Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Behavioral Genetics in Families
Caricato da
AssignmentLab.comDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Behavioral Genetics in Families
Caricato da
AssignmentLab.comCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Running head: BEHAVIORAL GENETICS IN FAMILIES
Behavioral Genetics in Families Name Professor Course Date
BEHAVIORAL GENETICS IN FAMILIES Introduction Research information pools indicate modifications in the environment could result to positive behavioral outcomes. Parallel to sociological research on behavior, bodies of scientific research on genetics have continuously linked behavior to genetics. This studies show that behavioral factors have relationships with genetic influences. Increased understanding of behavioral factors and their relationship to genetics will provide information on environmental mechanisms applicable in prevention sciences (Carnegie Mellon University, 2009). Family interactions provide crucial impetus for personal outcomes. The theory of inclusive fitness by Hamilton suggests that immense genetic relatedness results to altruistic actions between family members. In quantitative, behavioral genetics, in families, naturally occurring variations in genetic
relatedness members of the family identify environmental and genetic contributions to behavior. The twin design can be immensely useful in such a study. In the twin study, differences and similarities in fraternal and identical twins are compared with an aim of estimating environmental and genetic influences (Leve, Harold, & Patterson, 2010). In order for the study to obtain conclusive results, the adoption design is highly useful in determining environmental influences that identify similarities between family members. In this study, adopted children placed in nonrelated family members do not have genetic relatedness. However, they share the same setting with other family members (Turkheimer, 2008). Thereafter, molecular genetics studies are compared with a focus on measured genes through the collection of DNA. Various studies have shown interactions between measured genes and measured environments. Conclusion
BEHAVIORAL GENETICS IN FAMILIES Behavioral genetic can be studied through the application of a number of techniques.
These include selective breeding, which is unethical on humans. However, ethical studies such as family and adoption studies can be used. Family studies correlate the extent of genetic relatedness amongst family members with the scale of personality resemblance. Greater genetic relatedness results to higher heritability and similarities. Twin studies consider the heritability of identical and fraternal twins.
BEHAVIORAL GENETICS IN FAMILIES References Carnegie Mellon University. (2009). The Effects Of Genetic Relatedness And Age On Competition and Family Niches. Relatedness and Competition. Page 2-7. Leve, L. Harold, G. & Patterson, G. (2010). Refining Intervention Targets in Family Based
Research: Lessons from Quantitative Behavioral Genetics. Association for Psychological Science. Page 3-6. Turkheimer, E. (2008). Three Laws Of Behavior Genetics And What They Mean. Current Directions in Psychological Science. Page 160-165.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Polygraph and Lie DetectionDocumento4 pagineThe Polygraph and Lie DetectionAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Pursuit of HappinessDocumento4 pagineThe Pursuit of HappinessAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Principle of AutonomyDocumento2 pagineThe Principle of AutonomyAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Problem of Consequences and ForgivenessDocumento4 pagineThe Problem of Consequences and ForgivenessAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Principal-Agent ProblemDocumento9 pagineThe Principal-Agent ProblemAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Promise by C. Wright MillsDocumento4 pagineThe Promise by C. Wright MillsAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The Most Dangerous Moment Comes With VictoryDocumento3 pagineThe Most Dangerous Moment Comes With VictoryAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Opinion Essay On The Short Story "Seventh Grade" by Gary SotoDocumento2 pagineThe Opinion Essay On The Short Story "Seventh Grade" by Gary SotoAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Place of Endangered Languages in A Global SocietyDocumento3 pagineThe Place of Endangered Languages in A Global SocietyAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Old Testament Law and Its Fulfillment in ChristDocumento7 pagineThe Old Testament Law and Its Fulfillment in ChristAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The One Minute ManagerDocumento2 pagineThe One Minute ManagerAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Influence of Families On Children's SchoolDocumento8 pagineThe Influence of Families On Children's SchoolAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Origin of My NameDocumento4 pagineThe Origin of My NameAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Obscurities of Blue Collar Jobs and Sociological Factors Affecting Blue CollarDocumento7 pagineThe Obscurities of Blue Collar Jobs and Sociological Factors Affecting Blue CollarAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Lorax On Easter IslandDocumento4 pagineThe Lorax On Easter IslandAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Mini Mental Status ExaminationDocumento4 pagineThe Mini Mental Status ExaminationAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Models of Church "As A Communion" and "As A Political Society" TheDocumento7 pagineThe Models of Church "As A Communion" and "As A Political Society" TheAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Media and The GovernmentDocumento4 pagineThe Media and The GovernmentAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Merchant of VeniceDocumento5 pagineThe Merchant of VeniceAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The MetamorphosisDocumento4 pagineThe MetamorphosisAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Life StyleDocumento3 pagineThe Life StyleAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The LawDocumento4 pagineThe LawAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Issues Surrounding The Coding of SoftwareDocumento10 pagineThe Issues Surrounding The Coding of SoftwareAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Microsoft CaseDocumento3 pagineThe Microsoft CaseAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Marketing Mix 2 Promotion and Price CS3Documento5 pagineThe Marketing Mix 2 Promotion and Price CS3AssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of The Depression of The 1890s On Political Tensions of The TimeDocumento3 pagineThe Impact of The Depression of The 1890s On Political Tensions of The TimeAssignmentLab.com100% (1)
- The Implications On Mobile Commerce in The International Marketing CommunicationDocumento2 pagineThe Implications On Mobile Commerce in The International Marketing CommunicationAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Hand in Global WarmingDocumento10 pagineThe Human Hand in Global WarmingAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Impact of Media On Illicit Drug UseDocumento6 pagineThe Impact of Media On Illicit Drug UseAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- The Identity of Christianity Given by Early ArtDocumento6 pagineThe Identity of Christianity Given by Early ArtAssignmentLab.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Profiling Infant Olivia & FranzDocumento2 pagineProfiling Infant Olivia & FranzShane Frances SaborridoNessuna valutazione finora
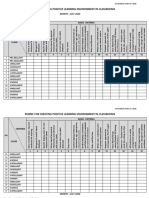
- Rubric For Creating Positive Learning Environment in ClassroomsDocumento6 pagineRubric For Creating Positive Learning Environment in ClassroomsABD RAHMAN MAT ALINessuna valutazione finora
- Matching Cause and Effect: 1. A. B. C. DDocumento2 pagineMatching Cause and Effect: 1. A. B. C. DGLENN SUAREZNessuna valutazione finora
- CTS Wireman - NSQF-4Documento52 pagineCTS Wireman - NSQF-4Allvin FachoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Physical Qualtities CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocumento6 pagine1.1 Physical Qualtities CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNessuna valutazione finora
- MD RAKIBUL ISLAM Update CVDocumento2 pagineMD RAKIBUL ISLAM Update CVনীল বেদনাNessuna valutazione finora
- Varun Sodhi Resume PDFDocumento1 paginaVarun Sodhi Resume PDFVarun SodhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Preventing College Debt Deliberation GuideDocumento18 paginePreventing College Debt Deliberation Guideapi-549298301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Matematik K1,2 Trial PMR 2012 MRSM S PDFDocumento0 pagineMatematik K1,2 Trial PMR 2012 MRSM S PDFLau Xin JieNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Primary Year 1 SK Scheme of WorkDocumento382 paginePrimary Year 1 SK Scheme of Workhelinary100% (1)
- Ornap 2012Documento2 pagineOrnap 2012Harby Ongbay AbellanosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sex Differences in The Perception of InfidelityDocumento13 pagineSex Differences in The Perception of Infidelityrebela29100% (2)
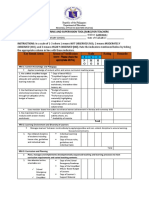
- Monitoring and Supervision Tool (M&S) For TeachersDocumento3 pagineMonitoring and Supervision Tool (M&S) For TeachersJhanice Deniega EnconadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects and Programmes Committee ReportDocumento5 pagineProjects and Programmes Committee ReportElbekriNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Map of Family Therapy ModelsDocumento3 pagineClinical Map of Family Therapy ModelsTe-Erika87% (15)
- Computer Vision Cover LetterDocumento6 pagineComputer Vision Cover Letterpenebef0kyh3100% (2)
- Student Handbook PDFDocumento51 pagineStudent Handbook PDFAssad SaghirNessuna valutazione finora
- Wcdma Optimization GuideDocumento2 pagineWcdma Optimization GuideBenaiad AbdellahNessuna valutazione finora
- BPC SyllabusDocumento3 pagineBPC SyllabusSivaram KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plans For English Form 5Documento1 paginaLesson Plans For English Form 5Hajar Binti Md SaidNessuna valutazione finora
- CURRICULUM VITAE Tugas Bhs Inggris CheckDocumento4 pagineCURRICULUM VITAE Tugas Bhs Inggris CheckRio Andrian SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- "Young Soul" by Amari BarakaDocumento3 pagine"Young Soul" by Amari Barakakenneth karong'aNessuna valutazione finora
- Mentoring Research Poster PortfolioDocumento1 paginaMentoring Research Poster Portfolioapi-463444835Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 Resume Template BlueDocumento2 pagine2020 Resume Template BlueAta DarayiNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Stages of Design ThinkingDocumento59 pagine5 Stages of Design ThinkingsampathsamudralaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae - Updated May 2020Documento6 pagineCurriculum Vitae - Updated May 2020api-513020529Nessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson Log in Grade 8 EnglishDocumento5 pagineDaily Lesson Log in Grade 8 EnglishJoyce Galang SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Woodwork Course CanberraDocumento7 pagineWoodwork Course Canberrafvntkabdf100% (2)
- Lesson Plan English Year 5Documento8 pagineLesson Plan English Year 5NurAiniNasirNessuna valutazione finora
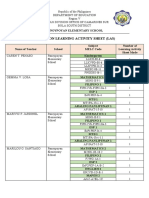
- PANOYPOYAN ES Report On LASDocumento4 paginePANOYPOYAN ES Report On LASEric D. ValleNessuna valutazione finora
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (392)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (378)