Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Experiment - 3 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of 3-Phase Full Controlled Bridge Converter. Theory
Caricato da
sahumanish9240Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Experiment - 3 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of 3-Phase Full Controlled Bridge Converter. Theory
Caricato da
sahumanish9240Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
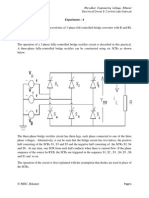
Experiment 3 Object:- Study and test the firing circuit of 3-phase full controlled bridge converter. Theory:Parallel connection via interphase transformers permits the implementation of rectifiers for high current applications. Series connection for high voltage is also possible, as shown in the fullwave rectifier of Fig. 1. With this arrangement, it can be seen that the three common cathode valves generate a positive voltage with respect to the neutral, and the three common anode valves produce a negative voltage. The result is a dc voltage twice the value of the half-wave rectifier. Each half of the bridge is a 3-pulse converter group. This bridge connection is a two-way connection, and alternating currentsflow in the valve-side transformer windings during both half periods, avoiding dc components into the windings, and saturation in the transformer magnetic core. These characteristics make the so-called Graetz bridge the most widely used linecommutated thyristor rectifier. The configuration does not need any special transformer, and works as a 6-pulserectifier. The series characteristic of this rectifier produces a dc voltage twice the value of the half-wave rectifier. The load average voltage is given by
where Vmax is the peak phase-to-neutral voltage at the secondary transformer terminals, its rms value, and the rms phase-to-phase secondary voltage, at the valve terminals of the rectifier.
1. Three-phase full-wave rectifier or Graetz bridge
MEC, Bikaner
Page 1
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
Figure 2 shows the voltages of each half-wave bridge of this topology and , the total instantaneous dc voltagevD, and the anode-to-cathode voltage vAK in one of the bridge thyristors. The maximum value of vAK is 3.Vmax, which is the same as that of the half-wave converter and the interphase transformer rectifier. The double star rectifier presents a maximum anode-tocathode voltage of 2 times Vmax.
2. Voltage waveforms for the Graetz bridge Figure 3 shows the currents of the rectifier, which assumes that LD is large enough to keep the dc current smooth. The example is for the same Y transformer connection shown in the topology of Fig. 12.12. It can be noted that the secondary currents do not carry any dc component, thereby avoiding overdesign of the windings and transformer saturation. These two figures have been drawn for a firing angle of 30. The perfect symmetry of the currents in all winding sand lines is one of the reasons why this rectifier is the most popular of its type. The transformer rating in this case is
MEC, Bikaner
Page 2
Marudhar Engineering College, Bikaner Electrical Drives & Control Lab Manual
3. Current waveforms for the Graetz bridge
Result:The firing circuit and characteristics waveform of the 3- full controlled bridge converter has been studied successfully.
MEC, Bikaner
Page 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Three-Phase TransformersDocumento74 pagineThree-Phase TransformersmadhubalansNessuna valutazione finora
- 220v Ac To 12vdc Rectifier CircuitDocumento10 pagine220v Ac To 12vdc Rectifier CircuitSandeep Guha NiyogiNessuna valutazione finora
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingDa EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Electric Propulsion Systems For LNG CarriersDocumento4 pagineClassification of Electric Propulsion Systems For LNG CarriersThomas StNessuna valutazione finora
- International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)Documento8 pagineInternational Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)www.irjes.comNessuna valutazione finora
- PAPER 2003 03 en HV Shunt Reactor Secrets For Protection EngineersDocumento30 paginePAPER 2003 03 en HV Shunt Reactor Secrets For Protection Engineerslamugre20003506Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABB HV Shunt ReactorDocumento30 pagineABB HV Shunt Reactortkdrt2166100% (1)
- Simulation Lab I Question BankDocumento3 pagineSimulation Lab I Question Bankkoushik bhatNessuna valutazione finora
- UPS Cable SizeDocumento1 paginaUPS Cable SizeSenthilkumaran VenkatasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Conmed Excalibur Plus PC ICU - Service ManualDocumento138 pagineConmed Excalibur Plus PC ICU - Service ManualVictoria Vazquez Perez100% (1)
- Comparison Between LCC and VSCDocumento5 pagineComparison Between LCC and VSCijsretNessuna valutazione finora
- The J&P Transformer Book 12EDocumento8 pagineThe J&P Transformer Book 12EDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 410 Lab1 Fall10-1305411901Documento27 pagineEE 410 Lab1 Fall10-1305411901Mohamad SyazwanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel ZVS Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocumento4 pagineA Novel ZVS Bidirectional DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsS B RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-5 - Harmonics & FiltersDocumento10 pagineUnit-5 - Harmonics & Filtersravikumar_ranganNessuna valutazione finora
- PWM 2 Level and 3 LevelDocumento7 paginePWM 2 Level and 3 LevelnewrajasinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Simulation of DC Links and AC MachinesDocumento8 pagineDigital Simulation of DC Links and AC MachinesNarges FallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Phase Transformers IntroductionDocumento7 pagineThree Phase Transformers Introductionsrikanth velpulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocumento5 pagineComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Transformers 77Documento15 pagineDC Transformers 77Keshavamurthy MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Controlled RectifiersDocumento19 pagineControlled Rectifiersbalaji1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6high Power Full-Bridge DC-DC Converter Using A Center-Tapped Transformer and A Full-Wave Type Rectifier PDFDocumento12 pagine6high Power Full-Bridge DC-DC Converter Using A Center-Tapped Transformer and A Full-Wave Type Rectifier PDFmajidNessuna valutazione finora
- TransformerDocumento6 pagineTransformerRichard GumanitNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Simulink of Three Phase Six-PulseDocumento6 pagineMatlab Simulink of Three Phase Six-PulseMohammed SelmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: Research Scholar Sathyabama University Chennai, IndiaDocumento13 pagineDigital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: Research Scholar Sathyabama University Chennai, Indiaaamirhussain_001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Three Phase Transformer InfoDocumento7 pagineThree Phase Transformer InfojbebinNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Phase Transformer InfoDocumento7 pagineThree Phase Transformer InfoMAHESWARA RAO CHALLANessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. TheoryDocumento6 pagineExperiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. Theorysahumanish9240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Analysis of 24 Pulse Ac-Dc Converter: May 2015, Volume 2, Issue 5 JETIR (ISSN-2349-5162)Documento8 pagineDesign and Analysis of 24 Pulse Ac-Dc Converter: May 2015, Volume 2, Issue 5 JETIR (ISSN-2349-5162)anuragpugaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- IEEE Trans - Reduce Inrush Current in Delta-Wye TransformerDocumento4 pagineIEEE Trans - Reduce Inrush Current in Delta-Wye TransformerOscar Gálvez IglesiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Final 1Documento78 pagineFinal 1Steve JantzenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac Link Buck Boost ConverterDocumento6 pagineAc Link Buck Boost ConverterrigowNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics: Fourth Sequence TestDocumento2 paginePower Electronics: Fourth Sequence TestNGOUNENessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDocumento7 pagineInternational Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Upgrading of Transmission Line by Combining AC-DC TransmissionDocumento6 paginePower Upgrading of Transmission Line by Combining AC-DC TransmissionrifamakhsumNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Study of 2-Level and 3-Level Frequency ConvertersDocumento5 pagineFundamental Study of 2-Level and 3-Level Frequency ConvertersAhmed BassamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Documento55 pagineEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Phase Semi ConverterDocumento18 pagineSingle Phase Semi Convertermohamed enanyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConverterDocumento4 pagine3 Phase Full Wave Bridge Convertersubhasishpodder100% (1)
- Bilotti 1966Documento3 pagineBilotti 1966dycsteiznNessuna valutazione finora
- Date: AIM: To Study Three-Phase Full-Wave Diode Rectifiers. TheoryDocumento2 pagineDate: AIM: To Study Three-Phase Full-Wave Diode Rectifiers. TheoryDharmistha VishwakarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cascaded TransformersDocumento3 pagineCascaded TransformersGiovanni SatriaNessuna valutazione finora
- 13IPST121Documento7 pagine13IPST121Anonymous 9VcxlFErfNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Z-Source Single-Phase Inverter For Single-Phase PM Synchronous Motor DrivesDocumento6 pagineModified Z-Source Single-Phase Inverter For Single-Phase PM Synchronous Motor DrivesPRACHI KATARENessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Transformer Connections, Operation, and Specialty TransformersDocumento38 pagineChapter 3 Transformer Connections, Operation, and Specialty TransformersSihamaSihamNessuna valutazione finora
- Single-Phase Seven-Level Grid-Connected Inverter For Photovoltaic SystemDocumento14 pagineSingle-Phase Seven-Level Grid-Connected Inverter For Photovoltaic Systemqais652002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Minimal Transient Switching of CapacitorsDocumento7 pagineMinimal Transient Switching of CapacitorsRuben MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- HVDC Notes PDFDocumento22 pagineHVDC Notes PDFupender raoNessuna valutazione finora
- LevelDocumento10 pagineLevelmücahitNessuna valutazione finora
- PWM Inverters With Common DC-DC Converter Supply: Stepped Wave Synthesis From Pre-ProgrammedDocumento7 paginePWM Inverters With Common DC-DC Converter Supply: Stepped Wave Synthesis From Pre-ProgrammedSumit HarwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Multilevel Inverter Topology For Grid Connected PV SystemsDocumento7 pagineModified Multilevel Inverter Topology For Grid Connected PV SystemsAJER JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Stability Enhancement by SiDocumento8 paginePower System Stability Enhancement by SiUdaiveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Transformers in Open DeltaDocumento11 pagineBank Transformers in Open DeltaAndré Conhak LinsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Three Windings Full Bridge Converter With A Lossless Clamp CircuitDocumento9 pagineA Three Windings Full Bridge Converter With A Lossless Clamp Circuiterode els erodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneous Ac-Dc Power TransmissionDocumento26 pagineSimultaneous Ac-Dc Power TransmissionAhsn ShkNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Content - Digital Water MeterDocumento44 pagineReport Content - Digital Water MeteramiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance of A Current-Fed Soft Switched Full-Bridge Boost Double Stage Converter Using ZVS PWMDocumento8 paginePerformance of A Current-Fed Soft Switched Full-Bridge Boost Double Stage Converter Using ZVS PWMiajerNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: AbstractDocumento13 pagineDigital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: AbstractjimmyNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnDocumento10 pagineDC-DC Converter: Four Switches V V 2, Capacitive Turn-Off Snubbing, ZV Turn-OnRomitan AlexandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsDa EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - 4: © MEC, BikanerDocumento5 pagineExperiment - 4: © MEC, Bikanersahumanish9240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RLDocumento4 pagineExperiment - 2 Object:-Study and Obtain Waveforms of 3-Ø Half Controlled Bridge Converter With R and RLsahumanish9240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. TheoryDocumento6 pagineExperiment - 1 Object:-Study and Test The Firing Circuit of Three Phase Half Controlled Bridge Converter. Theorysahumanish9240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marudhar Engg. College, Bikaner: AbstractDocumento1 paginaMarudhar Engg. College, Bikaner: Abstractsahumanish9240Nessuna valutazione finora
- AN3200 Application Note: 2.5 KW MMA Welding MachineDocumento19 pagineAN3200 Application Note: 2.5 KW MMA Welding MachinePascu AurelNessuna valutazione finora
- Speed Synchronization of Multiple Motors in Industries: Bachelor of Engineering in Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocumento10 pagineSpeed Synchronization of Multiple Motors in Industries: Bachelor of Engineering in Electrical and Electronics Engineeringcity cyberNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Source Lecture 1Documento8 paginePower Source Lecture 1Sutanwi LahiriNessuna valutazione finora
- P20PS024 PEC LabReport M.Tech (PS) PDFDocumento49 pagineP20PS024 PEC LabReport M.Tech (PS) PDFAjeet Kumar PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Excitation System - MarunII-Thyricon Operation Manual FullDocumento61 pagineExcitation System - MarunII-Thyricon Operation Manual FullGanesh Kumar ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Boost ConverterDocumento6 pagineDC Boost ConvertersabitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Documents - MX Battery-EliminatorDocumento35 pagineDocuments - MX Battery-EliminatorAliNessuna valutazione finora
- Vakumski Sklopnik PDFDocumento4 pagineVakumski Sklopnik PDFzakirNessuna valutazione finora
- 1N4001-1N4007 (ON) DatasheetDocumento6 pagine1N4001-1N4007 (ON) DatasheetShinwell JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chopper ReportDocumento37 pagineChopper ReportcoolsinghrkNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristic of DC Generators - Separately Excited Self Excited and Compound GeneratorDocumento9 pagineCharacteristic of DC Generators - Separately Excited Self Excited and Compound Generatormark amthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Module 2Documento13 pagineElectronics Module 2tirsollantadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijesrt: Power Quality Improvement Using FC-TCR (SVC) With Fuzzy Logic ControllerDocumento4 pagineIjesrt: Power Quality Improvement Using FC-TCR (SVC) With Fuzzy Logic ControllerDavid StuartNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Frequency Drive: Presented by Name-Avisek Mohanty REGD-0801214409 Under The Guidance of Miss - Anupama MajhiDocumento12 pagineVariable Frequency Drive: Presented by Name-Avisek Mohanty REGD-0801214409 Under The Guidance of Miss - Anupama MajhiDev KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 081 022 Minipack SystemDocumento32 pagine081 022 Minipack SystemdafremNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesis KolarDocumento423 pagineTesis KolarCarlos DPNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification and Maintenance Manual: Sequence Flashing Lights (SFL)Documento13 pagineSpecification and Maintenance Manual: Sequence Flashing Lights (SFL)Javier Eduardo Alzate BogotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Suspended Frictionless Windmill: Presentation OnDocumento17 pagineSuspended Frictionless Windmill: Presentation OnShri PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Year Physics CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademyDocumento10 pagine2nd Year Physics CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademyKamran Khan100% (5)
- Wycliffe ProjectDocumento50 pagineWycliffe ProjectSmartinz KarurizNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Construction of High Voltage Diode 100 KVDocumento7 pagineDesign and Construction of High Voltage Diode 100 KVBashir MtwaklNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb Brake MotorDocumento22 pagineAbb Brake MotorAmitesh DindaNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 Daily RCM Observations20.11.2023Documento3 pagineL4 Daily RCM Observations20.11.2023Muhammad Shoaib Aslam KhichiNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Test Paper Physics CBSE Class XII 2023 - I Part IDocumento4 pagineModel Test Paper Physics CBSE Class XII 2023 - I Part IAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNessuna valutazione finora
- GYRODocumento48 pagineGYROAlex SkriabikovNessuna valutazione finora
- SiprecienglDocumento7 pagineSiprecienglJun DUNessuna valutazione finora