Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
13 Pile Foundations Introduction
Caricato da
seljak_veseljakCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
13 Pile Foundations Introduction
Caricato da
seljak_veseljakCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 13.
Pile Foundations Introduction
The objective of this chapter is to explain the practical use of programs for the analysis of pile foundations in GEO 5.
GEO 5 software contains three pile foundation analysis programs Piles, Pile CPT and Pile Group. The text below contains closer explanation of which of the programs is to be used under particular conditions individual programs are subsequently described in other chapters.
Vertical load-bearing capacity of pile foundations is determined by various methods: by a static pile test: these tests are directly required in some countries and a structural analysis functions only as a preliminary pile foundation proposal; by an analysis based on soil shear strength parameters: using analysis methods NAVFAC DM 7.2, Tomlinson, CSN 73 1002 and Effective stress in programs PILES and PILE GROUP; by an analysis based on the assessment of penetration tests: PILE CPT program; by an analysis according to equations for regression curves obtained from the results of static loading tests (according to Masopust): PILES program; Vertical load-bearing capacity is determined from the pile loading curve for corresponding (allowable) settlement (CSN 73 1002 standard specifies the corresponding settlement value
s lim = 25.0 mm ).
by an analysis based on Mohr-Coulomb parameters and stress-strain properties of soils: using the so-called Spring Method in PILES and PILE GROUP programs; by numerical analysis using the Finite Element Method: the FEM program.
It follows from this list that piles can be assessed using many ways and on the basis of different input parameters. It means that analysis results can be identical, but often they can significantly differ.
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
The great advantage of GEO 5 is the fact that the user can try more variants and analysis methods, find the most likely behaviour of the pile foundation and subsequently determine the total bearing capacity or settlement of a single pile or a pile group.
The vertical load-bearing capacity of pile foundations is assessed in GEO 5 programs (with the only exception: Pile Group Spring Method) only for the loading by a vertical normal force. The loading by horizontal forces, bending and torsional moments has no influence on the analysis of the vertical load-bearing capacity of piles.
The procedure of the vertical load-bearing capacity of a single pile analysis in GEO 5 PILES is presented in Chapters 14 and 15, whilst the analysis for the same pile on the basis of CPT tests is described in Chapter 16.
Horizontal bearing capacity of pile foundations: The result of the analysis for a horizontally loaded pile is the pile horizontal deformation and the curve for internal forces along the pile shaft.
In the case of a single pile, its horizontal deformation and reinforcement depend on the calculated modulus of horizontal reaction of the sub-soil and the loading by the lateral force or the bending moment. The analysis procedure is explained in Chapter 17. The analysis for a pile group is presented in Chapter 19.
Settlement of pile foundations: The actual load-bearing capacity of a pile is directly associated with its settlement because of the fact that virtually any pile settles under the action of loading and gets vertically deformed.
The settlement of single piles is determined in the PILES program by the following methods: according to Masopust (non-linear): the program analyses the settlement of a single pile on the basis of the regression coefficients along the skin and under the pile base. according to Poulos (linear): the program analyses the value of the total settlement on the basis of the determined pile base bearing capacity Rb and the pile skin bearing capacity Rs .
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2 www.finesoftware.eu
by means of the Spring Method: the program analyses the loading curve on the basis of set parameters of soils using the Finite Element Method.
The PILES program constructs the loading curve (the so-called working diagram) for all of the methods.
The settlement of a pile group is described in Chapter 18, the settlement of piles designed on the basis of penetration tests CPT is presented in Chapter 16.
Program selection: 1. the decision according to the stiffness of the base slab (pile cap). When the pile cap is considered to be infinitely stiff, the Pile Group solution is used. In the other cases we investigate single piles.
2. the decision according the results of geological survey. If results of CPT tests are available, the Pile CPT program is used for the analysis of the single pile or the pile group (see Chapter 16). In the other cases the program Piles (or Pile Group) is used for the solution, on the basis of the set soil parameters.
Distinguished according to the analysis type are: analysis for drained conditions: effective parameters of shear strength of soils ef , cef
are used in the Piles and Pile Group programs as a standard for analysis methods CSN 73 1002 and Effective stress;
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
analysis for undrained conditions: only the value of the total soil cohesion cu is set
in the Piles and Pile Group programs. The vertical load-bearing capacity of a single pile is determined according to Tomlinson, whilst a pile group is analysed as the loadbearing capacity of a soil cylinder (block) according to the FHWA.
The NAVFAC DM 7.2 method combines both of the above-mentioned analysis procedures. It is possible for each soil layer to choose whether the soil is considered as drained (cohesionless) or undrained (cohesive).
General specification of the problem:
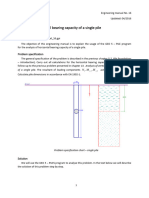
Analyse the vertical load-bearing capacity and settlement of a pile foundation (see the Chart) in the set geological profile; further determine the horizontal deformation of the piles and propose reinforcement for individual piles. The pile foundation consists of four bored piles with the diameter d = 1.0 m and length l = 12.0 m . The resultant of the total loading N , M y , H x acts at the level of the upper surface of the foundation slab (pile cap) namely in the slab centre. C 20/25 reinforced concrete is used for the piles.
Loads acting on piles:
For the problem simplification we will always consider 1 loading case in the program. The determination of loads acting on the pile foundation is different depending on the structure type and subsequent solution, i.e. whether we solve a single pile or a pile group.
Pile Group
We assume that the slab joining the piles is stiff. In our case we will consider a pile cap with the thickness t = 1.0 m . In this case we determine the total reaction in the pile cap centre.
Note: A simple method of obtaining loads on a pile group using any of the static programs is described in the Help for the Pile Group program Determination of loading on a pile group.
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
a) Design (calculation) loads: Vertical normal force: Bending moment: N = 5680 kN , M y = 480 kNm , H x = 310 kN .
Horizontal force
b) Imposed (working) loads:
Vertical normal force: Bending moment:
Horizontal force:
N = 4000 kN ,
M y = 320 kNm , H x = 240 kN .
Problem specification chart pile foundation
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
Single piles:
If the slab is soft in bending (non-stiff) or the building is founded on a pile cap, the structural diagram is different and we will obtain reactions at the heads of individual piles from a static program (e.g. GEO 5 Plate, FIN 3D, SCIA Engineer, Dlubal RStab etc.).
In this example, we will for simplification carry out the pile analysis using only 1 loading case.
a) Design loading: Vertical normal force: Bending moment: Horizontal force:
N1 = 1450 kN ,
M y ,1 = 120 kNm , H x ,1 = 85 kN .
b) Service loading: Vertical normal force: Bending moment: Horizontal force:
N 1 = 1015 kN ,
M y ,1 = 80 kNm , H x ,1 = 60 kN .
Loads action chart distribution of loading among individual single piles
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
Note: If we assume identical dimensions and reinforcement of piles, we can assess all piles as one pile, but with loading combinations acting on all piles.
Geological profile
0.0 to 6.0 m: down from 6,0 m:
Sandy Clay (CS, consistency firm), Sand with trace of fines (S-F, medium dense soil).
Note: The basic soil parameters are the same as for the calculation of single piles and for the verification of the pile group. Their values are given in the following table.
Soil parameters / Classification Unit weight kN m 3
Sandy Clay (CS) consistency firm 18,5
Sand with trace of fines (S-F) medium dense soil 17,5 19,5 0/0 29,5 0,45 0,3 21,0 15,5 Sand, gravel (cohesionless soil) 15,0 150,0 4,5 15,5
Unit weight of satur. soil sat kN m 3 Cohesion of soil cef / cu [kPa] Angle of internal friction ef [] Adhesion factor [] Bearing capacity coefficient p [] Poissons ratio [] Oedometric modulus E oed [MPa] Deformation modulus E def [MPa] Type of soil Angle of dispersion [] Coefficient k MN m 3
20,5 14,0 / 50,0 24,5 0,6 0,3 0,35 8,0 5,0 Clay (cohesive soil) 10,0 60,0
Modulus of horizont. comp. nh MN m 3 Modulus of elasticity E [MPa]
5,0
Table with the soil parameters pile foundations (summary)
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
List of chapters related to pile foundations:
Chapter 13: Chapter 14: Chapter 15: Chapter 16: Chapter 17: Chapter 18: Chapter 19:
Pile foundations Analysis of vertical load-bearing capacity of a single pile Analysis of single pile settlement CPT tests based pile analysis Analysis of horizontal load-bearing capacity of a single pile Analysis of vertical load-bearing capacity and settlement of a pile group Analysis of deformation and pile group dimensioning.
Engineering manuals for GEO5 programs - Part 2
www.finesoftware.eu
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- TWT Twta HandbookDocumento133 pagineTWT Twta HandbookMudassar RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 Analysis and Settlement of A Pile GroupDocumento10 pagine18 Analysis and Settlement of A Pile GroupjasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-NSF Design and EC7 (Prof Harry Tan)Documento66 pagine04-NSF Design and EC7 (Prof Harry Tan)thusiyanthanp100% (2)
- Accessing Cluster Tables in SAPDocumento5 pagineAccessing Cluster Tables in SAPrajeshb4usNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 1 UpDocumento102 pagine6 1 Upsoraandreea20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engi Neeri NG Manual SDocumento66 pagineEngi Neeri NG Manual SMaria Veronica GuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo5-Engineering Manuals Em2Documento66 pagineGeo5-Engineering Manuals Em2jasamnaj100% (1)
- Manual 12 en Piles IntroductionDocumento8 pagineManual 12 en Piles IntroductionGheorghe IonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pile Foundations - Introduction: Vertical Load-Bearing Capacity of Pile Foundations Is Determined Using Various MethodsDocumento8 paginePile Foundations - Introduction: Vertical Load-Bearing Capacity of Pile Foundations Is Determined Using Various MethodsMehedi HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Analysis of Deformation and Pile Group Dimensioning 1Documento9 pagine19 Analysis of Deformation and Pile Group Dimensioning 1jasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-18 en Pile-GroupDocumento8 pagineManual-18 en Pile-GroupKolé Mahamat BrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 Analysis of A Single Pile SettlementDocumento10 pagine15 Analysis of A Single Pile SettlementmavessNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Analysis of Horizontal Bearing Capacity of A Single Pile 1Documento8 pagine17 Analysis of Horizontal Bearing Capacity of A Single Pile 1jasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-13 en PileDocumento12 pagineManual-13 en PileGheorghe IonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Analysis of Vertical Load Bearing Capacity of A Single PileDocumento12 pagine14 Analysis of Vertical Load Bearing Capacity of A Single PilejasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-14 en Pile PDFDocumento12 pagineManual-14 en Pile PDFvedranNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Analysis of Vertical Load Bearing Capacity and Settlement CPTDocumento9 pagine16 Analysis of Vertical Load Bearing Capacity and Settlement CPTjasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-16 en PileDocumento18 pagineManual-16 en PileAmir JiggyNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of The Horizontal Bearing Capacity of A Single PileDocumento18 pagineAnalysis of The Horizontal Bearing Capacity of A Single PiledrNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of A Single Pile Settlement: Problem SpecificationDocumento12 pagineAnalysis of A Single Pile Settlement: Problem SpecificationMehedi HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- GEO5 Pile Vertical CapacityDocumento15 pagineGEO5 Pile Vertical CapacityDidik JunaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2 Foundation Modeling For Seismic Loads: 7.2.1 GeneralDocumento12 pagine7.2 Foundation Modeling For Seismic Loads: 7.2.1 GenerallingamkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Design of The Pallet ProgramDocumento16 pagineThe Design of The Pallet ProgramrenjisrsNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolated Spread Footing: Pile Appl Pile Appl Appl G Appl GDocumento5 pagineIsolated Spread Footing: Pile Appl Pile Appl Appl G Appl GSuhas NatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Vertical Load-Bearing Capacity of A Single Pile: Problem SpecificationDocumento17 pagineAnalysis of Vertical Load-Bearing Capacity of A Single Pile: Problem SpecificationMehedi HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21. Terrain Settlement Analysis: Task SpecificationDocumento12 pagineChapter 21. Terrain Settlement Analysis: Task Specification-Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-13 en PileDocumento14 pagineManual-13 en PileNoel IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- GTL S08 Ex 03 Elasto Plastic Analysis of Drained FootingDocumento0 pagineGTL S08 Ex 03 Elasto Plastic Analysis of Drained FootinglinoficNessuna valutazione finora
- KaeriDocumento74 pagineKaerihamadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-08 en Slope-StabilityDocumento13 pagineManual-08 en Slope-StabilityRashid ShamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual 10 en Spread FootingDocumento6 pagineManual 10 en Spread FootingalfrobiwongytNessuna valutazione finora
- Em15 enDocumento13 pagineEm15 enGheorghe ȘcrabNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines On Foundation Loading Jan2012Documento44 pagineGuidelines On Foundation Loading Jan2012PMHNessuna valutazione finora
- Slope Stability Manual 8Documento12 pagineSlope Stability Manual 8YawgmothNessuna valutazione finora
- Terrain Settlement AnalysisDocumento15 pagineTerrain Settlement AnalysisVinay BariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual-21 en FemDocumento14 pagineManual-21 en FemjessicaNessuna valutazione finora
- GEO5 Pile GroupDocumento26 pagineGEO5 Pile GroupDidik JunaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Teori Pile Geo5Documento27 pagineTeori Pile Geo5Rivana AyuningrumNessuna valutazione finora
- About Pushover Analysis and SAP 2000 MethodDocumento12 pagineAbout Pushover Analysis and SAP 2000 MethodHanush Anand100% (2)
- Geo5 Engineering Manuals Em3 1Documento127 pagineGeo5 Engineering Manuals Em3 1Adrian Tudor100% (1)
- Manual-16 en PileDocumento10 pagineManual-16 en Pilekomarjayagroup000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Deflections - Work-Energy MethodsDocumento52 pagineDeflections - Work-Energy MethodsZahretpalestineNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual 19 - en - Anti Slide Pile PDFDocumento20 pagineManual 19 - en - Anti Slide Pile PDFJose Manuel VieiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Soilin PDFDocumento54 pagineSoilin PDFstonerrrockNessuna valutazione finora
- Teori Pile Geo5Documento27 pagineTeori Pile Geo5Rivana AyuningrumNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilizing A Slope Using Anti-Slide PilesDocumento23 pagineStabilizing A Slope Using Anti-Slide PilesStefan NaricNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearing Pressure Calculation Rev 3Documento5 pagineBearing Pressure Calculation Rev 3hutuguoNessuna valutazione finora
- H1c. Second Presentation 1per PageDocumento23 pagineH1c. Second Presentation 1per PageAnonymous PDEpTC4Nessuna valutazione finora
- STAAD Pro - PDelta AnalysisDocumento9 pagineSTAAD Pro - PDelta Analysisswe_maniNessuna valutazione finora
- 22 Settlement of A Circular Silo FoundationDocumento10 pagine22 Settlement of A Circular Silo FoundationBza ZaBugNessuna valutazione finora
- FPS Bearing PDFDocumento5 pagineFPS Bearing PDFrohitgorasiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Analysis-Laterally Loaded Pile DesignDocumento55 pagineStatic Analysis-Laterally Loaded Pile DesignSravanthi MeharNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearing Pressure CalculationDocumento5 pagineBearing Pressure Calculationdsn_sarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Otc 26942 MsDocumento12 pagineOtc 26942 MsRituraj Singh SujawatNessuna valutazione finora
- GEO5 Pile Horizontal Bearing Capacity Broms MethodDocumento4 pagineGEO5 Pile Horizontal Bearing Capacity Broms MethodDidik JunaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsDa EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsDa EverandInternal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresDa EverandAnalysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionDa EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsDa EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of Complex Systems: Application to Aeronautical DynamicsDa EverandModeling of Complex Systems: Application to Aeronautical DynamicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Shallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingDa EverandShallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- How To Change The Network Type - (Solved) - Windows 7 - Windows 7Documento4 pagineHow To Change The Network Type - (Solved) - Windows 7 - Windows 7seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Genotyping STRVSSNP WebDocumento1 paginaGenotyping STRVSSNP Webseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Genotyping STRVSSNP WebDocumento1 paginaGenotyping STRVSSNP Webseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Difference Between Free Earth Support Method and Fixed Earth Support MethodDocumento1 paginaWhat Is The Difference Between Free Earth Support Method and Fixed Earth Support Methodseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Pressure MacinesDocumento3 pagineLow Pressure Macinesseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- FibreC PDFDocumento38 pagineFibreC PDFseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Baseline, Scheduled and Actual Fields: Project Project Standard and Professional General Questions and AnswersDocumento2 pagineBaseline, Scheduled and Actual Fields: Project Project Standard and Professional General Questions and Answersseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Load CasesDocumento10 pagineLoad Casesseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Milgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineMilgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaseljak_veseljak100% (1)
- Why Windows 10 Sucks or Everything Wrong With Windows 10Documento9 pagineWhy Windows 10 Sucks or Everything Wrong With Windows 10seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Beams On Elastic FoundationDocumento15 pagineBeams On Elastic FoundationOmar Eladel Mahmoud100% (2)
- Daclar Manual Jan06Documento43 pagineDaclar Manual Jan06seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Fibre CDocumento38 pagineFibre Cseljak_veseljak100% (1)
- Hyperdesmo - v2.2Documento5 pagineHyperdesmo - v2.2seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperdesmo PB 2K - 0Documento4 pagineHyperdesmo PB 2K - 0seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula RioDocumento1 paginaFormula RioGiuseppe ManginoNessuna valutazione finora
- Column Calculation To EN1993Documento3 pagineColumn Calculation To EN1993seljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Milgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineMilgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaseljak_veseljak100% (1)
- Formule TrigonometriceDocumento5 pagineFormule TrigonometriceandreiwlNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Software in MalasiaDocumento4 pagineStructural Software in Malasiaseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- EABASSOC Concrete Foaming AgentDocumento1 paginaEABASSOC Concrete Foaming Agentseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- ArianismDocumento8 pagineArianismseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Milgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineMilgram Experiment - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaseljak_veseljak100% (1)
- The Principles of Friesian PhilosophyDocumento6 pagineThe Principles of Friesian Philosophyseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Expert Tips For Facilitating Better MeetingsDocumento2 pagine8 Expert Tips For Facilitating Better Meetingsseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules of Thumb - Structural Engineering Other Technical Topics FAQ - Eng-TipsDocumento9 pagineRules of Thumb - Structural Engineering Other Technical Topics FAQ - Eng-Tipsseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Software in MalasiaDocumento4 pagineStructural Software in Malasiaseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- ArianismDocumento8 pagineArianismseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- Arianism - Christian HeresyDocumento1 paginaArianism - Christian Heresyseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- If Correlation Doesn't Imply Causation, Then What DoesDocumento49 pagineIf Correlation Doesn't Imply Causation, Then What Doesseljak_veseljakNessuna valutazione finora
- 03-Application List Moto, ATVDocumento97 pagine03-Application List Moto, ATVΗλίας ΓεωργιάδηςNessuna valutazione finora
- حالات تحميل الرياح والزلازل للكود الجديد PDFDocumento3 pagineحالات تحميل الرياح والزلازل للكود الجديد PDFmohamedmararNessuna valutazione finora
- Flocculation and ClarifiersDocumento17 pagineFlocculation and ClarifiersOnelNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Study and Static Analysis of Piston Using Solid Edge and AnsysDocumento23 pagineComparative Study and Static Analysis of Piston Using Solid Edge and AnsysIJRASETPublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- BibliographyDocumento5 pagineBibliographyMonal ParekhNessuna valutazione finora
- M Ishaq Electrical SupervisorDocumento7 pagineM Ishaq Electrical SupervisorMuhammad IshaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive (2) Lab: EXP3: Drive Axles and DifferentialDocumento7 pagineAutomotive (2) Lab: EXP3: Drive Axles and DifferentialMohammad YahyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidDocumento13 pagineModelling Microstructures With OOF2: Andrew C.E. ReidKaram JaradatNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase N 5Documento4 pagineClase N 5Xthian Vidal CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Roughness by Different Processing MethodsDocumento1 paginaSurface Roughness by Different Processing Methodsapi-3848892100% (1)
- P091 067 UmDocumento208 pagineP091 067 UmBojan MarkovićNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Cutting EquipmentDocumento92 pagineGas Cutting EquipmentFord KatimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bearing SPM Condition Analyser BVT 111Documento2 pagineBearing SPM Condition Analyser BVT 111industrialindiaNessuna valutazione finora
- AD5934Documento31 pagineAD5934PRADEEPKUMAR CHOUDHARYNessuna valutazione finora
- 3G Training Module-07 Nov-15Documento50 pagine3G Training Module-07 Nov-15technobrat_guy100% (1)
- EMC For Functional Safety: Introductory Manager's Guide ToDocumento2 pagineEMC For Functional Safety: Introductory Manager's Guide ToentindanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nte 123 ADocumento4 pagineNte 123 AAndres Mauricio Quiceno BetancourtNessuna valutazione finora
- 2N Lift1: Brief ManualDocumento12 pagine2N Lift1: Brief ManualMartijnMartensNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Longest Bridges in The WorldDocumento15 pagine7 Longest Bridges in The WorldWai Lana ButlerNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 7: Benchmark Test ResultsDocumento10 pagineCHAPTER 7: Benchmark Test Resultsnapoleon_velasc3617Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rexroth CDB01 CSB01 CSH01 Project Planning ManualDocumento198 pagineRexroth CDB01 CSB01 CSH01 Project Planning Manualdhanita yNessuna valutazione finora
- BlastingDocumento31 pagineBlastingTamerGalhoum100% (1)
- Voided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceDocumento10 pagineVoided Biaxial Slabs - State of Art: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental ScienceShinde vishalNessuna valutazione finora
- White Products CatalogDocumento49 pagineWhite Products CatalogjesusNessuna valutazione finora
- Ten Years To The SingularityDocumento375 pagineTen Years To The SingularityEdgar Martinez100% (1)
- Process Costing PDFDocumento52 pagineProcess Costing PDFsachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Principle of Diesel EngineDocumento30 pagineWorking Principle of Diesel EngineShahzaibUsmanNessuna valutazione finora