Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Unit 5 Notes
Caricato da
arunkumarnoolaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Unit 5 Notes
Caricato da
arunkumarnoolaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
FABTECH College of Engineering and Research, Sangola
UNIT 5
UNIT 5
Computer applications in foundry processes, foundry mechanization
Computer applications in foundry processes: Twenty-first century finds us with ever faster and less expensive computing time and extensive use of modeling; we see it on television every day.We can make effective use of this tool in the operations of our metal casting facilities. Modeling is now being used in many other areas of metal casting operations, from simulation of macro segregation and heat treatment to rapid prototyping and facility planning. Benefits: Cost reduction, higher yield, lower rejections, faster development, and Customer satisfaction. Concerns: Initial cost, maintenance cost, technical support, trained manpower. Extensive use of computers is driving the foundry industry in all aspects of development and change, it can not only improve productivity and reduce production costs, but also to promote new technology. Simulation and computer-aided engineering (CAE) applications, can scientifically predict the liquid metal filling process, the solidification process of the temperature field and stress field, and macro-defects and micro-organizations. It can optimize the process to ensure casting quality, reduce trial cycle times, improve competitiveness; can improve the casting at the same time achieve significant economic benefits. Computer applications in the foundry technology development can be described in the following aspects: 1 Casting process with computer-aided design (CAD) technology can be applied for following functional areas: 1. Casting geometry 2. Physical computing (including the casting volume, surface area, weight and thermal modulus calculation) 3. Gating system design calculations (including the choice of casting system type and size of each group element calculation) 4. Feeding system design calculations (including riser, cold iron, and reasonable feeding channel design calculations) 5. Graphics (including casting chart, graph casting process, casting process such as graphics cards Draw and output) As compared to the traditional casting process design, the casting process using computer design features are: 1. The calculation is accurate, rapid, eliminates human error calculation; to mass storage and use of the experience of a number of foundry workers, allows the user to design a more reasonable casting process; with automatic print records and the ability to draw a variety of technical documents.
Manufacturing Processes
Prepared by Prof.S.C.Kulkarni & Prof. Jay Gavade
Page 82
FABTECH College of Engineering and Research, Sangola
UNIT 5
2 Numerical simulation of solidification process technology with the numerical method for solving the physical process of forming the corresponding discrete mathematical equation, which is calculated by the computer displays the results. Achievable goals are: to predict the coagulation time, time out of the box, to determine productivity; predict the formation of shrinkage and shrinkage of the location and size; predict the mold surface and internal temperature distribution, easy cast (especially metal) of design; controlled solidification conditions, to predict the casting stress, micro-and macrosegregation, casting performance, etc. to provide the necessary basis for the calculation and analysis of the data. Numerical simulation of the solidification process can not only show the image of the cavity and the cavity filled with liquid cooling solidification process, can predict possible defects, so the site can be made before the implementation of plans, programs and comprehensive evaluation of various process parameters to optimize technology program to replace or reduce the field trial, which is large and complex shapes or valuable material solidified forming castings, its advantages and economic benefits especially because of the solidification process simulation can reveal the nature of many physical processes, it also contributed to the solidification theory development, research and development in recent years, the microstructure simulation can predict grain size and mechanical properties is expected in the near future for the actual production. 3 Rapid prototyping and manufacturing technology, which is the CAD design data directly into a physical process, it integrates CAD / CAM technology, modern CNC technology, laser technology and new materials technology, no need of drawings & the traditional mold design and processing, greatly improved production efficiency. Has been made using rapid prototyping technology in sand casting, investment casting and solid casting in Rapid appearance of a complex shape or with a laser beam directly to the coated sand mold is made to complete the casting. This high-tech is fundamentally changing the Foundry casting mold making process, showing the efficient, high-quality features. 4 Computer as a production process and the solidification process control methods have been widely used when working conditions are relatively poor, complicated factors, it is necessary to cast the production of in-depth research and extensive. In recent years, there have been a lot of computer analysis of the changes in the production process, using a computer to select the best parameters to regulate the control of the production process, the casting production automation, so as to achieve stable casting quality, increase productivity, reduce the casting cost of the sample. Shape of the current generation of computer-controlled production line has been used to computer-based automatic control system has been used for melting, casting, sand handling, quality inspection processes. The use of computer technology is a prerequisite for producing high-quality castings in foundry.
Manufacturing Processes
Prepared by Prof.S.C.Kulkarni & Prof. Jay Gavade
Page 83
FABTECH College of Engineering and Research, Sangola
UNIT 5
MODERNISATION AND MECHANISATION OF FOUNDRIES
Persons engaged in founding industry have to lead a very hazardous life because of the unhealthy atmosphere inside a foundry. There is thus a vital need for modernisation in this particular field of industry. Measures that lead to increased production, improved quality and reduction in production costs, measures that aim to improve working conditions with an eye to ensuring a safe, healthy and happy life for the worker deserve both modernisation and machanisation.
MODERNISATION
* Modernisation of foundries includes: (1) Changing over to better and newer foundry equipments (2) Employing newer, better, and more economical moulding, melting and casting techniques
(3) Creating conditions which do not make a foundry dirty, dusty and smoke-filled, i.e. improving working condition in foundries, providing adequate illumination, air circulation, dust extraction, etc. * Advantages of modernisation: 1. Improving quality of the casting. 2. Boosting production. 3. Reducing production cost. 4. Increasing safety to the workers. 5. Making working conditions pleasant and less tiring. 6. Building up morale of the workers.
MECHANISATION
Mechanisation implies the utilisation of machinery to accomplish the work previously done by hand. Machinery may be used for preparing sand, moulding and core making, pouring, material handling and many other similar conditions. The extent to which a foundry can be mechanized depends upon the quantity and type of production. For small orders as well as for the production of large-sized castings, mechanisation is both uneconomical and unpractical. On the other hand, a foundry making automobile parts, electric motors, and similar parts where the jobs are of a repetitive nature, mechanisation is economical and practical.
Areas of mechanisation:
Mechainsation has a distinct impact on areas concerned with the preparation and control of sand, moulding and core making, melting and pouring, shake-out operations, material handling, and the control of dust and fume. 1. Sand preparation unit. The sand preparation unit consists of a magnetic separator which removes iron particles from return sand, a auto-riddle which rids foreign materials, a muller which collects the sand for re-use, and aerator which helps to improve the flowability of sand, and a hopper which acts as storage for sand before it is sent for mulling.
Manufacturing Processes Prepared by Prof.S.C.Kulkarni & Prof. Jay Gavade Page 84
FABTECH College of Engineering and Research, Sangola
UNIT 5
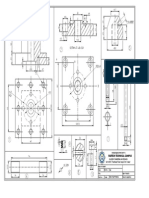
2. Moulding and core making unit: This unit uses a large number of different types of moulding and core making machines. The extent to which these equipments can be used depends on the nature of production. 3. Melting, pouring and shake-out unit: It consists of various types of melting furnaces, mechanical charging devices for furnaces, mechanically operated ladles, cranes, lifting tackles, conveyors and vibrating shake-out mechanisms, etc. 4. Material handling unit: This unit includes various types of material handling equipments such as belt conveyors, apron conveyors, flight conveyors, reciprocating and oscillating conveyors, roller conveyors, bucket elevators, mono-rail hoists, different types of cranes and many others for transportation of sand, moulds, cores, molten metal, castings and raw materials required for production. 5. Dust and fume controlling unit: This unit consists of a well-designed dust and fume collector which can clear the polluted air and maintain hygienic working conditions. This includes filter, cyclone, centrifugal dust collector, scrubbers. Fig. shows an automated line for medium moulds with pattern circulating facility, semiautomatic pouring and secondry cooling.
Figure: Automated line for medium size mould production
Advantages of Mechanisation:
1. Increased production from a given foundry floor space and higher productivity. 2. Production of castings that possesses a higher degree of accuracy, closures tolerance, and better surface finish. 3. Enormous saving of time and labour since all operations are carried out mechanically. 4. More hygienic and healthy working conditions, and improved job satisfaction. 5. Minimised casting defects. 6. Reduced production cost and higher profits. 7. increased earnings of the workers.
Manufacturing Processes Prepared by Prof.S.C.Kulkarni & Prof. Jay Gavade Page 85
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Results Mapping PDFDocumento3 pagineResults Mapping PDFarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansa Meta For Marine Industry Lowres PDFDocumento145 pagineAnsa Meta For Marine Industry Lowres PDFarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- AnsaDocumento12 pagineAnsaarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Results Mapping PDFDocumento3 pagineResults Mapping PDFarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACT II AttendenceDocumento29 pagineACT II AttendencearunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis: Name of College: Course 3. Project MemberDocumento7 pagineSynopsis: Name of College: Course 3. Project MemberarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11 NotesDocumento7 pagineUnit 11 NotesarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fem Ut IiDocumento2 pagineFem Ut IiarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 NotesDocumento27 pagineUnit 1 NotesarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 NotesDocumento12 pagineUnit 3 NotesarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- JOB Evalua Tion AND Merit Rating: N ManagementDocumento8 pagineJOB Evalua Tion AND Merit Rating: N ManagementarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dye Penetrant TestDocumento4 pagineDye Penetrant Testarunkumarnoola100% (1)
- Part Drawings ModelDocumento1 paginaPart Drawings ModelarunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Loops Effect in Ductile Failure of Mild Steel: O.O. OluwoleDocumento10 pagineStress Loops Effect in Ductile Failure of Mild Steel: O.O. OluwolearunkumarnoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Morphometric Characterization of Jatropha Curcas Germplasm of North-East IndiaDocumento9 pagineMorphometric Characterization of Jatropha Curcas Germplasm of North-East IndiafanusNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit B: What Is Customer-Based Brand Equity?Documento3 pagineUnit B: What Is Customer-Based Brand Equity?So-Nam Dorji Dr-UKpaNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 27001 Gap Analysis ChecklistDocumento6 pagineISO 27001 Gap Analysis Checklistlijo jacob70% (10)
- Bioinformatics Computing II: MotivationDocumento7 pagineBioinformatics Computing II: MotivationTasmia SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Daikin LXE10E-A - Service Manual (TR 01-09B) PDFDocumento238 pagineDaikin LXE10E-A - Service Manual (TR 01-09B) PDFmail4ksnNessuna valutazione finora
- Zoom and Re-Zoom Team ActivityDocumento2 pagineZoom and Re-Zoom Team ActivityWalshie28050% (1)
- Experimental Psychology & The Scientific MethodDocumento73 pagineExperimental Psychology & The Scientific MethodRuru LavariasNessuna valutazione finora
- Present Simple Present ContinuousDocumento3 paginePresent Simple Present ContinuousFernando SabinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Komatsu Wheel Loaders Wa250pz 5 Shop ManualDocumento20 pagineKomatsu Wheel Loaders Wa250pz 5 Shop Manualmarcia100% (48)
- EagleBurgmann H7N ENDocumento5 pagineEagleBurgmann H7N ENlamtony2013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stelma & Cameron PDFDocumento35 pagineStelma & Cameron PDFCatarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- PCI Express Test Spec Platform 3.0 06182013 TSDocumento383 paginePCI Express Test Spec Platform 3.0 06182013 TSDeng XinNessuna valutazione finora
- Extenso MeterDocumento8 pagineExtenso MeterVijayanandh Raja100% (1)
- BFC+43103. 1213 SEM1pdfDocumento19 pagineBFC+43103. 1213 SEM1pdfAdibah Azimat100% (1)
- Community Policing EssaysDocumento7 pagineCommunity Policing Essaysgqdknjnbf100% (2)
- ( (2004) Yamamuro & Wood) - Effect of Depositional Method On The Undrained Behavior and Microstructure of Sand With SiltDocumento10 pagine( (2004) Yamamuro & Wood) - Effect of Depositional Method On The Undrained Behavior and Microstructure of Sand With SiltLAM TRAN DONG KIEMNessuna valutazione finora
- Erich Segal Doctors PDFDocumento2 pagineErich Segal Doctors PDFAlicia13% (8)
- TCL 1Documento29 pagineTCL 1Nikita Mudras0% (2)
- Autodesk 3ds Max SkillsDocumento18 pagineAutodesk 3ds Max SkillsJuan UrdanetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Approaches To Curriculum DesigningDocumento20 pagineApproaches To Curriculum DesigningCristel CatapangNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 9: Cities of The World I. ObjectivesDocumento4 pagineUnit 9: Cities of The World I. ObjectivesTrang Hoang NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- English 4 Q.2 Module 2Documento6 pagineEnglish 4 Q.2 Module 2RjVValdezNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei FusionServer RH2288 V3 Data Sheet PDFDocumento2 pagineHuawei FusionServer RH2288 V3 Data Sheet PDFMartenMattisenNessuna valutazione finora
- 226-Article Text-601-1-10-20210702Documento12 pagine226-Article Text-601-1-10-20210702Leni NopriyantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Norsok Well IntegrityDocumento162 pagineNorsok Well IntegrityAshish SethiNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual of Armacad v9 PDFDocumento102 pagineManual of Armacad v9 PDFCristiana FelicianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Panasonic Sa Akx10ph PNDocumento114 paginePanasonic Sa Akx10ph PNimmortalwombatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chart and Compass (London Zetetic Society)Documento8 pagineChart and Compass (London Zetetic Society)tjmigoto@hotmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- C-L-X® Type MC-HL (XHHW-2)Documento3 pagineC-L-X® Type MC-HL (XHHW-2)Xin LiNessuna valutazione finora
- MP65557-1 Manual Técnico - 4900Documento371 pagineMP65557-1 Manual Técnico - 4900Tecnico IncoderNessuna valutazione finora