Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Iso M 5
Caricato da
boopelectraTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Iso M 5
Caricato da
boopelectraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Insulation Co-ordination: Numerical Example 1
Case 1: Without Capacitor Switching in Sub.2 Case 2: With Capacitor Switching in Sub.2
Existing Substation
New Substation with Un=230kV
Us=Um=245kV Pollution level: Heavy Altitude from sea level: 1000m
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -1-
Insulation Co-ordination: Numerical Example 1
Range I: Um<245kV Requierd standard withstand voltages: - Power Frequency Withstand Voltage (PFWV) - Lightning Impulse Withstand Voltage (LIWV) Step 1: determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp) Step 2: determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
Step 4: determination of the standard withstand voltages (Uw)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -2-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Power Frequency Voltage Us=Um=245kV minimum Creepage Distance for insulators =25mm/kV (Pollution: Heavy)
-Temporary Overvoltages
earth fault factor load rejection factor earth fault and load rejection factor -Slow-front Overvoltages surge arrester effect line entrance equipments other equipment -Fast-front Overvoltages
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -3-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Temporary Overvoltages earth fault factor
k 3 ... 2
HV side of power transformer in Sub.1 is solidly earthed.
System study: k=1.5 ! (global network simulation) P-E Overvoltage:
k 1.4
1.4 k 1.8
k 3 ...1.85
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -4-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Temporary Overvoltages load rejection factor
moderately extended systems: < 1.2 p.u. for up to several minutes widely extended systems: 1.5 p.u. for some seconds close to turbo generator: 1.3 p.u. close to salient pole (German: "Schenkelpol") generator: 1.5 p.u.
System study: k=1.4 (overspeed genarator in Sub. 1) P-E Overvoltage: P-P Overvoltage:
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -5-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Temporary Overvoltages earth fault and load rejection factor Will be opened after load rejection k load rejection* k earth fault << k earth fault
Earth Fault factor extremely decreases. (D/Y grounded of Tr.)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -6-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Power Frequency Voltage Us=Um=245kV minimum Creepage Distance for insulators =25mm/kV (Pollution: Heavy) -Temporary Overvoltages earth fault factor k=1.5; Urp=212kV Urp=212kV(P-E) Urp=343kV(P-P)
load rejection factor k=1.4; Urp=198kV(P-E); Urp=343kV(P-P) earth fault and load rejection factor not applicable
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -7-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Slow-front Overvoltages
energization and re-energization
Range of 2% slow-front phase-to-earth overvoltages at the receiving end due to line energization (Approximately Value)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -8-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Slow-front Overvoltages
energization and re-energization
Range of 2% slow-front phase-to-earth overvoltages at the receiving end due to line energization (Exact Value) System study : Overvoltages originating from Sub.1 Ue2=1.9 p.u Up2=2.9 p.u Overvoltages originating from Sub.2
Ue2=3.0 p.u Up2=4.5 p.u
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 -9-
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Slow-front Overvoltages
energization and re-energization Probability distribution of the representative amplitude of the prospective overvoltage phase-to-earth
Using phase-peak method: Overvoltages originating from Sub.1 Ue2=1.9 p.u Uet=1.25*1.9-0.25=2.125 p.u
Overvoltages originating from Sub.2 Ue2=3.0 p.u Uet=1.25*3.0-0.25=3.5 p.u
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 10 -
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Slow-front Overvoltages
energization and re-energization Probability distribution of the representative amplitude of the prospective overvoltage phase-to-phase
Using phase-peak method: Overvoltages originating from Sub.1 Up2=2.9 p.u Upt=1.25*2.9-0.43=3.195 p.u
Overvoltages originating from Sub.2 Up2=4.5 p.u Upt=1.25*4.5-0.43=5.195 p.u
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 11 -
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Slow-front Overvoltages
Surge Arrester effect
energization and re-energization without S.A:
O.V from Sub. 1 O.V from Sub. 2 phase-earth phase-phase Uet=425kV Upt=639kV Uet=700kV Upt=1039kV
Surge Arrester Characteristics:
Using Surge Arrester:
Phase-to-earth: Ure = Ups = 410kV < 425 & 700 Phase-to-phase: the lower value of Urp = 2 Ups = 820kV < 1039 but >639 Urp = Upt = 639kV < 820
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 12 -
Step 1:determination of the representative overvoltages (Urp)
-Power Frequency Voltage Us=Um=245kV minimum Creepage Distance for insulators =25kV/mm (Pollution: Heavy)
-Temporary Overvoltages
earth fault factor load rejection factor earth fault and load rejection factor -Slow-front Overvoltages surge arrester effect line entrance equipments other equipment -Fast-front Overvoltages: Simplified Statistical Approach (see step2)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Urp=212kV(P-E) Urp=343kV(P-P)
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 13 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Temporary Overvoltages Ucw=Urp (Kc=1) Urp=212kV(P-E) Urp=343kV(P-P) Ucw=212kV(P-E) Ucw=343kV(P-P)
-Slow Front Overvoltages S.A Characteristics:
System study : Overvoltages originating from Sub.1 Ue2=1.9 p.u Up2=2.9 p.u Overvoltages originating from Sub.2 Ue2=3.0 p.u Up2=4.5 p.u
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 14 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Slow Front Overvoltages
Line entrance equipments: Ups / Ue2 = 410/600 = 0.68 Ucw = 1.10 * Urp 2Ups / Up2 = 820/900 = 0.91 Ucw = 1.00 * Urp All other equipments: Ups / Ue2 = 410/380 = 1.08 Ucw = 1.03 * Urp 2Ups / Up2 = 820/580 = 1.41 Ucw = 1.00 * Urp
(b) (a) (b) (a)
Kcd = 1.10
Kcd = 1.00
Kcd = 1.03
S.A Characteristics: Ups= 410kV
Kcd = 1.00
Line entrance equipments: Ue2=3.0 p.u=600kV Up2=4.5 p.u=900kV All other equipments: Ue2=1.9 p.u=380kV Up2=2.9 p.u=580kV
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 15 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Slow Front Overvoltages
Step. 1:
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 16 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Fast Front Overvoltages Simplified Statistical Approach
S.A Characteristics:
n: minimum Nos. of lines connected to the Sub.
n=2
Upl = 500 A = 4500 n = 2
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 17 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Fast Front Overvoltages Simplified Statistical Approach
Lsp = 300m Span Length
Ra = acceptable failure rate = 1 in 400 years Rkm = outage per 100km per year = 1
La = Ra / Rkm = 1/400 = 0.25 km = 250 m
L = 30m for internal insulation L = 60m for external insulation
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 18 -
Step 2:determination of the co-ordination withstand voltages (Ucw)
-Fast Front Overvoltages Simplified Statistical Approach
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 19 -
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
-Ks : Safety Factor for any type of Overvoltages (P-E & P-P) internal insulation : Ks=1.15
external insulation : Ks=1.05
-Ka : Altitude Factor Only for external insulation !
H=Altitude above sea level = 1000 m
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 20 -
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
For Switching withstand voltages:
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 21 -
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
For Switching withstand voltages:
Step. 2:
Ucw=451 , curve (a): m=0.94 Ucw=820 , curve (c): m=1.00
For Lightning withstand voltages:
m = 1.00 m = 0.50
For Power Frequency withstand voltages:
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 22 -
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
For Switching withstand voltages:
Ka= e Ka= e
0.94 . (1000/8150) 1.00 . (1000/8150)
= 1.122 (P-E) = 1.130 (P-P)
For Lightning withstand voltages:
Ka= e
1.00 . (1000/8150)
= 1.130 (P-E & P-P)
For Power Frequency withstand voltages:
Ka= e
0.50 . (1000/8150)
= 1.063 (P-E & P-P)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 23 -
Step 3: determination of the required withstand voltages (Urw)
Urw= Ucw . Ks . Ka
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 24 -
Step 4: Conversion to withstand voltages normalized for range I
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 25 -
Step 4: Conversion to withstand voltages normalized for range I
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 26 -
Step 4: Conversion to withstand voltages normalized for range I
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 27 -
Step 5: Selecting of standard withstand voltage values
Summary:
Urw(s): minimum required withstand voltage obtained directly Urw(c): minimum required withstand voltage obtained by conversion
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 28 -
Step 5: Selecting of standard withstand voltage values
Short duration power frequency withstand voltages are selected according to direct values Urw(s) Lightning withstand voltages are selected as a highest value of Lightning Urw(s) or converted value of switching withstand voltage into lightning withstand voltage Urw(c)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 29 -
Step 5: Selecting of standard withstand voltage values
Results: minimum required withstand voltage PFWV(kVrms) / LIWV (kVpeak) : 395/950 only P-P minimum required withstand voltage for line enterance equipement is 1127kV which is more than 950 kV standardized value and next standard value of 1175kV shall be selected. Since there is no three phase equipment in line entrance, minimum P-P clearance can be specified instead of testing. (IEC 71-2: page:101; )
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 30 -
Step 5: Selecting of standard withstand voltage values
2.35m P-P clearane for line equipments and 1.9m P-P and P-E clerance for other equipments.
LIWV (kVpeak) P-P & P-E for other equipments: 950 LIWV (kVpeak) P-P for line equipments: 1175
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 31 -
Step 5: Selecting of standard withstand voltage values
Results (cont.): Refeinment in system study leads to lower value of PFWV for external insulations. So 360kV for PFWV and 850kV for LIWV may be possible to select as an insulation levels. for internal insulation, it is economic to select 750 and 850kV lightning withstand voltage for Phase to Earth and Phase to Phase, respectively. But PFWV shall be at least 395kV.
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 32 -
Insulation Co-ordination: Numerical Example 1
Case 2: With Capacitor Switching in Sub.2
With Capacitor Switching
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 33 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.1: Urp)
Having a capacitor switching in Sub.2 affects only in Slow-front Overvoltages. System study shows the following maximum amplitude of O.V in new Sub. Due to capacitor switching in Sub. 2:
Surge Arrester Characteristics:
Ups < Uet
and
2 Ups < Upt
Urp = 410 kV (P-E) Urp = 820 kV (P-P)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 34 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.2: Ucw)
Ups = 410 kV (P-E) 2 . Ups = 820 kV (P-P)
IEC 60071-2 page: 215,
Mistake !!!
Kcd = 1.075 , Ucw = 441 kV;
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 35 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.3: Urw)
Ucw = 441 kV (P-E) Ucw = 820 kV (P-P)
Ucw=441 , curve (a): m=0.94 Ucw=820 , curve (c): m=1.00 Ka= e Ka= e
0.94 (1000/8150)
1.0 (1000/8150)
= 1.122 (P-E) = 1.130 (P-P)
Safety Factor : internal insulation : Ks=1.15 external insulation : Ks=1.05
-External insulation: (P-E): Urw = 441 * 1.05 * 1.122 = 519 kV (P-P): Urw = 820 * 1.05 * 1.13 = 973 kV
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
-Internal insulation: (P-E): Urw = 441 * 1.15 = 507kV (P-P): Urw = 820 * 1.15 = 943 kV
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 36 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.4: Conversion)
-Conversion to short-duration power-frequency withstand voltage (SDW): -External Insulation: (P-E): SDW = 519 * (0.6 + 519 / 8500) = 343 kV; (P-P): SDW = 973 * (0.6 + 973 / 12700) = 658 kV; -Internal Insulation: (P-E): SDW = 507 * 0.5 = 254 kV; (P-P): SDW = 943 * 0.5 = 472 kV.
-Conversion to lightning impulse withstand voltage (LIW): -External Insulation: (P-E): SDW = 519 * 1.3 = 675 kV; (P-P): SDW = 973 * (1.05 + 973 / 9000) = 1127 kV; -Internal Insulation: (P-E): SDW = 507 * 1.1 = 558 kV; (P-P): SDW = 943 * 1.1 = 1037 kV.
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 37 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.5)
Summary:
Urw - kV rms for PFWV -kV peak for SIWV or LIWV P-E P-P P-E P-P P-E P-P
External Insulation
Internal Insulation Urw(s) 243 395 507 943 715 715 Urw(c) 254 472 558 1037
PFWV
SIWV
LIWV
Urw(s) 237 383 519 973 884 884
Urw(c) 343 658 675 1127
Urw(s): minimum required withstand voltage obtained directly Urw(c): minimum required withstand voltage obtained by conversion
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 38 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Step.5)
Results: minimum required withstand voltage PFWV(kVrms) / LIWV (kVpeak) : 395/950 only P-P minimum required withstand voltage for all equipments (not only line enterance equipement) is 1127kV which is more than 950 kV standardized value and next standard value of 1175kV shall be selected. 2.35m P-P clearane for all external equipments needed if no P-P test would like to be provided. for internal insulation, 460/1050 kV (due to capacitor switching in Sub.2)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 39 -
Case 2: Capacitor Switching in Sub. 2 (Comparision)
Fachgebiet Hochspannungstechnik
Overvoltage Protection and Insulation Coordination / Chapter 6 Numerical Example 1 - 40 -
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Dong DissertationDocumento173 pagineDong Dissertationvijayasiva86Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- 111 - 2. 2025 MVA 13233 KV Power TFDocumento32 pagine111 - 2. 2025 MVA 13233 KV Power TFGanesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Distribution Transformers G210-12-1Documento14 pagineDistribution Transformers G210-12-1boopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Earthing ExothermicDocumento2 pagineEarthing ExothermicboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Preparation of Transformer SpecDocumento57 paginePreparation of Transformer SpecboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Name of The Area Type of Luminaire MakeDocumento1 paginaName of The Area Type of Luminaire MakeboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Current Carrying CalculationDocumento1 paginaCurrent Carrying CalculationboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- GIS Vs AIS - Substation EarthingDocumento6 pagineGIS Vs AIS - Substation EarthingboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Theory LecturesDocumento522 pagineTheory LecturesboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- LS Fiber Optics enDocumento48 pagineLS Fiber Optics enboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- ConradDocumento3 pagineConradboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
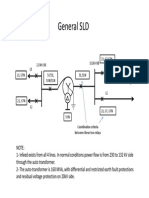
- General SLD: 230kV BB L1 132kV BB 21, 67,67NDocumento1 paginaGeneral SLD: 230kV BB L1 132kV BB 21, 67,67NboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- GRD140D 6F2S0897 5.0Documento438 pagineGRD140D 6F2S0897 5.0boopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Energies: Harmonic Propagation and Interaction Evaluation Between Small-Scale Wind Farms and Nonlinear LoadsDocumento26 pagineEnergies: Harmonic Propagation and Interaction Evaluation Between Small-Scale Wind Farms and Nonlinear LoadsboopelectraNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- XLPE Insulated Low Voltage Cables 2012Documento40 pagineXLPE Insulated Low Voltage Cables 2012Jeremy McfaddenNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Keywords Earthing Designs Substation Earthing Resistance Grid Potential Rise Mesh Voltage Step Voltage and Matlab Figures - CompressDocumento6 pagineKeywords Earthing Designs Substation Earthing Resistance Grid Potential Rise Mesh Voltage Step Voltage and Matlab Figures - CompressDebasish RahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Between GIS & AIS PDFDocumento9 pagineComparison Between GIS & AIS PDFneharoybhushan100% (3)
- Wind Power Connection To The Grid: Aalto University 30.10.2015 Sanna UskiDocumento39 pagineWind Power Connection To The Grid: Aalto University 30.10.2015 Sanna UskiSuperhypoNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- En B06 Inverter, Soft - StarterDocumento20 pagineEn B06 Inverter, Soft - Startertokio2424Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Revisiting PSMP2016 (Full Report) - Signed PDFDocumento148 pagineRevisiting PSMP2016 (Full Report) - Signed PDFMd Foyzul HaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Bentley Substation IEC Tutorial PDFDocumento122 pagineBentley Substation IEC Tutorial PDFPablo CabotNessuna valutazione finora
- KP-00+++-MQ758-V0010-Rev 0-MS For CB Installation Works PDFDocumento27 pagineKP-00+++-MQ758-V0010-Rev 0-MS For CB Installation Works PDFUtku Can Kılıç100% (1)
- Electrical Deliverables and Its Interdisciplinary InterfacesDocumento25 pagineElectrical Deliverables and Its Interdisciplinary Interfacesamarnetha100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- IEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LR PDFDocumento18 pagineIEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LR PDFIsuru WijewardeneNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid Code 2005Documento249 pagineGrid Code 2005Muhammad ShahzebNessuna valutazione finora
- Btps Project Report Elec EnggDocumento41 pagineBtps Project Report Elec Enggsukanya dasguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revenue Interchange Metering Application GuideDocumento54 pagineRevenue Interchange Metering Application Guidelbk50Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- PGCIL GIS Specification Rev-5 PDFDocumento107 paginePGCIL GIS Specification Rev-5 PDFPeyush Jain100% (1)
- 7SJ64xx Catalog SIP-2006 enDocumento47 pagine7SJ64xx Catalog SIP-2006 enjunaid_libraNessuna valutazione finora
- KKS Handbook Edition 07Documento126 pagineKKS Handbook Edition 07Hüseyin ÖnözNessuna valutazione finora
- T&C. Mechanical ScheduleDocumento18 pagineT&C. Mechanical ScheduleMohd HaroonNessuna valutazione finora
- BOQ Cum Price Scedule - Package A - BudhapalDocumento34 pagineBOQ Cum Price Scedule - Package A - BudhapalSanjay GulatiNessuna valutazione finora
- KS-321 Kiosk Substation Schneider KPX Equipment DetailsDocumento1 paginaKS-321 Kiosk Substation Schneider KPX Equipment DetailsRickNessuna valutazione finora
- Eead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedDocumento190 pagineEead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedFrinz Mardie GañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Rig 400kV Substation Extension: Consultation Environmental ReportDocumento2 pagineCrystal Rig 400kV Substation Extension: Consultation Environmental ReportAmmar Lateef GakharNessuna valutazione finora
- Reyrolle 5 7SR511 Overcurrent Protection ProfileDocumento2 pagineReyrolle 5 7SR511 Overcurrent Protection ProfileDiego Alejandro Cetina MezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Document of Intial ShareDocumento3 pagineDocument of Intial SharerameshNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Single Phase Earth-Faults Solutions Using Reclosers To Meet The Demands of The Modern NetworkDocumento7 pagineSingle Phase Earth-Faults Solutions Using Reclosers To Meet The Demands of The Modern NetworkSaraMuzaffarNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Protection 7SJ64Documento49 pagineMotor Protection 7SJ64Filip MilicNessuna valutazione finora
- Ps 1Documento13 paginePs 1पंकज काळेNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspection of Electrical Equipment: OISD - 137Documento45 pagineInspection of Electrical Equipment: OISD - 137Suraj SarojNessuna valutazione finora
- S-Curve GI 150 KVDocumento1 paginaS-Curve GI 150 KVrizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 543Documento2 pagineEe 543Ahmed SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of MV and LV Earthing Systems in Electrical Distribution Substations - 2 ColumnDocumento3 pagineSeparation of MV and LV Earthing Systems in Electrical Distribution Substations - 2 ColumnsanibubaNessuna valutazione finora
- 0109 Specification For Earthing FINALDocumento15 pagine0109 Specification For Earthing FINALhardeepsingh_08Nessuna valutazione finora