Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Book Reww
Caricato da
Monica ThakurTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Book Reww
Caricato da
Monica ThakurCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Process Level Improvements Business process reengineering (BPR) is the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between
enterprises. The authors promoted the idea that sometimes radical redesign and reorganization of an enterprise (wiping the slate clean) was necessary to lower costs and increase quality of ser ice and that information technology was the key enabler for that radical change. !ammer and "hampy felt that the design of workflow in most large corporations was based on assumptions about technology# people# and organizational goals that were no longer alid. They suggested se en principles of reengineering to streamline the work process and thereby achie e significant le els of impro ement in quality# time management# and cost$ %. &rganize around outcomes# not tasks. '. (dentify all the processes in an organization and prioritize them in order of redesign urgency. ). (ntegrate information processing work into the real work that produces the information. *. Treat geographically dispersed resources as though they were centralized. +. ,ink parallel acti ities in the workflow instead of -ust integrating their results. .. Put the decision point where the work is performed# and build control into the process. /. "apture information once and at the source. Lean Six Sigma 0 business impro ement methodology that ma1imizes shareholder alue by achie ing the fastest rate of impro ement in customer satisfaction# cost# quality# process speed# and in ested capital. 2i1 2igma impro ement methods is required because$ 3 ,ean cannot bring a process under statistical control 3 2i1 2igma alone cannot dramatically impro e process speed or reduce in ested capital 3 Both enable the reduction of the cost of comple1ity. 2i1 2igma supporters point out that ,ean fails to address key concepts like customer needs and ariation. Both sides are right. 4et these arguments are more often used to ad ocate choosing one o er the other# rather than to support the more logical conclusion that we blend ,ean and 2i1 2igma. Quality Assurance / Quality Control 5uality assurance (50) is a set of acti ities whose purpose is to demonstrate that an entity meets all quality requirements. 50 acti ities are carried out in order to inspire the confidence of both customers and managers 5uality control is a set of acti ities or techniques whose purpose is to ensure that all quality requirements are being met. (n order to achie e this purpose# processes are monitored and performance problems are sol ed.
The Lifecycle Performance Management it pro ides all of the processes# techniques and frameworks to implement a successful go ernment performance solution. The &rganizational Performance and Best Practices 0nalysis will identify your strengths# weaknesses# and cost sa ings opportunities# and will plan out the e1act steps to reaching your performance goals. Activity Level Improvements 2trategy 6apping is the process of diagramming how an organization creates alue by connecting strategic ob-ecti es in e1plicit cause7and7effect relationship with each other in the four B2" ob-ecti es (financial# customer# processes# learning and growth) !u"get Cross#al$s# commonly used in finance and budgeting# con ert one set of alues to another by applying a specific set of business rules and can describe the relationship between the budget8s allocated funds and the programs those funds are e1pected to impact. 9sed in the :ederal Budget Process# Budget "rosswalks are defined as a# ;term for the allocation of budget authority and outlay amounts in a budget resolution to congressional committees according to their -urisdictions and the committees< subdi ision of those amounts among their programs or subcommittees.= 0cti ity Based "osting (0B") is an alternati e to the traditional way of accounting. Traditionally it is belie ed that high olume customers are profitable customers# a loyal customer is also a profitable one# and profits will follow a happy customer. 2tudies on customer profitability ha e un eiled that the abo e is not necessarily true. 0B" is a costing model that identifies the cost pools# or acti ity centers# in an organization and assigns costs to products and ser ices (cost dri ers) based on the number of e ents or transactions in ol ed in the process of pro iding a product or ser ice Activity !ase" Management (0B6) is a discipline that focuses on the management of acti ities as a way to impro e customer alue and profit. 0B6 includes cost dri er analysis# acti ity analysis# and performance measurement. The 6ost >fficient &rganization (6>&) is management8s ;bid= to perform a certain function. (f the 6>& wins an 07/. competition# it succeeds or takes o er the work of the e1isting go ernment function. The President8s 6anagement 0genda urges federal leadership to ;compete= functions that are commercial in nature. %inancial Management is the ?planning# directing# monitoring# organizing# and controlling of the monetary resources of an organization. The &ffice of :ederal :inancial 6anagement (&::6) was created within the &ffice of 6anagement and Budget (&6B) by the "hief :inancial &fficers (":&) 0ct of %@@A. &::6# led by the &6B "ontroller under the direction of the Beputy Birector for 6anagement# is responsible for the financial management policy of the :ederal Co ernment
The Strategic Prioriti&ation an" Planning (2P') process is an e olution of5uality >ngineering 6ethods# including 5uality :unction Beployment and Besign for 2i1 2igma# and incorporates arious dynamic aspects to form a portable and powerful decision making en ironment. The process can be tailored to any desired le el of detail to enhance the decision making process for in estment strategies as more information becomes a ailable. The end product allows for ;what if= games to be played through a dynamic and interacti e en ironment and the results of the process can be the foundation for detailed strategic road mapping and quantitati e technology assessments and tracking. 2P' is a li ing process that should guide strategic planning and be continuously updated as a program e ol es. Portfolio Analysis is a method to impro e Co ernment business practices by analyzing a portfolio of systems as a whole# rather than analyzing indi idual acquisition programs. Portfolio analysis is the art and science of allocating scarce resources to satisfy strategic ob-ecti es. !usiness Case Analysis is a method companies use for pro-ect selection. (t analyzes how fulfilling the business case for the pro-ect will implement the corporate strategy and sustain the competiti e ad antage of the company. Performance'!ase" !u"geting is a results focused planning and budgeting framework which focuses on three elements$ the strategy (how to achie e outcome)# outputs (acti ities to achie e final outcome)# and the result (final outcome). Performance budgets use missions# goals and ob-ecti es to -ustify funding. Through the allocation of resources# performance7based budging achie es specific ob-ecti es based on program goals and measured results. (ecision Support Systems Becision 2upport 2ystems include software# frameworks and other tools that can be used as part of a structured decision7making process. Types of decision support systems include information control models# paradigm models# decision models# simulation models# isualization models and process models.
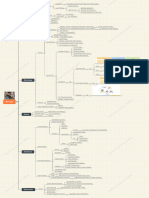
Becision 2upport 2ystems and Tools :ramework
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- What Is The Balanced ScorecardDocumento21 pagineWhat Is The Balanced ScorecardAndi Yanuar100% (1)
- Forecasting Short-Term Financial RequirementsDocumento22 pagineForecasting Short-Term Financial RequirementsArmando Robles100% (1)
- Balanced Scorecard For AIESECDocumento15 pagineBalanced Scorecard For AIESECsandrolourencoNessuna valutazione finora
- TEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 19Documento48 pagineTEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 19polkadots939Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On Cost Analysis and ControlDocumento88 pagineA Project Report On Cost Analysis and ControlNagireddy KalluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Management ScienceDocumento3 pagineManagement ScienceAlfredo Loaiza V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gcreddy PDFDocumento17 pagineGcreddy PDFVeerraghavaReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Synchronization of Chaotic System1Documento52 pagineSynchronization of Chaotic System1vivek_may12100% (1)
- Balance ScorecardDocumento5 pagineBalance ScorecardSwarroop M H SwaroopNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pyramids and Pitfalls of Performance MeasurementDocumento8 pagineThe Pyramids and Pitfalls of Performance MeasurementNavigators ReunionNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Control Is The Process by Which Managers Influence OtherDocumento21 pagineManagement Control Is The Process by Which Managers Influence OtherFernandes RudolfNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Repackage Reformulate Cumulative Cf. 0 1 20,000,000 10,000,000 20,000,000 2 1,250,000 9,000,000 21,250,000Documento9 pagineYear Repackage Reformulate Cumulative Cf. 0 1 20,000,000 10,000,000 20,000,000 2 1,250,000 9,000,000 21,250,000Manish BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- See The Front Matte R of This Solutions Manual For Suggestions Regarding Your Choices of Assignment Material For Each Chapter. Management AccountingDocumento16 pagineSee The Front Matte R of This Solutions Manual For Suggestions Regarding Your Choices of Assignment Material For Each Chapter. Management AccountingArdy PiliangNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisa Potensi Pasar Internasional Produk Asli Indonesia Ban Mobil GT Radial Di MesirDocumento9 pagineAnalisa Potensi Pasar Internasional Produk Asli Indonesia Ban Mobil GT Radial Di MesirPrawira AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Control SystemsDocumento50 pagineManagement Control SystemsMapuia Lal PachuauNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Costing - Why It's Important and How To Do ItDocumento23 pagineManagerial Costing - Why It's Important and How To Do ItPedro CasaleiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced Scorecard 513Documento8 pagineBalanced Scorecard 513shahidul alamNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management ProjectDocumento3 pagineStrategic Management ProjectZubaidahNessuna valutazione finora
- EPM Study MaterialsDocumento88 pagineEPM Study MaterialsKetan KathaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Practices For Planning and BudgetingDocumento20 pagineBest Practices For Planning and BudgetingSilky SmoothNessuna valutazione finora
- Hilton7e SM CH6Documento51 pagineHilton7e SM CH6VivekRaptorNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance ManagementDocumento4 paginePerformance ManagementPhillip DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- BPMS BasicsDocumento14 pagineBPMS BasicsGopal Krishna RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance Score CardDocumento9 pagineBalance Score Cardsathishsep18100% (1)
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocumento9 pagineStrategic Cost ManagementPreethi PadmanabhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBPMG514Documento21 pagineBSBPMG514tvatNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced Scorecard Basics: Edscorecard/Tabid/55/Default - AspxDocumento9 pagineBalanced Scorecard Basics: Edscorecard/Tabid/55/Default - AspxNaveen Kumar NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean AccountingDocumento6 pagineLean AccountingSivaguru SanNessuna valutazione finora
- Budgetary ControlDocumento81 pagineBudgetary ControlVirendra JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Points For PresentationDocumento5 paginePoints For PresentationmohammedjunaidshaikhmeNessuna valutazione finora
- New Dimension in Management and Post Review of Budget.: National SeminarDocumento13 pagineNew Dimension in Management and Post Review of Budget.: National Seminarminal bhojaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ActivityDocumento3 pagineActivityJaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Costing AnalysisDocumento4 pagineStrategic Costing AnalysisOwais BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- TASK PERFORMANCE-Strategic Cost Acctg-PrelimDocumento5 pagineTASK PERFORMANCE-Strategic Cost Acctg-PrelimAnonymouslyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On BSCDocumento18 pagineAssignment On BSCKomalJindalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment On BSCDocumento18 pagineAssignment On BSCginnz66Nessuna valutazione finora
- PM0008Documento5 paginePM0008souvik_dazNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Reduction Strategies for the Manufacturing Sector With Application of Microsoft ExcelDa EverandCost Reduction Strategies for the Manufacturing Sector With Application of Microsoft ExcelNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced ScorecardDocumento27 pagineBalanced ScorecardharshbhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced Scorecar1Documento6 pagineBalanced Scorecar1Amruta TurméNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost AccountingDocumento77 pagineCost Accountinghayenje rebeccaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2003 Management-Control-SystemDocumento11 pagine2003 Management-Control-SystemMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNessuna valutazione finora
- BPR and LogisticsDocumento3 pagineBPR and LogisticsYogesh Kumar0% (1)
- Balanced Scorecard 5Documento44 pagineBalanced Scorecard 5Cicy AmbookenNessuna valutazione finora
- Marisol Guino BSA-3A Midterm Exam-Strategic Business AnalysisDocumento5 pagineMarisol Guino BSA-3A Midterm Exam-Strategic Business AnalysisMarisol GuinoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successDa EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (4)
- Managment AccountingDocumento27 pagineManagment Accountingkalgi_joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational Analysis Template PDFDocumento7 pagineOperational Analysis Template PDFYasserAl-mansourNessuna valutazione finora
- A Fact-Based Management ApproachDocumento2 pagineA Fact-Based Management ApproachAbril BarbosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Accounting Financial Accounting: Performance ReportsDocumento5 pagineManagerial Accounting Financial Accounting: Performance ReportsrohaanNessuna valutazione finora
- WP Analytic Hierarchy Process Project SelectionDocumento8 pagineWP Analytic Hierarchy Process Project SelectionPallav Paban BaruahNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Business PlanningDocumento4 pagineIntegrated Business Planningolivia523Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento3 pagineChapter 1Andrea QuetzalNessuna valutazione finora
- An Intelligent Performance Management Framework WhitepaperDocumento16 pagineAn Intelligent Performance Management Framework WhitepaperAlamin SheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Controlling TechniquesDocumento15 pagineControlling TechniquesManna ManniNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Accounting NotesDocumento12 pagineFinancial Accounting Notesmanoj royNessuna valutazione finora
- The Balanced Scorecard - SummaryDocumento10 pagineThe Balanced Scorecard - SummaryGuest HouseNessuna valutazione finora
- Benchmarking Project ManagementDocumento13 pagineBenchmarking Project ManagementpparkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management Is Concerned With Converting Materials and LaborDocumento7 pagineOperations Management Is Concerned With Converting Materials and LaborlucasNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Process ManagementDocumento28 pagineBusiness Process ManagementAhmad Tariq Bhatti100% (1)
- Swathi SDocumento18 pagineSwathi SPreetham GowdaNessuna valutazione finora
- BSC - Balanced Scorecard As Strategic Navigational ChartsDocumento12 pagineBSC - Balanced Scorecard As Strategic Navigational ChartsKristelNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestDocumento2 pagineQuestMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Question ArshuuuuuuuuuDocumento6 pagineFinal Question ArshuuuuuuuuuMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Khwaja Meeran Alavandi: ObjectiveDocumento3 pagineKhwaja Meeran Alavandi: ObjectiveMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Monica 1Documento15 pagineMonica 1Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Wheelen Smbp13 PPT 01Documento36 pagineWheelen Smbp13 PPT 01sofikhdyNessuna valutazione finora
- Monica RESUMEDocumento4 pagineMonica RESUMEMonica Thakur100% (1)
- BeDocumento5 pagineBeMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- AirtechDocumento75 pagineAirtechMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Documento37 pagineA Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Iñigo, Ma. Danna P.: # 144 Brgy. San Antonio Mabitac, Laguna 4020 Contact #: 09125210396Documento4 pagineIñigo, Ma. Danna P.: # 144 Brgy. San Antonio Mabitac, Laguna 4020 Contact #: 09125210396Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire RSBDocumento3 pagineQuestionnaire RSBMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire RSBDocumento3 pagineQuestionnaire RSBMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By. Under The Guidance of Manjunath Neelagar Prof. Kiran Magavi MBA12007043Documento6 paginePresented By. Under The Guidance of Manjunath Neelagar Prof. Kiran Magavi MBA12007043Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- This Is An Example of How To Not Write Your Resume: Career ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineThis Is An Example of How To Not Write Your Resume: Career Objectivemonica_ajit_thakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Book RewwDocumento4 pagineBook RewwMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Larsen & ToubroDocumento2 pagineLarsen & ToubroMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue PrintDocumento8 pagineBlue PrintMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Documento35 pagineA Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- HUMANRESOURCEDEVELOPMENTfinalDocumento53 pagineHUMANRESOURCEDEVELOPMENTfinalilansakthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Field TheoryDocumento42 pagineField TheoryMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Documento35 pagineA Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento8 pagineNew Microsoft Word DocumentMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Documento35 pagineA Project Report On: "Ratio Analysis"Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ElectronicsDocumento48 paginePower ElectronicsMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceuticals Industry ProfileDocumento4 paginePharmaceuticals Industry ProfileMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Power ElectronicsDocumento48 paginePower ElectronicsMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Miniproject 120831111515 Phpapp01Documento18 pagineMiniproject 120831111515 Phpapp01Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformers and Induction MachinesDocumento36 pagineTransformers and Induction MachinesMonica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Financial Ratios of Lupi11Documento2 pagineKey Financial Ratios of Lupi11Monica ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- SCRUM (Mind Mapping)Documento1 paginaSCRUM (Mind Mapping)Rounak VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 MuDocumento4 pagine3 MuEndi KustamsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Valve Response Truth or Consequences by Gregory McMillan and Pierce Wu PDFDocumento13 pagineValve Response Truth or Consequences by Gregory McMillan and Pierce Wu PDFJavier LondoñoNessuna valutazione finora
- SereneAir HRISDocumento2 pagineSereneAir HRISWaqas ZaheerNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE320Documento2 pagineCSE320Devansh YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Nirwan Banerjee: Integrated M.Tech - Mathematics and Computing - IIT, DhanbadDocumento1 paginaNirwan Banerjee: Integrated M.Tech - Mathematics and Computing - IIT, DhanbadNirwan BanerjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Iot and Machine LearningDocumento12 pagineIot and Machine LearningAmogh AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyberbullying Detection On Twitter Using Machine Learning A ReviewDocumento5 pagineCyberbullying Detection On Twitter Using Machine Learning A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- HANDOUT - Rapid Control Prototyping With MATLAB PDFDocumento19 pagineHANDOUT - Rapid Control Prototyping With MATLAB PDFmiaauuwwNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean ProductionDocumento3 pagineLean ProductionnaveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Code: (CSI-621) Bioinformatics Software Development II 3 (1-2) by Hafiza Mahwash Faryad Email: 14msishfaryad@seecs - Edu.pkDocumento8 pagineCourse Code: (CSI-621) Bioinformatics Software Development II 3 (1-2) by Hafiza Mahwash Faryad Email: 14msishfaryad@seecs - Edu.pkMavra KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Control SystemsDocumento3 pagineControl SystemsselvajothiNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi Agent Systems Meet Aggregate ProgrDocumento16 pagineMulti Agent Systems Meet Aggregate ProgrMILON KUMAR HORENessuna valutazione finora
- Systems Computer Integrated Manufacturing 4th Edition Mikell P GrooverDocumento4 pagineSystems Computer Integrated Manufacturing 4th Edition Mikell P GrooverCedric SuriyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance and Reliability ApproachesDocumento27 pagineMaintenance and Reliability ApproachesSyed Nadeem AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- MemoriaDocumento76 pagineMemoriaAleksandar CekovNessuna valutazione finora
- RL Network: Control Systems Engineering, Fourth Edition by Norman S. NiseDocumento33 pagineRL Network: Control Systems Engineering, Fourth Edition by Norman S. NiseEmir ÇokdoğanNessuna valutazione finora
- VGG16 ArchitectureDocumento30 pagineVGG16 ArchitectureMehak SmaghNessuna valutazione finora
- c12. Developing Business-IT Solutions.gDocumento21 paginec12. Developing Business-IT Solutions.gMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unlocking The Potential of Deep Learning For MarinDocumento44 pagineUnlocking The Potential of Deep Learning For MarinGlmNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Smart Logistics and Smart MaintenanceDocumento21 pagine3 - Smart Logistics and Smart MaintenancedeanisaNessuna valutazione finora
- CIM Wheel-Product Design To Manufacturing Management.Documento13 pagineCIM Wheel-Product Design To Manufacturing Management.Kartheek Musalimadugu33% (3)
- Ekam - Associate Product Manager AssignmentDocumento8 pagineEkam - Associate Product Manager AssignmentraghavcrazzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Maintenance & Reliability Management: Planning and Estimating Workshop by TetrahedronDocumento2 pagineModern Maintenance & Reliability Management: Planning and Estimating Workshop by TetrahedrontetrahedronNessuna valutazione finora
- CH1 - 5 Significance of The StudyDocumento2 pagineCH1 - 5 Significance of The StudyJerry GayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonfunctional Requirements PDFDocumento118 pagineNonfunctional Requirements PDFJayshree KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- F 201505221432274593Documento8 pagineF 201505221432274593Yogesh ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora