Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Case of Cavitary Lung Lesions Following Pharyngitis
Caricato da
alexandra1378Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Case of Cavitary Lung Lesions Following Pharyngitis
Caricato da
alexandra1378Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Case of
Case of
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesions
Lung Lesions
Following
Following
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis
Courtney L. Lockhart, HMS III
Courtney L. Lockhart, HMS III
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School
Gillian Lieberman, MD
Gillian Lieberman, MD
Our Patient: Initial Presentation
Our Patient: Initial Presentation
17
17
yo
yo
M presents with one
M presents with one
-
-
week
week
history of
history of
pleuritic
pleuritic
chest pain,
chest pain,
worse with inspiration
worse with inspiration
Our Patient: Cavitations on CXR
Our Patient: Cavitations on CXR
Two lung lesions in the anterior lung fields suggestive of cavitations (yellow). Mild
blunting of the costophrenic angles (blue) consistent with atelectasis or acute
pleural effusion.
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesion
Lung Lesion
Pulmonary
Pulmonary
cavitary
cavitary
lesion
lesion
Air
Air
-
-
containing area surrounded by definitive wall
containing area surrounded by definitive wall
Wall thickness of at least 4mm
Wall thickness of at least 4mm
Sometimes mistaken for cysts which are thin
Sometimes mistaken for cysts which are thin
-
-
walled air
walled air
-
-
containing lesions
containing lesions
Cavity may also contain blood, pus, fluid, or
Cavity may also contain blood, pus, fluid, or
debris
debris
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesions on CXR and CT
Lung Lesions on CXR and CT
Imaging
Imaging
CXR
CXR
Initial test of choice for all cardiopulmonary
Initial test of choice for all cardiopulmonary
complaints
complaints
Defined area of increased
Defined area of increased
lucency
lucency
surrounded by
surrounded by
rim of density
rim of density
Limitations: small lesions may be missed, limited
Limitations: small lesions may be missed, limited
characterization
characterization
Chest CT
Chest CT
10
10
-
-
20 times more sensitive for evaluation of lung
20 times more sensitive for evaluation of lung
nodules of all types
nodules of all types
Provides more detail of lung parenchyma
Provides more detail of lung parenchyma
Provides better characterization and localization of
Provides better characterization and localization of
lesions
lesions
Our Patient: Nodular Lesions on
Our Patient: Nodular Lesions on
Axial Chest CT
Axial Chest CT
Axial Chest
Axial Chest
CT
CT
Non
Non
-
-
cavitary
cavitary
peripheral
peripheral
lung nodule
lung nodule
in right
in right
upper lobe
upper lobe
Evolving
Evolving
cavitation
cavitation
within
within
nodule
nodule
along left
along left
major
major
fissure
fissure
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Axial Chest
Axial Chest
CT
CT
Peripheral
Peripheral
cavitary
cavitary
lung
lung
lesion in
lesion in
the left
the left
lobe
lobe
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lesions on
Lesions on
Axial Chest CT
Axial Chest CT
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lesion on
Lesion on
Coronal Chest CT
Coronal Chest CT
Coronal CT
Coronal CT
Peripheral
Peripheral
cavitary
cavitary
lung lesion
lung lesion
in the left
in the left
upper lobe
upper lobe
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Differential
Differential
Dx
Dx
for
for
cavitary
cavitary
nodules
nodules
C
C
Carcinoma
Carcinoma
typically
typically
squamous
squamous
,
,
mets
mets
,
,
lymphomas
lymphomas
A
A
Autoimmune
Autoimmune
Wegener
Wegener
s
s
granulomatosis
granulomatosis
,
,
rheumatoid nodules
rheumatoid nodules
V
V
Vascular
Vascular
emboli (septic or bland)
emboli (septic or bland)
I
I
Infection
Infection
lung abscess, bacterial pneumonia,
lung abscess, bacterial pneumonia,
fungal pneumonia, TB,
fungal pneumonia, TB,
hydatid
hydatid
cysts (parasitic
cysts (parasitic
infections)
infections)
T
T
Trauma
Trauma
lung laceration
lung laceration
Y
Y
Young (congenital)
Young (congenital)
cystic
cystic
adenomatoid
adenomatoid
malformation, sequestration,
malformation, sequestration,
bronchogenic
bronchogenic
cyst
cyst
MedPix Medical Image Database
Narrowing the Differential of
Narrowing the Differential of
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesions
Lung Lesions
Characterization of
Characterization of
cavitary
cavitary
lung lesions
lung lesions
Focal or multifocal v. diffuse
Focal or multifocal v. diffuse
Wall thickness
Wall thickness
Contour of inner lining (irregular or smooth)
Contour of inner lining (irregular or smooth)
Nature of contents
Nature of contents
Location
Location
Clinical parameters
Clinical parameters
Rapidity of disease process
Rapidity of disease process
Clinical context
Clinical context
Ryu Ryu, Jay, et al. Mayo , Jay, et al. Mayo Clin Clin Proc. 2003; 78:744 Proc. 2003; 78:744- -752 752
Our Patient: History and Physical Exam
Our Patient: History and Physical Exam
HPI Continued
HPI Continued
1 week of sore throat, fever, pain, rigors
1 week of sore throat, fever, pain, rigors
Throbbing HA,
Throbbing HA,
hematuria
hematuria
,
,
n/v/d
n/v/d
Right flank pain
Right flank pain
Bilateral knee pain
Bilateral knee pain
Physical Exam
Physical Exam
VS: T 37.1 BP 124/68 P 80 RR 20 O2Sat 95%RA
VS: T 37.1 BP 124/68 P 80 RR 20 O2Sat 95%RA
Erythematous
Erythematous
,
,
exudative
exudative
oropharynx
oropharynx
,
,
shotty
shotty
LAD
LAD
Diminished breath sounds over right lung base
Diminished breath sounds over right lung base
CVA tenderness bilaterally
CVA tenderness bilaterally
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy
on
on
Coronal Chest CT
Coronal Chest CT
Coronal Chest
Coronal Chest
CT
CT
Peribronchial
Peribronchial
lymph node in
lymph node in
the
the
mediastinum
mediastinum
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesion
Lung Lesion
on Axial Chest CT
on Axial Chest CT
Axial Chest
Axial Chest
CT
CT
Medial
Medial
cavitary
cavitary
lung
lung
lesion in
lesion in
right lobe
right lobe
anterior to
anterior to
pericardium
pericardium
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesion
Lung Lesion
on Axial Chest CT Lung Window
on Axial Chest CT Lung Window
Axial Chest
Axial Chest
CT
CT
Medial
Medial
cavitary
cavitary
lung
lung
lesion
lesion
anterior to
anterior to
pericardium
pericardium
at the end of
at the end of
pulmonary
pulmonary
vessel
vessel
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient:
Our Patient:
Cavitary
Cavitary
Lung Lesion
Lung Lesion
on Axial and
on Axial and
Sagittal
Sagittal
Chest CT
Chest CT
Chest CT
Chest CT
Same medial lung Same medial lung cavitation cavitation
anterior to the pericardium anterior to the pericardium
Inferior section showing intact Inferior section showing intact
pericardium pericardium
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient: Lab Results
Our Patient: Lab Results
CBC
CBC
WBC 9.14, RBC 4.28 (
WBC 9.14, RBC 4.28 (
Hct
Hct
36.7%),
36.7%),
Plt
Plt
452
452
Urine
Urine
Turbid, pH 7.0, 2+ blood, 10
Turbid, pH 7.0, 2+ blood, 10
-
-
20 RBC/
20 RBC/
hpf
hpf
Blood culture
Blood culture
Positive for gram negative rods
Positive for gram negative rods
Diagnosis????
Diagnosis????
Lemierre
Lemierre
s
s
Disease
Disease
Also known as post
Also known as post
-
-
anginal
anginal
sepsis
sepsis
characterized internal jugular vein septic
characterized internal jugular vein septic
thrombophlebitis
thrombophlebitis
Characteristically seen in adolescents or
Characteristically seen in adolescents or
young adults
young adults
Sepsis following a
Sepsis following a
tonsillar
tonsillar
or
or
peritonsillar
peritonsillar
infection
infection
May also be preceded by
May also be preceded by
mastoiditis
mastoiditis
,
,
cellulitis
cellulitis
or
or
odontogenic
odontogenic
infection
infection
Spread via lymphatic and venous systems
Spread via lymphatic and venous systems
into the lateral pharyngeal space
into the lateral pharyngeal space
Lemierre
Lemierre
s
s
Disease Continued
Disease Continued
Classically caused by
Classically caused by
Fusobacterium
Fusobacterium
necroporum
necroporum
Staph, Strep,
Staph, Strep,
Eikinella
Eikinella
,
,
Bacteroides
Bacteroides
are other
are other
causative organisms
causative organisms
Sore throat, fever, rigors, productive cough w/
Sore throat, fever, rigors, productive cough w/
blood
blood
-
-
tinged sputum, neck swelling along the
tinged sputum, neck swelling along the
sternocleidmastoid
sternocleidmastoid
m.
m.
Reports of carotid rupture,
Reports of carotid rupture,
dysphagia
dysphagia
, Horner
, Horner
s
s
syndrome, and
syndrome, and
trapezius
trapezius
paralysis during initial
paralysis during initial
spread to the internal jugular vein
spread to the internal jugular vein
Metastatic abscesses to the lungs, pleura, joints, and
Metastatic abscesses to the lungs, pleura, joints, and
soft tissues
soft tissues
Pleuritic
Pleuritic
chest pain,
chest pain,
dyspnea
dyspnea
,
,
hepatomegaly
hepatomegaly
,
,
jaundice, joint pain, encephalopathy,
jaundice, joint pain, encephalopathy,
hematuria
hematuria
Head and Neck Anatomy
Head and Neck Anatomy
Peritonsillar
Peritonsillar
Abscess on Head CT
Abscess on Head CT
Head and Neck CT with
Head and Neck CT with
contrast
contrast
Low
Low
-
-
attenuation mass
attenuation mass
with a minimally
with a minimally
enhancing wall in the
enhancing wall in the
right
right
peritonsillar
peritonsillar
region
region
Associated edema, mild
Associated edema, mild
compression of the
compression of the
internal carotid and
internal carotid and
internal jugular vein, and
internal jugular vein, and
deviation of the airway
deviation of the airway
are present.
are present.
*
Emerg Med 37(5):18-47, 2005
Examination of Internal Jugular Vein
Examination of Internal Jugular Vein
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Test of choice: Cost effective, easily accessible,
Test of choice: Cost effective, easily accessible,
real
real
-
-
time evaluation, no radiation
time evaluation, no radiation
Lumenal
Lumenal
for dilatation, filling defect and flow
for dilatation, filling defect and flow
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis
:
:
Echogenicity
Echogenicity
within a
within a
dilated lumen; decreased
dilated lumen; decreased
compressibilty
compressibilty
CT
CT
Rapid test, more sensitive in the evaluation of
Rapid test, more sensitive in the evaluation of
fresh thrombus and additional pathology
fresh thrombus and additional pathology
Better visualization of anatomy
Better visualization of anatomy
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis
: Low
: Low
attentuation
attentuation
of filling
of filling
defect with soft tissue swelling
defect with soft tissue swelling
Our Patient: Internal Jugular Vein
Our Patient: Internal Jugular Vein
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
IJV Ultrasound
- IJV lumen with and without
compression
- Normal lumenal diameter
- Full compression with probe
- IJV flow for stasis or filling defect
- Normal flow with no filling defects
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Companion Patient:
Companion Patient:
Thrombosed
Thrombosed
Internal Jugular Vein Ultrasound
Internal Jugular Vein Ultrasound
IJV Ultrasound
IJV examination for
stasis or filling defect
Filling defect with
disruption of flow
IJV Ultrasound
IJV lumen
Increased lumenal diameter
Echogenic foci within the
lumen
Courtesy of Dr. D. Ferris, PACS Childrens Hospital Boston
Courtesy of Dr. D. Ferris, PACS
Childrens Hospital Boston
Our Patient: Treatment and Outcome
Our Patient: Treatment and Outcome
Patient treated with long course of
Patient treated with long course of
high dose antibiotic
high dose antibiotic
Follow
Follow
-
-
up CXR was normal
up CXR was normal
Take Home Points
Take Home Points
Lemierre
Lemierre
s
s
disease is an easily forgotten
disease is an easily forgotten
DDx
DDx
even when characteristic signs and
even when characteristic signs and
symptoms are present
symptoms are present
Blood cultures and radiological
Blood cultures and radiological
examination of IJV and effected organs are
examination of IJV and effected organs are
essential to confirm diagnosis and assess
essential to confirm diagnosis and assess
the extent of disease
the extent of disease
Our patient had a good outcome but most
Our patient had a good outcome but most
are fatal, though mortality has decreased
are fatal, though mortality has decreased
in the era of antibiotic use
in the era of antibiotic use
Take Home Points Continued
Take Home Points Continued
CT is the best imaging modality for
CT is the best imaging modality for
characterizing cystic or
characterizing cystic or
cavitary
cavitary
lung
lung
lesions
lesions
US is the most convenient, cost effective,
US is the most convenient, cost effective,
and rapid imaging modality for evaluation
and rapid imaging modality for evaluation
of thrombus in vessels of the neck,
of thrombus in vessels of the neck,
especially in the pediatric population
especially in the pediatric population
Neck CT is the test of choice when neck
Neck CT is the test of choice when neck
pathology such as abscess or tumor is
pathology such as abscess or tumor is
suspected
suspected
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
Dr. Diane Ferris, BIDMC Radiology
Dr. Diane Ferris, BIDMC Radiology
Resident
Resident
Dr. Katie Taylor, CHB PGYI
Dr. Katie Taylor, CHB PGYI
Dr. Amanda
Dr. Amanda
Growdon
Growdon
, CHB Attending
, CHB Attending
Dr. Lieberman, Radiology Clerkship
Dr. Lieberman, Radiology Clerkship
Director
Director
References
References
Ryu Ryu, Jay H., , Jay H., Swensen Swensen, Stephen J. Cystic and , Stephen J. Cystic and Cavitary Cavitary Lung Diseases: Focal Lung Diseases: Focal
and Diffuse. Mayo and Diffuse. Mayo Clin Clin Proc. 2003; 78:744 Proc. 2003; 78:744- -752. 752.
Reeder and Reeder and Felson Felson s s Gamuts Gamuts in Radiology: Comprehensive Lists of in Radiology: Comprehensive Lists of
Roentgen Differential Diagnoses. Roentgen Differential Diagnoses.
Muhammad Muhammad Ahsan Ahsan Baig Baig, , Javeria Javeria Rasheed Rasheed, D. , D. Subkowitz Subkowitz, Jeffrey Vieira: A , Jeffrey Vieira: A
Review Of Review Of Lemierre Lemierre Syndrome Syndrome. The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases. . The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases.
2006. Volume 5 Number 2. 2006. Volume 5 Number 2.
Lieberman Lieberman s s eRadiology eRadiology. .
Meschan Meschan, , Isadore Isadore. Analysis of Roentgen Signs in General Radiology: . Analysis of Roentgen Signs in General Radiology:
Respiratory System/Heart. W.B. Saunders Company. Philadelphia. 1 Respiratory System/Heart. W.B. Saunders Company. Philadelphia. 1973. 973.
Alvarez, Ana and Schreiber, John R. Alvarez, Ana and Schreiber, John R. Lemierre Lemierre s s Syndrome in Adolescent Syndrome in Adolescent
Children Children Anaerobic Sepsis With Internal Jugular Vein Anaerobic Sepsis With Internal Jugular Vein Thrombophlebitis Thrombophlebitis
Following Following Pharyngitis Pharyngitis. Experience and Reason. . Experience and Reason.
Netter, Frank H., Atlas of Human Anatomy, Third Edition. Icon Le Netter, Frank H., Atlas of Human Anatomy, Third Edition. Icon Learning arning
Systems, New Jersey. 2003. Systems, New Jersey. 2003.
Moorre Moorre, Keith, , Keith, Dalley Dalley, Arthur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, Fifth Edition. , Arthur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, Fifth Edition.
Lippincott, William, and Wilkins. 2006 Lippincott, William, and Wilkins. 2006
Erasmus JJ, Connolly JE, McAdams HP, Erasmus JJ, Connolly JE, McAdams HP, Roggli Roggli VL. Solitary pulmonary VL. Solitary pulmonary
nodules. I. Morphologic evaluation for differentiation of benign nodules. I. Morphologic evaluation for differentiation of benign and and
malignant lesions. malignant lesions. RadioGraphics RadioGraphics 2000; 20:43 2000; 20:43- -58. 58.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PLE 2019 Anatomy and Histology Questions and AnswersDocumento18 paginePLE 2019 Anatomy and Histology Questions and Answersdickson93% (15)
- 1.3 Describe Factors That May Impact Upon The Development of The Baby During: Pre-ConceptionDocumento2 pagine1.3 Describe Factors That May Impact Upon The Development of The Baby During: Pre-Conceptionjoel TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest X-RayDocumento35 pagineChest X-RayKhairul Saleh PulunganNessuna valutazione finora
- Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration: Incidental Finding in An Asymptomatic PatientDocumento4 pagineIntralobar Pulmonary Sequestration: Incidental Finding in An Asymptomatic PatienteduardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Pediatric Radiology Pediatric Radiology Online Course by Dr. Ashraf Abotaleb PDFDocumento436 pagineIntroduction To Pediatric Radiology Pediatric Radiology Online Course by Dr. Ashraf Abotaleb PDFRicardo VallejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thoracic 428 Edited2Documento87 pagineThoracic 428 Edited2Mihary RamanandraitsioryNessuna valutazione finora
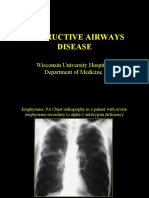
- Obstructive Airways Disease: Wisconsin University Hospital. Department of MedicineDocumento27 pagineObstructive Airways Disease: Wisconsin University Hospital. Department of MedicineAlfina Aulia RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiography of The Thorax: BY Abubakar ADocumento70 pagineRadiography of The Thorax: BY Abubakar AJameeluh TijjanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Anatomy of The Chest Wall, Pleura, and MediastinumDocumento8 pagineSurgical Anatomy of The Chest Wall, Pleura, and MediastinumNooneNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Neck Space InfectionDocumento48 pagineDeep Neck Space InfectionhaneiyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Review Part 1Documento54 pagineAnatomy Review Part 1Daniel SitungkirNessuna valutazione finora
- Superior Vena Cava SyndromeDocumento0 pagineSuperior Vena Cava Syndromemissvi86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Dhanti - CSL Membaca Foto PolosDocumento74 pagineDr. Dhanti - CSL Membaca Foto Polosm zainul fikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute AppendicitisDocumento49 pagineAcute AppendicitisUsman Ali AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Symptoms of Respiratory DiseaseDocumento70 pagineSymptoms of Respiratory DiseaseDr-i BarreNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Chest RadDocumento112 pagineBasic Chest Radtesfayegermame95.tgNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Neck InfectionDocumento46 pagineDeep Neck InfectionVicky SankaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Chest UltrasoundDocumento60 pagineBasic Chest UltrasoundAdriana Villarreal100% (1)
- 3 Med EngDocumento50 pagine3 Med EngSarojini naiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatiDocumento42 pagineGambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatisabariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Retropharyngeal Abscess: Shumaila Ather 5-1/2012/070Documento21 pagineRetropharyngeal Abscess: Shumaila Ather 5-1/2012/070Essam Hassan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- PneumothoraxDocumento12 paginePneumothoraxFairuz Az ZabiedahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest X Ray Made SimpleDocumento103 pagineChest X Ray Made SimpleMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Piercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi RuslieDocumento34 paginePiercing Wound of The Thorax: Dr. Jason Rahmadi Rusliearryandres11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medical MnemonicsDocumento25 pagineMedical MnemonicsChristian Jay Pulangco50% (2)
- Physical Exam - Chest 2006Documento84 paginePhysical Exam - Chest 2006api-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curs Pneumologie StudențiDocumento39 pagineCurs Pneumologie StudențiToma DănilăNessuna valutazione finora
- Shift of Heart and Trachea To Left: Tension PneumothoraxDocumento44 pagineShift of Heart and Trachea To Left: Tension PneumothoraxlettasamudraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rsexm 170207141549Documento72 pagineRsexm 170207141549gpete321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Forum Thorax DoneDocumento8 pagineAnatomy Forum Thorax DoneMedShareNessuna valutazione finora
- Fri 7 30 Am AlpertDocumento58 pagineFri 7 30 Am AlpertMaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest Radiology Med Students2Documento137 pagineChest Radiology Med Students2Mike Oluwaseun AmooNessuna valutazione finora
- Pleural DiseasesDocumento33 paginePleural DiseasesDarawan MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- AirwayDocumento15 pagineAirwayYonathan asnakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Emad Efat Chest CT BestDocumento260 pagineEmad Efat Chest CT Bestdr Mohit TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest Examination New SsDocumento16 pagineChest Examination New SsNAINessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia 2006Documento80 paginePneumonia 2006grace_10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Trauma Resuscitation Acute Care Emerg MedDocumento67 pagineTrauma Resuscitation Acute Care Emerg MedsyasyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deep Neck Spaces: Dr.S.A.Mirvakili Shahid Sadughi UniversityDocumento55 pagineDeep Neck Spaces: Dr.S.A.Mirvakili Shahid Sadughi UniversityGrace KahonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest X-Ray InterpretationDocumento116 pagineChest X-Ray Interpretation6130016019 AISYAH WANDA PUSPANINGTYASNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic CXR Mod AdamDocumento59 pagineBasic CXR Mod AdamCheska TumulakNessuna valutazione finora
- PneumothoraxDocumento81 paginePneumothoraxAnonymous gYeEkemDNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuDocumento41 pagineDr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuYuni SaviraNessuna valutazione finora
- Neck DesDocumento47 pagineNeck DesGrethel Joy DuroNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretasi Foto DadaDocumento137 pagineInterpretasi Foto DadaRofi Irman100% (1)
- L13 - Diseases of LarynxI&IIDocumento90 pagineL13 - Diseases of LarynxI&IINouf Al-orainiNessuna valutazione finora
- in The Given Chest X-Ray, Normal Cardiothoracic Ratio IsDocumento63 paginein The Given Chest X-Ray, Normal Cardiothoracic Ratio Is李建明Nessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory AssessmentDocumento54 pagineRespiratory Assessmentraima ayazNessuna valutazione finora
- Large Substernal Thyroid Goiter Associated With Saddle Pulmonary EmbolismDocumento3 pagineLarge Substernal Thyroid Goiter Associated With Saddle Pulmonary Embolismsantri safiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Radioanatomi ThoraxDocumento63 pagineRadioanatomi Thoraxica aftotunnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung Abscess - Lecture 2015Documento19 pagineLung Abscess - Lecture 2015Okta Dwi Kusuma AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-History Taking & Chest ExaminationDocumento149 pagine4-History Taking & Chest Examinationaeisy4049Nessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Trauma: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocumento54 pagineApproach To Trauma: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesAhmed Tawfig GamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory System: Physical Diagnosis Course II Physical ExamDocumento57 pagineRespiratory System: Physical Diagnosis Course II Physical ExamashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Pulmonary Pathology: Applying Pathological Findings in Therapeutic Decision MakingDa EverandUnderstanding Pulmonary Pathology: Applying Pathological Findings in Therapeutic Decision MakingNessuna valutazione finora
- Phlebology, Vein Surgery and Ultrasonography: Diagnosis and Management of Venous DiseaseDa EverandPhlebology, Vein Surgery and Ultrasonography: Diagnosis and Management of Venous DiseaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementDa EverandFetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaflet - ProsoganDocumento7 pagineLeaflet - ProsoganurmymelodyNessuna valutazione finora
- 616062692662Documento34 pagine616062692662ABHISHEK YADAVNessuna valutazione finora
- Centers For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesDocumento6 pagineCenters For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesabhinavrautNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityDocumento3 pagineInstitute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityaleccespirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Arnica Montana - FayazuddinDocumento13 pagineArnica Montana - FayazuddinMohammad AtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Midwifery KitDocumento3 pagineMidwifery KitRitzel CreusNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?Documento4 pagineEjercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?LenNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Examination 1Documento53 pagineComprehensive Examination 1Love Gonzales90% (21)
- Review of Antibacterial Medicines For The Treatment of Enteric Fever For The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 2019 UpdateDocumento19 pagineReview of Antibacterial Medicines For The Treatment of Enteric Fever For The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 2019 UpdateSundas EjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Illizarov and Principle of Distraction OsteogenesisDocumento7 pagineIllizarov and Principle of Distraction OsteogenesisThiru MuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Benning Vanessa - Resume-2Documento1 paginaBenning Vanessa - Resume-2api-489132887Nessuna valutazione finora
- Paper-Organ DonationDocumento7 paginePaper-Organ Donationapi-400417633Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerDocumento5 pagineDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocumento17 pagineNursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseLyka Joy DavilaNessuna valutazione finora
- SodaPDF-converted-ayoon Saqr ProfileDocumento22 pagineSodaPDF-converted-ayoon Saqr ProfileM BNessuna valutazione finora
- Onset Depression Health Related Risc Dztp2Documento7 pagineOnset Depression Health Related Risc Dztp2Levente DobaiNessuna valutazione finora
- CSF Catalogue enDocumento76 pagineCSF Catalogue enHarshitShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Injectable Anesthesia and Analgesia of Birds 5-Aug PDFDocumento15 pagineInjectable Anesthesia and Analgesia of Birds 5-Aug PDFYaserAbbasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 2Documento9 pagineNursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 2ZiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical AffixDocumento6 pagineMedical AffixOlib OlieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep Physiology and Disorders in Aging and DementiaDocumento17 pagineSleep Physiology and Disorders in Aging and DementiaJúlio EmanoelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Introduction of CytopathologyDocumento41 pagine1 - Introduction of CytopathologyAyu Rizky Fitriawan AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in A Premature Baby: Rare Case ReportDocumento3 pagineJuvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in A Premature Baby: Rare Case ReportKevin Wladimir ChanchicochaNessuna valutazione finora
- BCS Guidance On Workload For Cardiologists - Final March 2010Documento9 pagineBCS Guidance On Workload For Cardiologists - Final March 2010Narendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2UDocumento47 pagine2Uucnursingcesdev2008100% (3)
- Theories of AddictionDocumento30 pagineTheories of AddictionAmyOesau100% (1)
- CHAMPP Part 1 20130104 NewDocumento240 pagineCHAMPP Part 1 20130104 NewMarcu QuerubinNessuna valutazione finora
- Epilepsy MCQDocumento7 pagineEpilepsy MCQko naythweNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Worry About: High Blood Pressure?Documento8 pagineWhy Worry About: High Blood Pressure?mattvestrandNessuna valutazione finora