Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3
Caricato da
Zuraini ArshadCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3
Caricato da
Zuraini ArshadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
MARK SCHEME
SECTION A
NO ANSWER EXPLAINATION
1.
B
2.
C
3.
D
F = 0.5, = 1/0.1
V = f = 0.5(1/0.1)= 5.0 ms
-1
4.
A
I =
)
= 0.32 Wm
-2
5.
B
L =
= 22.67 x 10-3 = 0.02267 m = 2.3 cm
6.
B
F1 = (
) = 206.25 Hz
F2 = (
)
Beat frequency = (212.5 -206.25 ) Hz = 6.25 Hz
7.
C
8.
A
but u = v =
v = f = -20 cm
Distance of emerging ray from the first lens = 25 20 = 5 cm
9.
C
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
10.
C
d sin = n , d = 10
-3
/750 m
= 2.06 x 10
-7
m
From c = f
F =
11.
D
12.
B
E
hc
hc
hf
E E E
i f
A
=
=
=
= A
13.
A
The K characteristic line is produced by electronic transition in the target atom.
The intensity is determined by the number of electrons hitting the target and the
number of collisions determines the number of electronic transition.
14.
B E is the energy equivalent of . m A
15.
B
hours
e
e N N
t
10
0693 . 0
2 ln 2 ln
life half
0693 . 0
20 4 ln
40 10
) 10 30 (
0
= = =
=
=
=
=
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
SECTION B
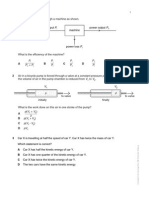
16a A note of higher frequency than the fundamental note. 2
b-i
For the first resonance:
l
1
+ c =
4
=
v
4 f
(i)
For the second resonance:
l
2
+ c =
3
4
=
3v
4 f
(ii)
(ii) (i) l
2
l
1
=
v
2 f
speed of sound, v = 2 f (l
2
l
1
) = 2(250)(0.96 0.30)
= 330 ms
-1
1
1
1
1
b-ii
Substitute the value of v into (i)
0.30+ c =
330
4(250)
the end correction,c = 0.03 m
1
1
17
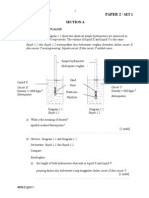
a-i
( ) ( )
0
0
49
00 . 1 30 510 . 1
=
=
red
red
i
Sini Sin
1
1
a-ii
( ) ( )
0
0
5 . 49
00 . 1 30 521 . 1
=
=
blue
blue
i
Sini Sin
1
1
a-iii Angle between the red and the blue refracted rays
0 0 0
5 . 0 49 5 . 49 = =
1
b
( )( )( ) ( )( )( )
0
7 5 1 7 5 1
1 1
0 . 4
10 9 . 4 1 10 0 . 4 10 66 . 1 1 10 0 . 4
1 1
= A
= A
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
u
u
u
Sin Sin
n
d
Sin n
d
Sin
blue red
1
1
SECTION C
18
(a)
the acceleration of an object undergoing oscillation
i. is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the
equilibrium position
ii. always points toward the equilibrium position
1
1
(b) i. the elastic limit of the spring is not exceed 1
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
- the spring is light and obey Hookes Law
ii- the angular displacement less than 10
0
- the string has to be inelastic
-
1
1
1
(c)
i. T = 2t
g
L
= 2.00 s
ii. K
i
+ U
i
= K
f
+U
f
0 +mgh =
2
1
mv
2
+ 0
v
2
= 2gh = 2(9.81)(1 cos 10
0
)
= 0.55 ms
-1
1
1
1
1
1
(d) i. k= mw
2
= 0.5(2t f)
2
= 33.4 Nm
-1
1
1
ii. E =
2
1
kA
2
0.5 = (33.4)A
2
A=0.17 m
1
1
19
(a)(i)
The quantum of electromagnetic radiation , having an energy related to the
frequency f, of the light by E = hf where E is the photon energy and h is Plancks
constant.
1
(a)(ii)
Quantum theory include:
1. the effect of frequency on the photoelectric effect
2. the existence of threshold frequency
3. the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons does not depend on the
incident light intensity
4. the instantaneous emission of the photoelectrons
1
1
1
1
(b)(i)
Maximum kinetic energy,
1
2
mv
m
2
= h
c
W
= (6.6310
34
)
3.0010
8
4.1310
7
|
\
|
.
|
(
(
20(1.6 10
19
)
( )
=1.6210
19
J
1
1
1
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
(b)(ii)
1
2
mv
m
2
=1.6210
19
J
mv
m
2
= 2(1.6 10
19
)m
mv
m
= 2(1.6 10
19
)(9.1110
31
)
de Broglie wavelength of electron, =
h
mv
m
=
6.6310
34
2(1.6 10
19
)(9.1110
31
)
=1.2210
9
m
1
1
1
(b)(iii)
If n is the number of electrons per second falling on the cesium surface, hence
n
hc
= I A
n =
I A
hc
=
(5) (2510
4
)(4.1310
7
)
(6.6310
34
)(310
8
)
The number of electrons per second extracted
= 60%
(5) (2510
4
)(4.1310
7
)
(6.6310
34
)(310
8
)
=1.5610
16
1
1
1
1
20
(a) (i)
An -particle is a helium nucleus which consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons. When an
atom X emits an -particle, the new atom produced will have its mass number reduced
by 4 and its atomic number reduced by 2.
Y He X
A
Z
A
Z
4
2
4
2
+
2
(ii) A -particle is high velocity electron. When an atom emits a -particle , a neutron in
its nucleus has been converted to a proton and a -particle.
|
0
1
1
1
1
0
+ p n
1
1
(iii) -particle is an electromagnetic radiation which has energy but no mass. It is emitted
when a radioactive nucleus converts its mass defect into energy in order to become
another more stable nucleus.
1
1
(b)(i) Radioactive decay refers to the random and spontaneous process whereby a less stable
nucleus changes to a more stable nuclide with the emission of radioactive radiation.
Activity is the number of radioactive atoms decay in unit time.
3
(ii)
The activity
dt
dN
of a radioactive source is directly proportional to the number of
Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013
nuclei N before decay in the radioactive source, i.e
N dt
dN
N
dt
dN
N
dt
dN
1
- = =
Hence, the decay constant can be defined as the ratio of the activity to the number of
radioactive nuclei in the source before decay.
3
(iii) Half life is the time taken for a radioactive nuclide sample to decay until half of its
initial number of nuclei are left behind.
From
N
dt
dN
=
If N
0
is the number of nuclei at time t= 0. and N is the number of nuclei at time t,
| |
693 . 0 2 ln
2 ln 2
,
2
, ,
ln
2
1
2
1
2 / 1
0
0
0
0
0
= =
= =
= = =
= =
} }
T
T e
half time T t
N
N if e
N
N
t N dt
N
dN
t
t
N
N
t
N
N
4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Documento6 pagineAnswer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Documento13 pagineSMK Tinggi Klang Trial Term 1 2014Souseiseki ChromeNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuDocumento7 pagineTrial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2 - MSDocumento8 pagineG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2 - MSannahiazNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM Trial 2012 Physics Qa KelantanDocumento31 pagineSTPM Trial 2012 Physics Qa KelantanChan Q ONNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM2023 S1 PhysicsDocumento18 pagineSTPM2023 S1 PhysicsNatasha TasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)Documento11 pagineTrial Fizik s2 2022 (Question)CHRISTOPHER EMMANUEL RAJ A/L VELLAN Moe100% (1)
- STPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionDocumento5 pagineSTPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionChong Yin Ping0% (1)
- Actual 2009 STPMDocumento16 pagineActual 2009 STPMtweihuai100% (1)
- Sem 2 ChecklistDocumento23 pagineSem 2 ChecklistBestah Joewellster TeoNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - Circular MotionDocumento23 pagine5 - Circular Motionannahiaz100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - DifferentiationDocumento8 pagineChapter 8 - DifferentiationSelvarani NadarajahNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome: Pra U / STPM Physics 960Documento7 pagineWelcome: Pra U / STPM Physics 960ROSAIMI BIN ABD WAHAB MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsDocumento9 pagineSTPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsSouseiseki ChromeNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Scheme of Work STPM Physics Semester 2 2019Documento8 pagineYearly Scheme of Work STPM Physics Semester 2 2019LAU HUEI CHOO -67% (3)
- Physics CourseworkDocumento21 paginePhysics CourseworkSUZANNA KUEH SIEW PING A20SC0389Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Note 1 - 1Documento39 pagineLecture Note 1 - 1Mohamad Faiz100% (3)
- STPM2023 S2 PhysicsDocumento20 pagineSTPM2023 S2 PhysicsEdison lee100% (1)
- RPT Physics STPM Term 2 2020Documento8 pagineRPT Physics STPM Term 2 2020marcella silunNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1Documento12 pagineTrial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1annahiaz0% (1)
- RPT Physics F6 Second Term 2019Documento8 pagineRPT Physics F6 Second Term 2019Norhazli IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 p1 Work Energy Power AllDocumento15 pagine9702 p1 Work Energy Power AllkwaikunNessuna valutazione finora
- RPT Physics STPM Term 2 2020Documento8 pagineRPT Physics STPM Term 2 2020marcella silunNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Physics STPMDocumento18 pagineChapter 6 Physics STPMredroseNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy, Work and PowerDocumento47 pagineEnergy, Work and PowerMaria BhaijiNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrostaticsDocumento9 pagineElectrostaticsapi-283216587Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trial Terengganu - QDocumento9 pagineTrial Terengganu - Qshinichi_kesian6117Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Electromagnetic Theory PDFDocumento49 pagineIntermediate Electromagnetic Theory PDFMalvado Aun Mas Malvado0% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentDocumento1 paginaSTPM Physics Chapter 14 Electric CurrentChris LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Cakna KelantanDocumento22 pagineModul Cakna KelantanNALLATHAMBYNessuna valutazione finora
- Matriculation Physics (X-Rays)Documento44 pagineMatriculation Physics (X-Rays)ridwan100% (2)
- Dokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006Documento18 pagineDokumen - Tips Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006lllNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia Physics, 10thDocumento6 pagineGuia Physics, 10thEspinal Karla YohelyNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDocumento1 paginaSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- Kepong Baru 2013 M1 (Q&a)Documento10 pagineKepong Baru 2013 M1 (Q&a)STPMmathsNessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Scheme of Work STPM Physics Term 2 2017Documento9 pagineYearly Scheme of Work STPM Physics Term 2 2017Nur 'Aisyah Abdul HashimNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 2 NSEMBILAN SMKStPaul Seremban MATHS QADocumento7 pagine2014 2 NSEMBILAN SMKStPaul Seremban MATHS QASK100% (1)
- Math T STPM Sem 3 2022Documento2 pagineMath T STPM Sem 3 2022tchinhuat82Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula List New STPM - 2nd TermDocumento6 pagineFormula List New STPM - 2nd TermOne_sofian2715Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 07Documento13 pagineExperiment 07Nisa Abdullah0% (2)
- Form 5 Radioactive ExerciseDocumento10 pagineForm 5 Radioactive Exercisetini277Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Documento3 pagineChemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Viknish Arumugam50% (2)
- Q Biology 2008Documento19 pagineQ Biology 2008SPM Tips STPM Trial Papers94% (18)
- Thermodynamics 2Documento22 pagineThermodynamics 2Gowri ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics STPM Chapter 12Documento11 paginePhysics STPM Chapter 12Chloyee LkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionDocumento2 paginePhysics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionBen67% (3)
- Important 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersDocumento23 pagineImportant 2 and 3 Mark Questions and AnswersirannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Paper 3 SPM Planning An Experiment Form 5Documento2 paginePhysics Paper 3 SPM Planning An Experiment Form 5Sung100% (4)
- Convex LensDocumento2 pagineConvex Lensadithya4rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1 - MATTERDocumento131 paginePresentation 1 - MATTERAzniwati AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Matriculation Physics (Nucleus)Documento39 pagineMatriculation Physics (Nucleus)ridwan67% (3)
- Electrostatic ForceDocumento3 pagineElectrostatic ForceAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Tutorial 1.4 C D e Computer System 25 MeiDocumento17 pagineTutorial 1.4 C D e Computer System 25 MeiVani SriNessuna valutazione finora
- Allied Physics PDFDocumento9 pagineAllied Physics PDFrajia1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDocumento16 pagineYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiHelmi TarmiziNessuna valutazione finora
- Newton's Rings: X - X Diameter M Bi-Convex LensDocumento7 pagineNewton's Rings: X - X Diameter M Bi-Convex LensRadhika GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics SolutionDocumento28 paginePhysics SolutionsharadamastaNessuna valutazione finora
- Karnataka CET / KCET 2014 Physics Solutions With AnswersDocumento11 pagineKarnataka CET / KCET 2014 Physics Solutions With AnswersLokesh Kumar78% (9)
- Electron and Photon With SolutionDocumento8 pagineElectron and Photon With SolutionChiruhaasNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationDa EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 P1 Pahang StateDocumento3 pagine2016 P1 Pahang StateZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 P1 SARAWAK ST Joseph ADocumento8 pagine2016 P1 SARAWAK ST Joseph AZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 P1 Pahang State ADocumento8 pagine2016 P1 Pahang State AZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- Anwers Revision Exercise Mathematics MDocumento4 pagineAnwers Revision Exercise Mathematics MZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Limit and Continuty (S)Documento6 pagineLimit and Continuty (S)Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Documento2 pagineSTPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Zuraini Arshad0% (1)
- Mathematics M Pre Test p1 2016Documento2 pagineMathematics M Pre Test p1 2016Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- SCHEME CHEMISTRY Trial First Term 2013Documento7 pagineSCHEME CHEMISTRY Trial First Term 2013Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- 3P: Chapter 2 Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube RootsDocumento4 pagine3P: Chapter 2 Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube RootsZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Documento2 pagineSTPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Zuraini Arshad50% (2)
- Past Year Questions of Circle 1: PMR 2004 PMR 2005Documento2 paginePast Year Questions of Circle 1: PMR 2004 PMR 2005Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Documento12 pagineCHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (2)
- Skema Trial TERM 2 MATEMATICS T 2013Documento11 pagineSkema Trial TERM 2 MATEMATICS T 2013Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Documento10 paginePHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Zuraini Arshad0% (1)
- SCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Documento11 pagineSCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (1)
- (Q) - TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Documento14 pagine(Q) - TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (1)
- Revision Mathematics TDocumento5 pagineRevision Mathematics TZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry HandbookDocumento82 pagineGeometry HandbookZuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial TERM 2 MATHEMATICS T 2013Documento3 pagineTrial TERM 2 MATHEMATICS T 2013Zuraini ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- ListOf PHD Students OngoingDocumento5 pagineListOf PHD Students OngoingBiswajit DebnathNessuna valutazione finora
- PLLDP BSCDocumento6 paginePLLDP BSCmounhacNessuna valutazione finora
- BOSS Slow Gear SG-1 Attack DelayDocumento1 paginaBOSS Slow Gear SG-1 Attack Delay大石 真義Nessuna valutazione finora
- General Notes 1.0: Automatic Sweep-Off Depalletiser Mod. UNI 700Documento11 pagineGeneral Notes 1.0: Automatic Sweep-Off Depalletiser Mod. UNI 700Reza KühnNessuna valutazione finora
- About Stopwatch and TimerDocumento3 pagineAbout Stopwatch and TimerBarsan ArtNessuna valutazione finora
- Mit Lab 01Documento6 pagineMit Lab 01api-247714257Nessuna valutazione finora
- Regulador Avc63-4 Basler ElectricDocumento4 pagineRegulador Avc63-4 Basler ElectricJose Manuel Bautista MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- A Multi-Functional In-Memory Inference Processor Using A Standard 6T SRAM ArrayDocumento14 pagineA Multi-Functional In-Memory Inference Processor Using A Standard 6T SRAM ArrayNavritaBeniwalNessuna valutazione finora
- tdr100 - DeviceDocumento4 paginetdr100 - DeviceSrđan PavićNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Quarter g12 CssDocumento4 pagine2nd Quarter g12 CssJohn Crist Gabriel YeshuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer 1Documento2 pagineReviewer 1Jhonlee Nicolas ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Based Fire Alert & Gas Leakage Detector System: Israth Jahan Romana Abdullah Al-MamunDocumento49 pagineGSM Based Fire Alert & Gas Leakage Detector System: Israth Jahan Romana Abdullah Al-MamunMahabub AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Theory: DR Paul S SpencerDocumento13 pagineCircuit Theory: DR Paul S SpencerMathew ClewlowNessuna valutazione finora
- 19-9-2014Documento3 pagine19-9-2014MANSA MARKETINGNessuna valutazione finora
- 18F4520Documento5 pagine18F4520Bruno ViniciusNessuna valutazione finora
- EV Charger Price ListDocumento5 pagineEV Charger Price ListSoud AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Genicom 5000 Series Full ManualDocumento223 pagineGenicom 5000 Series Full ManualRJNessuna valutazione finora
- Number SystemDocumento6 pagineNumber SystemJoerel NicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Instruction Manual Linea DH-360, DH-460 and DH-650Documento10 pagineProduct Instruction Manual Linea DH-360, DH-460 and DH-650Richmond DarkoNessuna valutazione finora
- A - ATG - PR 2014 0006 GB - HyPower Geko OCT - BR - K1 02 2015 - 150dpi PDFDocumento16 pagineA - ATG - PR 2014 0006 GB - HyPower Geko OCT - BR - K1 02 2015 - 150dpi PDFionutenacheNessuna valutazione finora
- LCD InterfacingDocumento5 pagineLCD InterfacingRokibul hasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Carte Tehnica UPS-uri Powertronix Quasar enDocumento27 pagineCarte Tehnica UPS-uri Powertronix Quasar enEnsign Budi HandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- ISPF Test Paper 7Documento6 pagineISPF Test Paper 7sreelabdhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ordering Guide & Technical Information: Absolute Process Control Know Where You Are... RegardlessDocumento56 pagineOrdering Guide & Technical Information: Absolute Process Control Know Where You Are... RegardlessEduard RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- DWDM Network Design and ODFDocumento3 pagineDWDM Network Design and ODFhaivqvnpt1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ads 1298Documento87 pagineAds 1298Rui AllesNessuna valutazione finora
- VRV Ii Rsxy R22Documento96 pagineVRV Ii Rsxy R22Carlos Manriquez100% (2)
- Ade Lab ManualDocumento73 pagineAde Lab ManualAshutosh PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper Real Time Multimedia Transcoding WP Final - RADISYSDocumento11 paginePaper Real Time Multimedia Transcoding WP Final - RADISYSlouie mabiniNessuna valutazione finora
- MisII Manual PageDocumento21 pagineMisII Manual PageMorgan PeemanNessuna valutazione finora