (maximum 10 points + bonus points for single
integrated components)
Indices for structural systems are indicated in Table 1. Indices for wall systems are indicated in Table 2.
Buildability points for other buildable design features are indicated in Table 3.
If you have other queries that are not addressed in this Guide, please contact us at:
Technology Development Division
Building and Construction Authority
5 Maxwell Road, #16-00
Tower Block, MND Complex
Singapore 069110
Tel: 63257720 Fax: 63254800
General Guidelines
Gross Floor Area
Constructed Floor Area
Minimum Buildability Score
Decimal Points
Module
Structures to be Included in Computation
Basics of Buildable Design Appraisal System
Worked Examples
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System 2
General Guidelines
1 Gross Floor Area
The gross floor area (GFA) of a project is used to determine whether a project is required to comply
with the minimum buildability score requirement or not. Once a project is affected by the buildability
legislation (GFA of at least 2000 square metres), then depending on the amount of GFA involved and
the category of building work, the corresponding minimum buildability score as set out in the Code of
Practice on Buildable Design (COP) will apply.
For new developments, the GFA would be as spelt out in the planning permission issued by URA,
including any bonus GFA granted (e.g. for balconies etc). This GFA shall be the final and regularised
GFA as verified by URA.
In the case of projects involving additions and alterations (A&A) work, the GFA would be the total GFA
of all new floor and/or reconstruction of existing floor. As such, an A&A project could be affected by the
legislation even if there is no increase in GFA to the existing building or the increase in total GFA of the
existing development is less than 2000 square metres as illustrated by the following examples:-
Example 1
Proposed A&A to an existing industrial development involving change of use and a new
extension
In this example, there is a decrease in GFA of 2000 m
2
of the existing building due to the change of use
of part of the building from warehouse to carpark. At the same time, there is an increase in GFA of
2000 m
2
to the existing building from the new side extension. Overall, there is no increase in the total
GFA of the A&A project.
However, the above project is subjected to the buildability legislation. This is because the legislation
looks at GFA of constructed floors, whether new or reconstructed. The amount of GFA in this case is
2000 m
2
(assuming that there is no work done for the portion of the building undergoing a change of
use).
PLAN
Existing Building
Change of use from
warehouse to carpark
(affected GFA = 2000 m
2
)
New extension with
GFA = 2000 m
2
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System 3
Example 2
Proposed A&A and addition of a new mezzanine floor and 2 new storeys to an existing
7-storey commercial building
In this example, the net change in GFA of the existing development is 1350 m
2
while the total GFA of
new and reconstructed floors is 2950 m
2
.
The breakdown of the respective GFA is as shown in the
table below.
Net Change in GFA
Total GFA of new and
reconstructed floors
Re-layout of 1
st
storey - 900 m
2
0 m
2
New mezzanine floor + 300 m
2
+ 300 m
2
Reconstruction of 8
th
storey no change in GFA + 700 m
2
Construction of 2 new floors + 1950 m
2
+ 1950 m
2
Total GFA +1350 m
2
+ 2950 m
2
As in Example 1, by virtue of the definition of GFA in the context of A&A work, the above project is
subjected to the buildable design legislation since the total GFA of the new and reconstructed floors is
2950 m2. This is despite the increase in the total GFA of the existing building being only 1350 m
2
which
is less than 2000 m
2
.
roof
9
th
storey
mezzanine
3
rd
storey
8
th
storey
7
th
storey
6
th
storey
5
th
storey
4
th
storey
1
st
storey
reconstruction of part of existing floor involving GFA of 700 m
2
new mezzanine floor with GFA of 300 m
2
re-layout of existing floor with GFA of 900 m
2
less
2 new floors with GFA of 1950 m
2
2
nd
storey
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System 4
2 Constructed Floor Area
Once a project is subjected to the minimum buildability score requirement, all constructed floor areas
(including reconstructed floor areas) are to be considered when computing the project buildability score
(except minor structures as defined in item 6). The constructed floor area is also used to derive the
overall buildability score of a project comprising multiple blocks, by pro-rating the buildabilty scores of
each of the blocks with its constructed floor area and summing up the pro-rated scores (please also
refer to item 7).
3 Minimum Buildability Score
Different minimum buildability scores are given for different categories of development. For a new
development, the corresponding minimum buildability score can be found in the COP stipulated under
Table B (for projects with planning applications made from 1
st
September 2005 to 31
st
December 2006)
or Table D (for projects with planning applications made on or after 1
st
January 2007).
For a mixed development, the minimum buildability score will be pro-rated according to the GFA of
each type of development.
For an A&A project with the A&A work being carried out outside the existing building, such A&A work is
considered as new work. As such, the corresponding minimum buildability score required to be
complied by the A&A project is also set out in the COP under Table B (for projects with planning
applications made from 1
st
September 2005 to 31
st
December 2006) or Table D (for projects with
planning applications made on or after 1
st
January 2007). Examples of A&A work being carried out
outside the existing building are those that are constructed outside the envelope of the existing
building, such as
a new extension to the existing building,
additional storeys over the existing roof etc.
existing building
Illustration 1: Project with A&A work carried out outside an existing building
- Minimum buildability score for New Work shall apply
new extension
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System 5
For a project with A&A work being carried out within the existing building (envelope), the minimum
buildability score is as shown under Table C Minimum Buildability Score for A&A Work (for projects
with planning applications made from 1
st
September 2005 to 31
st
December 2006) or Table D (for
projects with planning applications made on or after 1
st
January 2007) in the COP. Examples of such
A&A work are
a new mezzanine floor,
the slabbing over of an existing void within a building,
the replacement or reconstruction of existing floor etc.
In the case of a project with A&A work being carried out both within and outside the existing building,
the minimum buildability score will be pro-rated according to the GFA of the A&A work outside the
existing building (new work Table B or Table D) and the GFA of the A&A work within the existing
building (Table C or Table D).
Illustration 2: Project with A&A work carried out within an existing building
- Minimum buildability score for A&A Work shall apply
roof
2
nd
storey
9
th
storey
new mezzanine
3
rd
storey
8
th
storey
7
th
storey
6
th
storey
5
th
storey
4
th
storey
1
st
storey
A&A work within existing building
A&A work outside existing building
(considered as new work)
Illustration 3: Project with A&A work carried out both within and outside an
existing building - Minimum buildability score for A&A Work
shall be pro-rated according to the GFA of each type of work
new mezzanine floor
Sep 2005 (rev Jan 07) Guide to the Buildable Design Appraisal System 6
4 Decimal Points
All calculations should be rounded off to the nearest 2 decimal places except for the overall buildability
score and percentage of coverage for other buildable design features, which should be expressed as
an integer.
5 Module
The basic module (M) denotes 100mm. For example, 3M denotes 300mm and 0.5M denotes 50mm.
6 Structures to be Included in Computation
All major structures, including clubhouse and multi-storey carpark, are to be considered when
computing the buildability score. Minor structures such as 22 KV substation, guard post, bin centre and
trellis can be excluded from the computation, provided that they are not within or structurally linked to
the main building.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Copbdapr 2011Documento50 pagineCopbdapr 2011Wai Khuin LumNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca BDDocumento35 pagineBca BDlim kang haiNessuna valutazione finora
- BCA Code of Practice On Buildable DesignDocumento78 pagineBCA Code of Practice On Buildable DesignIlluga Ta Phrom100% (1)
- Buildability ScoreDocumento6 pagineBuildability ScoreVachara PeansupapNessuna valutazione finora
- BD Practice Note 172 (OTTV)Documento3 pagineBD Practice Note 172 (OTTV)Kei WongNessuna valutazione finora
- MR - Ksenou L&T PrecastDocumento53 pagineMR - Ksenou L&T PrecastHarssh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ottv 1Documento4 pagineOttv 1iqbal_arch79Nessuna valutazione finora
- MSB02 Concept Design 2010-03-12Documento83 pagineMSB02 Concept Design 2010-03-12Vasil Georgiev Georgiev100% (1)
- Code Review ProcessDocumento11 pagineCode Review ProcesskmitriNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3 SCP201 Assignment Worksheet - Jan 2023 PDFDocumento4 pagine1.3 SCP201 Assignment Worksheet - Jan 2023 PDFfang weiNessuna valutazione finora
- APP067Documento3 pagineAPP067Emdad YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Part A Structure 2012Documento49 paginePart A Structure 2012John LiebermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Buildable Design: Code of Practice OnDocumento74 pagineBuildable Design: Code of Practice OnLin ZhiweiNessuna valutazione finora
- Enhanced Buildability Framework To Improve ProductivityDocumento5 pagineEnhanced Buildability Framework To Improve ProductivityJianhua WuNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrialised Building SystemDocumento20 pagineIndustrialised Building SystemreenaNessuna valutazione finora
- NIBS Guideline 3-2012 Building Enclosure Commissioning ProcessDocumento337 pagineNIBS Guideline 3-2012 Building Enclosure Commissioning ProcessJohn CleggNessuna valutazione finora
- BCA 1B - Code of Practice On Buildability-2015 PDFDocumento75 pagineBCA 1B - Code of Practice On Buildability-2015 PDFdelciogarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce1401 Eqs 1 - 2Documento12 pagineCe1401 Eqs 1 - 2Alex ChristopherNessuna valutazione finora
- EPC Civil06Documento6 pagineEPC Civil06MHanif ARNessuna valutazione finora
- CIS30 Productivity Measurement of Building Construction ProjectsDocumento24 pagineCIS30 Productivity Measurement of Building Construction ProjectsShafeek Ramlee100% (1)
- FR2 SoS For BIM Modelling (GBC Engineering) P01Documento10 pagineFR2 SoS For BIM Modelling (GBC Engineering) P01ramatchatNessuna valutazione finora
- Industry CircularDocumento43 pagineIndustry CircularSendil AdebbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 2 Architectural Design Standards: 2.1 General 2.1.1 Correlation and CoordinationDocumento7 pagineSection 2 Architectural Design Standards: 2.1 General 2.1.1 Correlation and CoordinationJennifer Salonga ManinangNessuna valutazione finora
- BCM614Documento10 pagineBCM614Nuri AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Conceptual Design in Revit Architecture WhitepaperDocumento13 pagineConceptual Design in Revit Architecture WhitepaperThoufil SalimNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Rcny 5000-01Documento18 pagine1 Rcny 5000-01persaudchrisNessuna valutazione finora
- URA Circular - Harmonisation of Floor Area Definitions by URA, SLA, BCA and SCDFDocumento14 pagineURA Circular - Harmonisation of Floor Area Definitions by URA, SLA, BCA and SCDFKahHoe ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca 2017Documento84 pagineBca 2017AnnahuynhNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A 30 Storey Office Building With Reinforced Concrete Design Using Etabs Structural SoftwareDocumento51 pagineDesign of A 30 Storey Office Building With Reinforced Concrete Design Using Etabs Structural SoftwareAyodele Oluwaseyi Dina100% (1)
- BCA - Fee Calculation Guideline 10-Aug-2017 - 1Documento10 pagineBCA - Fee Calculation Guideline 10-Aug-2017 - 1xuongrong_xdNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Rcny 5000-01Documento20 pagine1 Rcny 5000-01annaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To Creating WBSDocumento10 pagineA Guide To Creating WBSPrialNessuna valutazione finora
- IBS Score ManualDocumento32 pagineIBS Score Manualwanjailani83% (6)
- NIBS Guidelines For CommissioningDocumento337 pagineNIBS Guidelines For CommissioningWaseem SiddiqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Code ComplianceDocumento16 pagineEnergy Code ComplianceluissuazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Glasgow City Council - STR Calc GuidanceDocumento2 pagineGlasgow City Council - STR Calc GuidanceMichael KilpatrickNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Information Modelling - Group AssignmentDocumento43 pagineBuilding Information Modelling - Group AssignmentKainaaz F. VariavaNessuna valutazione finora
- AM Exam Paper 2007Documento20 pagineAM Exam Paper 2007romelramarack1858Nessuna valutazione finora
- dc22 09Documento22 paginedc22 09Teo See HwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Quality Control Planning According To UNI EN 13670Documento10 pagineConcrete Quality Control Planning According To UNI EN 13670Querubin R Yolando Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revit 2010 GuidanceDocumento30 pagineRevit 2010 GuidanceAlex Raiker Yañez CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Modelling - ASB - Part 2 For StudentsDocumento30 pagineCost Modelling - ASB - Part 2 For StudentsGloria DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendations For The Seismic Design of Tall BuildingsDocumento20 pagineRecommendations For The Seismic Design of Tall BuildingsAWAKSEORANGNessuna valutazione finora
- LOTUS Guidelines Energy Performance Calculation Method Rev DDocumento35 pagineLOTUS Guidelines Energy Performance Calculation Method Rev DVũ NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Analysis of MIVAN Formwork Building and Conventional Formwork Building Based On Cost and DurationDocumento4 pagineComparative Analysis of MIVAN Formwork Building and Conventional Formwork Building Based On Cost and DurationInnovative Research PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement For PILING WorkDocumento1 paginaMethod Statement For PILING WorkahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Integrity ReportDocumento24 pagineDesign Integrity Reportakankwasa100% (1)
- CoV - Bulletin Green Buildings Policy For RezoningDocumento4 pagineCoV - Bulletin Green Buildings Policy For RezoningAakash GoliyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Report BEDocumento64 pagineFinal Report BEsrivathsabestharNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 2 1Documento12 pagine3 2 1Izo SeremNessuna valutazione finora
- B02-Prepare Cost EstimateDocumento125 pagineB02-Prepare Cost Estimatedeepa_dspdesign0% (1)
- Clement CanopyDocumento14 pagineClement Canopytun20000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Category of IBS Structural Category of IBSDocumento12 pagineStructural Category of IBS Structural Category of IBSismanisaaNessuna valutazione finora
- CVL 222Documento14 pagineCVL 222Majd KlNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Urban Resilience through Change of UseDa EverandBuilding Urban Resilience through Change of UseNessuna valutazione finora
- Modernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresDa EverandModernisation, Mechanisation and Industrialisation of Concrete StructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesDa EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Career Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsDa EverandCareer Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneDa EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNessuna valutazione finora
- Stability of Temporary Bracing: Steel Industry Guidance NotesDocumento2 pagineStability of Temporary Bracing: Steel Industry Guidance Notesgtslty99Nessuna valutazione finora
- JOE Method of Installation & Method of Statement 2012 (Latest)Documento28 pagineJOE Method of Installation & Method of Statement 2012 (Latest)gtslty99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cad Test2Documento5 pagineCad Test2gtslty99Nessuna valutazione finora
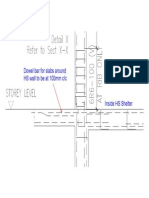
- Dowel Bar For Slabs Around HS Wall To Be at 100mm C/CDocumento1 paginaDowel Bar For Slabs Around HS Wall To Be at 100mm C/Cgtslty99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current Effective On 1 Apr 2014 First Schedule First ScheduleDocumento4 pagineCurrent Effective On 1 Apr 2014 First Schedule First Schedulegtslty99Nessuna valutazione finora
- ReinforcementDocumento11 pagineReinforcementgtslty99100% (1)
- Heslb Loan Application GuidelinesDocumento8 pagineHeslb Loan Application GuidelinesCleverence KombeNessuna valutazione finora
- Find A Cambridge SchoolDocumento1 paginaFind A Cambridge SchoolNiveen OshoNessuna valutazione finora
- DM No. 341 s.2023Documento5 pagineDM No. 341 s.2023Jennifer PomarNessuna valutazione finora
- 22B Office Hour: Oracle Fusion Cloud Risk ManagementDocumento38 pagine22B Office Hour: Oracle Fusion Cloud Risk Managementmeera2k10Nessuna valutazione finora
- The UK Government Digital ServiceDocumento11 pagineThe UK Government Digital Serviceilyas mabroukNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Telehanddler TH580B / SLH1-UpDocumento56 pagineManual Telehanddler TH580B / SLH1-UpRichard Peru100% (6)
- NIELIT Recruitment For Scientist and Technical Assistants 2017 Official NotificationDocumento6 pagineNIELIT Recruitment For Scientist and Technical Assistants 2017 Official NotificationKshitija100% (1)
- Unlimited Clients by Arnav Srivastv-1Documento170 pagineUnlimited Clients by Arnav Srivastv-1Xiang XingNessuna valutazione finora
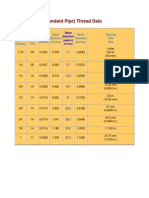
- BSP Pipe ThreadDocumento1 paginaBSP Pipe ThreadgvmindiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deeksha Negi: @negideekshaaDocumento6 pagineDeeksha Negi: @negideekshaaShrish PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Refractory Installation in The Cement Rotary KilnDocumento86 pagineChapter 3 Refractory Installation in The Cement Rotary KilnMKPashaPasha88% (8)
- P121.pdf (En US)Documento142 pagineP121.pdf (En US)Planeador MantenimientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Order Future Doctor Cake Online CakeNBake NoidaDocumento1 paginaOrder Future Doctor Cake Online CakeNBake NoidaprudhvipoosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Delta 4000 Instruction ManualDocumento20 pagineDelta 4000 Instruction ManualzeniekNessuna valutazione finora
- Robotics Unit4 SlidesDocumento72 pagineRobotics Unit4 SlidesJanarthanan BalakrishnasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- User Guide: Small in Size, With Grand FeaturesDocumento13 pagineUser Guide: Small in Size, With Grand Featuresjhfbty100% (1)
- Rs 485 SpecDocumento3 pagineRs 485 SpecJuan Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Acclarix LX9 Series Datasheet-V2.2Documento27 pagineAcclarix LX9 Series Datasheet-V2.2Marcos CharmeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar EnergyDocumento30 pagineSolar EnergyRushikesh RasalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lastexception 63837276287Documento1 paginaLastexception 63837276287darkmysiaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAL-00-E-0004 Rev-1 ELECTRICAL CABLE SIZINGDocumento5 pagineCAL-00-E-0004 Rev-1 ELECTRICAL CABLE SIZINGtceterexNessuna valutazione finora
- Perimeter 8 Specifications - July2022 - V6 - 240207 - 101351Documento3 paginePerimeter 8 Specifications - July2022 - V6 - 240207 - 101351dorodriguezvNessuna valutazione finora
- Experience The Excitement of Discovery: X-TERRA 505 X-TERRA 705Documento2 pagineExperience The Excitement of Discovery: X-TERRA 505 X-TERRA 705Inform7105Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Flight / Before Start Engine Start: Summarised Checklist PMDG B737-600/-700/-800Documento2 paginePre-Flight / Before Start Engine Start: Summarised Checklist PMDG B737-600/-700/-800IuriNessuna valutazione finora
- MXTDocumento18 pagineMXTMaxey HigginbothamNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing Effective Powerpoint Presentations: Adopted From: Victor Chen Erau - V.Chen@ErauDocumento49 pagineDesigning Effective Powerpoint Presentations: Adopted From: Victor Chen Erau - V.Chen@ErauChara etangNessuna valutazione finora
- British Signals Intelligence in The Trenches - 1915-1918 - Part1Documento24 pagineBritish Signals Intelligence in The Trenches - 1915-1918 - Part1maruka33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquozyme LPH Benefit SheetDocumento2 pagineLiquozyme LPH Benefit SheetcamilodomesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Text Information and MediaDocumento66 pagineText Information and MediaPaula Camille VegaNessuna valutazione finora
- API 16A 3rd Edition, 2004. Errata 1Documento2 pagineAPI 16A 3rd Edition, 2004. Errata 1Noralia Amanina Osman100% (2)